1. 五种不同场景下 @Autowired 的使用
第一种情况 上下文中只有一个同类型的bean
配置类
package org.example.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FruitConfiguration {
@Bean("apple")
public Fruit apple(){
return new Fruit("apple");
}
}
启动类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.example.bean")
public class AutowiredTestDemo {
@Autowired
private Fruit fruit;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
AutowiredTestDemo autowiredTestDemo = app.getBean(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
System.out.println(autowiredTestDemo.fruit);
}
}
输出
Fruit{name='apple', price=null}
第二种情况 上下文中有两个同类型不同名的bean 且都与注入字段名称不一致
配置类
@Configuration
public class FruitConfiguration {
@Bean("apple")
public Fruit apple(){
return new Fruit("apple");
}
@Bean("banana")
public Fruit banana(){
return new Fruit("banana");
}
}
启动类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.example.bean")
public class AutowiredTestDemo {
@Autowired
private Fruit fruit;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
AutowiredTestDemo autowiredTestDemo = app.getBean(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
System.out.println(autowiredTestDemo.fruit);
}
}
异常结果
No qualifying bean of type 'org.example.bean.Fruit' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: apple,banana
第三种情况 上下文中有两个同类型不同名的bean 且其中一个与注入字段名称一致
配置类
@Configuration
public class FruitConfiguration {
@Bean("apple")
public Fruit apple(){
return new Fruit("apple");
}
@Bean("banana")
public Fruit banana(){
return new Fruit("banana");
}
}
启动类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.example.bean")
public class AutowiredTestDemo {
@Autowired
private Fruit apple;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
AutowiredTestDemo autowiredTestDemo = app.getBean(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
System.out.println(autowiredTestDemo.apple);
}
}
输出结果
Fruit{name='apple', price=null}
第四种情况 上下文中有两个同类型不同名的bean 且都与注入字段名称不一致但其中一个使用@Primary 注解
配置类
package org.example.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
@Configuration
public class FruitConfiguration {
@Bean("apple")
public Fruit apple(){
return new Fruit("apple");
}
@Primary
@Bean("banana")
public Fruit banana(){
return new Fruit("banana");
}
}
启动类
package org.example;
import org.example.bean.Fruit;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.example.bean")
public class AutowiredTestDemo {
@Autowired
private Fruit fruit;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
AutowiredTestDemo autowiredTestDemo = app.getBean(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
System.out.println(autowiredTestDemo.fruit);
}
}
输出结果
Fruit{name='banana', price=null}
第五种情况 上下文中有两个同类型不同名的bean 且都与注入字段名称不一致但注入时使用@Qualifier注解
配置类
package org.example.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FruitConfiguration {
@Bean("apple")
public Fruit apple(){
return new Fruit("apple");
}
@Bean("banana")
public Fruit banana(){
return new Fruit("banana");
}
}
启动类
package org.example;
import org.example.bean.Fruit;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.example.bean")
public class AutowiredTestDemo {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("apple")
private Fruit fruit;
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
AutowiredTestDemo autowiredTestDemo = app.getBean(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
System.out.println(autowiredTestDemo.fruit);
}
}
输出结果
Fruit{name='apple', price=null}
2.源码分析
启动类
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建应用上下文的同时注册AutowiredTestDemo
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
AutowiredTestDemo autowiredTestDemo = app.getBean(AutowiredTestDemo.class);
System.out.println(autowiredTestDemo.fruit);
}
org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext#AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(java.lang.Class<?>…)
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
//调用无参构造方法
this();
//注册组件
//调用 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition 注册bd
register(componentClasses);
//刷新容器
refresh();
}
无参构造创建了一个AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader对象与ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner对象,用于读取和扫描带有注解的Bean定义信息
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader在初始化时将会往BeanFactory注册注解相关的处理器对象
org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader#AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry, org.springframework.core.env.Environment)
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
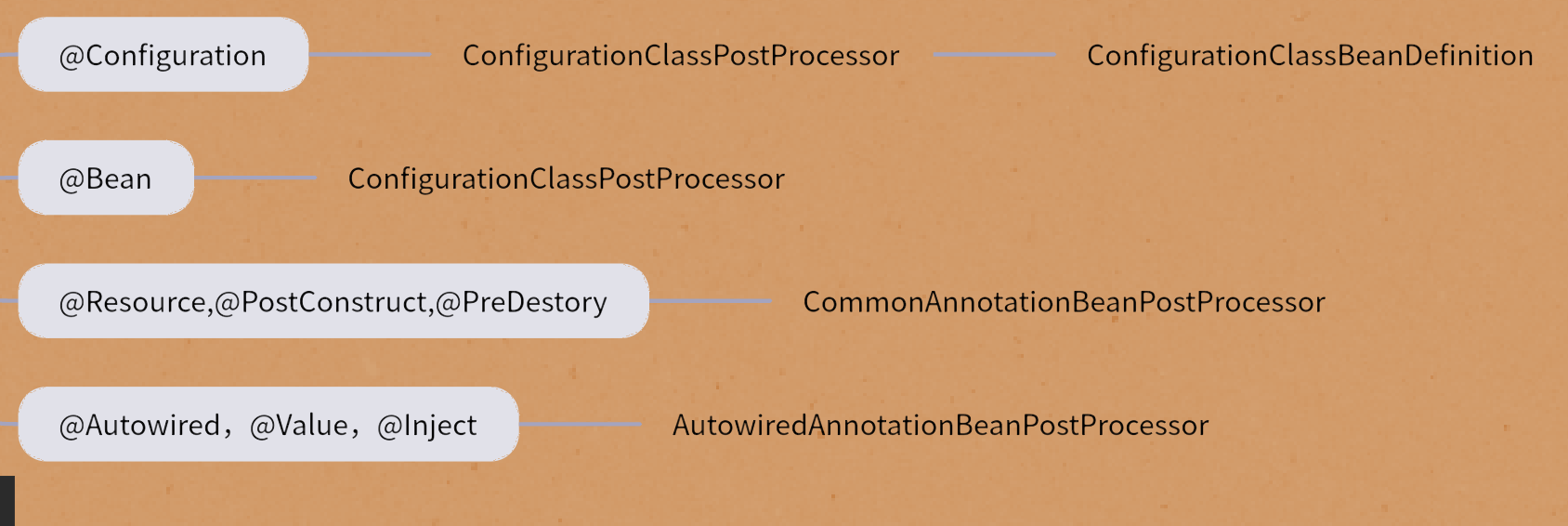
@Autowired注解是由 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 进行处理,而后者又实现了 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter 与 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 两个扩展点接口
重写 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition,在bean实例化前,合并定义信息后执行。将需要注入的字段和方法与之需要注入的bean建立映射关系并封装成InjectedElement集合,再与class对象建立映射关系封装为InjectionMetadata对象并存入缓冲中
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
//遍历类中的字段与方法,如果需要依赖注入,将封装成InjectionMetadata并放入缓冲中
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
//将成员添加到 beanDefinition 中,以便在配置过程中由外部管理器处理该成员的生命周期和依赖注入
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
重写 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter.postProcessProperties,此方法将在bean实例化后,属性填充前执行,此时当前bean已经完成了实例化,因此可以通过之前缓冲起来的映射关系,一一找出需要注入的字段和方法以及其对应需要注入的值,通过反射进行赋值操作
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
//从缓存中获取当前bean字节码对象的注解元信息
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
//进行属性注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
大概了解了@Autowired的核心处理类AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后,我们进一步分析上述五种情况,再源码底层是怎么处理的
情况一 有且仅有一个候选bean
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement#inject
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
//默认false
if (this.cached) {
try {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Unexpected removal of target bean for cached argument -> re-resolve
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
}
else {
//处理当前bean所属字段的依赖注入,获取需要注入的对象
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
if (value != null) {
//暴力访问
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
//通过反射给当前需要注入的字段设置值
field.set(bean, value);
}
跟进resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName)方法一路往下直到doResolveDependency方法
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
resolveMultipleBeans 方法是处理集合类型的依赖注入,而我们当前是非集合类型,因此会调用
findAutowireCandidates 处理依赖注入
//集合类型注入
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
//非集合类型注入
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates(
@Nullable String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
//根据需要注入的bean的类型 递归调用 beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors 获取父子BeanFactory中 类型的bean的名称
// 注入 此处可能返回多个 候选的beanName
String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager());
Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(candidateNames.length);
// 判断需要的类型是否是内建bean
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> classObjectEntry : this.resolvableDependencies.entrySet()) {
Class<?> autowiringType = classObjectEntry.getKey();
if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
Object autowiringValue = classObjectEntry.getValue();
autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType);
if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue);
break;
}
}
}
// ,isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) 用于判断候选项是否是自身引用。
// isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor) 用于判断候选项是否符合自动装配的条件
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
//调用DefaultListableBeanFactory.isAutowireCandidate() 完成@Qualifier注解过滤
// 如果不满足将不会添加到候选Map中
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
if (result.isEmpty()) {
boolean multiple = indicatesMultipleBeans(requiredType);
// Consider fallback matches if the first pass failed to find anything...
DependencyDescriptor fallbackDescriptor = descriptor.forFallbackMatch();
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor) &&
(!multiple || getAutowireCandidateResolver().hasQualifier(descriptor))) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
if (result.isEmpty() && !multiple) {
// Consider self references as a final pass...
// but in the case of a dependency collection, not the very same bean itself.
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
if (isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) &&
(!(descriptor instanceof MultiElementDescriptor) || !beanName.equals(candidate)) &&
isAutowireCandidate(candidate, fallbackDescriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
此时容器中只有一个Fruit类型的bean,回到doResolveDependency方法中,最终调用descriptor.resolveCandidate获取到bean实例,然后通过反射完成依赖注入
//匹配到一个beanName 不满足
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
//只匹配到一个beanName 不满足
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
//调用 beanFactory.getBean(beanName) 根据名称获取需要注入的bean对象
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
因此,情况一 容器中只有一个目标类型的bean进行依赖注入就此结束
情况二,三,四 有两个同类型bean的两种情况
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
如果根据类型匹配到两个beanName,将进入此判断语句中
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
//是否必须注入
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
由determineAutowireCandidate方法决定最终注入的beanName,如果无法选择出最合适的,将执行resolveNotUnique方法抛出NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException 异常,也就是我们情况二看到的异常
进入determineAutowireCandidate 方法
Class<?> requiredType = descriptor.getDependencyType();
//@Primary 注解处理 是否有标记了@Primary注解
String primaryCandidate = determinePrimaryCandidate(candidates, requiredType);
if (primaryCandidate != null) {
return primaryCandidate;
}
//javax.annotation.Priority 优先级匹配 值越小 优先级越高
String priorityCandidate = determineHighestPriorityCandidate(candidates, requiredType);
if (priorityCandidate != null) {
return priorityCandidate;
}
// Fallback
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : candidates.entrySet()) {
String candidateName = entry.getKey();
Object beanInstance = entry.getValue();
if ((beanInstance != null && this.resolvableDependencies.containsValue(beanInstance)) ||
//将候选的beanName与依赖注入的字段名称进行匹配
matchesBeanName(candidateName, descriptor.getDependencyName())) {
return candidateName;
}
}
return null;
首先针对第四种情况,如果有标记了@Primary注解的bean,将优先采用,如果都没有 ,则根据javax.annotation.Priority 注解的值选最小,值越小优先级越高。如果没有使用@Priority注解,将采用兜底方法
matchesBeanName(),哪一个候选的beanName与需要依赖注入的字段名称一致就使用谁
protected boolean matchesBeanName(String beanName, @Nullable String candidateName) {
return (candidateName != null &&
(candidateName.equals(beanName) || ObjectUtils.containsElement(getAliases(beanName), candidateName)));
}
此时就是情况三 候选的beanName的名称与需要依赖注入的字段名称一致,依然能完成注入。
情况五 注入时使用@Qualifier注解
回到
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#findAutowireCandidates
在获取到多个候选的beanName后,将会遍历集合,调用isSelfReference,isAutowireCandidate进行筛选,
而Qualifier注解的处理就在isAutowireCandidate方法中
for (String candidate : candidateNames) {
//调用DefaultListableBeanFactory.isAutowireCandidate() 完成@Qualifier注解过滤
// 如果不满足将不会添加到候选Map中
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) {
addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType);
}
}
跟进来到
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver#isAutowireCandidate
public boolean isAutowireCandidate(BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {
boolean match = super.isAutowireCandidate(bdHolder, descriptor);
if (match) {
//Qualifier 注解匹配 获取对象标准的Qualifier注解的值与候选的beanName进行匹配
//有Qualifier注解才进行比较判断
//否则直接返回true
match = checkQualifiers(bdHolder, descriptor.getAnnotations());
if (match) {
MethodParameter methodParam = descriptor.getMethodParameter();
if (methodParam != null) {
Method method = methodParam.getMethod();
if (method == null || void.class == method.getReturnType()) {
match = checkQualifiers(bdHolder, methodParam.getMethodAnnotations());
}
}
}
}
return match;
}
{
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(annotationsToSearch)) {
return true;
}
SimpleTypeConverter typeConverter = new SimpleTypeConverter();
for (Annotation annotation : annotationsToSearch) {
Class<? extends Annotation> type = annotation.annotationType();
boolean checkMeta = true;
boolean fallbackToMeta = false;
//有Qualifier注解才进行比较判断
if (isQualifier(type)) {
if (!checkQualifier(bdHolder, annotation, typeConverter)) {
fallbackToMeta = true;
}
else {
checkMeta = false;
}
}
if (checkMeta) {
boolean foundMeta = false;
for (Annotation metaAnn : type.getAnnotations()) {
Class<? extends Annotation> metaType = metaAnn.annotationType();
if (isQualifier(metaType)) {
foundMeta = true;
// Only accept fallback match if @Qualifier annotation has a value...
// Otherwise it is just a marker for a custom qualifier annotation.
if ((fallbackToMeta && StringUtils.isEmpty(AnnotationUtils.getValue(metaAnn))) ||
!checkQualifier(bdHolder, metaAnn, typeConverter)) {
return false;
}
}
}
if (fallbackToMeta && !foundMeta) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
至此,Spring针对 @Autowired 注解在五种不同的情况下进行依赖注入我们已经分析完毕
3. 结论
@Autowired 首先会通过 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors (递归获取父子BeanFactory调用getBeanNamesForType方法),根据需要进行依赖注入的字段的类型或者方法参数的类型取获取相应的beanName,如果注入的是非集合类型的对象,并且找到了一个以上的候选beanName,则下一步会去判断是否有标记优先级,如果都没有则会进行名称匹配,也就是将候选的beanName与字段名或参数名进行equals比较
byType -> 优先级比较 -> byName