前言
前面几篇我们简单的复习了一下自定义 View 的测量与绘制,并且回顾了常见的一些事件的处理方式。
那么如果我们想自定义 ViewGroup 的话,它和自定义View又有什么区别呢?其实我们把 ViewGroup 当做 View 来用的话也不是不可以。但是既然我们用到了容器 ViewGroup 当时是想用它的一些特殊的特性了。
比如 ViewGroup 的测量,ViewGroup的布局,ViewGroup的绘制。
- ViewGroup的测量:与 View 的测量不同,ViewGroup 的测量会遍历子 View ,获取子 View 的大小,从而决定自己的大小。当然我们也可以通过指定的模式来指定自身的大小。
- ViewGroup的布局:这个是 ViewGroup 核心与常用的功能。找到对于的子View 布局到指定的位置。
- ViewGroup的绘制:一般我们不会重写这个方法,因为一般来说它本身不需要绘制,并且当我们没有设置ViewGroup的背景的时候,onDraw()方法都不会被调用,一般来说 ViewGroup 只是会使用 dispatchDraw()方法来绘制其子View,其过程同样是通过遍历所有子View,并调用子View的绘制方法来完成绘制工作。
下面我们一起复习一下ViewGroup的测量布局方式。我们以入门级的 FlowLayout 为例,看看流式布局是如何测量与布局的。
话不多说,Let’s go
一、基本的测量与布局
我们先回顾一下ViewGroup的
一个经典的ViewGroup测量是怎样实现?一般来说,最简单的测量如下:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
for(int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++){
View childView = getChildAt(i);
measureChild(childView,widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
或者我们直接使用封装之后的默认方法
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
其内部也是遍历子View来实现的。当然如果有自定义的一些宽高测量规则,就不能使用这个方法,就需要自己遍历找到View自定义实现了。
需要注意的是,这里我们测量子布局传递的 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 是父布局的测量模式。
当父布局设置为固定宽度的时候,子View是不能超过这个宽度的,比如父控件设置为match_parent,自定义View无论是match_parent 还是 wrap_content 都是一样的,充满整个父控件。
相当于父布局调用子控件的onMeasure方法的时候告诉子控件,我就这么大,你看着办,不能超过它。
而父布局传递的是自适应AT_MOST模式,那么就是由子View来决定父布局的宽高。
相当于父布局调用子控件的onMeasure方法的时候问子控件,我也不知道我多大,你需要多大的位置?我又需要多大的地方才能容纳你?
其实也很好理解。那么一个经典的ViewGroup布局又是怎样实现?重写 onLayout 并且遍历拿到每一个View,进行Layout操作。
比如如下的代码,我们每一个View的高度设置为固定高度,并且垂直排列,类似一个ListView 的布局:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
//设置子View的高度
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
params.height = mFixedHeight * childCount;
setLayoutParams(params);
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != View.GONE) {
child.layout(l, i * mFixedHeight, r, (i + 1) * mFixedHeight);
}
}
}
注意我们 onLayout() 的参数
展示的效果就是这样:

二、流式的布局的layout
首先我们先不管测量,我们先指定ViewGroup的宽高为固定宽高,指定为match_parent。我们先做布局的操作:
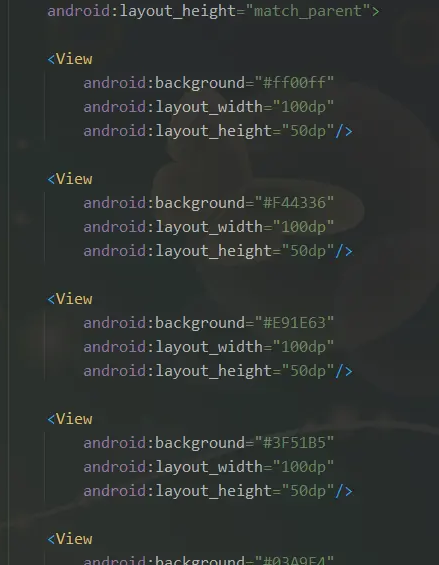
我们自定义 ViewGroup 中重写测量与布局的方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
* @param changed 当前ViewGroup的尺寸或者位置是否发生了改变
* @param l,t,r,b 当前ViewGroup相对于父控件的坐标位置,
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int mViewGroupWidth = getMeasuredWidth(); //当前ViewGroup的总宽度
int layoutChildViewCurX = l; //当前绘制View的X坐标
int layoutChildViewCurY = t; //当前绘制View的Y坐标
int childCount = getChildCount(); //子控件的数量
//遍历所有子控件,并在其位置上绘制子控件
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//子控件的宽和高
int width = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
//如果剩余控件不够,则移到下一行开始位置
if (layoutChildViewCurX + width > mViewGroupWidth) {
layoutChildViewCurX = l;
//如果换行,则需要修改当前绘制的高度位置
layoutChildViewCurY += height;
}
//执行childView的布局与绘制(右和下的位置加上自身的宽高即可)
childView.layout(layoutChildViewCurX, layoutChildViewCurY, layoutChildViewCurX + width, layoutChildViewCurY + height);
//布局完成之后,下一次绘制的X坐标需要加上宽度
layoutChildViewCurX += width;
}
}
最后我们就能得到对应的换行效果,如下:

通过上面我们的基础学习,我们应该能理解这样的布局方式,跟上面的基础布局方式相比,就是多了一个 layoutChildViewCurX 和 layoutChildViewCurY 。关于其它的逻辑这里已经注释的非常清楚了。
但是这样的效果好丑,我们加上间距 margin 试试?
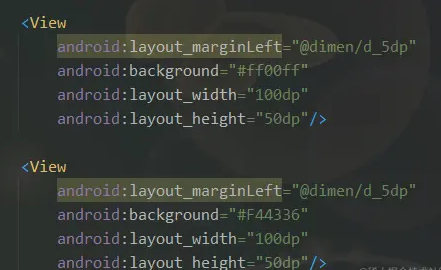
并没有效果,其实是内部 View 的 LayoutParams 就不支持 margin,我们需要定义一个内部类继承 ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams,并重写generateLayoutParams() 方法。
//要使子控件的margin属性有效必须继承此LayoutParams,内部还可以定制一些别的属性
public static class LayoutParams extends MarginLayoutParams {
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams) {
super(layoutParams);
}
}
@Override
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new ViewGroup2.LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new LayoutParams(p);
}
然后修改一下代码,在 layout 子布局的时候我们手动的把 margin 加上。
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int mViewGroupWidth = getMeasuredWidth(); //当前ViewGroup的总宽度
int layoutChildViewCurX = l; //当前绘制View的X坐标
int layoutChildViewCurY = t; //当前绘制View的Y坐标
int childCount = getChildCount(); //子控件的数量
//遍历所有子控件,并在其位置上绘制子控件
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//子控件的宽和高
int width = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
//如果剩余控件不够,则移到下一行开始位置
if (layoutChildViewCurX + width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > mViewGroupWidth) {
layoutChildViewCurX = l;
//如果换行,则需要修改当前绘制的高度位置
layoutChildViewCurY += height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
//执行childView的布局与绘制(右和下的位置加上自身的宽高即可)
childView.layout(
layoutChildViewCurX + lp.leftMargin,
layoutChildViewCurY + lp.topMargin,
layoutChildViewCurX + width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
layoutChildViewCurY + height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
//布局完成之后,下一次绘制的X坐标需要加上宽度
layoutChildViewCurX += width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
}
}
此时的效果就能生效了:

三、流式的布局的Measure
前面的设置我们都是使用的宽高 match_parent。那我们修改 ViewGroup 的高度为 wrap_content ,能实现高度自适应吗?

这…并不是我们想要的效果。并没有自适应高度。因为我们没有写测量的逻辑。
我们想一下,如果我们的宽度是固定的,想要高度自适应,那么我们就需要测量每一个子View的高度,计算出对应的高度,当换行之后我们再加上行的高度。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - this.getPaddingRight() - this.getPaddingLeft();
final int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - this.getPaddingTop() - this.getPaddingBottom();
final int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if (modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else if (modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && modeHeight == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
int layoutChildViewCurX = this.getPaddingLeft();
int totalControlHeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
final View childView = this.getChildAt(i);
if (childView.getVisibility() == GONE) {
continue;
}
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
childView.measure(
getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, this.getPaddingLeft() + this.getPaddingRight(), lp.width),
getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec, this.getPaddingTop() + this.getPaddingBottom(), lp.height)
);
int width = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
if (totalControlHeight == 0) {
totalControlHeight = height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
//如果剩余控件不够,则移到下一行开始位置
if (layoutChildViewCurX + width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > sizeWidth) {
layoutChildViewCurX = this.getPaddingLeft();
totalControlHeight += height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
layoutChildViewCurX += width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
}
//最后确定整个布局的高度和宽度
int cachedTotalWith = resolveSize(sizeWidth, widthMeasureSpec);
int cachedTotalHeight = resolveSize(totalControlHeight, heightMeasureSpec);
this.setMeasuredDimension(cachedTotalWith, cachedTotalHeight);
}
宽度固定和高度自适应的情况下,我们是这么处理的。计算出子View的总高度,然后设置 setMeasuredDimension 为ViewGroup的测量宽度和子View的总高度。即为最终 ViewGroup 的宽高。

这样我们就能实现高度的自适应了。那么宽度能不能自适应呢?
当然可以,我们只需要记录每一行的宽度,然后最终 setMeasuredDimension 的时候传入所有行中的最大宽度,就是 ViewGroup 的最终宽度,而高度的计算是和上面的方式一样的。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
else if (modeWidth == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && modeHeight == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//如果宽高都是Wrap-Content
int layoutChildViewCurX = this.getPaddingLeft();
//总宽度和总高度
int totalControlWidth = 0;
int totalControlHeight = 0;
//由于宽度是非固定的,所以用一个List接收每一行的最大宽度
List<Integer> lineLenghts = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
final View childView = this.getChildAt(i);
if (childView.getVisibility() == GONE) {
continue;
}
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
childView.measure(
getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, this.getPaddingLeft() + this.getPaddingRight(), lp.width),
getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec, this.getPaddingTop() + this.getPaddingBottom(), lp.height)
);
int width = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
if (totalControlHeight == 0) {
totalControlHeight = height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
//如果剩余控件不够,则移到下一行开始位置
if (layoutChildViewCurX + width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > sizeWidth) {
lineLenghts.add(layoutChildViewCurX);
layoutChildViewCurX = this.getPaddingLeft();
totalControlHeight += height + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
}
layoutChildViewCurX += width + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
}
//计算每一行的宽度,选出最大值
YYLogUtils.w("每一行的宽度 :" + lineLenghts.toString());
totalControlWidth = Collections.max(lineLenghts);
YYLogUtils.w("选出最大宽度 :" + totalControlWidth);
//最后确定整个布局的高度和宽度
int cachedTotalWith = resolveSize(totalControlWidth, widthMeasureSpec);
int cachedTotalHeight = resolveSize(totalControlHeight, heightMeasureSpec);
this.setMeasuredDimension(cachedTotalWith, cachedTotalHeight);
}
}
为了效果,我们把第一行的最后一个View宽度多一点,方便查看效果。

这样就可以得到ViewGroup自适应的宽度和高度了。并不复杂对不对!
后记
这样是不是就能实现一个简单的流式布局了呢?当然这些只是为方便学习和理解,真正的实战中并不推荐直接这样使用,因为内部还有一些兼容的逻辑没处理,一些逻辑没有封装,属性没有抽取。甚至连每一个View的高度,和每一行的最大高度也没有处理,其实这样健壮性并不好。
Android 知识点归整
Android 性能调优系列:https://0a.fit/dNHYY
Android 车载学习指南:https://0a.fit/jdVoy
Android Framework核心知识点笔记:https://0a.fit/acnLL
Android 音视频学习笔记:https://0a.fit/BzPVh
Jetpack全家桶(含Compose):https://0a.fit/GQJSl
Kotlin 入门到精进:https://0a.fit/kdfWR
Flutter 基础到进阶实战:https://0a.fit/xvcHV
Android 八大知识体系:https://0a.fit/mieWJ
Android 中高级面试题锦:https://0a.fit/YXwVq
后续如有新知识点,将会持续更新,尽请期待……