目录
1、LinkedBlokingQueue是一个有界队列
2、LinkedBlokingQueue是一个单向队列
3、LinkedBlokingQueue中的非阻塞方法
4、LinkedBlokingQueue中的阻塞方法
LinkedBlockingQueue是通过ReentrantLock实现的(有界/无界)阻塞队列,在线程池TheadPoolExecutor中的workQueue就是一个LinkedBlockingQueue的实例。
思考:为什么说LinkedBlockingQueue是一个队列?
根据数据结构中队列的特点判断:先进先出(FIFO),队尾进,队头出。
- LinkedBlockingQueue中的插入方法offer()、put()都是在队尾添加元素。
- LinkedBlockingQueue中的获取/删除方法peek()、poll()、take()都是在队头获取/删除元素。
与普通队列相比,线程池使用LinkedBlockingQueue作为缓存队列的好处是:
- 当队列满了的时候可以阻塞添加任务的线程(放到条件变量ConditionObject的条件队列notFull里),而不用丢弃当前线程
- 当队列为空时,会阻塞获取任务的线程(放到条件变量ConditionObject的条件队列notEmpty里),而不用丢弃当前线程
在这篇文章中,会详细介绍LinkedBlockingQueue的底层实现原理。
在此之前,你需要了解ReentrantLock、ConditionObject以及LockSupport几个并发相关的API
为了方便快速了解其结构,简单画了一下的LinkedBlockingQueue类图
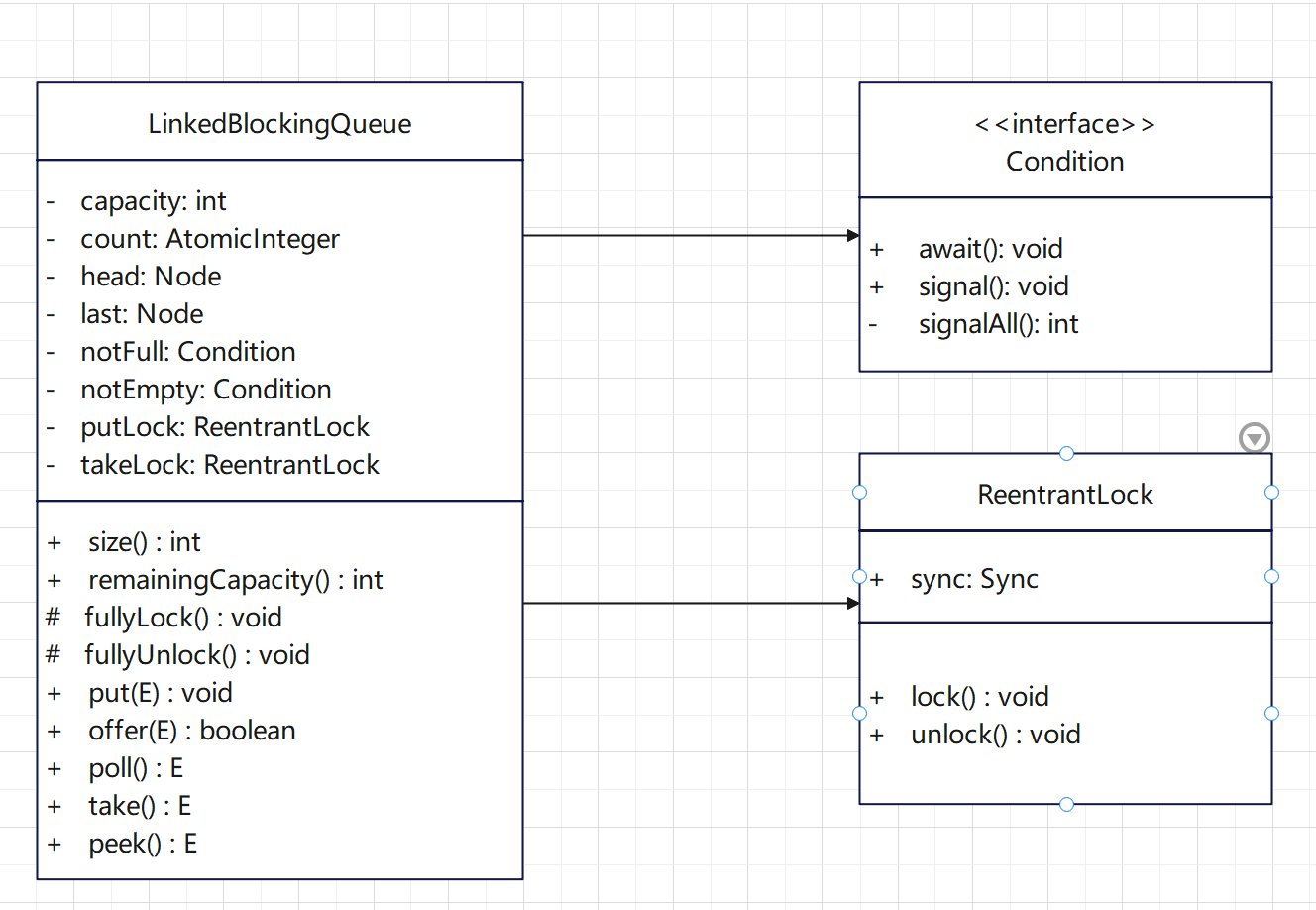
通过上面类图可以了解到,LinkedBlokingQueue中依赖了ReentrantLock来保证入队(putLock)和出队(takeLock)的线程安全,同时通过Condition(条件变量)来保存take()方法因队列为空而阻塞的线程(对应条件变量为notEmpty)和put()方法因队列已满而阻塞的线程(对应条件变量为notFull)。
/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();1、LinkedBlokingQueue是一个有界队列
LinkedBlokingQueue是一个有界队列,因为它内部通过int类型的capacity属性来保存当前队列的长度,可以通过实例化时传入int类型参数指定,当通过无参构造方法实例化时,队列长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE,所以这依然是一个无界队列。
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.capacity = capacity;
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
}2、LinkedBlokingQueue是一个单向队列
LinkedBlokingQueue是一个单向队列,因为其内部定义的Node是一个单向的链表,并且LinkedBlokingQueue只通过head和last保存了队头和队尾节点。
/**
* Linked list node class
*/
static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) { item = x; }
}3、LinkedBlokingQueue中的非阻塞方法
public boolean offer(E e):往队尾添加元素,如果队列已满,则直接返回false,不会阻塞线程。
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// 获取队列长度
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 队列已满,返回false,添加失败
if (count.get() == capacity) {
return false;
}
// 创建一个变量保存队列的大小(长度)
int c = -1;
// 根据数据创建Node节点
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
// 加锁
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() < capacity) {
// 入队
enqueue(node);
// 队列长度自增1
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 如果队列还没有满,唤醒notFull中因为添加失败被阻塞的一个线程
if (c + 1 < capacity) {
notFull.signal();
}
}
} finally {
// 释放锁
putLock.unlock();
}
// 如果入队之前队列为空,则入队之后队列中有一个元素
// 唤醒一个因为调用take()方法被阻塞的线程
if (c == 0) {
signalNotEmpty();
}
return c >= 0;
}入队操作
private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {
// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert last.next == null;
last = last.next = node;
}public E poll():在队头获取并删除一个元素,如果队列为空,直接返回null,不会阻塞线程。
public E poll() {
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 队列没有元素,返回null
if (count.get() == 0) {
return null;
}
E x = null;
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() > 0) {
// 出队操作
x = dequeue();
// 队列长度自减1
c = count.getAndDecrement();
// 队列不为空
// 唤醒notEmpty中因为队列为空,即通过take()获取元素失败而被阻塞的一个线程
if (c > 1) {
notEmpty.signal();
}
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 如果出队之前队列是满的,则出队之后队列中还有一个可用的位置
// 唤醒一个因为调用put()方法被阻塞的线程
if (c == capacity) {
signalNotFull();
}
return x;
}出队操作
private E dequeue() {
// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert head.item == null;
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
}public E peek():从队头获取一个元素,但是不删除元素。
这个方法非常简单,加锁获取队列的头结点,如果队列为空返回null。
public E peek() {
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
Node<E> first = head.next;
if (first == null)
return null;
else
return first.item;
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
}4、LinkedBlokingQueue中的阻塞方法
public E take() throws InterruptedException:获取队头的元素,如果队列为空,则阻塞当前线程。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 队列为空,当前线程(获取元素的线程)被阻塞
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
// 出队
x = dequeue();
// 队列长度自增
c = count.getAndDecrement();
// 队列不为空,唤醒notEmpty中的一个线程
if (c > 1) {
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity) {
signalNotFull();
}
return x;
}notEmpty.await();这行代码完成了阻塞当前线程,我们看一下他的实现
因为notEmpty是调用ReentrantLock的newCondition()方法得到的,所以用的是AQS的内部Condition实现类ConditionObject。
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 如果当前线程被中断了,清除中断状态,抛出中断异常返回
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 把当前线程放到条件队列中
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
// node节点已经在条件队列中
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// 中断线程
LockSupport.park(this);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}所以,最终是通过LockSupport.part()方法来中断线程的,对应的signal()和signalAll()方法也是通过LockSupport.unpark()方法来唤醒线程。
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) && (first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); // 唤醒线程
return true;
}public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException:往队尾添加元素,如果队列已满,则阻塞当前线程。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 添加的元素不能为空
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 队列已满,阻塞线程
while (count.get() == capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
// 入队
enqueue(node);
// 队列长度自增
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 如果队列还没有满,唤醒notFull中因为添加失败被阻塞的一个线程
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
}好了,这篇文章就分享到这里了,看完不要忘了点赞+收藏哦~