文章目录
- 序
- 节点添加
- Task
- 以DefaultTaskDisplayArea为父节点
- 以Task为父节点
- ActivityRecord
- WindowToken
- WindowState
- 以WindowToken为父节点
- 以ActivityRecord为父节点
- 小结
- 调用场景
- 添加差异
- 流程分析
- 添加log
- 堆栈打印流程
- Launcher
- StatusBar
序
尚未添加窗口的层级结构树,如图
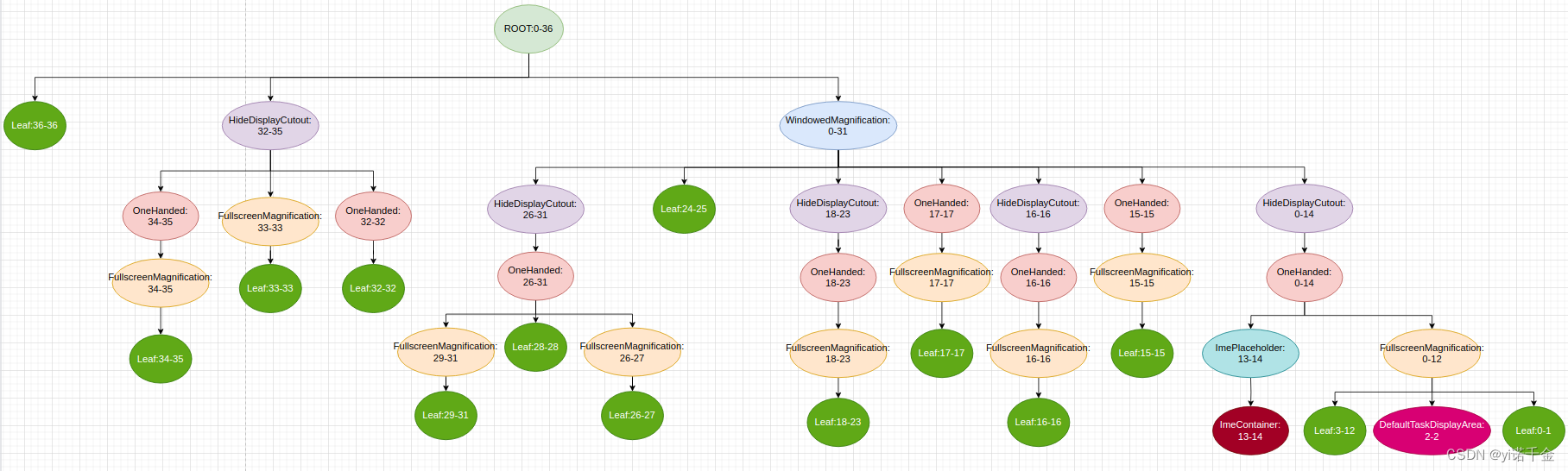 DisplayArea层级结构中的每一个DisplayArea,都包含着一个层级值范围,这个层级值范围表明了这个DisplayArea可以容纳哪些类型的窗口。
DisplayArea层级结构中的每一个DisplayArea,都包含着一个层级值范围,这个层级值范围表明了这个DisplayArea可以容纳哪些类型的窗口。
每种窗口类型,都可以通过WindowManagerPolicy.getWindowLayerFromTypeLw方法,返回一个相应的层级值。
/**
* Returns the layer assignment for the window type. Allows you to control how different
* kinds of windows are ordered on-screen.
*
* @param type The type of window being assigned.
* @param canAddInternalSystemWindow If the owner window associated with the type we are
* evaluating can add internal system windows. I.e they have
* {@link Manifest.permission#INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW}. If true, alert window
* types {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#isSystemAlertWindowType(int)}
* can be assigned layers greater than the layer for
* {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY} Else, their
* layers would be lesser.
* @return int An arbitrary integer used to order windows, with lower numbers below higher ones.
*/
default int getWindowLayerFromTypeLw(int type, boolean canAddInternalSystemWindow) {
return getWindowLayerFromTypeLw(type, canAddInternalSystemWindow,
false /* roundedCornerOverlay */);
}
/**
* Returns the layer assignment for the window type. Allows you to control how different
* kinds of windows are ordered on-screen.
*
* @param type The type of window being assigned.
* @param canAddInternalSystemWindow If the owner window associated with the type we are
* evaluating can add internal system windows. I.e they have
* {@link Manifest.permission#INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW}. If true, alert window
* types {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#isSystemAlertWindowType(int)}
* can be assigned layers greater than the layer for
* {@link android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams#TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY} Else, their
* layers would be lesser.
* @param roundedCornerOverlay {#code true} to indicate that the owner window is rounded corner
* overlay.
* @return int An arbitrary integer used to order windows, with lower numbers below higher ones.
*/
default int getWindowLayerFromTypeLw(int type, boolean canAddInternalSystemWindow,
boolean roundedCornerOverlay) {
// Always put the rounded corner layer to the top most.
if (roundedCornerOverlay && canAddInternalSystemWindow) {
return getMaxWindowLayer();
}
if (type >= FIRST_APPLICATION_WINDOW && type <= LAST_APPLICATION_WINDOW) {
return APPLICATION_LAYER;
}
switch (type) {
case TYPE_WALLPAPER:
// wallpaper is at the bottom, though the window manager may move it.
return 1;
case TYPE_PRESENTATION:
case TYPE_PRIVATE_PRESENTATION:
case TYPE_DOCK_DIVIDER:
case TYPE_QS_DIALOG:
case TYPE_PHONE:
return 3;
case TYPE_SEARCH_BAR:
return 4;
case TYPE_INPUT_CONSUMER:
return 5;
case TYPE_SYSTEM_DIALOG:
return 6;
case TYPE_TOAST:
// toasts and the plugged-in battery thing
return 7;
case TYPE_PRIORITY_PHONE:
// SIM errors and unlock. Not sure if this really should be in a high layer.
return 8;
case TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT:
// like the ANR / app crashed dialogs
// Type is deprecated for non-system apps. For system apps, this type should be
// in a higher layer than TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY.
return canAddInternalSystemWindow ? 12 : 9;
case TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY:
return 11;
case TYPE_INPUT_METHOD:
// on-screen keyboards and other such input method user interfaces go here.
return 13;
case TYPE_INPUT_METHOD_DIALOG:
// on-screen keyboards and other such input method user interfaces go here.
return 14;
case TYPE_STATUS_BAR:
return 15;
case TYPE_STATUS_BAR_ADDITIONAL:
return 16;
case TYPE_NOTIFICATION_SHADE:
return 17;
case TYPE_STATUS_BAR_SUB_PANEL:
return 18;
case TYPE_KEYGUARD_DIALOG:
return 19;
case TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION_STARTING:
return 20;
case TYPE_VOICE_INTERACTION:
// voice interaction layer should show above the lock screen.
return 21;
case TYPE_VOLUME_OVERLAY:
// the on-screen volume indicator and controller shown when the user
// changes the device volume
return 22;
case TYPE_SYSTEM_OVERLAY:
// the on-screen volume indicator and controller shown when the user
// changes the device volume
return canAddInternalSystemWindow ? 23 : 10;
case TYPE_NAVIGATION_BAR:
// the navigation bar, if available, shows atop most things
return 24;
case TYPE_NAVIGATION_BAR_PANEL:
// some panels (e.g. search) need to show on top of the navigation bar
return 25;
case TYPE_SCREENSHOT:
// screenshot selection layer shouldn't go above system error, but it should cover
// navigation bars at the very least.
return 26;
case TYPE_SYSTEM_ERROR:
// system-level error dialogs
return canAddInternalSystemWindow ? 27 : 9;
case TYPE_MAGNIFICATION_OVERLAY:
// used to highlight the magnified portion of a display
return 28;
case TYPE_DISPLAY_OVERLAY:
// used to simulate secondary display devices
return 29;
case TYPE_DRAG:
// the drag layer: input for drag-and-drop is associated with this window,
// which sits above all other focusable windows
return 30;
case TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_OVERLAY:
// overlay put by accessibility services to intercept user interaction
return 31;
case TYPE_ACCESSIBILITY_MAGNIFICATION_OVERLAY:
return 32;
case TYPE_SECURE_SYSTEM_OVERLAY:
return 33;
case TYPE_BOOT_PROGRESS:
return 34;
case TYPE_POINTER:
// the (mouse) pointer layer
return 35;
default:
Slog.e("WindowManager", "Unknown window type: " + type);
return 3;
}
}
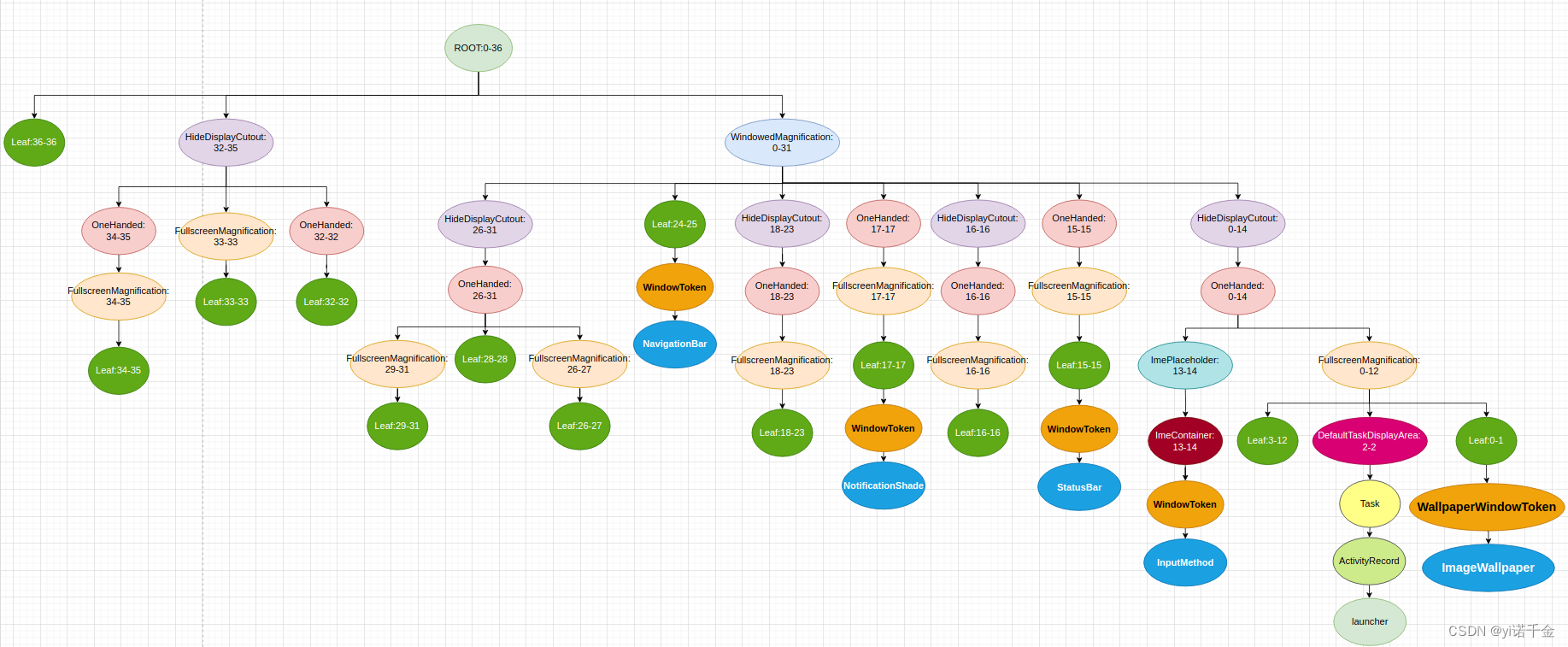
在DisplayArea层级结构中,可以直接容纳窗口的父节点,有三种类型:
- TaskDisplayArea用于容纳App类型窗口,Task的容器是TaskDisplayArea,该容器也就是对应我们层级结构树中的DefaultTaskDisplayArea,ActivityRecord的容器是Task
- DisplayArea.Tokens用于容纳非App类型窗口,WindowToken的容器是DisplayArea.Tokens,该容器对应层级结构树中的Leaf节点。其中WallpaperWindowToken继承WindowToken,是用来存放和Wallpaper相关的窗口
- ImeContainer用于容纳输入法窗口,输入法的容器是ImeContainer
这里我们根据上面的代码,以及adb shell dumpsys activity containers的信息简单画出如下树形图
节点添加
如何知道这些窗口是在什么时候添加的?
我们需要理清各个节点的父子关系,从有助于我们找到关键代码
Task
从以及adb shell dumpsys activity containers和树形图我们知道Task节点的父亲是DefaultTaskDisplayArea

当然还有一种情况是Task的父节点为Task的情况。
 那么DefaultTaskDisplayArea和Task中一定有添加Task相关的方法,比如addTask、addChild。
那么DefaultTaskDisplayArea和Task中一定有添加Task相关的方法,比如addTask、addChild。
以DefaultTaskDisplayArea为父节点
我们顺着这个思路在TaskDisplayArea.java中看看有没有相关方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/TaskDisplayArea.java
void addChild(WindowContainer child, int position) {
if (child.asTaskDisplayArea() != null) {
if (DEBUG_ROOT_TASK) {
Slog.d(TAG_WM, "Set TaskDisplayArea=" + child + " on taskDisplayArea=" + this);
}
super.addChild(child, position);
} else if (child.asTask() != null) {
addChildTask(child.asTask(), position);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"TaskDisplayArea can only add Task and TaskDisplayArea, but found "
+ child);
}
}
private void addChildTask(Task task, int position) {
if (DEBUG_ROOT_TASK) Slog.d(TAG_WM, "Set task=" + task + " on taskDisplayArea=" + this);
addRootTaskReferenceIfNeeded(task);
position = findPositionForRootTask(position, task, true /* adding */);
super.addChild(task, position);
if (mPreferredTopFocusableRootTask != null
&& task.isFocusable()
&& mPreferredTopFocusableRootTask.compareTo(task) < 0) {
// Clear preferred top because the adding focusable task has a higher z-order.
mPreferredTopFocusableRootTask = null;
}
mAtmService.updateSleepIfNeededLocked();
onRootTaskOrderChanged(task);
}
我们发现在void addChild(WindowContainer child, int position)中满足条件child.asTask() != null时,就会调用addChildTask(child.asTask(), position);这也是我们添加Task的方法。可以看到里面有一个关键的调用super.addChild(task, position);,也就是说实际的添加在这里
对应的是WindowContainer的void addChild(E child, int index)
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
/**
* Adds the input window container has a child of this container at the input index.
*/
@CallSuper
void addChild(E child, int index) {
if (!child.mReparenting && child.getParent() != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("addChild: container=" + child.getName()
+ " is already a child of container=" + child.getParent().getName()
+ " can't add to container=" + getName()
+ "\n callers=" + Debug.getCallers(15, "\n"));
}
if ((index < 0 && index != POSITION_BOTTOM)
|| (index > mChildren.size() && index != POSITION_TOP)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("addChild: invalid position=" + index
+ ", children number=" + mChildren.size());
}
if (index == POSITION_TOP) {
index = mChildren.size();
} else if (index == POSITION_BOTTOM) {
index = 0;
}
mChildren.add(index, child);
// Set the parent after we've actually added a child in case a subclass depends on this.
child.setParent(this);
}
实际上调用的我们构建层级结构树时的方法。
以Task为父节点
在Task.java中查找添加节点的相关方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Task.java
void addChild(WindowContainer child, final boolean toTop, boolean showForAllUsers) {
Task task = child.asTask();
try {
if (task != null) {
task.setForceShowForAllUsers(showForAllUsers);
}
// We only want to move the parents to the parents if we are creating this task at the
// top of its root task.
addChild(child, toTop ? MAX_VALUE : 0, toTop /*moveParents*/);
} finally {
if (task != null) {
task.setForceShowForAllUsers(false);
}
}
}
/**
* Put a Task in this root task. Used for adding only.
* When task is added to top of the root task, the entire branch of the hierarchy (including
* root task and display) will be brought to top.
* @param child The child to add.
* @param position Target position to add the task to.
*/
private void addChild(WindowContainer child, int position, boolean moveParents) {
// Add child task.
addChild(child, null);
// Move child to a proper position, as some restriction for position might apply.
positionChildAt(position, child, moveParents /* includingParents */);
}
这里的addChild(child, null);实际调用的是WindowContainer的protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator),因为其父类TaskFragment中没有符合该入参的addChild方法,因此继续向上查找TaskFragment的父类WindowContainer中的addChild方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.java
/**
* Adds the input window container has a child of this container in order based on the input
* comparator.
* @param child The window container to add as a child of this window container.
* @param comparator Comparator to use in determining the position the child should be added to.
* If null, the child will be added to the top.
*/
@CallSuper
protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator) {
......
//记录插入数组的位置,若为-1则将当前child加入到后面
int positionToAdd = -1;
if (comparator != null) {
//判断当前节点中孩子的数量
//依次比较将要加入的窗口与已经存在的child的BaseLayer
//mChildren越大放到数组最前面
final int count = mChildren.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//比较baseLayer,如果child大于列表中已经存在的,则需要返回1,否则返回-1
//新加入的的child大于mChildren.get(i)则返回1,小于则返回-1
//注:comparator比较器的逻辑见上面代码的mWindowComparator
if (comparator.compare(child, mChildren.get(i)) < 0) {
//记录当前要插入的位置
positionToAdd = i;
break;
}
}
}
//如果新加入的窗口大于现在所有窗口
if (positionToAdd == -1) {
//将该窗口加入到列表最后
mChildren.add(child);
} else {
mChildren.add(positionToAdd, child);
}
// Set the parent after we've actually added a child in case a subclass depends on this.
//此处将child的mParent设置为this
child.setParent(this);
}
protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)是重载addChild,和之前的void addChild(E child, int index)有所不同
ActivityRecord
ActivityRecord的父节点是Task,同样的在Task.java中找添加ActivityRecord的方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Task.java
@Override
void addChild(WindowContainer child, int index) {
index = getAdjustedChildPosition(child, index);
super.addChild(child, index);
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE, "addChild: %s at top.", this);
// A rootable task that is now being added to be the child of an organized task. Making
// sure the root task references is keep updated.
if (mTaskOrganizer != null && mCreatedByOrganizer && child.asTask() != null) {
getDisplayArea().addRootTaskReferenceIfNeeded((Task) child);
}
// Make sure the list of display UID allowlists is updated
// now that this record is in a new task.
mRootWindowContainer.updateUIDsPresentOnDisplay();
// Only pass minimum dimensions for pure TaskFragment. Task's minimum dimensions must be
// passed from Task constructor.
final TaskFragment childTaskFrag = child.asTaskFragment();
if (childTaskFrag != null && childTaskFrag.asTask() == null) {
childTaskFrag.setMinDimensions(mMinWidth, mMinHeight);
}
}
super.addChild(child, index);调用的是Task父类TaskFragment的addChild方法
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/TaskFragment.java
@Override
void addChild(WindowContainer child, int index) {
ActivityRecord r = topRunningActivity();
mClearedTaskForReuse = false;
mClearedTaskFragmentForPip = false;
final ActivityRecord addingActivity = child.asActivityRecord();
final boolean isAddingActivity = addingActivity != null;
final Task task = isAddingActivity ? getTask() : null;
// If this task had any activity before we added this one.
boolean taskHadActivity = task != null && task.getTopMostActivity() != null;
// getActivityType() looks at the top child, so we need to read the type before adding
// a new child in case the new child is on top and UNDEFINED.
final int activityType = task != null ? task.getActivityType() : ACTIVITY_TYPE_UNDEFINED;
super.addChild(child, index);
if (isAddingActivity && task != null) {
// TODO(b/207481538): temporary per-activity screenshoting
if (r != null && BackNavigationController.isScreenshotEnabled()) {
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_BACK_PREVIEW, "Screenshotting Activity %s",
r.mActivityComponent.flattenToString());
Rect outBounds = r.getBounds();
SurfaceControl.ScreenshotHardwareBuffer backBuffer = SurfaceControl.captureLayers(
r.mSurfaceControl,
new Rect(0, 0, outBounds.width(), outBounds.height()),
1f);
mBackScreenshots.put(r.mActivityComponent.flattenToString(), backBuffer);
}
child.asActivityRecord().inHistory = true;
task.onDescendantActivityAdded(taskHadActivity, activityType, addingActivity);
}
}
super.addChild(child, index);调用TaskFragment父类方法,即WindowContainer的void addChild(E child, int index)
WindowToken
WindowToken的父节点是叶子节点或者输入法节点,叶子节点和输入法节点其实都是DisplayArea.Tokens类型。
WallpaperWindowToken继承WindowToken,因此同理。
所以我们只需在DisplayArea.java的Tokens类中查找相关的添加WindowToken的方法。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/DisplayArea.java
void addChild(WindowToken token) {
addChild(token, mWindowComparator);
}
这里的addChild(token, mWindowComparator);调用的就是WindowContainer的protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)
WindowState
WindowState的父节点是WindowToken和ActivityRecord,我们在WindowToken.java和中ActivityRecord.java找添加WindowState的方法
以WindowToken为父节点
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowToken.java
void addWindow(final WindowState win) {
ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS,
"addWindow: win=%s Callers=%s", win, Debug.getCallers(5));
if (win.isChildWindow()) {
// Child windows are added to their parent windows.
return;
}
// This token is created from WindowContext and the client requests to addView now, create a
// surface for this token.
if (mSurfaceControl == null) {
createSurfaceControl(true /* force */);
// Layers could have been assigned before the surface was created, update them again
reassignLayer(getSyncTransaction());
}
if (!mChildren.contains(win)) {
ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE, "Adding %s to %s", win, this);
addChild(win, mWindowComparator);
mWmService.mWindowsChanged = true;
// TODO: Should we also be setting layout needed here and other places?
}
}
addChild(win, mWindowComparator);调用的就是WindowContainer的protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)添加WindowState
以ActivityRecord为父节点
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityRecord.java
@Override
void addWindow(WindowState w) {
super.addWindow(w);
boolean gotReplacementWindow = false;
for (int i = mChildren.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final WindowState candidate = mChildren.get(i);
gotReplacementWindow |= candidate.setReplacementWindowIfNeeded(w);
}
// if we got a replacement window, reset the timeout to give drawing more time
if (gotReplacementWindow) {
mWmService.scheduleWindowReplacementTimeouts(this);
}
checkKeyguardFlagsChanged();
}
ActivityRecord的父类是WindowToken,其super.addWindow(w);调用的就是WindowToken的addWindow方法,因此最终也是通过WindowContainer的protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)添加WindowState
小结
通过前面的分析,添加窗口最终都是通过WindowContainer的void addChild(E child, int index)和protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)来添加的,我们来汇总一下这两种方法的调用情况与区别
调用场景
调用void addChild(E child, int index)的情况
- DefaultTaskDisplayArea添加Task
- Task添加ActivityRecord
调用protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)的情况
- Task添加Task
- 叶子节点和输入法节点(Token)添加WindowToken
- WindowToken添加WindowState
- ActivityRecord添加WindowState
添加差异
WindowContainer中的void addChild(E child, int index)和protected void addChild(E child, Comparator comparator)方法区别是什么?
它们之间的区别其实在于添加子容器的方式和顺序。
void addChild(E child, int index)方法:
- 该方法通过传入的index参数指定了子容器的插入位置。index表示子容器在当前容器的子容器列表中的位置索引。
- 调用该方法会将子容器添加到指定的位置,而不会根据任何比较器进行排序。
- 这种方式适用于需要直接指定子容器的插入位置的情况。
protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)方法:
- 该方法通过传入的Comparator参数定义了子容器的排序规则。
- 调用该方法会将子容器添加到当前容器的子容器列表中,并根据指定的比较器对子容器进行排序。
- 这种方式适用于根据特定的排序规则对子容器进行动态排序的情况。
总结起来,addChild(E child, int index)方法允许直接指定子容器的插入位置,而addChild(E child, Comparator comparator)方法则通过比较器对子容器进行排序并添加到合适的位置。根据实际需求,可以选择适合的方法来添加子容器。
流程分析
添加log
既然从上述分析中发现添加窗口最终都是通过WindowContainer的void addChild(E child, int index)和protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator)来添加的,那么我们可以添加相关的log,来看看其对应的流程是怎么样的
void addChild(E child, int index) {
if (child instanceof Task || child instanceof ActivityRecord || child instanceof WindowToken || child instanceof WindowState) {
android.util.Log.i("WindowContainer.TAG:", this + "addChild child = " + child , new Exception());
}
......
}
protected void addChild(E child, Comparator<E> comparator) {
if (child instanceof Task || child instanceof ActivityRecord || child instanceof WindowToken || child instanceof WindowState) {
android.util.Log.i("WindowContainer.TAG:", this + "addChild Comparator child = " + child , new Exception());
}
......
}
堆栈打印流程
这里我们以Launcher和StatusBar为例
Launcher
WindowContainer.TAG : DefaultTaskDisplayArea@243571827 addChild child = Task{a13d730 #1 type=home ?? U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=undefined translucent=true sz=0}
WindowContainer.TAG : java.lang.Exception
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.addChild(WindowContainer.java:727)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskDisplayArea.addChildTask(TaskDisplayArea.java:334)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskDisplayArea.addChild(TaskDisplayArea.java:320)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Task$Builder.build(Task.java:6551)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskDisplayArea.createRootTask(TaskDisplayArea.java:1066)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskDisplayArea.createRootTask(TaskDisplayArea.java:1040)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskDisplayArea.getOrCreateRootHomeTask(TaskDisplayArea.java:1640)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.setWindowManager(RootWindowContainer.java:1321)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityTaskManagerService.setWindowManager(ActivityTaskManagerService.java:1006)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.am.ActivityManagerService.setWindowManager(ActivityManagerService.java:1923)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.startOtherServices(SystemServer.java:1595)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.run(SystemServer.java:939)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.main(SystemServer.java:649)
WindowContainer.TAG : at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(RuntimeInit.java:548)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:914)
WindowContainer.TAG : Task{a13d730 #1 type=home ?? U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=0} addChild Comparator child = Task{63f31d4 #2 type=undefined A=1000:com.android.settings.FallbackHome U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=undefined translucent=true sz=0}
WindowContainer.TAG : java.lang.Exception
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.addChild(WindowContainer.java:694)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Task.addChild(Task.java:5935)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Task.-$$Nest$maddChild(Unknown Source:0)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Task$Builder.build(Task.java:6548)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Task.reuseOrCreateTask(Task.java:5819)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.setNewTask(ActivityStarter.java:2872)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.startActivityInner(ActivityStarter.java:1864)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.startActivityUnchecked(ActivityStarter.java:1661)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.executeRequest(ActivityStarter.java:1216)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.execute(ActivityStarter.java:702)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStartController.startHomeActivity(ActivityStartController.java:179)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnTaskDisplayArea(RootWindowContainer.java:1493)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.lambda$startHomeOnDisplay$12$com-android-server-wm-RootWindowContainer(RootWindowContainer.java:1434)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer$$ExternalSyntheticLambda7.apply(Unknown Source:16)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskDisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(TaskDisplayArea.java:513)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(WindowContainer.java:2283)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnDisplay(RootWindowContainer.java:1433)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnDisplay(RootWindowContainer.java:1420)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnAllDisplays(RootWindowContainer.java:1405)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityTaskManagerService$LocalService.startHomeOnAllDisplays(ActivityTaskManagerService.java:5892)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.am.ActivityManagerService.systemReady(ActivityManagerService.java:8203)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.startOtherServices(SystemServer.java:2801)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.run(SystemServer.java:939)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.main(SystemServer.java:649)
WindowContainer.TAG : at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(RuntimeInit.java:548)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:914)
WindowContainer.TAG : Task{63f31d4 #2 type=undefined A=1000:com.android.settings.FallbackHome U=0 rootTaskId=1 visible=true visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=0} addChild child = ActivityRecord{983a135 u0 com.android.settings/.FallbackHome}
WindowContainer.TAG : java.lang.Exception
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.addChild(WindowContainer.java:727)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskFragment.addChild(TaskFragment.java:1835)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Task.addChild(Task.java:1429)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.addOrReparentStartingActivity(ActivityStarter.java:2927)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.setNewTask(ActivityStarter.java:2877)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.startActivityInner(ActivityStarter.java:1864)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.startActivityUnchecked(ActivityStarter.java:1661)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.executeRequest(ActivityStarter.java:1216)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStarter.execute(ActivityStarter.java:702)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityStartController.startHomeActivity(ActivityStartController.java:179)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnTaskDisplayArea(RootWindowContainer.java:1493)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.lambda$startHomeOnDisplay$12$com-android-server-wm-RootWindowContainer(RootWindowContainer.java:1434)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer$$ExternalSyntheticLambda7.apply(Unknown Source:16)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.TaskDisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(TaskDisplayArea.java:513)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(DisplayArea.java:404)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.reduceOnAllTaskDisplayAreas(WindowContainer.java:2283)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnDisplay(RootWindowContainer.java:1433)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnDisplay(RootWindowContainer.java:1420)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.RootWindowContainer.startHomeOnAllDisplays(RootWindowContainer.java:1405)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityTaskManagerService$LocalService.startHomeOnAllDisplays(ActivityTaskManagerService.java:5892)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.am.ActivityManagerService.systemReady(ActivityManagerService.java:8203)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.startOtherServices(SystemServer.java:2801)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.run(SystemServer.java:939)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.SystemServer.main(SystemServer.java:649)
WindowContainer.TAG : at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(RuntimeInit.java:548)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:914)
WindowContainer.TAG : ActivityRecord{983a135 u0 com.android.settings/.FallbackHome} t2} addChild Comparator child = Window{ae9b359 u0 com.android.settings/com.android.settings.FallbackHome}
WindowContainer.TAG : java.lang.Exception
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.addChild(WindowContainer.java:694)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowToken.addWindow(WindowToken.java:302)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.ActivityRecord.addWindow(ActivityRecord.java:4212)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.addWindow(WindowManagerService.java:1773)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Session.addToDisplayAsUser(Session.java:209)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.view.IWindowSession$Stub.onTransact(IWindowSession.java:652)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Session.onTransact(Session.java:175)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.os.Binder.execTransactInternal(Binder.java:1280)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.os.Binder.execTransact(Binder.java:1244)
home task直接被TaskDisplayArea持有为孩子,这里可以明显看出Task{a13d730 #1 type=home 是在第一次创建WMS就已经创建好了,通过的是TaskDisplayArea.getOrCreateRootHomeTask开始一直到com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.addChild
之后home task加入一个具体Launcher的task,这里最开始当然是我们的FallbackHome。
具体堆栈可以看出是ActivityManagerService.systemReady时候触发了ActivityTaskManagerService$LocalService.startHomeOnAllDisplays然后把HomeActivity拉起,由于此时还是加密状态,所以获取的的Home当然是setting的fallbackhome
最后ActivityRecord添加WindowState,就是通过跨进程通信addWindow。
StatusBar
WindowContainer.TAG : Leaf:15:15@65133355 addChild Comparator child = WindowToken{ea411e9 type=2000 android.os.BinderProxy@46a0296}
WindowContainer.TAG : java.lang.Exception
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.addChild(WindowContainer.java:694)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayArea$Tokens.addChild(DisplayArea.java:605)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.DisplayContent.addWindowToken(DisplayContent.java:1235)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowToken.<init>(WindowToken.java:214)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowToken$Builder.build(WindowToken.java:817)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.addWindow(WindowManagerService.java:1577)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Session.addToDisplayAsUser(Session.java:209)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.view.IWindowSession$Stub.onTransact(IWindowSession.java:652)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Session.onTransact(Session.java:175)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.os.Binder.execTransactInternal(Binder.java:1280)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.os.Binder.execTransact(Binder.java:1244)
WindowContainer.TAG : WindowToken{ea411e9 type=2000 android.os.BinderProxy@46a0296} addChild Comparator child = Window{c86ce6e u0 StatusBar}
WindowContainer.TAG : java.lang.Exception
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowContainer.addChild(WindowContainer.java:694)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowToken.addWindow(WindowToken.java:302)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.addWindow(WindowManagerService.java:1773)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Session.addToDisplayAsUser(Session.java:209)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.view.IWindowSession$Stub.onTransact(IWindowSession.java:652)
WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.Session.onTransact(Session.java:175)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.os.Binder.execTransactInternal(Binder.java:1280)
WindowContainer.TAG : at android.os.Binder.execTransact(Binder.java:1244)
WindowToken和WindowState都是通过跨进程通信Session.addToDisplayAsUser来调用。
WindowToken的堆栈中WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.addWindow(WindowManagerService.java:1577),在1577行开始添加WindowToken,而WindowState的堆栈中WindowContainer.TAG : at com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService.addWindow(WindowManagerService.java:1773)1773行开始添加WindowState,正好是在添加WindowToken之后。
具体流程可参考Android T WMS窗口相关流程