目录
1.protostuff 的 Maven 依赖
2.定义实体类
3.序列化工具类 ProtostuffSerializer 提供了序列化和反序列化方法
4.测试
利用 Jedis 提供的字节数组参数方法,如:
public String set(String key, String value)
public String set(byte[] key, byte[] value)
public byte[] get(byte[] key)
public String get(String key)
拥用这些 API 的支持,就可以将 Java 对象序列化为二进制,当应用需要获取 Java 对象时,使用 public byte[] get(byte[] key) 函数将字节数组取出,然后反序列化为 Java 对象即可。和很多 NoSQL 数据库 (例如Memchache、Ehcache)的客户端不同,Jedis 本身没有提供序列化的工具,也就是说开发者需要自己引入序列化的工具。序列化的工具有很多,例如 XML、Json、谷歌的 Protobuf 、Facebook 的 Thrift 等等,对于序列化工具的选择开发者可以根据自身的需求决定,下面以 protostuff (Protobuf 的 Java 客户端)为例子进行说明。
1.protostuff 的 Maven 依赖
<properties>
<protostuff.version>1.0.11</protostuff.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
//redis客户端
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</dependency>
//protostuff 客户端
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-runtime</artifactId>
<version>${protostuff.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-core</artifactId>
<version>${protostuff.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.定义实体类
package org.example.Entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
public class Club implements Serializable {
private int id; //id
private String name;//名称
private String info;//描述
private Date createDate;//创建日期
private int rank;
public Club(int id, String name, String info, Date createDate, int rank) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.info = info;
this.createDate = createDate;
this.rank = rank;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
public Date getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public int getRank() {
return rank;
}
public void setRank(int rank) {
this.rank = rank;
}
//测试使用
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Club{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", info='" + info + '\'' +
", createDate=" + createDate +
", rank=" + rank +
'}';
}
}
3.序列化工具类 ProtostuffSerializer 提供了序列化和反序列化方法
package org.example.until;
import com.dyuproject.protostuff.LinkedBuffer;
import com.dyuproject.protostuff.ProtostuffIOUtil;
import com.dyuproject.protostuff.Schema;
import com.dyuproject.protostuff.runtime.RuntimeSchema;
import org.example.Entity.Club;
//序列化工具类
public class ProtostuffSerializer {
// 通过反射机制创建了 Club 类型的模式(schema)
private Schema<Club> schema = RuntimeSchema.createFrom(Club.class);
//序列化
public byte[] serialize(Club club){
//初始化序列化缓冲
LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
try {
//序列化成字节数组
return serializeInternal(club,schema,buffer);
}catch (Exception e){
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(),e);
}finally {
buffer.clear();
}
}
//反序列化
public Club deserialize(byte[] bytes){
try {
//拿到反序列化对象
Club club = deserializeInternal(bytes,schema.newMessage(),schema);
if (club != null){
return club;
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(),e);
}
return null;
}
//返回序列化数组
private <T> byte[] serializeInternal(final T source,final Schema<T> schema,LinkedBuffer buffer) {
return ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(source,schema,buffer);
}
//将字节数组反序列化操作
private <T> T deserializeInternal(byte[] bytes, T result, Schema<T> schema) {
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(bytes,result,schema);
return result;
}
}
4.测试
package org.example;
import org.example.Entity.Club;
import org.example.until.ProtostuffSerializer;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.Date;
// 按两次 Shift 打开“随处搜索”对话框并输入 `show whitespaces`,
// 然后按 Enter 键。现在,您可以在代码中看到空格字符。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//生成序列化工具类
ProtostuffSerializer protostuffSerializer = new ProtostuffSerializer();
Jedis jedis = JedusUtils.getJedis();
String key = "club:1";
//定义实体对象
Club club = new Club(1,"AC","米兰",new Date(),1);
System.out.println("序列化:"+club);
//序列化
byte[] clubBytes = protostuffSerializer.serialize(club);
jedis.set(key.getBytes(),clubBytes);
//反序列化
byte[] resultBytes = jedis.get(key.getBytes());
//反序列化 1,"AC","米兰",new Date(),1
Club resultClub = protostuffSerializer.deserialize(resultBytes);
System.out.println("反序列化: "+resultClub);
}
}运行结果如图:
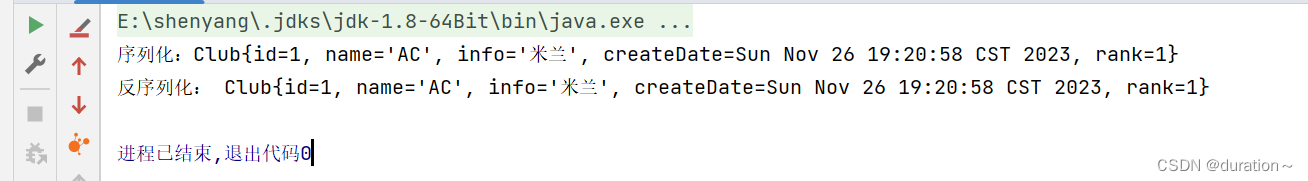
最终成功实现。