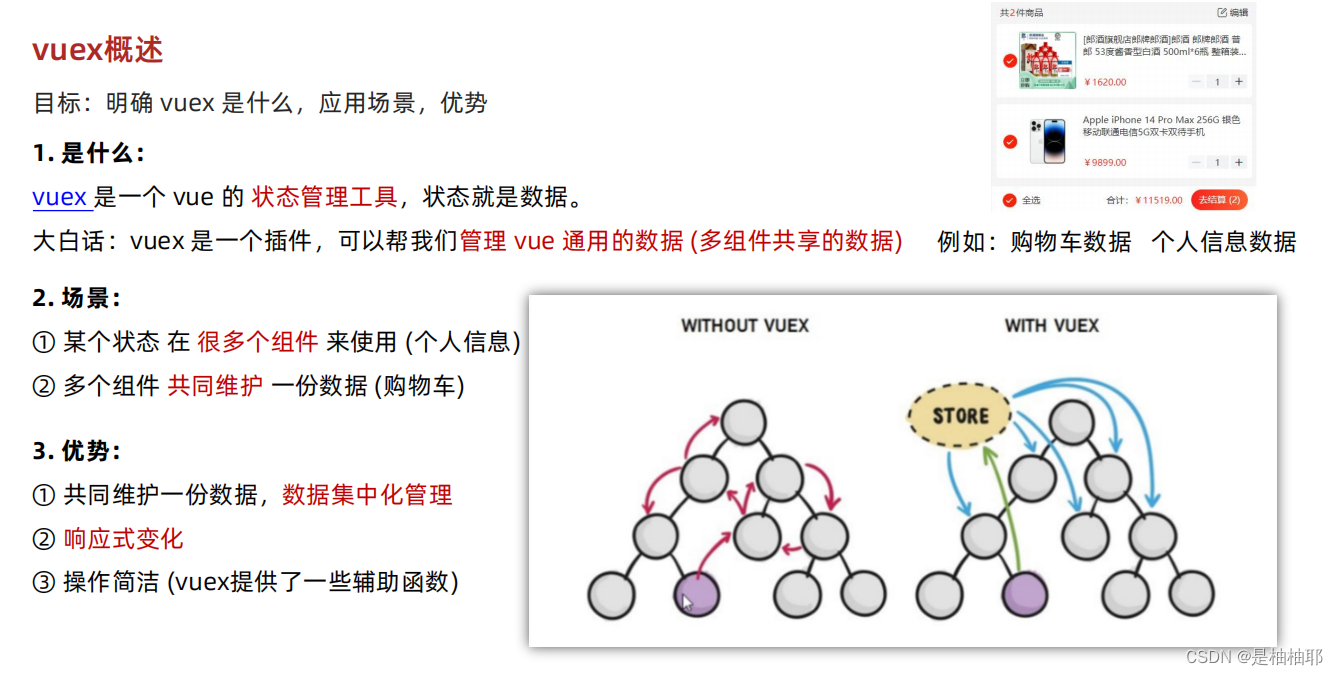
1.1 vuex概述
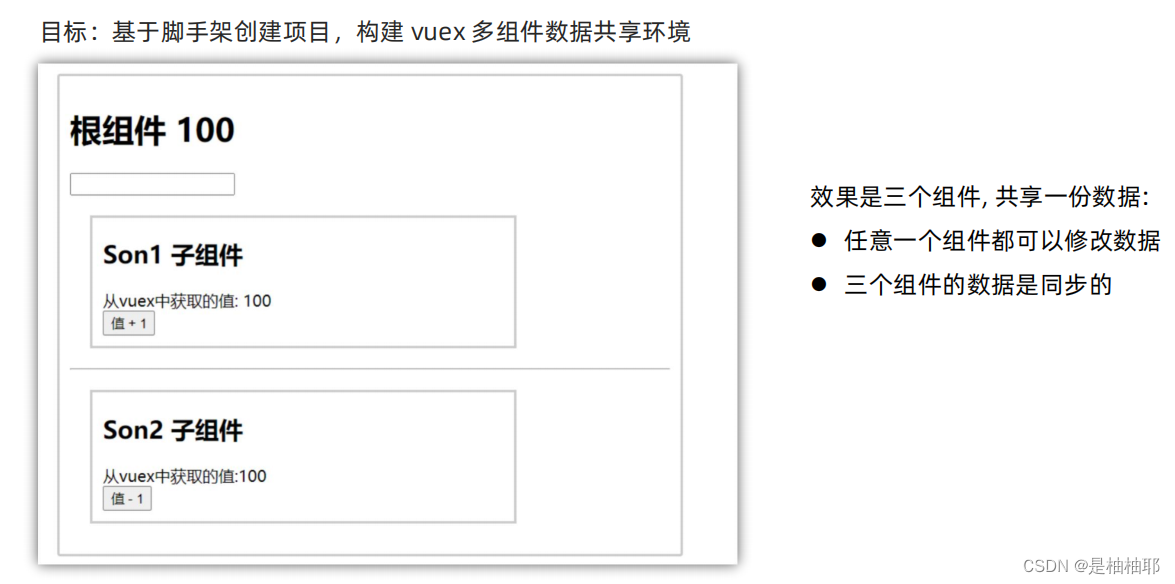
1.2 构建 vuex [多组件数据共享] 环境
1.创建项目
vue create vuex-demo
2.创建三个组件, 目录如下
|-components
|--Son1.vue
|--Son2.vue
|-App.vue
3.源代码如下
App.vue在入口组件中引入 Son1 和 Son2 这两个子组件
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件</h1>
<input type="text">
<Son1></Son1>
<hr>
<Son2></Son2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
data: function () {
return {
}
},
components: {
Son1,
Son2
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
Son1.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值: <label></label>
<br>
<button>值 + 1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son1Com'
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box{
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label></label>
<br />
<button>值 - 1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son2Com'
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
1.3 创建一个空仓库
PS:
vue2对应router3、vuex3
vue3对应router4、vuex4
因为创建vue时没有勾选vuex,所以要装包,勾选就不需要装包了
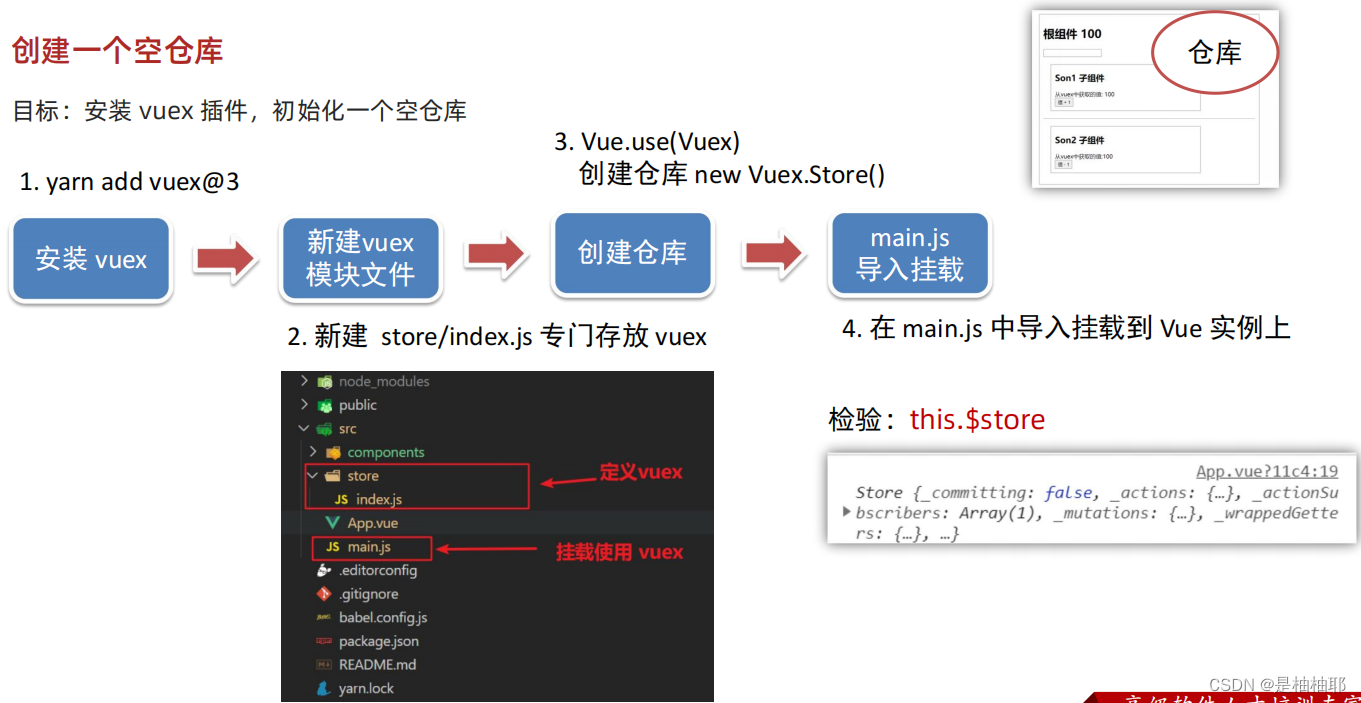
src → store → index.js
// 在这里存放的就是 Vuex 相关的核心代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 插件安装
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store()
// 导出给main.js使用
export default store
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from '@/store/index'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')
1.4 核心概念 - state 状态
目标:明确如何给仓库 提供 数据,如何 使用 仓库的数据

1. 提供数据:
State 提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到 Store 中的 State 中存储。
在 state 对象中可以添加我们要共享的数据。

src - store - index.js
// 在这里存放的就是 Vuex 相关的核心代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 插件安装
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 通过state可以提供数据(所有组件共享的数据)
state: {
title: '大标题',
count: 100
}
}
)
// 导出给main.js使用
export default store
2. 使用数据:
① 通过 store 直接访问

App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ $store.state.title }}</h1>
<input type="text">
<Son1></Son1>
<hr>
<Son2></Son2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
created () {
console.log(this.$store.state.title)
},
data: function () {
return {
}
},
components: {
Son1,
Son2
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from '@/store/index'
console.log(store.state.count)
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')
② 通过辅助函数 (简化)
mapState是辅助函数,帮助我们把 store中的数据 自动 映射到 组件的计算属性中

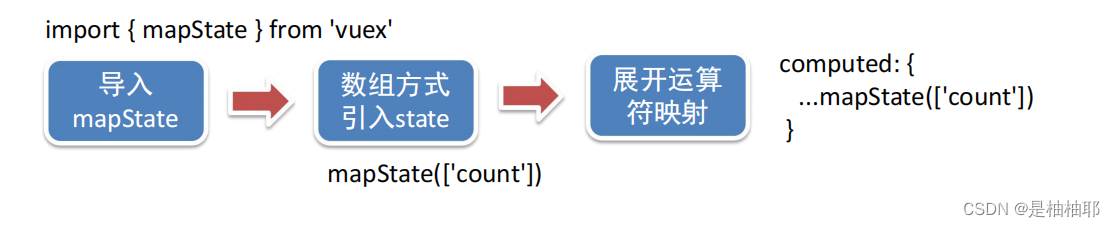
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ title }}</h1>
<input type="text">
<Son1></Son1>
<hr>
<Son2></Son2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
console.log(mapState(['count', 'title']))
export default {
name: 'app',
created () {
console.log(this.$store.state.title)
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count', 'title'])
},
data: function () {
return {
}
},
components: {
Son1,
Son2
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
1.5 核心概念 - mutations

son.vue(不开严格模式可以用)
methods: {
handleAdd () {
// 错误代码(vue默认不会监测,检测需要成本)
// this.$store.state.count++
// console.log(this.$store.state.count)
// 应该通过 mutation 核心概念,进行修改数据
}
}
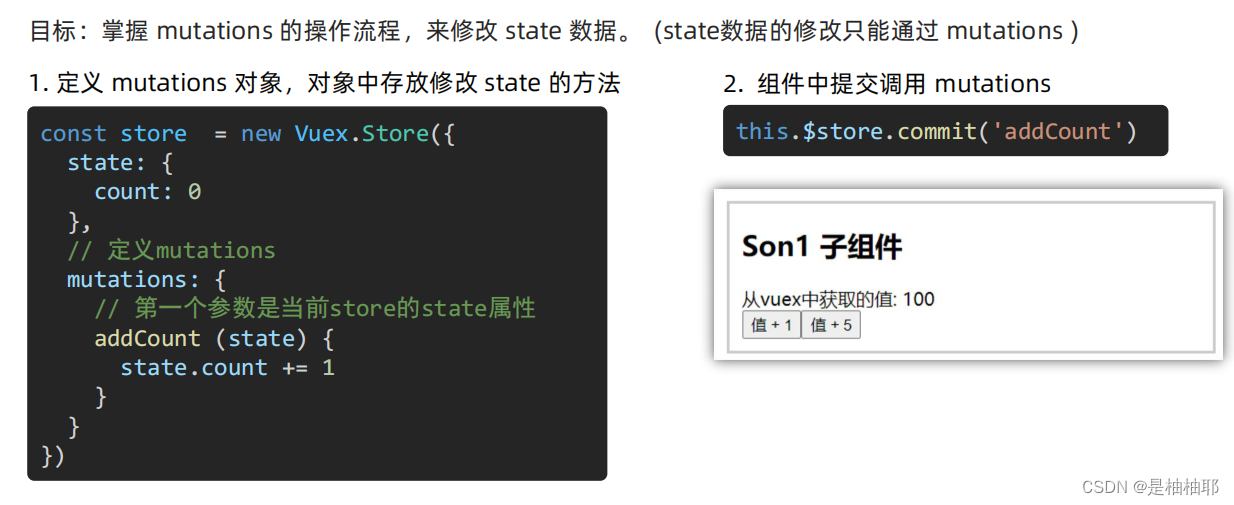
str - store - index.js
mutations: {
// 所有mutation函数,第一个参数,都是state
addCount (state) {
// 修改数据
state.count += 1
},
addFive (state) {
state.count += 5
}
}
Son1.vue
methods: {
handleAdd () {
// 错误代码(vue默认不会监测,检测需要成本)
// this.$store.state.count++
// console.log(this.$store.state.count)
// 应该通过 mutation 核心概念,进行修改数据
this.$store.commit('addCount')
},
addFive () {
this.$store.commit('addFive')
}
}
}

str - store - index.js
mutations: {
// 所有mutation函数,第一个参数,都是state
addCount (state, n) {
// 修改数据
state.count += n
},
changeTitle (state, newTitle) {
state.title = newTitle
}
}
Son1.vue
methods: {
handleAdd (n) {
// 错误代码(vue默认不会监测,检测需要成本)
// this.$store.state.count++
// console.log(this.$store.state.count)
// 应该通过 mutation 核心概念,进行修改数据
// this.$store.commit('addCount')
// 调用带参数的mutation函数
this.$store.commit('addCount', n)
},
changeFn () {
this.$store.commit('changeTitle', '黑马程序员')
}
}
1.5.1 核心概念 - mutations - 练习1

str - store - index.js
// 2.通过mutations可以提供修改数据的方法
mutations: {
// 所有mutation函数,第一个参数,都是state
addCount (state, n) {
// 修改数据
state.count += n
},
subCount (state, n) {
state.count -= n
},
changeTitle (state, newTitle) {
state.title = newTitle
}
}
Son2.vue
methods: {
handleSub (n) {
this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
}
}
1.5.2 核心概念 - mutations - 练习2
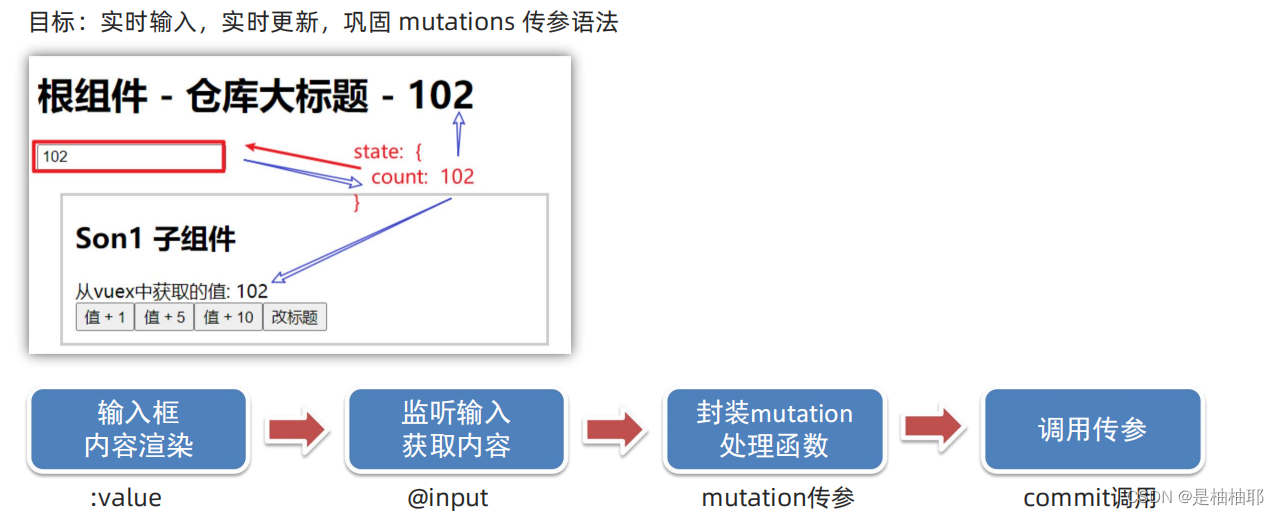
src - store - index.js
// 在这里存放的就是 Vuex 相关的核心代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 插件安装
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 严格模式(有利于初学者,检测不规范的代码 => 上线时需要关闭)
strict: true,
// 通过state可以提供数据(所有组件共享的数据)
state: {
title: '仓库大标题',
count: 100
},
// 2.通过mutations可以提供修改数据的方法
mutations: {
// 所有mutation函数,第一个参数,都是state
addCount (state, n) {
// 修改数据
state.count += n
},
subCount (state, n) {
state.count -= n
},
changeTitle (state, newTitle) {
state.title = newTitle
},
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
}
}
)
// 导出给main.js使用
export default store
Son2.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ title }}</h1>
<input :value="count" @input="handleInput" type="text">
<Son1></Son1>
<hr>
<Son2></Son2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
// console.log(mapState(['count', 'title']))
export default {
name: 'app',
created () {
console.log(this.$store.state.title)
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count', 'title'])
},
data: function () {
return {
}
},
components: {
Son1,
Son2
},
methods: {
handleInput (e) {
// console.log(+e.target.value)
const num = +e.target.value
this.$store.commit('changeCount', num)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
1.6 辅助函数 - mapMutations
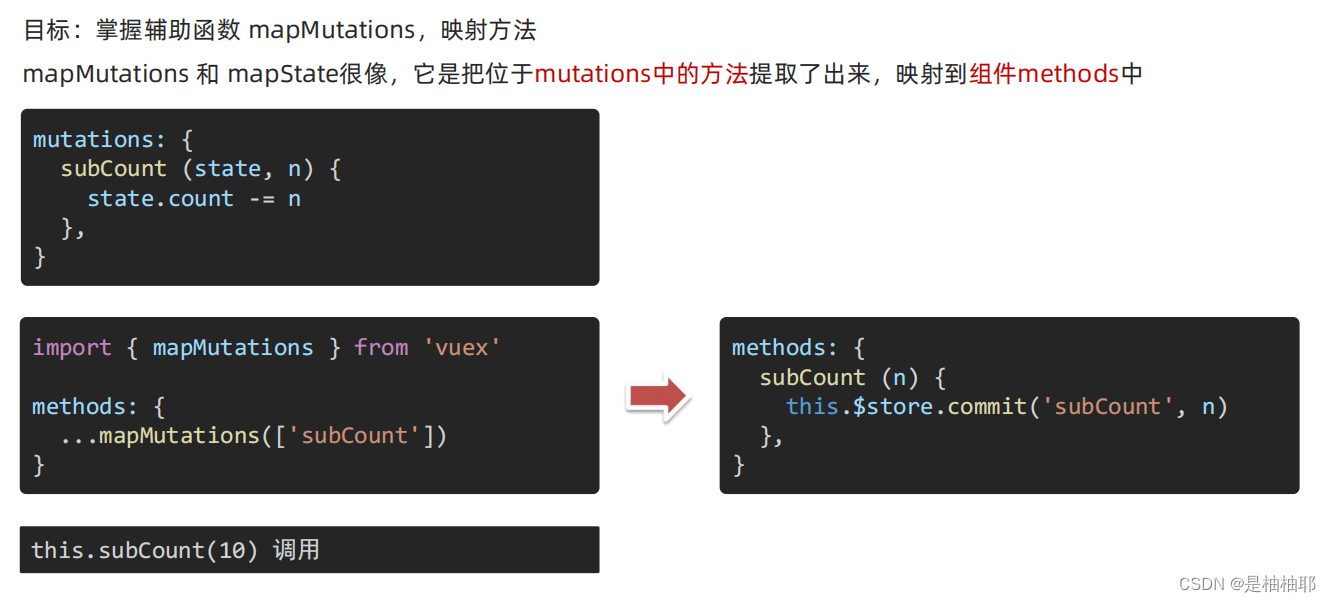
PS:就是在仓库里面写好方法,通过辅助函数mapMutation把仓库中的方法提取出来了,可以直接使用
Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br />
<button @click="subCount(1)">值 - 1</button>
<button @click="subCount(5)">值 - 5</button>
<button @click="subCount(10)">值 - 10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
...mapState(['count', 'title'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['subCount', 'changeCount'])
// handleSub (n) {
// // this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
// this.subCount(n)
// }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
1.7 核心概念 - actions
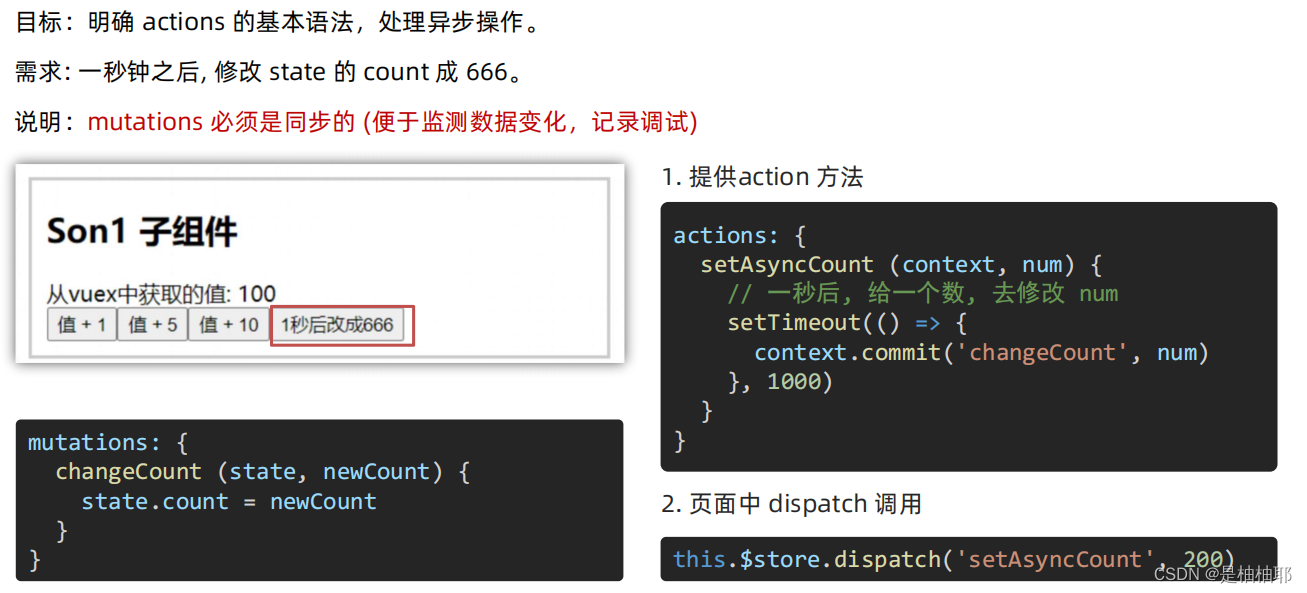
str - store - index.js
// 在这里存放的就是 Vuex 相关的核心代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 插件安装
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 严格模式(有利于初学者,检测不规范的代码 => 上线时需要关闭)
strict: true,
// 通过state可以提供数据(所有组件共享的数据)
state: {
title: '仓库大标题',
count: 100
},
// 2.通过mutations可以提供修改数据的方法
mutations: {
// 所有mutation函数,第一个参数,都是state
addCount (state, n) {
// 修改数据
state.count += n
},
subCount (state, n) {
state.count -= n
},
changeTitle (state, newTitle) {
state.title = newTitle
},
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
},
// 3.actions 处理异步
// 注意: 不能直接操作 state, 操作 state, 还是需要 commit mutation
actions: {
// context 上下文(此处未分模块,可以当成store仓库)
// context.commit('mutation名字',额外参数)
changeCountAction (context, num) {
// 这里是setTimeout模拟异步,以后大部分场景是发请求
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
}
}
)
// 导出给main.js使用
export default store
Son1.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值: <label>{{ $store.state.count }}</label>
<br>
<button @click="handleAdd(1)">值 + 1</button>
<button @click="handleAdd(5)">值 + 5</button>
<button @click="handleAdd(10)">值 + 10</button>
<button @click="changeFn">改标题</button>
<button @click="handleChange">一秒之后修改成666</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son1Com',
methods: {
handleAdd (n) {
// 错误代码(vue默认不会监测,检测需要成本)
// this.$store.state.count++
// console.log(this.$store.state.count)
// 应该通过 mutation 核心概念,进行修改数据
// this.$store.commit('addCount')
// 调用带参数的mutation函数
this.$store.commit('addCount', n)
},
changeFn () {
this.$store.commit('changeTitle', '黑马程序员')
},
handleChange () {
// 调用action
// this.$store.dispatch('action名字', 额外参数)
this.$store.dispatch('changeCountAction', 666)
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box{
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
1.8 辅助函数 - mapActions

Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br />
<button @click="subCount(1)">值 - 1</button>
<button @click="subCount(5)">值 - 5</button>
<button @click="subCount(10)">值 - 10</button>
<button @click="changeCountAction(888)">一秒之后修改成888</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
...mapState(['count', 'title'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['subCount', 'changeCount']),
...mapActions(['changeCountAction'])
// handleSub (n) {
// // this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
// this.subCount(n)
// }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
1.9 核心概念 - getters

src - store - index.js
// 在这里存放的就是 Vuex 相关的核心代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 插件安装
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 严格模式(有利于初学者,检测不规范的代码 => 上线时需要关闭)
strict: true,
// 通过state可以提供数据(所有组件共享的数据)
state: {
title: '仓库大标题',
count: 100,
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
},
// 2.通过mutations可以提供修改数据的方法
mutations: {
// 所有mutation函数,第一个参数,都是state
addCount (state, n) {
// 修改数据
state.count += n
},
subCount (state, n) {
state.count -= n
},
changeTitle (state, newTitle) {
state.title = newTitle
},
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
},
// 3.actions 处理异步
// 注意: 不能直接操作 state, 操作 state, 还是需要 commit mutation
actions: {
// context 上下文(此处未分模块,可以当成store仓库)
// context.commit('mutation名字',额外参数)
changeCountAction (content, num) {
// 这里是setTimeout模拟异步,以后大部分场景是发请求
setTimeout(() => {
content.commit('changeCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
},
// 4.getters 类似于计算属性
getters: {
// 注意点:
// 1.形参第一个参数,就是state
// 2.必须有返回值,返回值就是getters的值
filterList (state) {
return state.list.filter(item => item > 5)
}
}
}
)
// 导出给main.js使用
export default store
方法一:通过 store 访问 getters
Son1.vue
<div>{{ $store.state.list }}</div>
<div>{{ $store.getters.filterList }}</div>
方法二:通过辅助函数 mapGetters 映射
Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br />
<button @click="subCount(1)">值 - 1</button>
<button @click="subCount(5)">值 - 5</button>
<button @click="subCount(10)">值 - 10</button>
<button @click="changeCountAction(888)">一秒之后修改成888</button>
<hr>
<div>{{ filterList }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
// mapStore 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
...mapState(['count', 'title']),
...mapGetters(['filterList'])
},
methods: {
// mapMutation 和 mapActions 都是映射方法
...mapMutations(['subCount', 'changeCount']),
...mapActions(['changeCountAction'])
// handleSub (n) {
// // this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
// this.subCount(n)
// }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
1.10 核心概念 - 模块 module (进阶语法)
1.10.1module 模块的创建

模块拆分:
user模块: store/modules/user.js
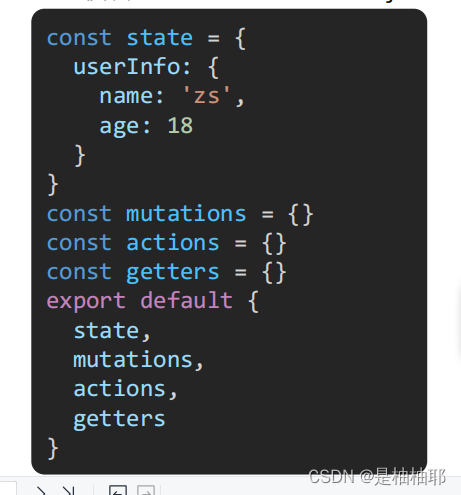
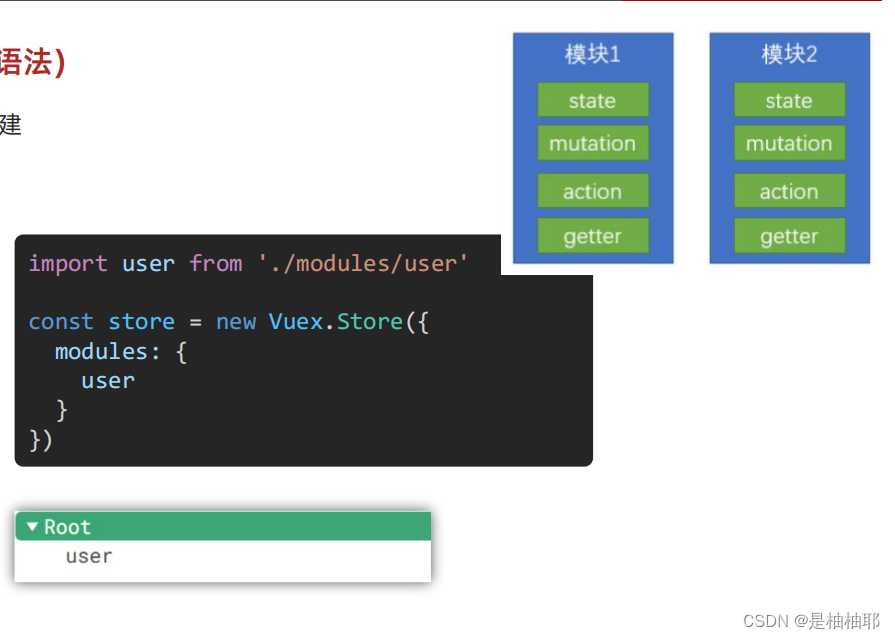
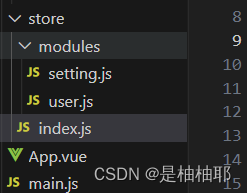
index.js
// 在这里存放的就是 Vuex 相关的核心代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import user from './modules/user'
import setting from './modules/setting'
// 插件安装
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 严格模式(有利于初学者,检测不规范的代码 => 上线时需要关闭)
strict: true,
// 通过state可以提供数据(所有组件共享的数据)
state: {
title: '仓库大标题',
count: 100,
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
},
// 2.通过mutations可以提供修改数据的方法
mutations: {
// 所有mutation函数,第一个参数,都是state
addCount (state, n) {
// 修改数据
state.count += n
},
subCount (state, n) {
state.count -= n
},
changeTitle (state, newTitle) {
state.title = newTitle
},
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
},
// 3.actions 处理异步
// 注意: 不能直接操作 state, 操作 state, 还是需要 commit mutation
actions: {
// context 上下文(此处未分模块,可以当成store仓库)
// context.commit('mutation名字',额外参数)
changeCountAction (content, num) {
// 这里是setTimeout模拟异步,以后大部分场景是发请求
setTimeout(() => {
content.commit('changeCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
},
// 4.getters 类似于计算属性
getters: {
// 注意点:
// 1.形参第一个参数,就是state
// 2.必须有返回值,返回值就是getters的值
filterList (state) {
return state.list.filter(item => item > 5)
}
},
// 5.modules模块
modules: {
user,
setting
}
})
// 导出给main.js使用
export default store
modules - setting.js
// setting模块
const state = {
theme: 'light', // 主题色
desc: '测试demo'
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
1.10.2 state 的访问语法
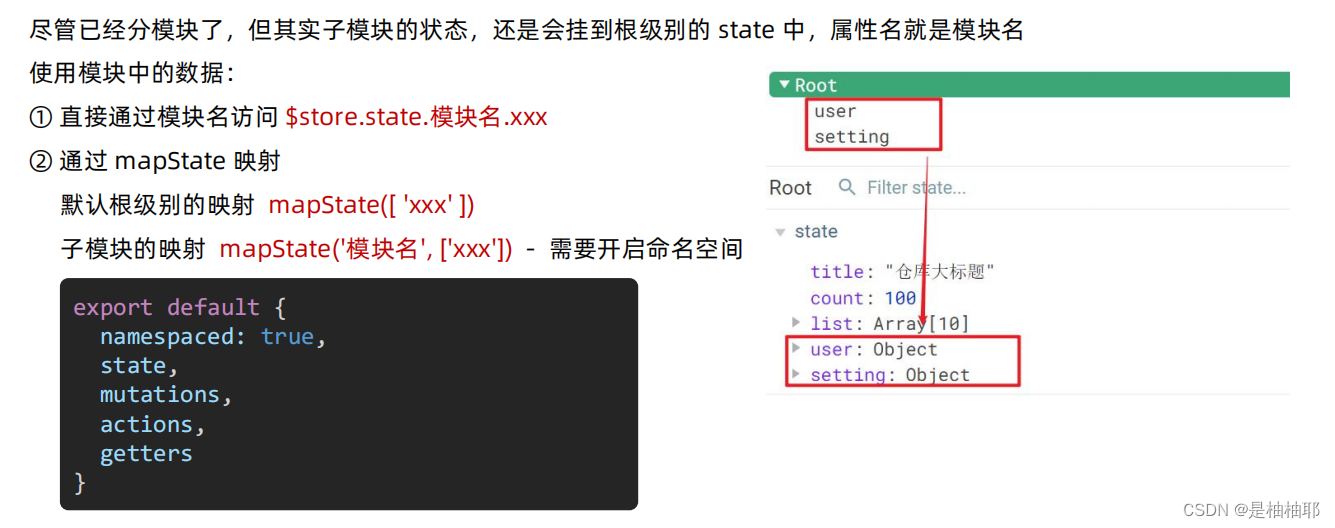
方法一:直接通过模块名访问 $store.state.模块名.xxx
Son2.vue
<!-- 测试访问模块中的state - 原生 -->
<div>{{ $store.state.user.userInfo.name }}</div>
<div>{{ $store.state.setting.theme }}</div>
方法二:通过 mapState 映射
Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br />
<button @click="subCount(1)">值 - 1</button>
<button @click="subCount(5)">值 - 5</button>
<button @click="subCount(10)">值 - 10</button>
<button @click="changeCountAction(888)">一秒之后修改成888</button>
<hr>
<div>{{ filterList }}</div>
<hr>
<!-- 访问模块中的state -->
<div>{{ user.userInfo.name }}</div>
<div>{{ setting.theme }}</div>
<div>user模块的数据{{ userInfo }}</div>
<div>setting模块的数据{{ theme }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
// mapStore 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
...mapState(['count', 'title', 'user', 'setting']),
...mapState('user', ['userInfo']),
...mapState('setting', ['theme', 'desc']),
...mapGetters(['filterList'])
},
methods: {
// mapMutation 和 mapActions 都是映射方法
...mapMutations(['subCount', 'changeCount']),
...mapActions(['changeCountAction'])
// handleSub (n) {
// // this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
// this.subCount(n)
// }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
setting.js
// setting模块
const state = {
theme: 'light', // 主题色
desc: '测试demo'
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
1.10.3 getters 的访问语法
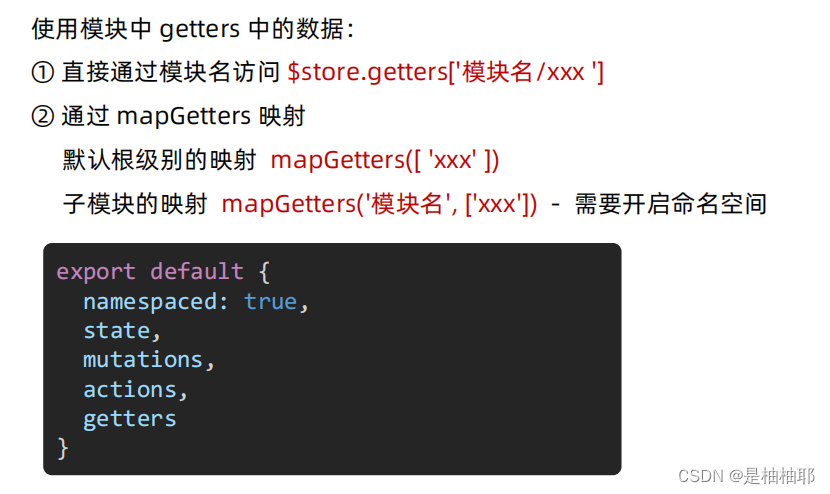
方法一:直接通过模块名访问 $store.getters['模块名/xxx ']
user.js
// user模块
const state = {
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18
},
score: 80
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {
// 分模块后,state指代子模块的state
UpperCaseName (state) {
return state.userInfo.name.toUpperCase()
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
Son1.vue
<!-- 测试访问模块中的getters - 原生 - -->
<div>{{ $store.getters['user/UpperCaseName'] }}</div>
方法二:通过 mapGetters 映射
Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br />
<button @click="subCount(1)">值 - 1</button>
<button @click="subCount(5)">值 - 5</button>
<button @click="subCount(10)">值 - 10</button>
<button @click="changeCountAction(888)">一秒之后修改成888</button>
<hr>
<div>{{ filterList }}</div>
<hr>
<!-- 访问模块中的state -->
<div>{{ user.userInfo.name }}</div>
<div>{{ setting.theme }}</div>
<div>user模块的数据{{ userInfo }}</div>
<div>setting模块的数据{{ theme }}</div>
<hr>
<!-- 访问模块中的getters -->
<div>{{ UpperCaseName }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
// mapStore 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
...mapState(['count', 'title', 'user', 'setting']),
...mapState('user', ['userInfo']),
...mapState('setting', ['theme', 'desc']),
...mapGetters(['filterList']),
...mapGetters('user', ['UpperCaseName'])
},
methods: {
// mapMutation 和 mapActions 都是映射方法
...mapMutations(['subCount', 'changeCount']),
...mapActions(['changeCountAction'])
// handleSub (n) {
// // this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
// this.subCount(n)
// }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
1.10.4 mutation 的调用语法
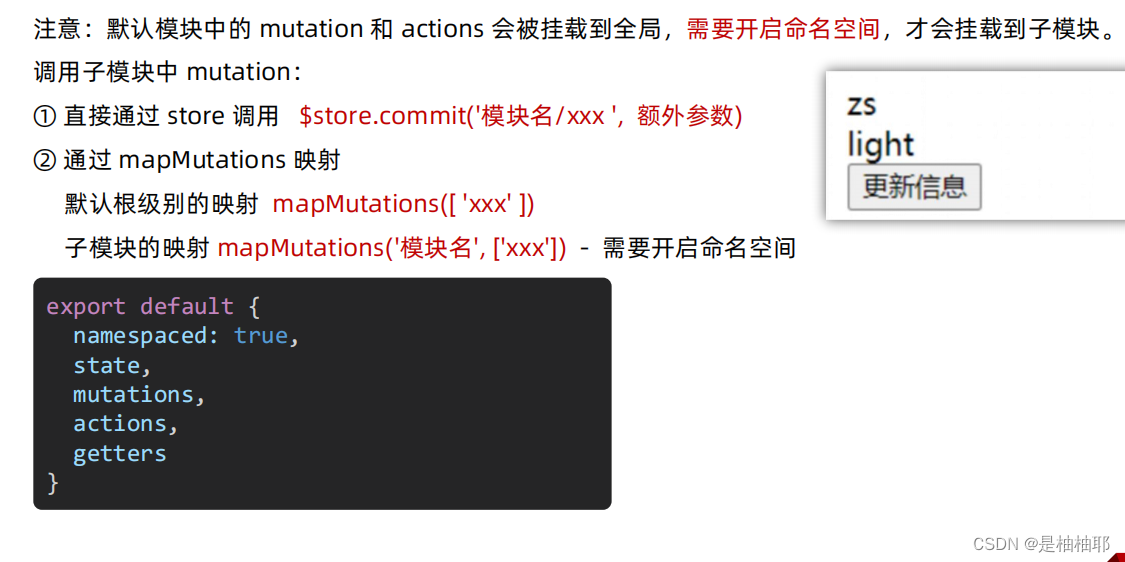
方法一:直接通过 store 调用
user.js
// user模块
const state = {
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18
},
score: 80
}
const mutations = {
setUser (state, newUserinfo) {
state.userInfo = newUserinfo
}
}
const actions = {}
const getters = {
// 分模块后,state指代子模块的state
UpperCaseName (state) {
return state.userInfo.name.toUpperCase()
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
Son1.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值: <label>{{ $store.state.count }}</label>
<br>
<button @click="handleAdd(1)">值 + 1</button>
<button @click="handleAdd(5)">值 + 5</button>
<button @click="handleAdd(10)">值 + 10</button>
<button @click="changeFn">改标题</button>
<button @click="handleChange">一秒之后修改成666</button>
<hr>
<div>{{ $store.state.list }}</div>
<div>{{ $store.getters.filterList }}</div>
<hr>
<!-- 测试访问模块中的state - 原生 -->
<div>{{ $store.state.user.userInfo.name }}</div>
<button @click="updateUser">更改个人信息</button>
<div>{{ $store.state.setting.theme }}</div>
<button @click="updateTheme">更改主题色</button>
<hr>
<!-- 测试访问模块中的getters - 原生 - -->
<div>{{ $store.getters['user/UpperCaseName'] }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son1Com',
methods: {
handleAdd (n) {
// 错误代码(vue默认不会监测,检测需要成本)
// this.$store.state.count++
// console.log(this.$store.state.count)
// 应该通过 mutation 核心概念,进行修改数据
// this.$store.commit('addCount')
// 调用带参数的mutation函数
this.$store.commit('addCount', n)
},
changeFn () {
this.$store.commit('changeTitle', '黑马程序员')
},
handleChange () {
// 调用action
// this.$store.dispatch('action名字', 额外参数)
this.$store.dispatch('changeCountAction', 666)
},
updateUser () {
// this.$store.commit('模块名/mutation名', 额外参数)
this.$store.commit('user/setUser', {
name: 'xiaowang',
age: 25
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box{
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
方法二:通过 mapMutations 映射
Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br />
<button @click="subCount(1)">值 - 1</button>
<button @click="subCount(5)">值 - 5</button>
<button @click="subCount(10)">值 - 10</button>
<button @click="changeCountAction(888)">一秒之后修改成888</button>
<hr>
<div>{{ filterList }}</div>
<hr>
<!-- 访问模块中的state -->
<div>{{ user.userInfo.name }}</div>
<div>{{ setting.theme }}</div>
<div>user模块的数据{{ userInfo }}</div>
<button @click="setUser({name: 'xiaoli', age: 80})">更新个人信息</button>
<div>setting模块的数据{{ theme }}</div>
<button @click="setTheme('skyblue')">更新主题</button>
<hr>
<!-- 访问模块中的getters -->
<div>{{ UpperCaseName }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
// mapStore 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
...mapState(['count', 'title', 'user', 'setting']),
...mapState('user', ['userInfo']),
...mapState('setting', ['theme', 'desc']),
...mapGetters(['filterList']),
...mapGetters('user', ['UpperCaseName'])
},
methods: {
// mapMutation 和 mapActions 都是映射方法
// 全局级别的映射
...mapMutations(['subCount', 'changeCount']),
...mapActions(['changeCountAction']),
// handleSub (n) {
// // this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
// this.subCount(n)
// }
// 分模块的映射
...mapMutations('setting', ['setTheme']),
...mapMutations('user', ['setUser'])
}
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
1.10.5 action 的调用语法 (同理 - 直接类比 mutation 即可)

方法一:直接通过 store 调用
user.js
const actions = {
setUserSecond (context, newUserinfo) {
// 将异步在action中进行封装
setTimeout(() => {
// 调用mutation context上下文,默认提交的就是自己模块的action和mutation
context.commit('setUser', newUserinfo)
}, 1000)
}
}
Son1.vue
updaterUser2 () {
// 调用action dispatch
this.$store.dispatch('user/setUserSecond', {
name: 'xiaohong',
age: 28
})
},
方法二:通过 mapMutations 映射
Son2.vue
...mapActions('user', ['setUserSecond'])
<button @click="setUserSecond({name: 'xiaoli', age: 80})">一秒后更新个人信息</button>
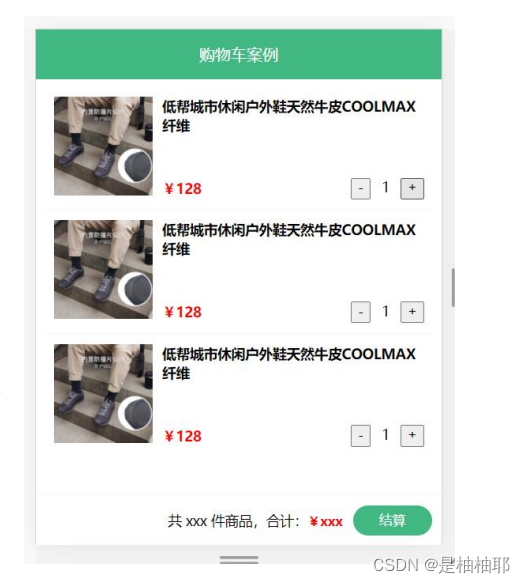
1.11 综合案例 - 购物车
1.目标:功能分析,创建项目,构建分析基本结构
- 功能模块分析
① 请求动态渲染购物车,数据存 vuex
② 数字框控件 修改数据
③ 动态计算 总价和总数量 - 脚手架新建项目 (注意:勾选vuex)
vue create vue-cart-demo - 将原本src内容清空,替换成素材的《vuex-cart-准备代码》并分析
2.目标:构建 cart 购物车模块
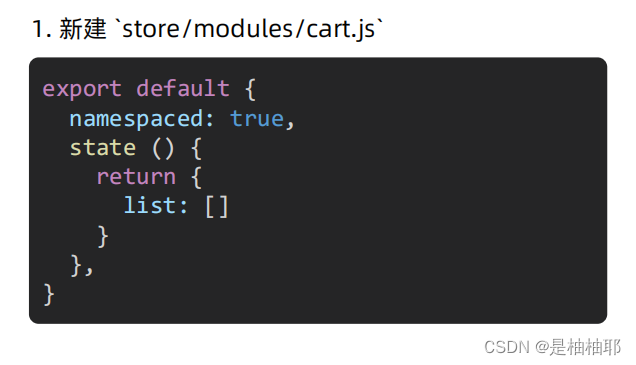
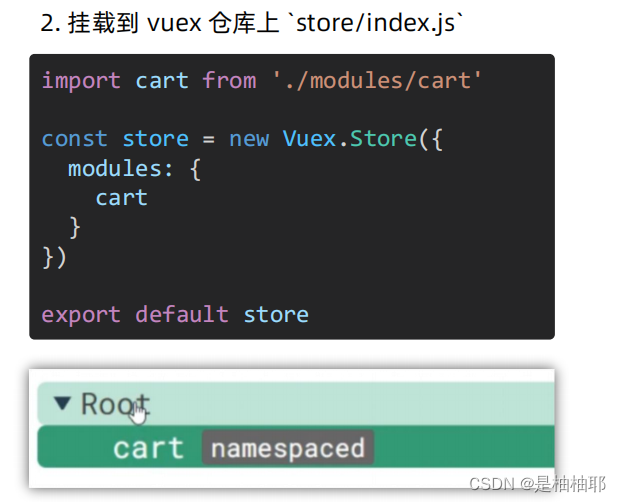
说明:既然明确数据要存 vuex,建议分模块存,购物车数据存 cart 模块,将来还会有 user 模块,article 模块…
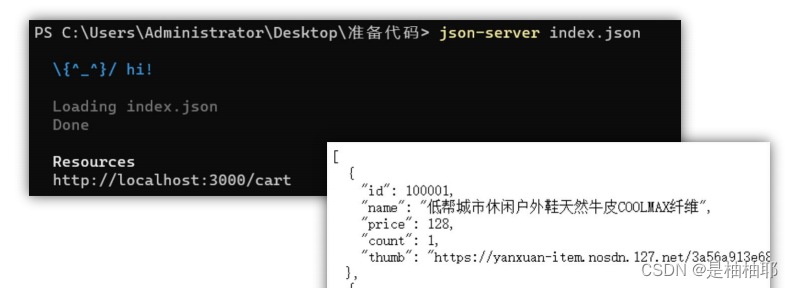
3.目标:基于 json-server 工具,准备后端接口服务环境
- 安装全局工具 json-server (全局工具仅需要安装一次)官网
yarn global add json-server 或 npm i json-server -g - 代码根目录新建一个 db 目录
- 将资料 index.json 移入 db 目录
- 进入 db 目录,执行命令,启动后端接口服务
json-server index.json - 访问接口测试 http://localhost:3000/cart
推荐: json-server --watch index.json (可以实时监听 json 文件的修改)
4.目标:请求获取数据存入 vuex, 映射渲染

npm install axios --save --legacy-peer-deps
- 1.安装axios
npm i axios
安装过程中出现如下报错: code ERESOLVE ERESOLVE could not resolve
出现问题的原因:由于npm不同版本库之间命令不兼容。
解决方法:
终端输入命令:npm install axios -save --legacy-peer-deps
5.目标:修改数量功能完成
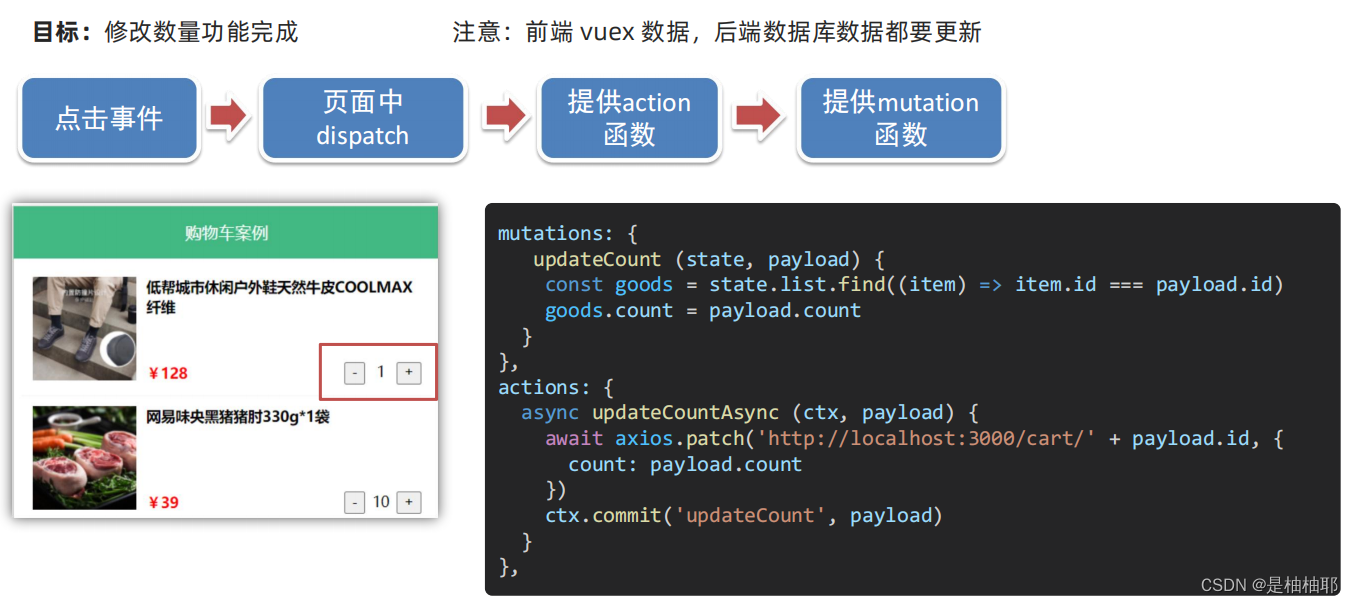
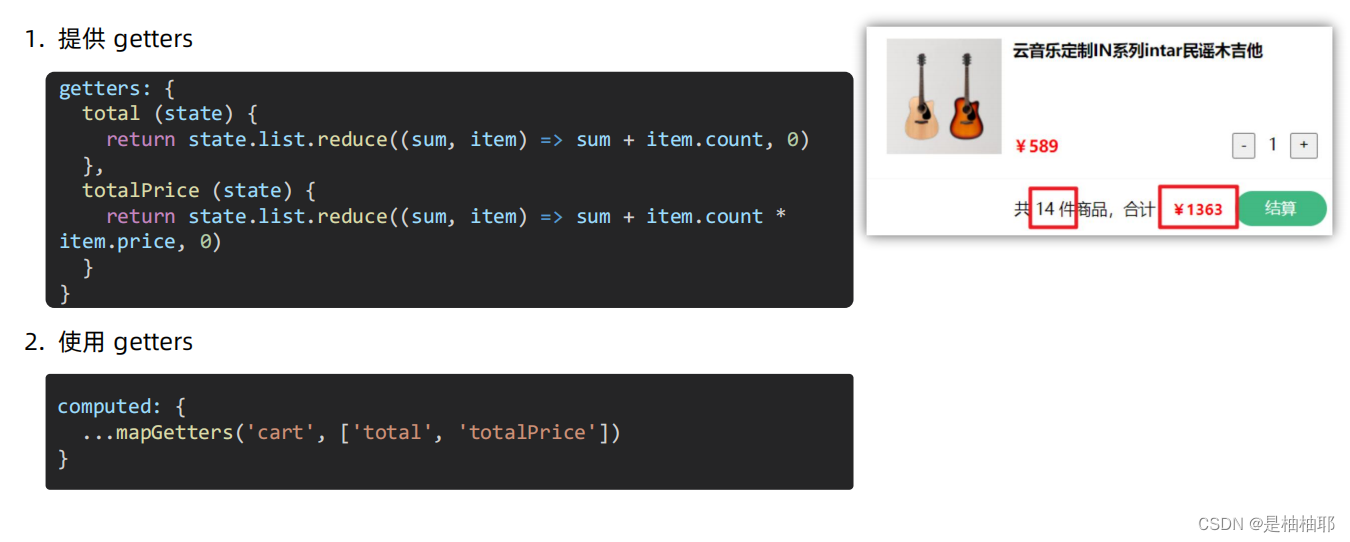
6.目标:底部 getters 统计
index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import cart from './modules/cart'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart
}
})
modules - cart.js
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
namespaced: true,
state () {
return {
// 购物车数据[{}, {}]
list: []
}
},
mutations: {
updateList (state, newList) {
state.list = newList
},
updateCount (state, obj) {
// console.log(obj)
const goods = state.list.find(item => item.id === obj.id)
goods.count = obj.newCount
}
},
actions: {
// 请求方式: get
// 请求地址: http://localhost:3000
async getList (context) {
const res = await axios.get('http://localhost:3000/cart')
// console.log(res.data)
context.commit('updateList', res.data)
},
// 请求方式:patch
// 请求地址:http://localhost:3000/cart/:id值 表示修改的是哪个对象
// {
// name: '新值', 【可选】
// price: '新值', 【可选】
// count: '新值', 【可选】
// thumb: '新值', 【可选】
// }
async updateCountAsync (context, obj) {
// console.log(obj)
// 将修改更新同步到后台服务器
await axios.patch(`http://localhost:3000/cart/${obj.id}`, {
count: obj.newCount
})
// console.log(res)
// 将修改更新同步到vuex
context.commit('updateCount', {
id: obj.id,
newCount: obj.newCount
})
}
},
getters: {
// 商品总数量 累加count * price
total (state) {
return state.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.count, 0)
},
// 商品总价格 累加count * price
totalPrice (state) {
return state.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.count * item.price, 0)
}
}
}
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app-container">
<!-- Header 区域 -->
<cart-header></cart-header>
<!-- 商品 Item 项组件 -->
<cart-item v-for="item in list" :key="item.id" :item="item"></cart-item>
<!-- Foote 区域 -->
<cart-footer></cart-footer>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CartHeader from '@/components/cart-header.vue'
import CartFooter from '@/components/cart-footer.vue'
import CartItem from '@/components/cart-item.vue'
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'App',
created () {
this.$store.dispatch('cart/getList')
},
computed: {
...mapState('cart', ['list'])
},
components: {
CartHeader,
CartFooter,
CartItem
}
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.app-container {
padding: 50px 0;
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>
components - cart-item.vue
<template>
<div class="goods-container">
<!-- 左侧图片区域 -->
<div class="left">
<img :src="item.thumb" class="avatar" alt="">
</div>
<!-- 右侧商品区域 -->
<div class="right">
<!-- 标题 -->
<div class="title">{{ item.name }}</div>
<div class="info">
<!-- 单价 -->
<span class="price">¥{{ item.price }}</span>
<div class="btns">
<!-- 按钮区域 -->
<button class="btn btn-light" @click="btnClick(-1)">-</button>
<span class="count">{{ item.count }}</span>
<button class="btn btn-light" @click="btnClick(1)">+</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'CartItem',
methods: {
btnClick (step) {
// console.log(step)
const newCount = this.item.count + step
const id = this.item.id
// console.log(id, newCount)
if (newCount < 1) return
this.$store.dispatch('cart/updateCountAsync', {
id,
newCount
})
}
},
props: {
item: {
type: Object,
required: true
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.goods-container {
display: flex;
padding: 10px;
+ .goods-container {
border-top: 1px solid #f8f8f8;
}
.left {
.avatar {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
margin-right: 10px;
}
.right {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
flex: 1;
.title {
font-weight: bold;
}
.info {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
.price {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
.btns {
.count {
display: inline-block;
width: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
}
}
}
}
.custom-control-label::before,
.custom-control-label::after {
top: 3.6rem;
}
</style>
cart-footer.vue
<template>
<div class="footer-container">
<!-- 中间的合计 -->
<div>
<span>共 {{total}} 件商品,合计:</span>
<span class="price">¥{{ totalPrice }}</span>
</div>
<!-- 右侧结算按钮 -->
<button class="btn btn-success btn-settle">结算</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CartFooter',
computed: {
...mapGetters('cart', ['total', 'totalPrice'])
}
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.footer-container {
background-color: white;
height: 50px;
border-top: 1px solid #f8f8f8;
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
align-items: center;
padding: 0 10px;
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
z-index: 999;
}
.price {
color: red;
font-size: 13px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.btn-settle {
height: 30px;
min-width: 80px;
margin-right: 20px;
border-radius: 20px;
background: #42b983;
border: none;
color: white;
}
</style>