五、域对象共享数据
1、使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据
首页:
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>您已进入首页!</h1>
<a th:href="@{/testRequestByServletAPI}">通过servletAPI向request域对象共享数据</a>
</body>
</html>跳转页:
@Controller
public class ScopeController {
//使用servletAPI向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testRequestByServletAPI")
public String testRequestByServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
//共享数据。参数一个是键,一个是值
request.setAttribute("testRequestScope","hello,servletAPI");
return "success";
}
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>跳转成功!</h1><br>
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}"></p>
</body>
</html>

2、使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testModelAndView")
//必须使用ModelAndView作为该方法的返回值返回
public ModelAndView testModelAndView(){
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
//处理模型数据,即向请求域request共享数据
mav.addObject("testRequestScope","hello,ModelAndView");
//设置视图名称
mav.setViewName("success");
return mav;
}<a th:href="@{/testModelAndView}">通过ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据</a><br><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>跳转成功!</h1><br>
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}"></p>
</body>
</html>

3、使用Model向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testModel")
public String testModel(Model model){
model.addAttribute("testRequestScope","hello,model");
return "success";
}<a th:href="@{/testModel}">通过Model向request域对象共享数据</a><br><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>跳转成功!</h1><br>
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}"></p>
</body>
</html>

4、使用map向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testMap")
public String testMap(Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("testRequestScope","hello,map");
return "success";
}<a th:href="@{/testMap}">通过Map向request域对象共享数据</a><br><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>跳转成功!</h1><br>
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}"></p>
</body>
</html>

5、使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testModelMap")
public String testModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){
modelMap.addAttribute("testRequestScope","hello,ModelMap");
return "success";
}<a th:href="@{/testModelMap}">通过ModelMap向request域对象共享数据</a><br><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>跳转成功!</h1><br>
<p th:text="${testRequestScope}"></p>
</body>
</html> 

6、Model、ModelMap、Map的关系
Model
、
ModelMap
、
Map
类型的参数其实本质上都是
BindingAwareModelMap
类型的
publicinterfaceModel{}public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>publicclassModelMapextendsLinkedHashMap<String,Object>{}publicclassExtendedModelMapextendsModelMapimplementsModel{}publicclassBindingAwareModelMapextendsExtendedModelMap{}
7、向session域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testSession")
public String testSession(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("testSessionScope","hello,Session");
return "success";
}<a th:href="@{/testSession}">通过ServletAPI向session域对象共享数据</a><br><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>跳转成功!</h1><br>
<!--<p th:text="${testRequestScope}"></p>-->
<p th:text="${session.testSessionScope}"></p>
</body>
</html>

8、向application域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testApplication")
public String testApplication(HttpSession session){
ServletContext application = session.getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("testApplicationScope","hello,Application");
return "success";
}<a th:href="@{/testApplication}">通过ServletAPI向Application域对象共享数据</a><br><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>跳转成功!</h1><br>
<!--<p th:text="${testRequestScope}"></p>-->
<!--<p th:text="${session.testSessionScope}"></p>-->
<p th:text="${application.testApplicationScope}"></p>
</body>
</html>

六、SpringMVC的视图
SpringMVC
中的视图是
View
接口,视图的作用渲染数据,将模型
Model
中的数据展示给用户
SpringMVC
视图的种类很多,默认有转发视图和重定向视图
当工程引入
jstl
的依赖,转发视图会自动转换为
JstlView
若使用的视图技术为
Thymeleaf
,在
SpringMVC
的配置文件中配置了
Thymeleaf
的视图解析器,由此视图解析器解析之后所得到的是ThymeleafView
1、ThymeleafView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会被
SpringMVC
配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,视图名称拼接视图前缀和视图后缀所得到的最终路径,会通过转发的方式实现跳转
@Controller
public class ViewController {
@RequestMapping("/testThymeleafView")
public String testThymeleafView(){
return "success";
}
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a th:href="@{/testThymeleafView}">测试ThymeleafView</a>
</body>
</html>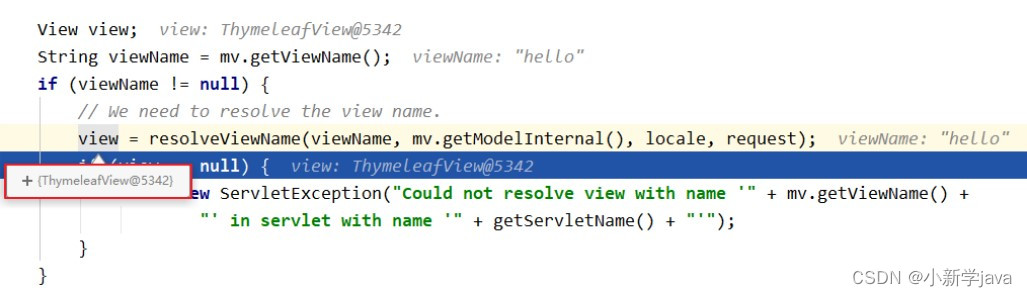
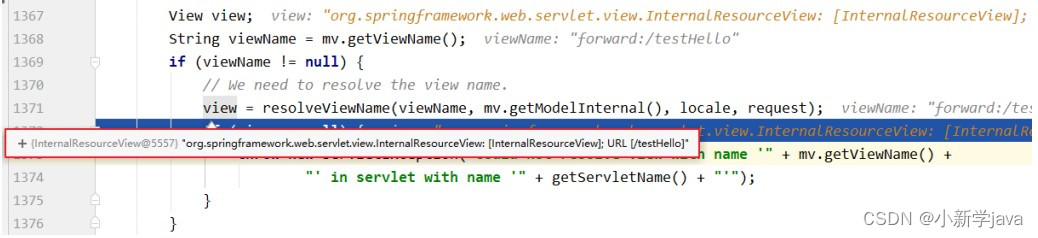
2、转发视图
SpringMVC
中默认的转发视图是
InternalResourceView
SpringMVC
中创建转发视图的情况:
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以
"forward:"
为前缀时,创建
InternalResourceView
视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC
配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀
"forward:"
去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过转发的方式实现跳转
例如
"forward:/"
,
"forward:/employee"
@RequestMapping("/testForward")
public String testForward(){
return "forward:/testThymeleafView";
}<a th:href="@{/testForward}">测试InternalResourceView</a><br>