前言
最近在尝试逆向方向相关的探索,针对某款运动APP的登录协议进行了分析,此文记录一下分析过程与结果,仅供学习研究,使用的工具较少,内容也比较简单,新手项,大佬请跳过。针对密码登录模块进行分析,随便输入一个手机号与密码,后续使用抓包工具分析,针对登录协议的几个字段从学习角度还是值得看下实现逻辑的。
抓包
- 抓包使用 Charles,请自行安装并配置证书
- 抓取登陆接口,点击密码登陆。使用假账密测试抓包,能够抓包成功
Sign分析
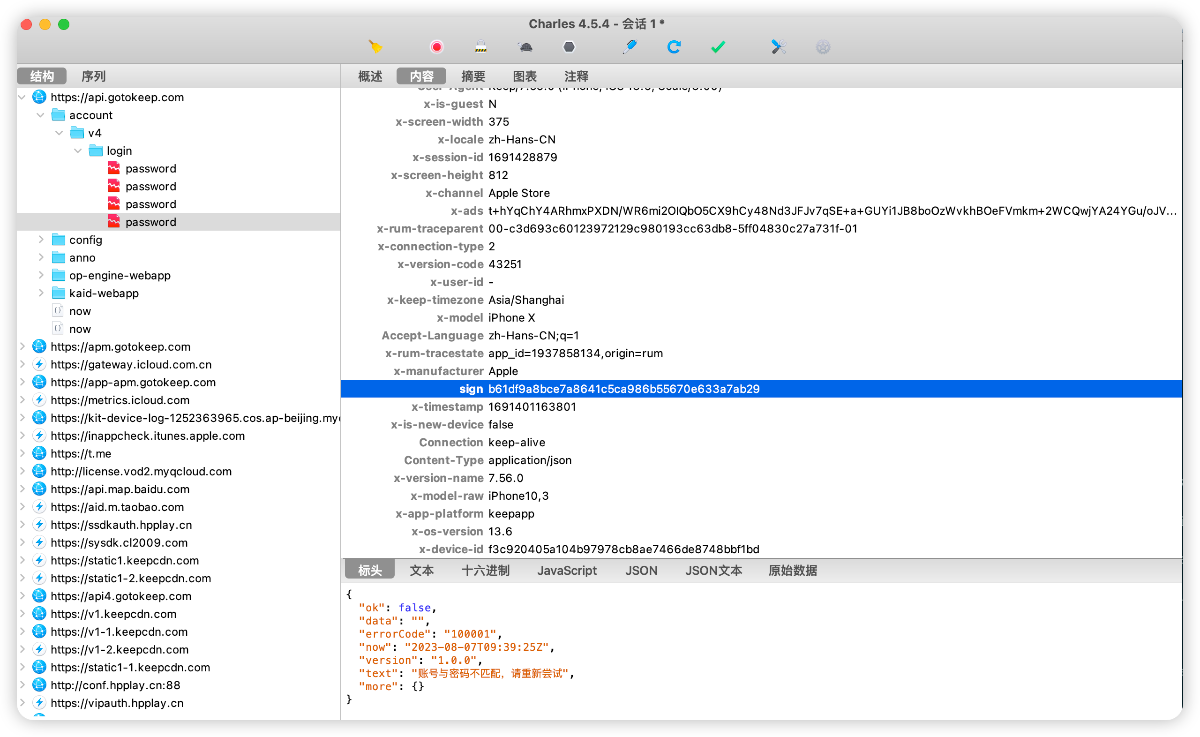
首先能看到请求头里面有sign字段,针对该字段进行分析:
sign: b61df9a8bce7a8641c5ca986b55670e633a7ab29
整体长度为40,常用的MD5长度为32,第一反应不太像,但是也有可能md5以后再拼接其它字段,sha1散列函数的长度是40,正好吻合。那我们就一一验证,先看下是否有MD5的痕迹,直接写脚本frida试着跑下。 脚本内容比较明确,针对MD5的Init、Update、Final分别hook打印看下输入与输出,下面给到关键代码:
// hook CC_MD5
// unsigned char * CC_MD5(const void *data, CC_LONG len, unsigned char *md);
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcommonCrypto.dylib", g_funcName), {
onEnter:function(args) {
console.log(g_funcName +" begin");
varlen = args[1].toInt32();
console.log("input:");
dumpBytes(args[0], len);
this.md = args[2];
},
onLeave:function(retval) {
console.log(g_funcName +" return value");
dumpBytes(this.md, g_funcRetvalLength);
console.log(g_funcName +' called from:\n'+
Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
.map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') +'\n');
}
});
// hook CC_MD5_Update
// int CC_MD5_Update(CC_MD5_CTX *c, const void *data, CC_LONG len);
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcommonCrypto.dylib", g_updateFuncName), {
onEnter:function(args) {
console.log(g_updateFuncName +" begin");
varlen = args[2].toInt32();
console.log("input:");
dumpBytes(args[1], len);
},
onLeave:function(retval) {
console.log(g_updateFuncName +' called from:\n'+
Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
.map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') +'\n');
}
});
// hook CC_MD5_Final
// int CC_MD5_Final(unsigned char *md, CC_MD5_CTX *c);
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcommonCrypto.dylib", g_finalFuncName), {
onEnter:function(args) {
//console.log(func.name + " begin");
finalArgs_md = args[0];
},
onLeave:function(retval) {
console.log(g_finalFuncName +" return value");
dumpBytes(finalArgs_md, g_funcRetvalLength);
console.log(g_finalFuncName +' called from:\n'+
Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
.map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') +'\n');
}
});
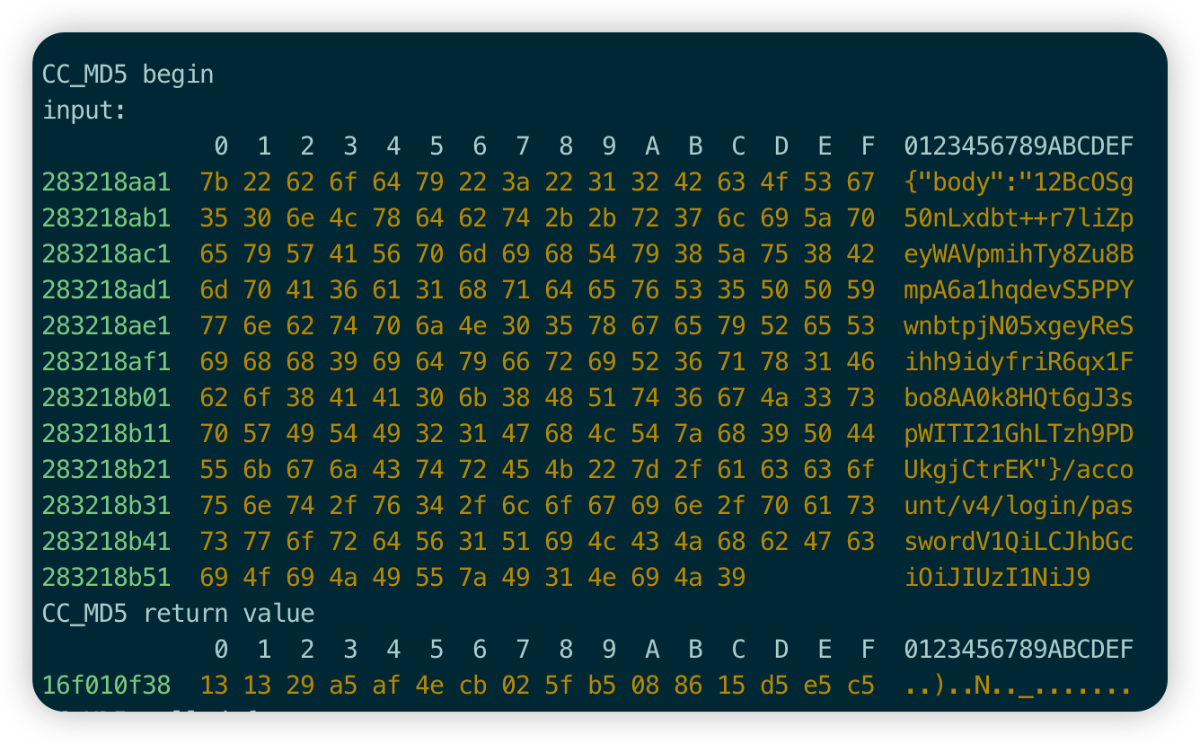
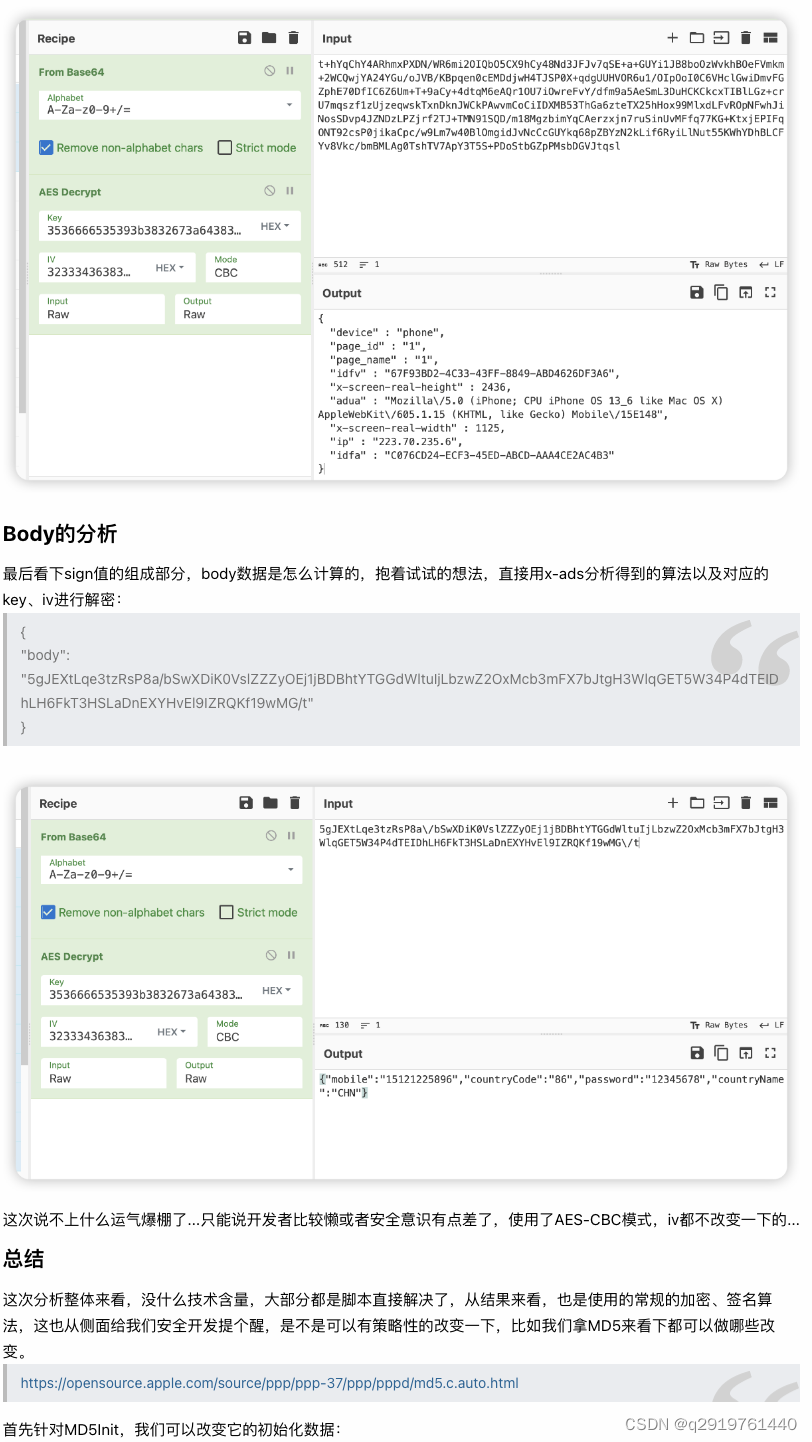
很幸运,在打印中明显看到了sign相关的内容打印,但是缺少sign的后面一部分,那就明确sign值的构成为32(md5)+8,先看下md5的数据构造过程。
b61df9a8bce7a8641c5ca986b55670e6 33a7ab29
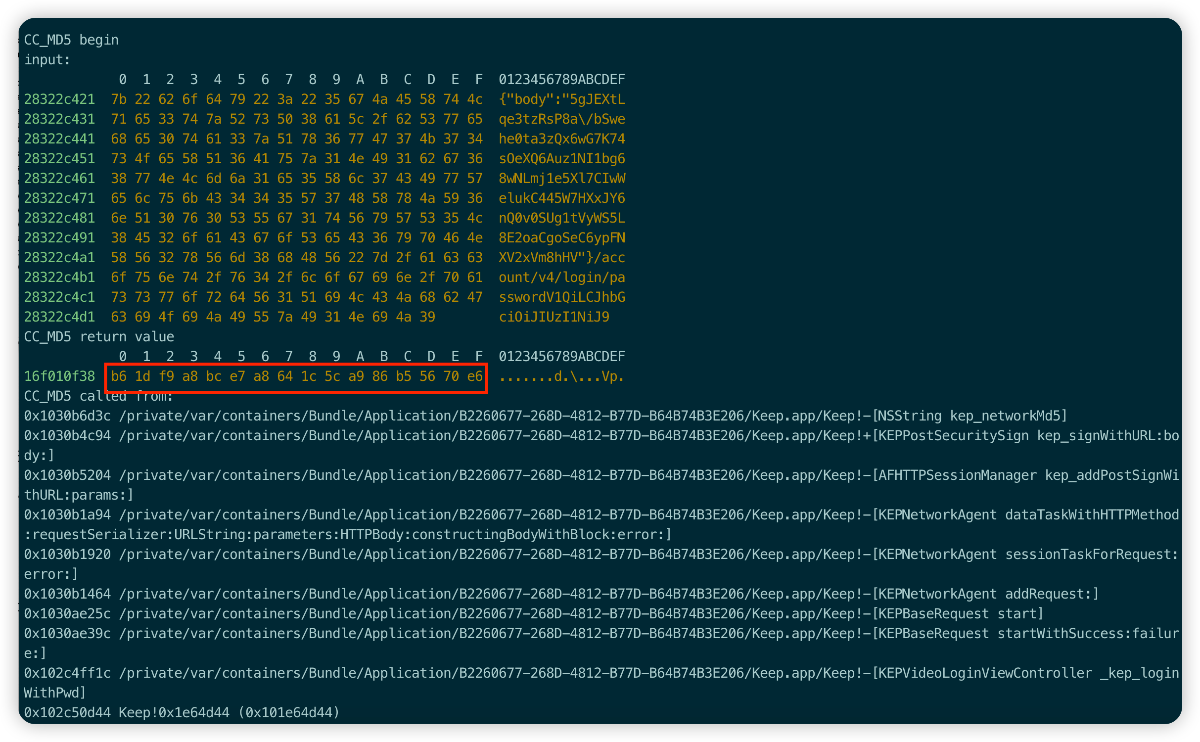
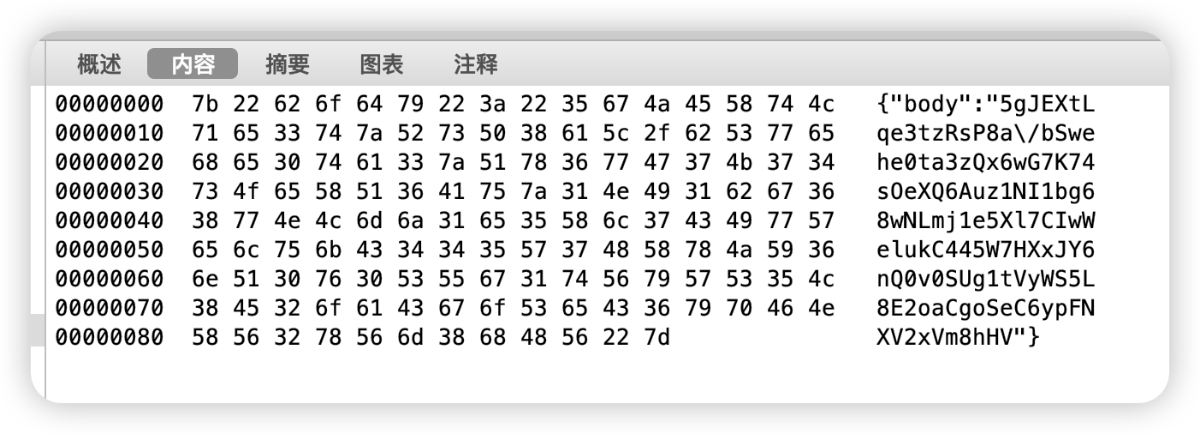
通过打印可以明确的看到,sign的MD5由三部分数据组成,分别为:bodyData+Url+Str,body数据也可从Charles获取到。
-
{"body":"5gJEXtLqe3tzRsP8a/bSwehe0ta3zQx6wG7K74sOeXQ6Auz1NI1bg68wNLmj1e5Xl7CIwWelukC445W7HXxJY6nQ0v0SUg1tVyWS5L8E2oaCgoSeC6ypFNXV2xVm8hHV"}
-
/account/v4/login/password
-
V1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9
-

Sign尾部分析
接下来我们针对Sign的尾部数据进行分析,单纯盲猜或者挂frida脚本已经解决不了问题了,我们用IDA看下具体的实现逻辑,当然上面的MD5分析也可以直接从IDA反编译入手,通过搜索sign关键字进行定位,只是我习惯先钩一下脚本,万一直接命中就不用费时间去分析了...
通过MD5的脚本打印,我们也能看到相关的函数调用栈,这对于我们快速定位也提供了很大的方便。我们直接搜索[KEPPostSecuritySign kep_signWithURL: body:]方法,可以看到明显的字符串拼接的痕迹,IDA还是比较智能的,已经识别出了MD5的salt值。
-
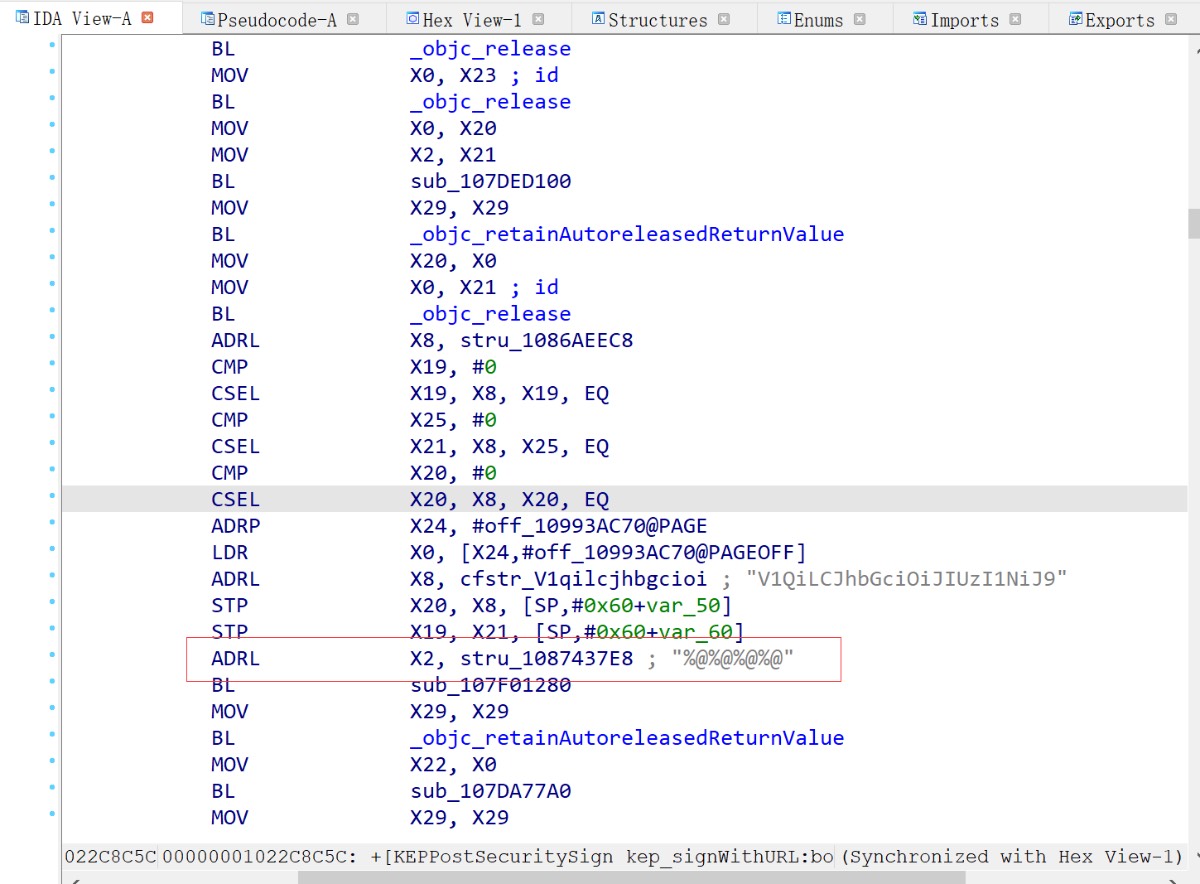
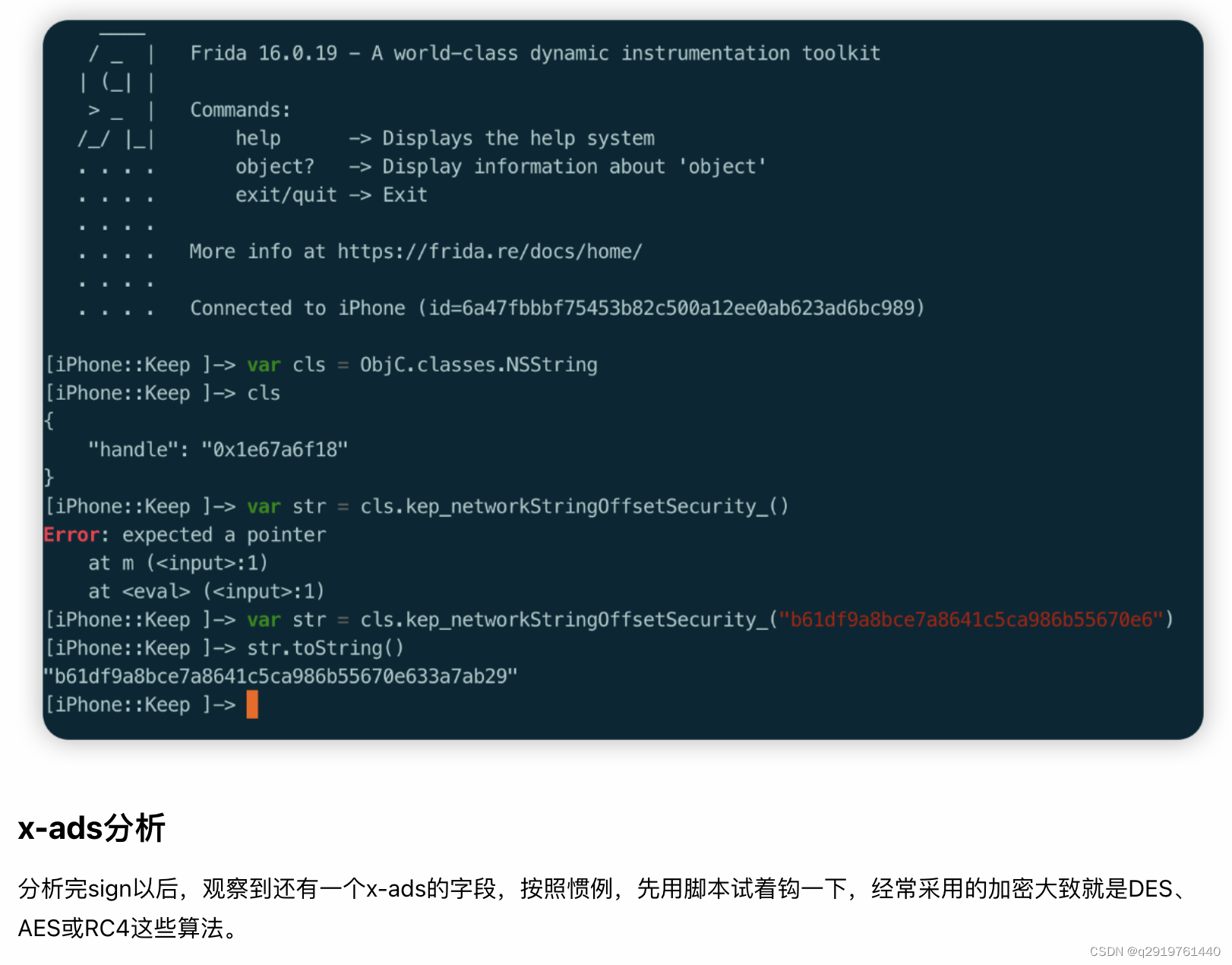
通过分析,定位到[NSString kep_networkStringOffsetSecurity]函数,在内部进行了字符串的处理,在循环里面进行了各种判断以及移位操作,不嫌麻烦的话可以分析一下逻辑,重写一下处理流程。
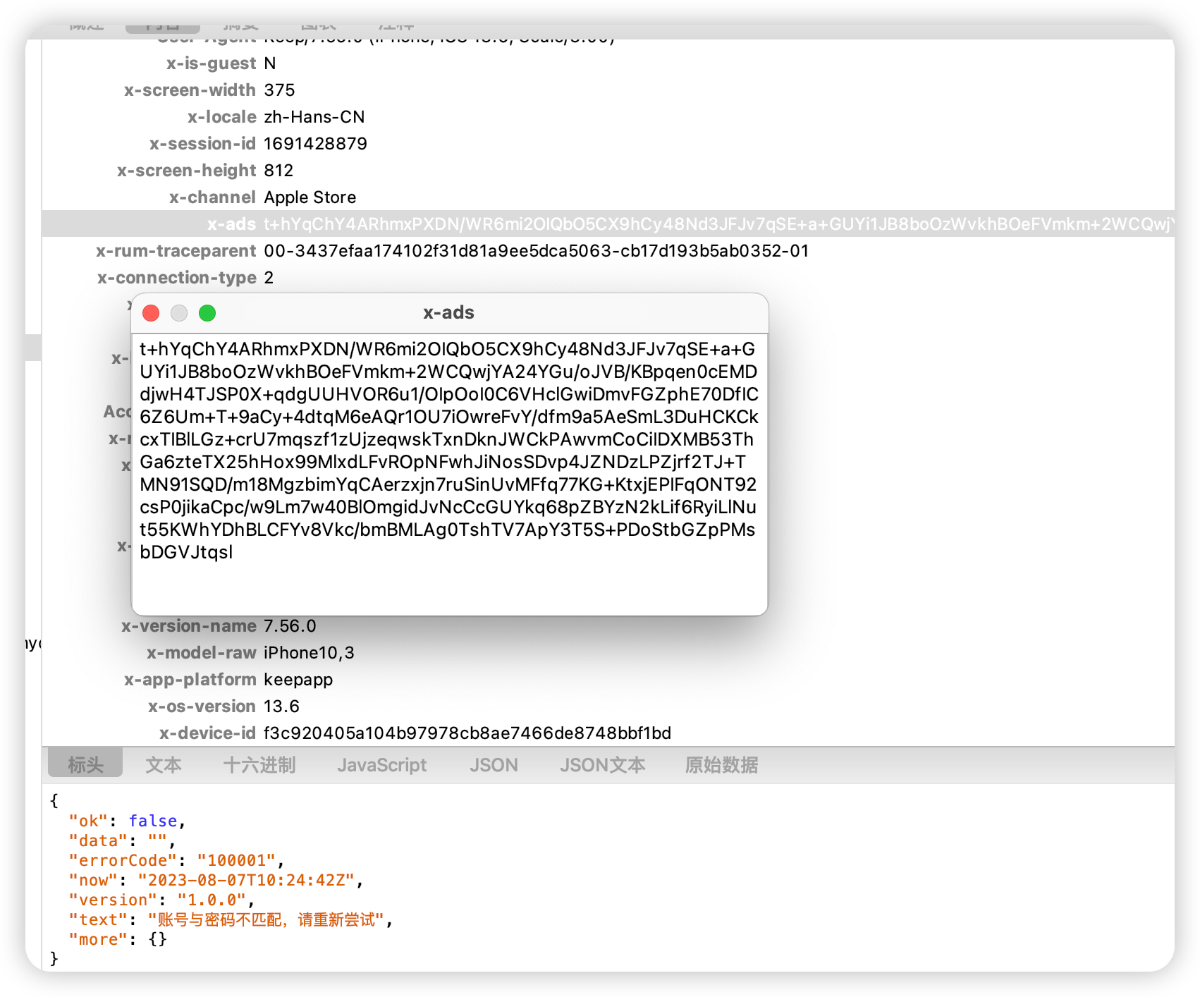
针对 AES128、DES、3DES、CAST、RC4、RC2、Blowfish等加密算法进行hook,脚本的关键代码如下:
varhandlers = {
CCCrypt: {
onEnter:function(args) {
varoperation = CCOperation[args[0].toInt32()];
varalg = CCAlgorithm[args[1].toInt32()].name;
this.options = CCoptions[args[2].toInt32()];
varkeyBytes = args[3];
varkeyLength = args[4].toInt32();
varivBuffer = args[5];
varinBuffer = args[6];
this.inLength = args[7].toInt32();
this.outBuffer = args[8];
varoutLength = args[9].toInt32();
this.outCountPtr = args[10];
if(this.inLength < MIN_LENGTH ||this.inLength > MAX_LENGTH){
return;
}
if(operation ==="kCCEncrypt") {
this.operation ="encrypt"
console.log("***************** encrypt begin **********************");
}else{
this.operation ="decrypt"
console.log("***************** decrypt begin **********************");
}
console.log("CCCrypt("+
"operation: "+this.operation +", "+
"CCAlgorithm: "+ alg +", "+
"CCOptions: "+this.options +", "+
"keyBytes: "+ keyBytes +", "+
"keyLength: "+ keyLength +", "+
"ivBuffer: "+ ivBuffer +", "+
"inBuffer: "+ inBuffer +", "+
"inLength: "+this.inLength +", "+
"outBuffer: "+this.outBuffer +", "+
"outLength: "+ outLength +", "+
"outCountPtr: "+this.outCountPtr +")"
);
//console.log("Key: utf-8 string:" + ptr(keyBytes).readUtf8String())
//console.log("Key: utf-16 string:" + ptr(keyBytes).readUtf16String())
console.log("key: ");
dumpBytes(keyBytes, keyLength);
console.log("IV: ");
// ECB模式不需要iv,所以iv是null
dumpBytes(ivBuffer, keyLength);
varisOutput =true;
if(!SHOW_PLAIN_AND_CIPHER &&this.operation =="decrypt") {
isOutput =false;
}
if(isOutput){
// Show the buffers here if this an encryption operation
console.log("In buffer:");
dumpBytes(inBuffer,this.inLength);
}
},
onLeave:function(retVal) {
// 长度过长和长度太短的都不要输出
if(this.inLength < MIN_LENGTH ||this.inLength > MAX_LENGTH){
return;
}
varisOutput =true;
if(!SHOW_PLAIN_AND_CIPHER &&this.operation =="encrypt") {
isOutput =false;
}
if(isOutput) {
// Show the buffers here if this a decryption operation
console.log("Out buffer:");
dumpBytes(this.outBuffer, Memory.readUInt(this.outCountPtr));
}
// 输出调用堆栈,会识别类名函数名,非常好用
console.log('CCCrypt called from:\n'+
Thread.backtrace(this.context, Backtracer.ACCURATE)
.map(DebugSymbol.fromAddress).join('\n') +'\n');
}
},
};
if(ObjC.available) {
console.log("frida attach");
for(varfuncinhandlers) {
console.log("hook "+ func);
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcommonCrypto.dylib", func), handlers[func]);
}
}else{
console.log("Objective-C Runtime is not available!");
}
查看脚本的输出日志,直接命中了AES128的加密算法,并且输出的Base64数据完全匹配,只能说运气爆棚。

简单的变形以后,即使脚本能hook到对应的函数,但是想直接脱机调用结果还是不可以的,此时就要不得不进行反编译分析或者动态调试,此时配合代码混淆、VMP等静态防护手段,再加上反调试等安全手段,对于攻击的门槛也相应的提高。