💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
2.1 2D
2.2 3D
🎉3 参考文献
🌈4 Matlab代码实现
💥1 概述
2D/3D RRT*算法是一种基于快速探索随机树的最佳路径规划算法。它是RRT*算法的扩展版本,能够在二维或三维环境中寻找最优路径。
该算法的核心思想是通过随机采样的方式构建一颗探索树,其中树的节点表示机器人的位置,边表示机器人从一个位置移动到另一个位置的路径。探索树的生长过程中,会不断进行路径优化,以找到最佳路径。
具体实现过程中,算法首先生成一个起始节点,并随机采样其他节点。然后,对于每个采样的节点,算法会在树中查找最近邻节点,并以此节点为起点,通过插值和优化等方式生成一条新的路径。新路径的代价(如路径长度或代价函数)将与之前的路径进行比较,选择代价更小的路径,将新节点插入树中。
该算法的最终目标是在有限的探索时间内找到从起始位置到目标位置的最优路径。通过不断优化路径,RRT*算法能够找到接近最短路径的解,同时具有较低的计算复杂度。
在二维或三维的路径规划问题中,2D/3D RRT*算法具有广泛的应用。例如,它可以用于地图导航、机器人路径规划、无人机航迹规划等场景。通过灵活调整采样策略、路径优化策略等参数,该算法能够适应各种复杂的环境和约束条件。
总之,2D/3D RRT*算法利用快速探索随机树的方式,在二维或三维环境中进行最佳路径规划,具有较高的搜索效率和路径质量,为机器人和自主系统的路径规划问题提供了有效的解决方案。
📚2 运行结果
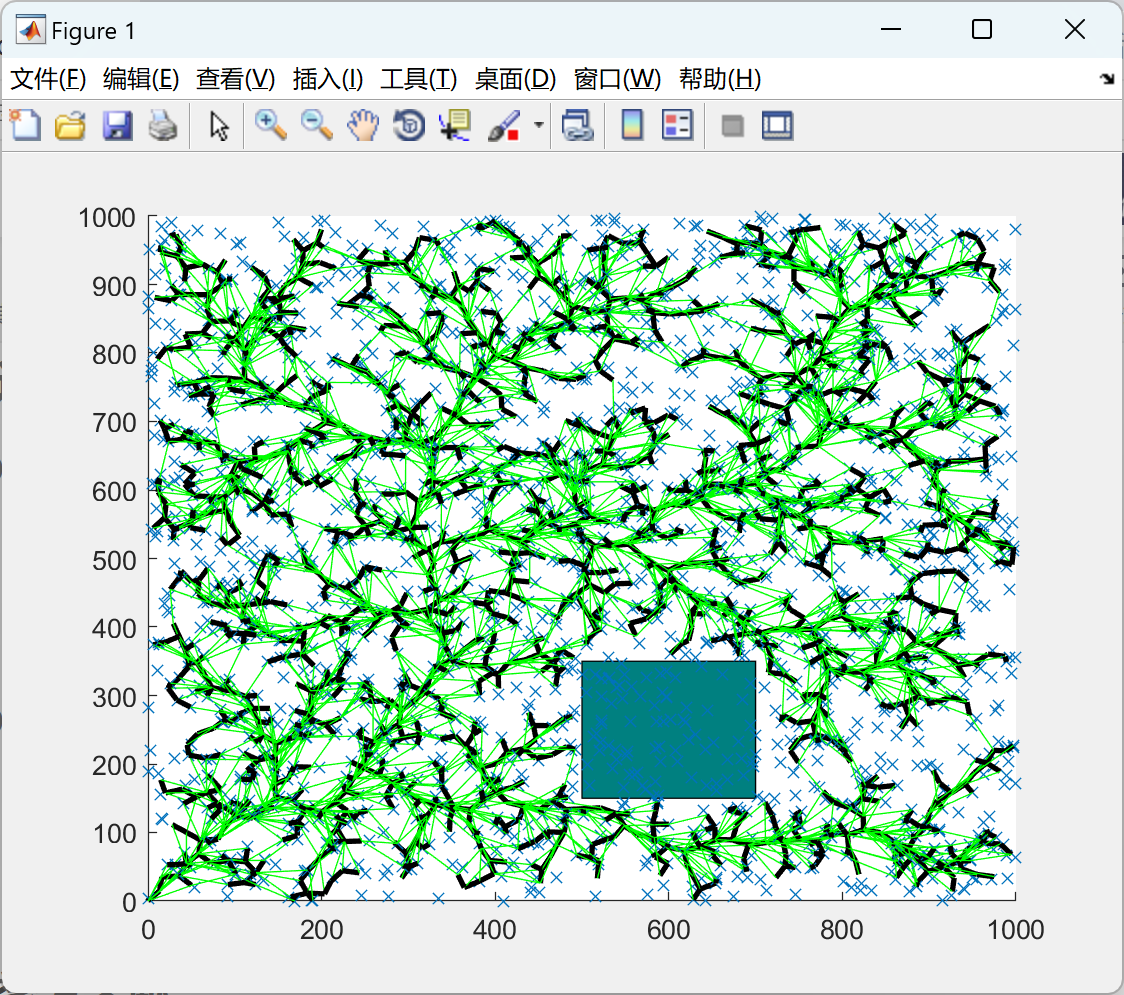
2.1 2D


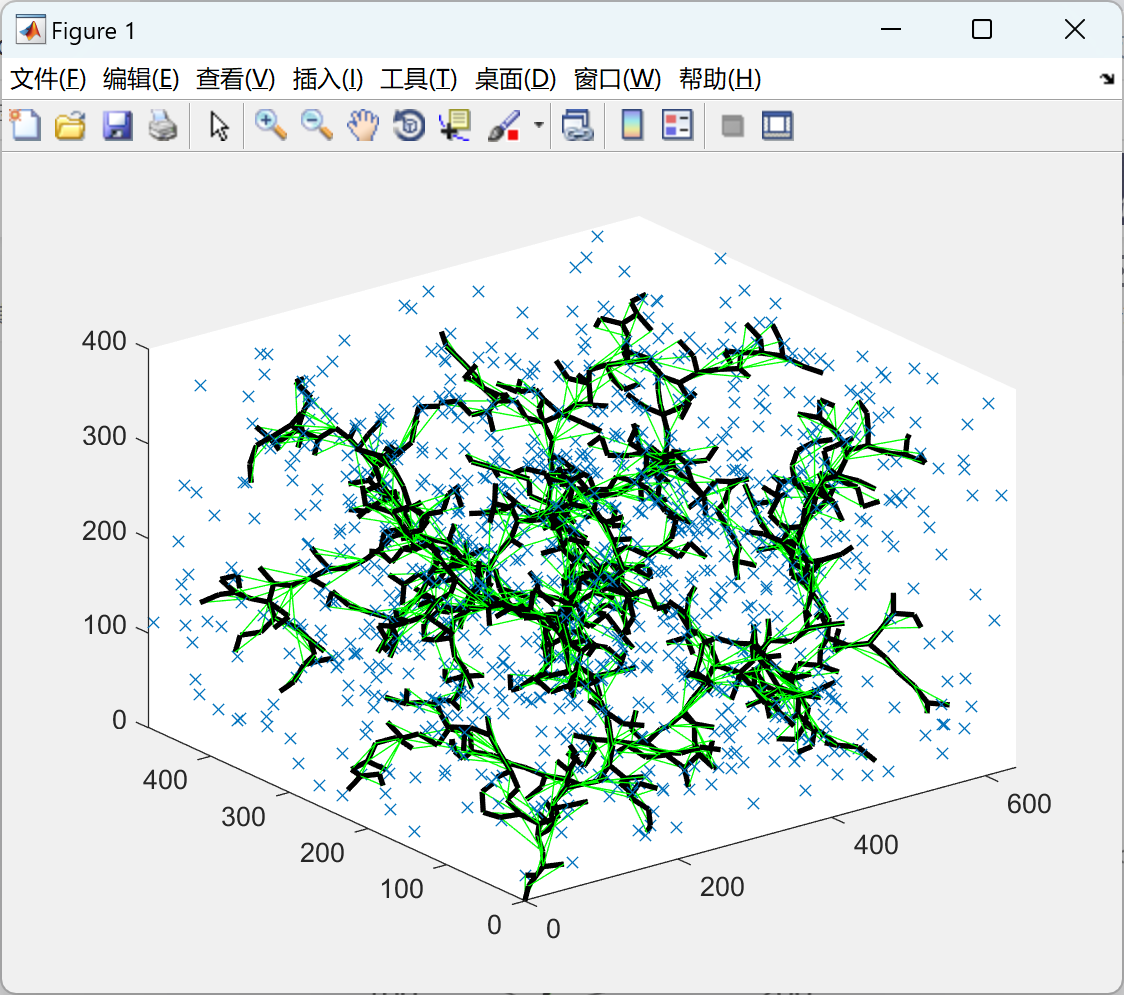
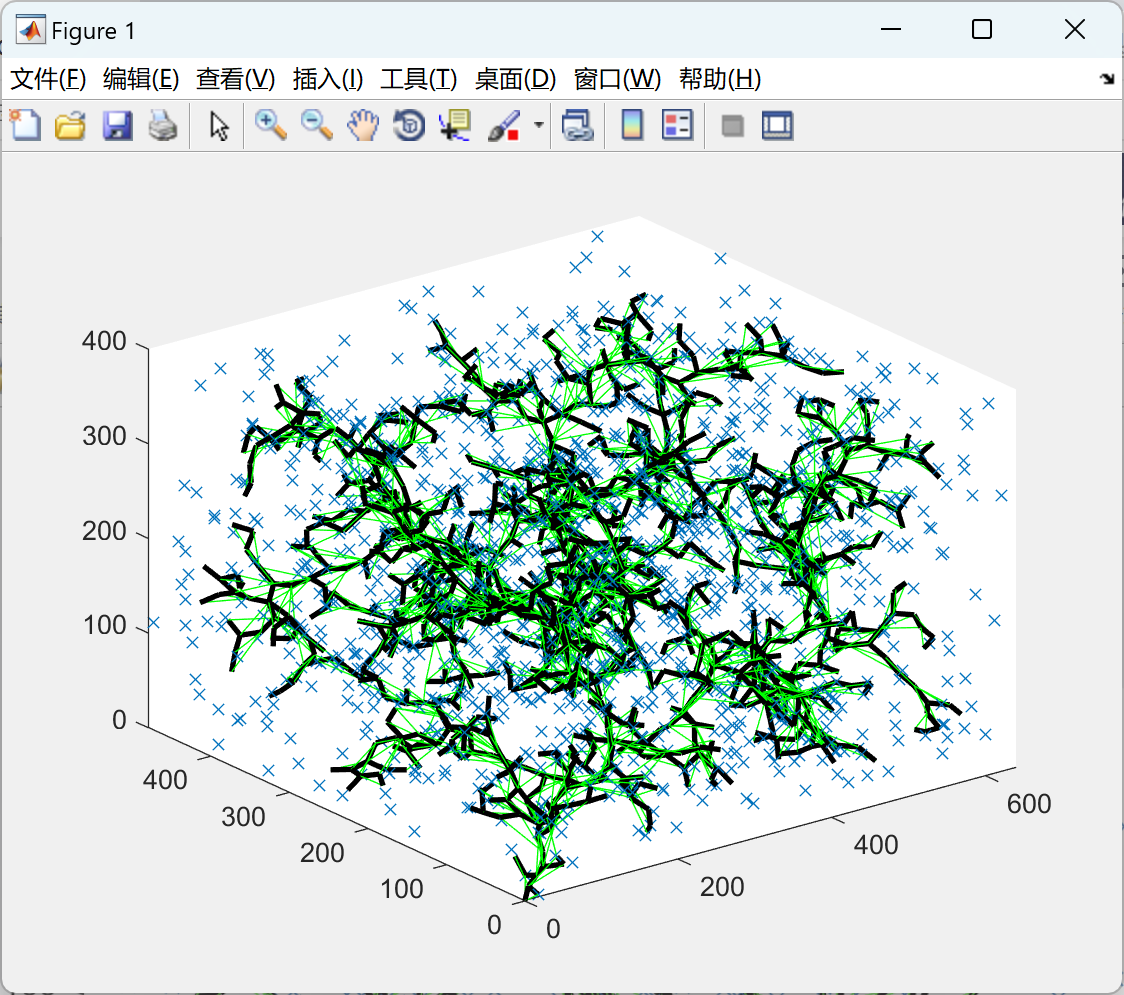
2.2 3D

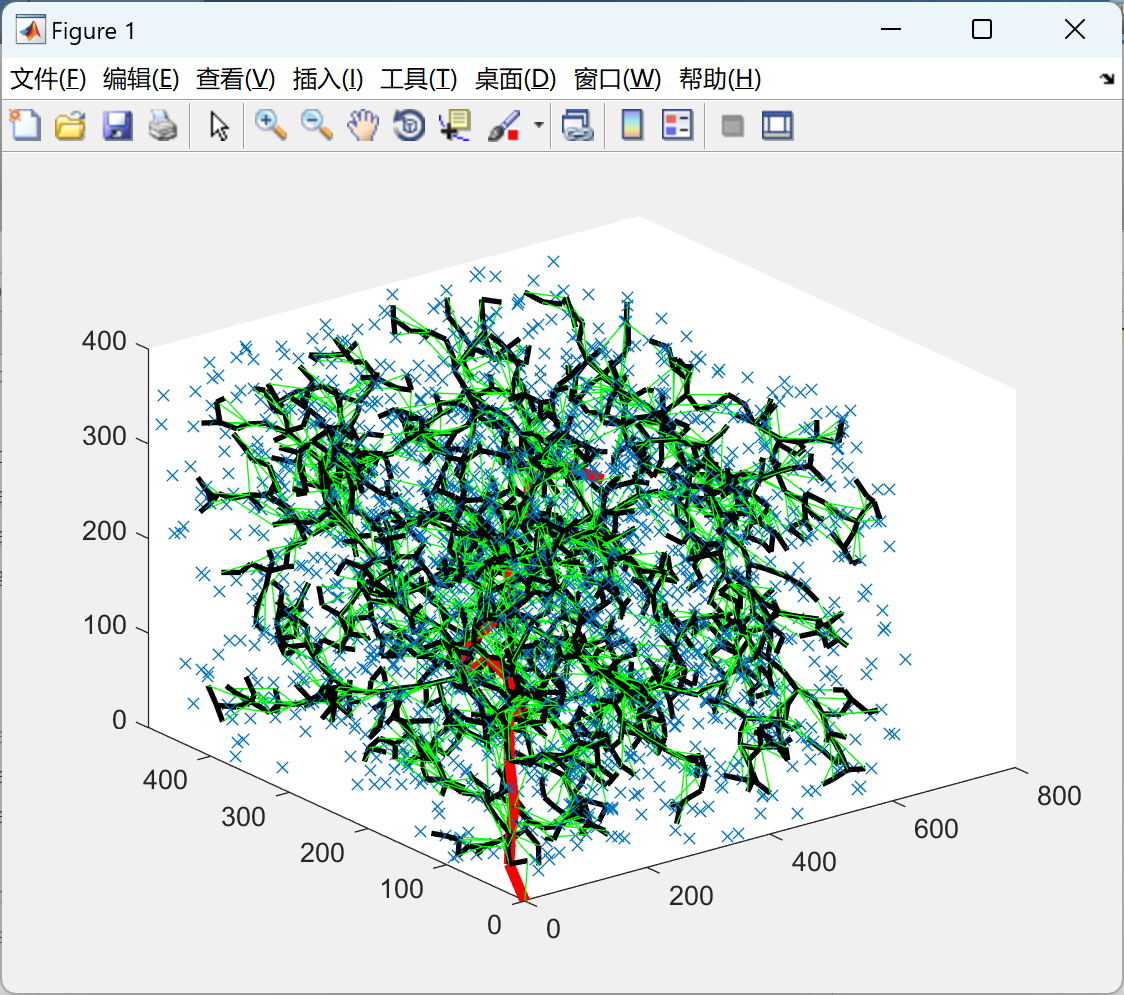
部分代码:
for i = 1:1:numNodes
q_rand = [floor(rand(1)*x_max) floor(rand(1)*y_max)];
plot(q_rand(1), q_rand(2), 'x', 'Color', [0 0.4470 0.7410])
% Break if goal node is already reached
for j = 1:1:length(nodes)
if nodes(j).coord == q_goal.coord
break
end
end
% Pick the closest node from existing list to branch out from
ndist = [];
for j = 1:1:length(nodes)
n = nodes(j);
tmp = dist(n.coord, q_rand);
ndist = [ndist tmp];
end
[val, idx] = min(ndist);
q_near = nodes(idx);
q_new.coord = steer(q_rand, q_near.coord, val, EPS);
if noCollision(q_rand, q_near.coord, obstacle)
line([q_near.coord(1), q_new.coord(1)], [q_near.coord(2), q_new.coord(2)], 'Color', 'k', 'LineWidth', 2);
drawnow
hold on
q_new.cost = dist(q_new.coord, q_near.coord) + q_near.cost;
% Within a radius of r, find all existing nodes
q_nearest = [];
r = 60;
neighbor_count = 1;
for j = 1:1:length(nodes)
if noCollision(nodes(j).coord, q_new.coord, obstacle) && dist(nodes(j).coord, q_new.coord) <= r
q_nearest(neighbor_count).coord = nodes(j).coord;
q_nearest(neighbor_count).cost = nodes(j).cost;
neighbor_count = neighbor_count+1;
end
end
% Initialize cost to currently known value
q_min = q_near;
C_min = q_new.cost;
% Iterate through all nearest neighbors to find alternate lower
% cost paths
for k = 1:1:length(q_nearest)
if noCollision(q_nearest(k).coord, q_new.coord, obstacle) && q_nearest(k).cost + dist(q_nearest(k).coord, q_new.coord) < C_min
q_min = q_nearest(k);
C_min = q_nearest(k).cost + dist(q_nearest(k).coord, q_new.coord);
line([q_min.coord(1), q_new.coord(1)], [q_min.coord(2), q_new.coord(2)], 'Color', 'g');
hold on
end
end
% Update parent to least cost-from node
for j = 1:1:length(nodes)
if nodes(j).coord == q_min.coord
q_new.parent = j;
end
end
% Append to nodes
nodes = [nodes q_new];
end
end
D = [];
for j = 1:1:length(nodes)
tmpdist = dist(nodes(j).coord, q_goal.coord);
D = [D tmpdist];
end
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1] LaValle, S. M., ‘Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees: A New Tool for Path Planning’, TR 98-11, Computer Science Department, Iowa State University, Oct. 1998.
[2] Karaman, Sertac, and Emilio Frazzoli. "Incremental sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning." Robotics Science and Systems VI 104 (2010).
[3]莫栋成,刘国栋.改进的快速探索随机树双足机器人路径规划算法[J].计算机应用, 2013, 33(01):199-201.DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1087.2013.00199.

![java八股文面试[多线程]——阻塞队列](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a57feb4a2a1141ea880de86953a2282f.png)