文档:map、set
文章目录
- 🍯1. 关联式容器
- 🫖2. set
- 🍼1. 模板参数
- 🍼2. 构造函数
- 🍼3. 修改
- 🍼4.操作
- 🥛find
- 🥛count
- 🥛lower_bound & upper_bound & equal_range
- 🍭3. map
- 🍬1. 模板参数
- 🍬2. 构造函数
- 🍬3. insert
- 🍬4. operator[]
- image-20230906114657420
🍯1. 关联式容器
前几篇文章中写的STL容器:vector、list、dequeue等都是序列式容器,它们都是线性结构;而map和set都是关联式容器,与序列式容器不同的是,它们里面存储的是<key,value>结构的键值对,这个在数据检索的时候,比序列式容器的效率更高
键值对:
键值对用来表示一一对应的关系结构,
key表示键值,value表示与key对应的信息template <class T1, class T2> struct pair { typedef T1 first_type; typedef T2 second_type; T1 first; //key T2 second; //value pair(): first(T1()), second(T2()) {} pair(const T1& a, const T2& b): first(a), second(b) {} };
🫖2. set
set是一种key模型,可用于判断元素在不在、元素去重
🍼1. 模板参数
template < class T, // set::key_type/value_type
class Compare = less<T>, // set::key_compare/value_compare
class Alloc = allocator<T> // set::allocator_type
> class set;
这里的模板参数里面多了一个Compare = less<T>,它的底层是红黑树,可以用来给我们比较大小
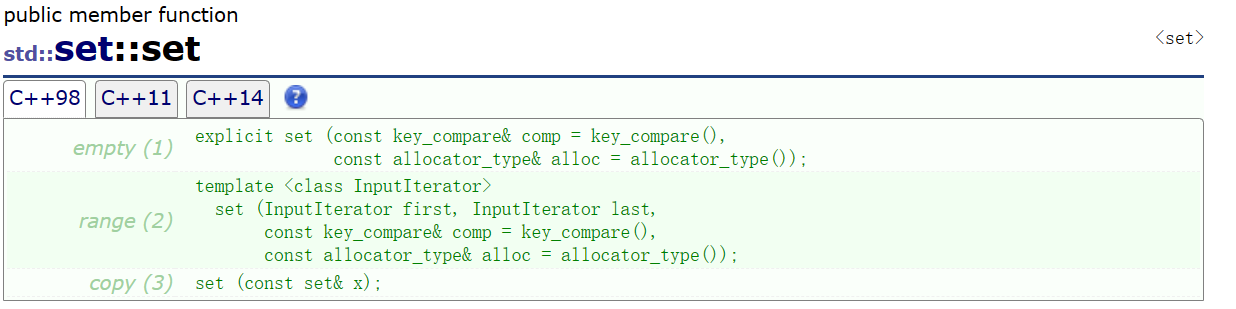
🍼2. 构造函数
🍼3. 修改
这些就和之前的容器使用差不多,这里就不再过多赘述了

🍼4.操作
🥛find
iterator find (const value_type& val) const;
如找到了,返回一个它的迭代器
代码示例:
void t_find()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(9);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(23);
s.insert(9);
s.insert(6);
auto it = s.find(2); //搜索树查找
auto stl_it = std::find(s.begin(), s.end(), 9); //stl提供的find暴力查找
if (it != s.end())
cout << "get it" << endl;
else
cout << "error" << endl;
if (stl_it != s.end())
cout << "get it" << endl;
else
cout << "error" << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}cout << endl;
}
如果用
set查找元素,使用set提供的接口即可,如果使用库里面的查找函数,效率会比较低另外,如果是
multiset,其中有多个相同元素,则查找的是第一个中序遍历出现的元素
🥛count
size_type count (const value_type& val) const;
count是统计这个元素出现的多少次,而set只是一个key模型,用处并不是很大,但我们也可以用count来进行元素查找
void t_count()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(9);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(23);
s.insert(9);
s.insert(6);
if (s.count(9))
cout << "get it" << endl;
else
cout << "error" << endl;
}
这个主要是为
multiset设计的,找相同元素有多少个
🥛lower_bound & upper_bound & equal_range
iterator lower_bound (const value_type& val) const;
iterator upper_bound (const value_type& val) const;
pair<iterator,iterator> equal_range (const value_type& val) const;
lower_bound、upper_bound和equal_range通常用来找区间
void t_lower_upper_bound()
{
set<int> s;
set<int>::iterator itlow, itup;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
s.insert(i * 10);
}
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}cout << endl;
auto range = s.equal_range(40);
//[first,secont)
cout << *range.first << endl;
cout << *range.second << endl;
//[35,70]
itlow = s.lower_bound(35); //>=35的值
itup = s.upper_bound(70); //>70的值
s.erase(itlow, itup);
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}cout << endl;
//cout << *itlow << endl;
//cout << *itup << endl;
}
这个
equal_range对于set的作用并不大,这个主要是为multiset提供,可以指定删除某个值void t_multiset() { multiset<int> mt; mt.insert(1); mt.insert(4); mt.insert(2); mt.insert(5); mt.insert(1); mt.insert(9); mt.insert(4); for (auto e : mt) { cout << e << " "; }cout << endl; //如果没有找到,返回一个不存在的区间 auto range = mt.equal_range(4); mt.erase(range.first, range.second);//删除全部的4 for (auto e : mt) { cout << e << " "; }cout << endl; }
🍭3. map
map是<key,value>模型,接口和set类似
🍬1. 模板参数
template < class Key, // map::key_type
class T, // map::mapped_type
class Compare = less<Key>, // map::key_compare
class Alloc = allocator<pair<const Key,T> > // map::allocator_type
> class map;
相比于set多了一个value,存储值的时候采用的是pair
pair<const key_type,mapped_type>
key不可修改,value可以修改
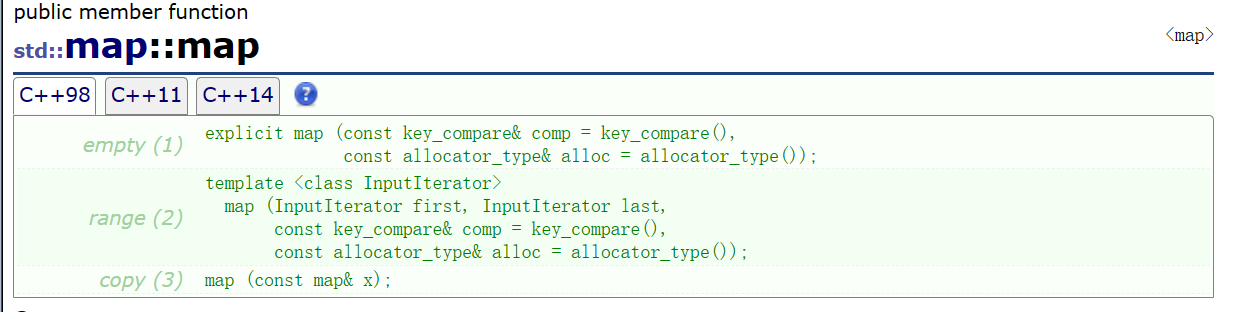
🍬2. 构造函数
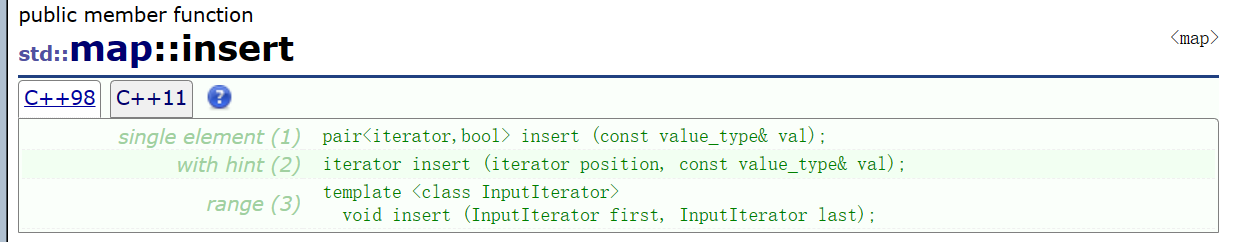
🍬3. insert
参数列表:
代码示例:
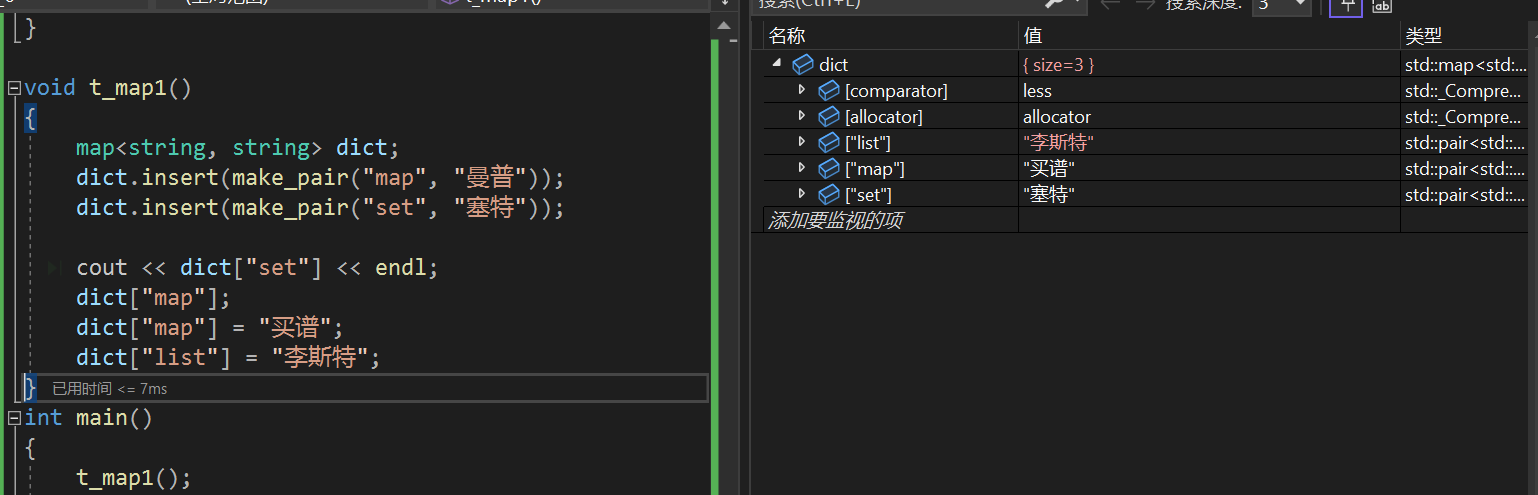
void t_map_insert()
{
map<string, string> dict;
pair<string, string> kv1("apple", "苹果");
pair<string, string> kv2("banana", "香蕉");
dict.insert(kv1);
dict.insert(kv2);
//匿名对象插入
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("orange", "橙子"));
//函数模板make_pair C++98 建议使用这个方式
dict.insert(make_pair("watermelon", "西瓜"));
//key相同,value不同,不插入不覆盖 只比较key
dict.insert(make_pair("watermelon", "北瓜"));
//C++11支持多参数构造函数隐式类型转换
dict.insert({ "lemon","柠檬" });
}
make_pair函数模板
要遍历这map,不能将迭代器直接解引用,因为它里面存了2个值,这里的排序是按照key的大小进行排序
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
it++;
}
//范围for
//值不可修改, map内容较复杂,传引用,减少拷贝
for (const auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
🍬4. operator[]
void t_mapCount()
{
string arr[] = { "冬瓜","西瓜","南瓜","北瓜","中瓜","西瓜","西瓜","北瓜" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto e : arr)
{
//通过insert实现
countMap[e]++;
}
//for (auto e : arr)
//{
// map<string, int>::iterator it = countMap.find(e);
// if (it == countMap.end()) //没有出现过
// {
// countMap.insert(make_pair(e,1));
// }
// else //出现过,统计次数
// {
// it->second++;
// }
//}
for (const auto& e : countMap)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
}
这里的[]不再像之前普通的[]
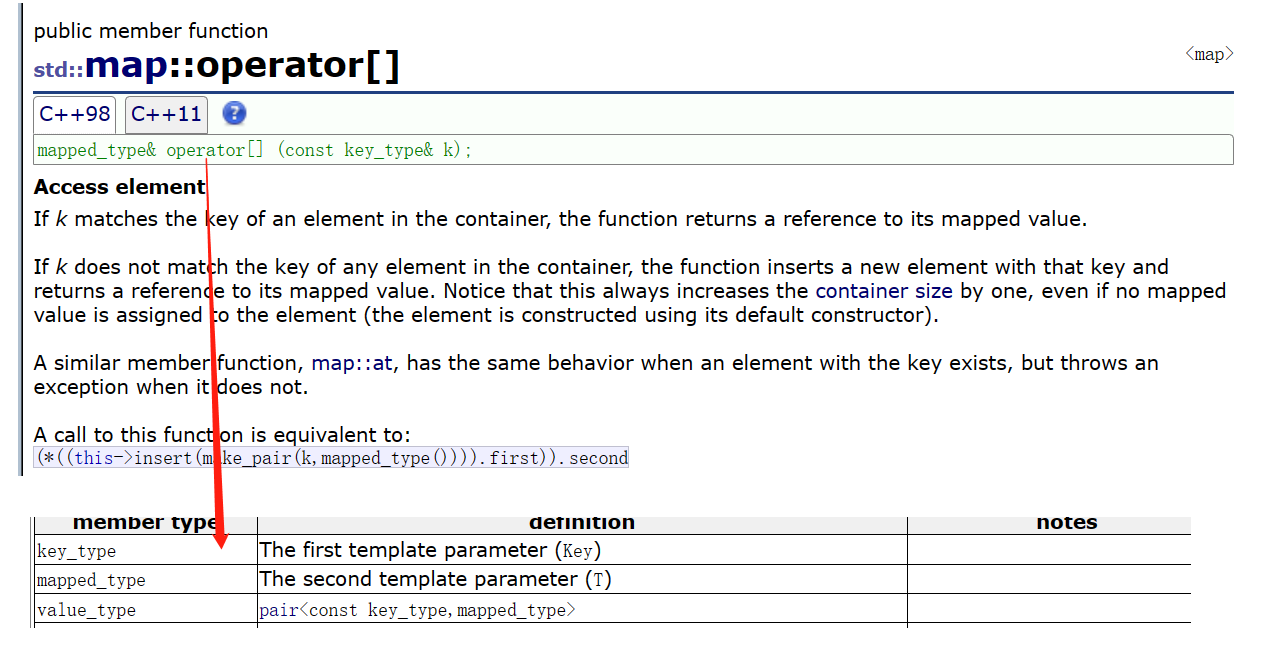
它通过key,返回value,底层调用的insert

key如果在这个树里面,返回pari<树里key所在节点的iterator,false>key不在树里面,返回pari<key所在节点的iterator,true>
所以[]可以用来进行插入操作或者是统计次数或者修改value值
map和set底层都是搜索树,随后会模拟实现,所以此篇文章只做大概的介绍
那么本期分享就到这里,我们下期再见







![[漏洞复现] metinfo_6.0.0_file-read(任意文件读取)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/b39812fa3f35b0d98f1bba93b6b14484.png)