定义节点
class Node {
var num: Int = _
var next: Node = _
def this(num: Int) {
this
this.num = num
}
override def toString: String = s"num=[${this.num}]"
}
定义方法
class LinkStack {
private var head = new Node(0)
def getHead: Node = head
//判断是否为空
def isEmpty: Boolean = {
head.next == null
}
//无需判断是否为满
//查看当前链表
def list(): Unit = {
if (isEmpty) {
println(s"栈已空")
return
}
var temp = head.next
while (temp.next != null) {
println(s"${temp}")
temp = temp.next
Thread.sleep(500)
}
}
//入栈
def push(value: Int): Unit = {
if (isEmpty) head.next = new Node(1)
//使用头插法
val newNode = new Node(value)
newNode.next = head.next
head.next = newNode
}
//出栈
def pop(): Int = {
if (isEmpty) throw new RuntimeException("栈空")
val temp = head.next
if (temp.next != null) {
println(s"弹栈=>${temp.num}")
head = temp.next
} else {
println(s"弹栈=>${temp.num}")
}
temp.num
}
}主函数
package Algotithm
object LinkedListStackDemo {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val stack = new LinkStack
stack.push(1)
stack.push(3)
println(s"原链表=====")
stack.list()
println(s"弹栈一次=====")
stack.pop()
stack.list()
println(s"弹栈二次=====")
stack.pop()
stack.list()
}
}结果

总结
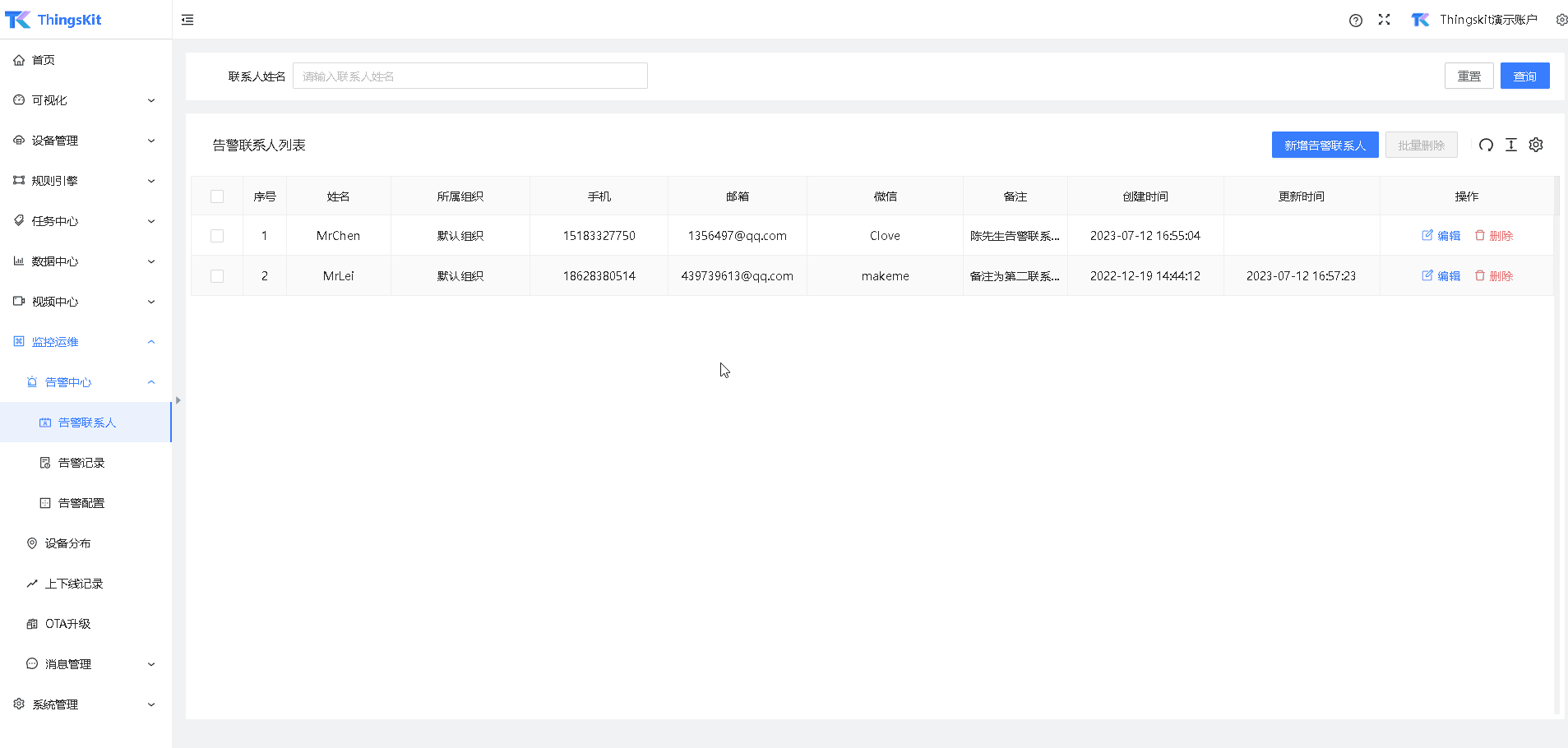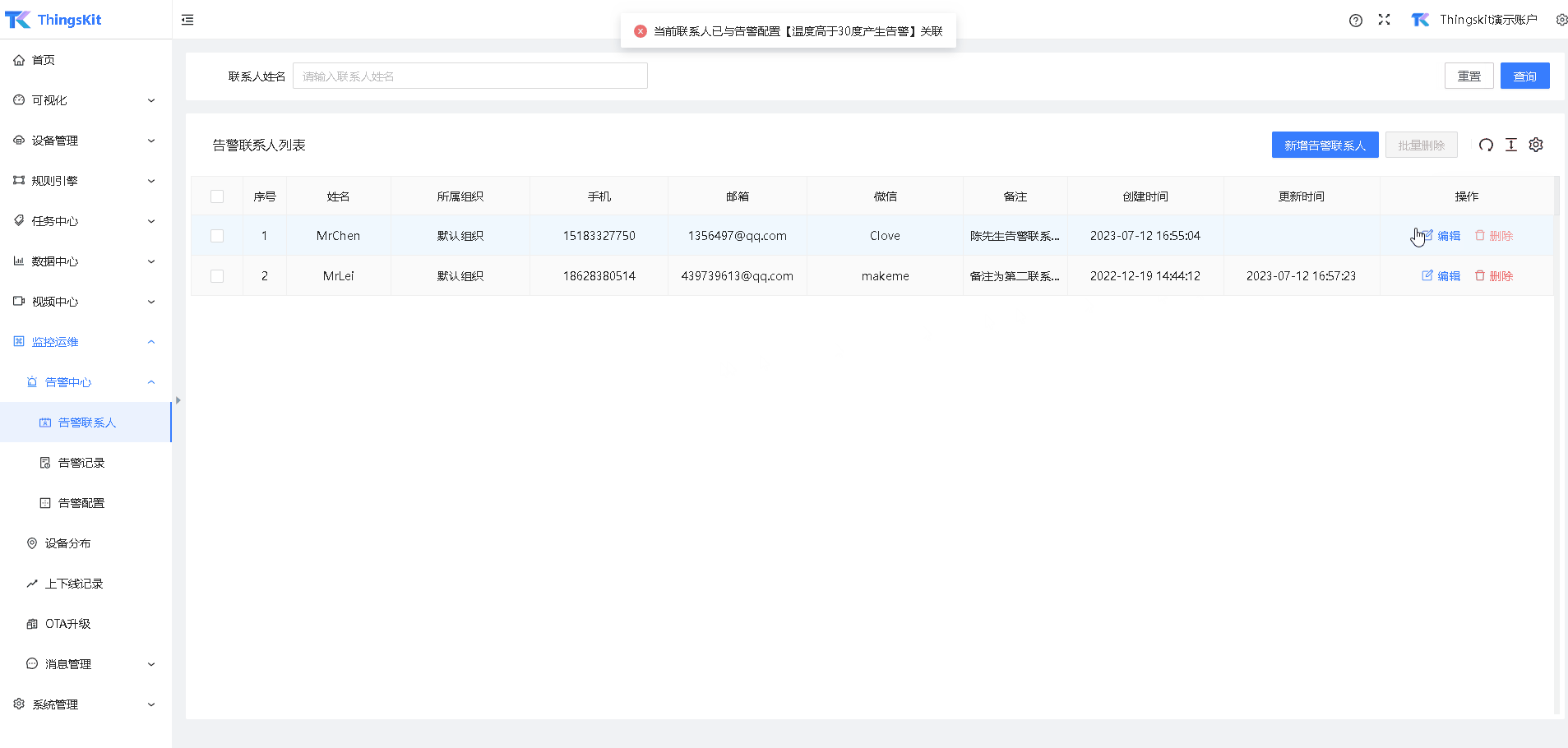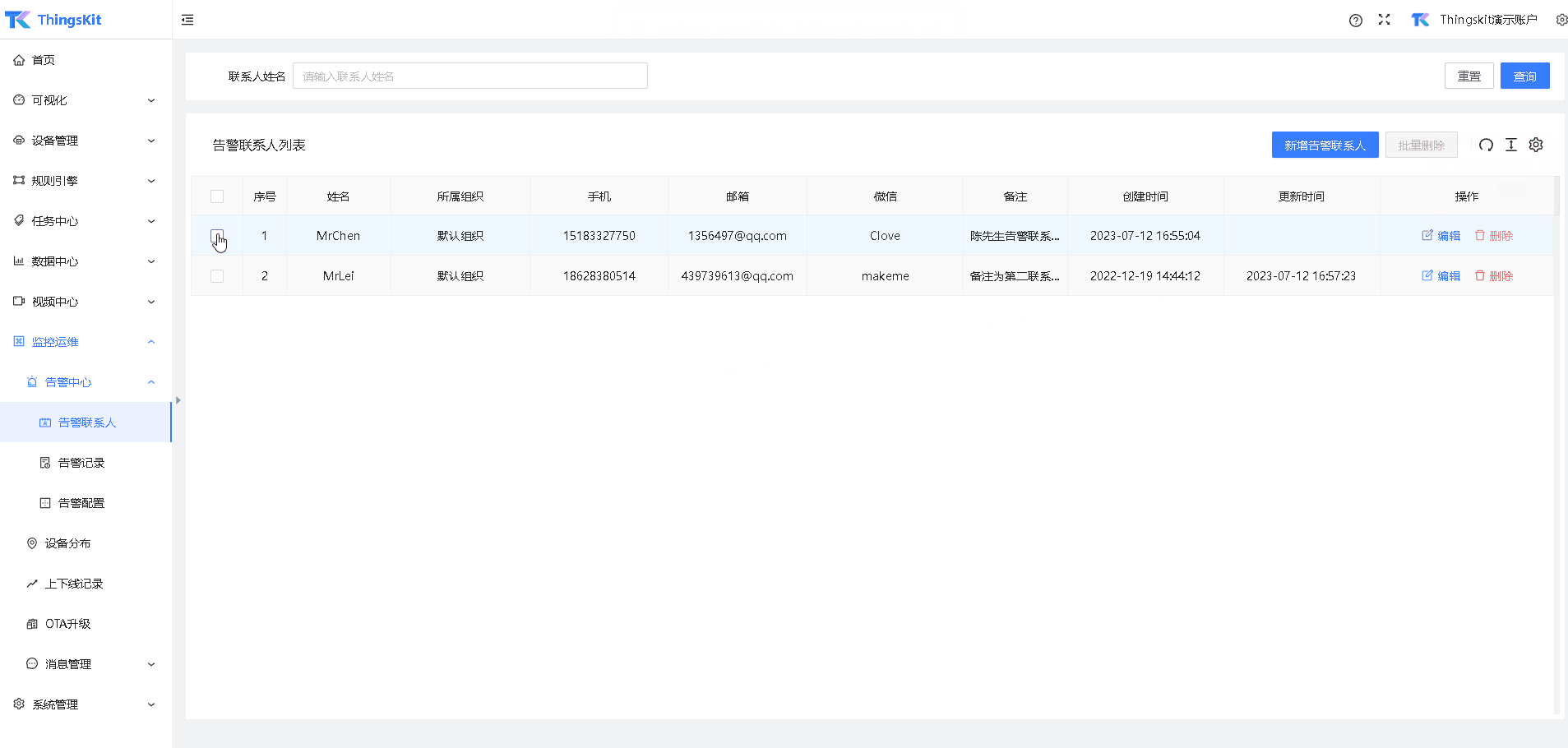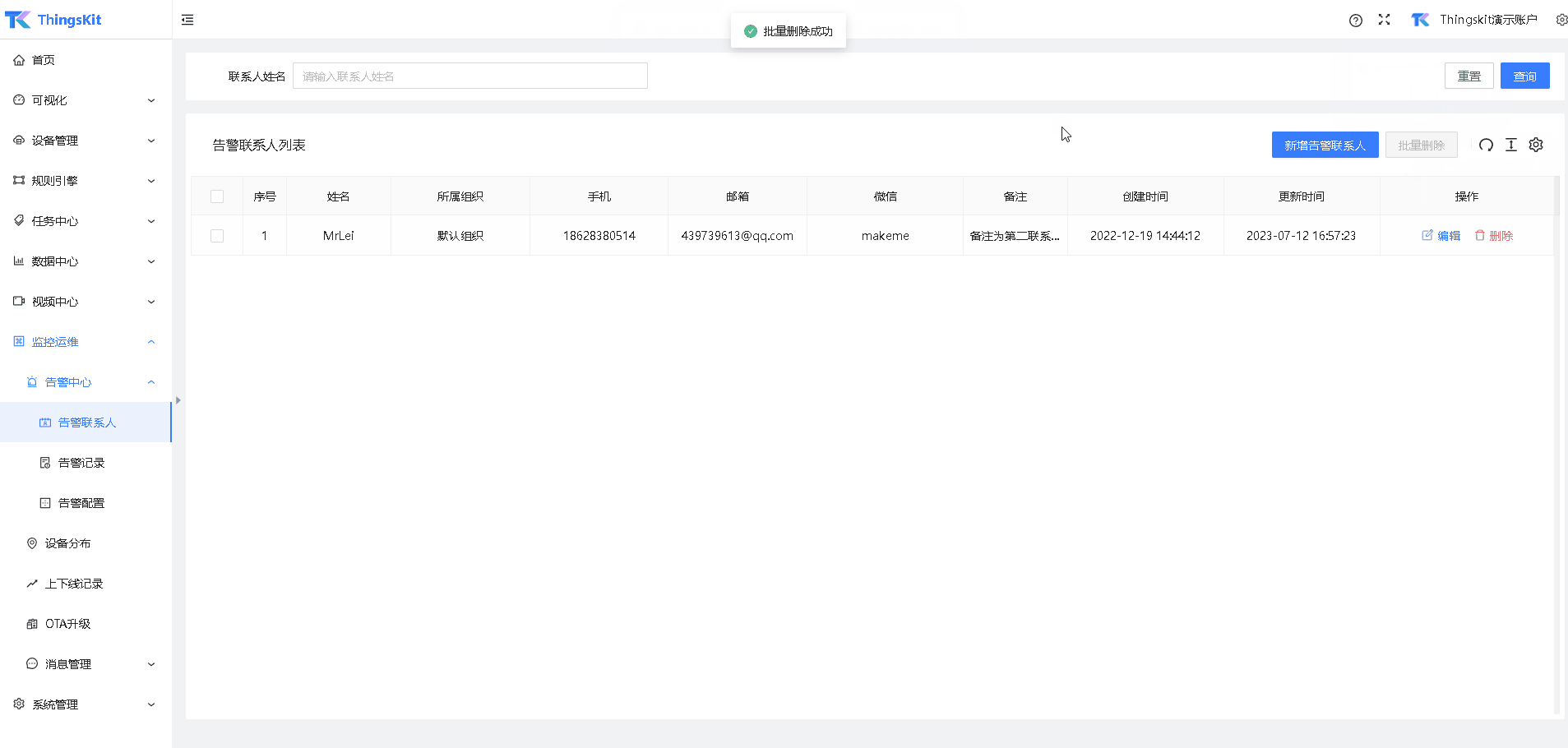
1、入栈时使用头插法,将新节点插入在 head头节点后面
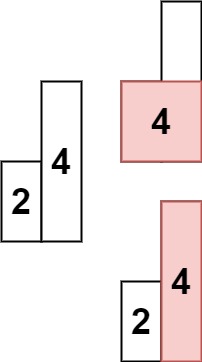
2、 pop出栈 时需要对当前链表进行非空判定。如果取出后节点为空,则不需要对 head.next 进行赋值