每一个不曾起舞的日子都是对生命的辜负
string类的模拟实现
- 前言
- 代码:
- 1. string.h
- 2. test.cpp
- 扩展:内置类型的拷贝构造
- 总结
前言
本篇文章是衔接上一篇string,进行string的模拟实现,其中包含了众多重载函数,以及一些实现的细节,由于上篇已经知道具体函数的含义,这一篇就以纯代码的方式进行叙述。此外,这篇还对内置类型的知识进行了进一步的扩展。
代码:
1. string.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace cfy
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
/*string()
{
_str = new char[1];
_str[0] = '\0';
_capacity = _size = 0;
}*/
string(const char* str = "")
{
_size = strlen(str);
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_size + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
//s2(s1)
//拷贝构造的现代写法
string(const string& s)
:_str(nullptr)//tmp指向随机值会有影响,未初始化会导致野指针的情况,因此在拷贝构造之前要给其初始化为nullptr
,_size(0)
,_capacity(0)
{
string tmp(s._str); // 是构造函数,因为s._str是一个值,不是一个对象
//this->swap(tmp);
swap(tmp);
}//tmp作为临时变量除了作用域会自动调用析构,因此上面进行了解释。
//s2(s1)
//拷贝构造的传统写法
/*string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
_capacity = s._capacity;
_size = s._size;
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}*/
// s1 = s3
/*string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tmp, s._str);
_size = s.size();
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
return *this;
}*/
/*string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
string tmp(s);
swap(tmp);
}
return *this;
}*/
// s1 = s3
string& operator=(string s)
{
swap(s);
return *this;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
//普通对象:可读可写
char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
// const对象:只读
char& operator[](int pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
void reserve(size_t n)//扩展容量
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n + 1;
}
}
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
else
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
size_t newCapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(newCapacity);
_capacity = newCapacity;
}
_str[_size++] = ch;
_str[_size] = '\0';//注意处理末尾
}
void append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size >= _capacity - 1)//改
{
size_t newCapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(newCapacity);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
++_size;
return *this;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos + len -1)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
--end;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
return *this;
}
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
size_t find(const char ch, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
while (pos < _size)
{
if (_str[pos] == ch)
{
return pos;
}
++pos;
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (ptr == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return ptr - _str;
}
}
void clear()
{
_size = 0;
_str[0] = '\0';
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
const static size_t npos = -1;//只有这个是特例
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
out << s[i];
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
/*char ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;*/
char buff[128] = { '\0' };//防止扩容代价大,通过buff暂时储存,一段一段进
size_t i = 0;
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
if (i < 127)
{
buff[i++] = ch;
}
else
{
s += buff;
i = 0;
buff[i++] = ch;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
}
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
(*it1)--;
it1++;
}
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
for (auto ch : s1)//底层是调用迭代器iterator,官方库就是这样
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s1.push_back('!');
s1.push_back('!');
s1.push_back('!');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string2()
{
string s1("hello");
s1 += ' ';
s1 += '!';
s1 += '!';
s1 += "happy";
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2;
s2 += 'x';
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.insert(6, " cfy ");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, "");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string4()
{
string s1("hello hello world");
s1.erase(0, 6);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello hello world");
s1.resize(25, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
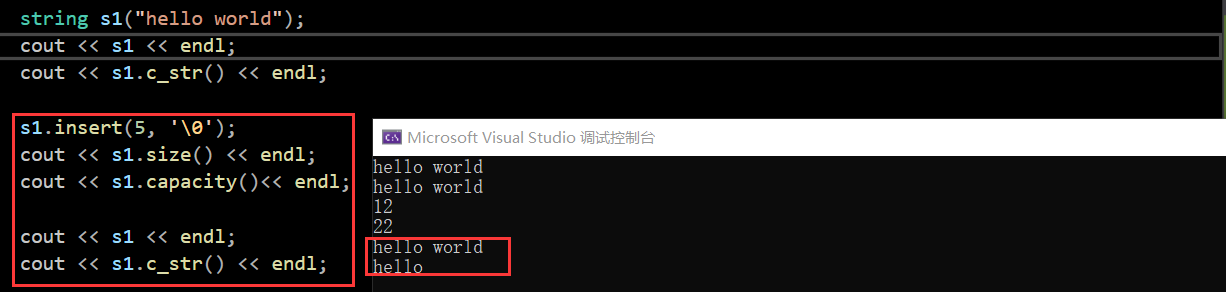
void test_string6()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(5, '\0');
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//string s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1 << endl;
}
void test_string7()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2(s1); // 默认的拷贝构造是浅拷贝,指针指向同一个位置,对开辟的空间的析构会析构多次,导致错误。
cout << s2 << endl;
}
void test_string8()
{
string s1("hello");
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2("world");
cout << s2 << endl;
s1.swap(s2);
cout << "s1:" << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2:" << s2 << endl;
}
}
2. test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"string.h"
int main()
{
cfy::test_string8();
/*int i(10);
cout << i << endl;
int j = int();
cout << j;*/
return 0;
}
扩展:内置类型的拷贝构造

对于C++来说,我们知道其具有默认的拷贝构造函数,这是对自定义的类实现的,但由于C++含有泛型模板template<T>,我们发现其也可以作为类,因此也具有构造和拷贝构造、析构等默认成员函数,因此这也让内置类型支持了拷贝构造,因为我们可以将T替换成相应的内置类型时间比如我们耳熟能详的int、char、double,那我们就来看一下具体做法:
#inclue<iostream>
using namespace std;
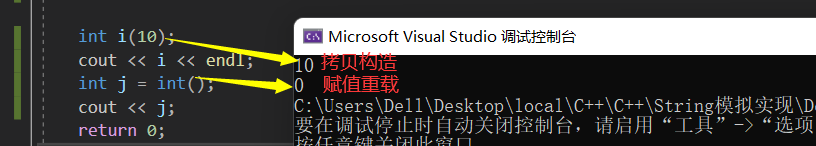
int main()
{
int i(10);
cout << i << endl;
int j = int();
cout << j;
return 0;
}
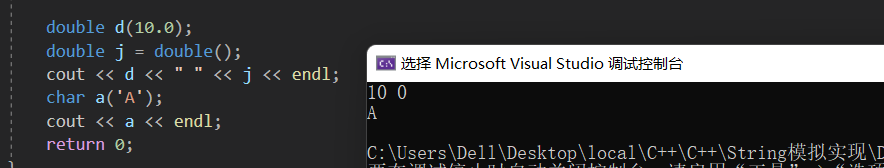
#inclue<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double d(10.0);
double j = double();
cout << d << " " << j << endl;
char a('A');
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
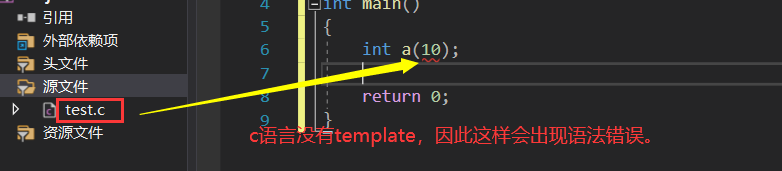
因此,由于C++有泛型模板可以进行这样的操作,但对于C而言,这样的操作就是错误的了。
总结
此篇文章不长,大多通过直接展示代码的形式介绍了string内部函数的模拟实现,此外又添加了template的扩展知识,希望对你有所帮助。