目录
1.本文实现目标
2.自定义注解
3. 定义controller加上自定义的注释
4. 识别到这个注解
5.扫描目录,返回该目录下所有文件名(全限定名)
6.扫描该文件所在包中所有带这两个注解的类和方法放到map中
7.通过反射的方式创建实例
8.通过exec方法调动实例,执行实例中的方法
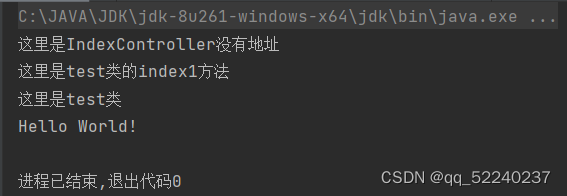
9.执行结果
1.本文实现目标
- 自定义注解
- 识别到这个注解
- 通过反射的方式创建实例
- 通过exec方法调动实例,执行实例中的方法
2.自定义注解
详见:自定义注解(Annontation)_qq_52240237的博客-CSDN博客
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @ interface Controller {
}
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface RequestMapping {
/**
*
* @return
*/
String value() default "";
}
3. 定义controller加上自定义的注释
@Controller
@RequestMapping("test")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping
public String index(){
System.out.println("这里是test类");
return "";
}
@RequestMapping("index1")
public String index1(){
System.out.println("这里是test类的index1方法");
return "";
}
}
4. 识别到这个注解
private static boolean isController(Class cl){
Annotation annotation = cl.getAnnotation(Controller.class);
if(annotation!=null){
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static boolean isRequestMapping(Class cl){
Annotation annotation = cl.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
if(annotation!=null){
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static boolean isRequestMapping(Method method){
Annotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
if(annotation!=null){
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static RequestMapping getRequestMapping(Class cl){
Annotation annotation = cl.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
if(annotation instanceof RequestMapping){
return (RequestMapping) annotation;
}
return null;
}
private static RequestMapping getRequestMapping(Method method){
Annotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
if(annotation instanceof RequestMapping){
return (RequestMapping) annotation;
}
return null;
}
5.扫描目录,返回该目录下所有文件名(全限定名)
private static List<String> traverseFolder2(String path) {
File file = new File(path);
List<String> classFiles=new ArrayList<>();
if (file.exists()) {
LinkedList<File> list = new LinkedList<File>();
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File file2 : files) {
if (file2.isDirectory()) {
list.add(file2);
} else {
classFiles.add(file2.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
File temp_file;
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
temp_file = list.removeFirst();
//.listFiles():该目录中的文件和目录
files = temp_file.listFiles();
for (File file2 : files) {
//.isDirectory():检查该目录是不是一个标准文件夹
if (file2.isDirectory()) {
list.add(file2);
} else {
//.getAbsolutePath():返回抽象路径名的绝对路径名字符串
classFiles.add(file2.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
} else {
}
return classFiles;
}
6.扫描该文件所在包中所有带这两个注解的类和方法放到map中
private static HashMap<String, Map<String,Method>> map=new HashMap<>(); private static HashMap<String, Object> objMap=new HashMap<>();public static void scanner(String path,String packageName){ List<String> paths = traverseFolder2(path); for (String p : paths) { p=p.substring(path.length()-1); try { String className=packageName+"."+p.replaceAll( Matcher.quoteReplacement(File.separator),"."); String replace = className.replace(".class", ""); Class<?> cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass(replace); if(isController(cl)){ if(isRequestMapping(cl)){ RequestMapping requestMapping = getRequestMapping(cl); if(map.containsKey(requestMapping.value())){ throw new RuntimeException("类多注解值:"+requestMapping.value()); }else { map.put(requestMapping.value(),new HashMap<>()); objMap.put(requestMapping.value(),cl.newInstance()); } Method[] declaredMethods = cl.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) { if(isRequestMapping(declaredMethod)){ RequestMapping mapping = getRequestMapping(declaredMethod); if(map.get(requestMapping.value()).containsKey(mapping.value())){ throw new RuntimeException("方法多注解值:"+requestMapping.value()); }else { map.get(requestMapping.value()).put(mapping.value(),declaredMethod); } } } }else { throw new RuntimeException("类无requestMapping"); } } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
7.通过反射的方式创建实例
private static HashMap<String, Map<String,Method>> map=new HashMap<>();
private static HashMap<String, Object> objMap=new HashMap<>();
public static void exec(String classPath,String methodPath){
if(objMap.get(classPath)==null){
System.out.println("没有这个类 404");
}else {
if(map.get(classPath).get(methodPath)==null){
System.out.println("没有这个方法 404");
}else {
try {
map.get(classPath).get(methodPath).invoke(objMap.get(classPath));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
8.通过exec方法调动实例,执行实例中的方法
public class Main {
static {
//在当前调用类所在的同一路径下查找该fileName文件
String path = Main.class.getResource("").getPath();
//返回此类的包的名字
String packageName = Main.class.getPackage().getName();
HeaboyMvc.scanner(path,packageName);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeaboyMvc.exec("","");
HeaboyMvc.exec("test","index1");
HeaboyMvc.exec("test","");
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
9.执行结果










![[保研/考研机试] KY129 简单计算器 浙江大学复试上机题 C++实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2397235da5da434d96b767297e4328d8.png)
