目录
- 引出
- java内存分配
- java内存分布概略图
- 堆
- 方法区
- 常量池
- 创建对象内存分配
- 反射
- class文件的底层
- 类加载顺序
- 1.检查
- 2.开辟静态资源空间
- 3.常量池
- 4.其他...
- 5.创建一个唯一的类的对象
- 获取Class对象的几种方式
- 创建对象几种方式
- new 看到new : new Book()
- 反射 Class.forName(“包名.类名”)
- 克隆(拷贝)
- 浅拷贝
- 深拷贝
- 案例
- 序列化和反序列化
- 什么时候加载.class文件进入内存(JVM)
- 类的加载过程
- 连接:
- 初始化:JVM对类进行初始化
- 如何获取Class对象【反射的基础】
- 类什么时候被加载
- 怎么被加载?
- 双亲委托(委派)机制
- 例子:创建了java.lang.String报错
- 反射
- 注解
- 注解的本质
- 反射+自定义注解案例
- 1.执行某些方法,不执行某些方法
- 2.模拟springBoot的自动注入@Autowired
- 3.简单模拟MybatisPLus工作流程
- @TableName, @TableField注解
- 实体类加入注解
- 映射
- 总结
引出
1.java运行时的内存分配,创建对象时内存分配;
2.类加载的顺序,创建一个唯一的类的类对象;
3.创建对象的方式,new,Class.forName,clone;
4.什么时候加载.class文件进入JVM内存中,看到new,Class.forName;
5.如何加载?双亲委托(委派)机制:安全;AppClassLoader;
6.反射实质:能够获取属性,获取方法;
7.注解的本质:标记;注解+反射才能实现工作;
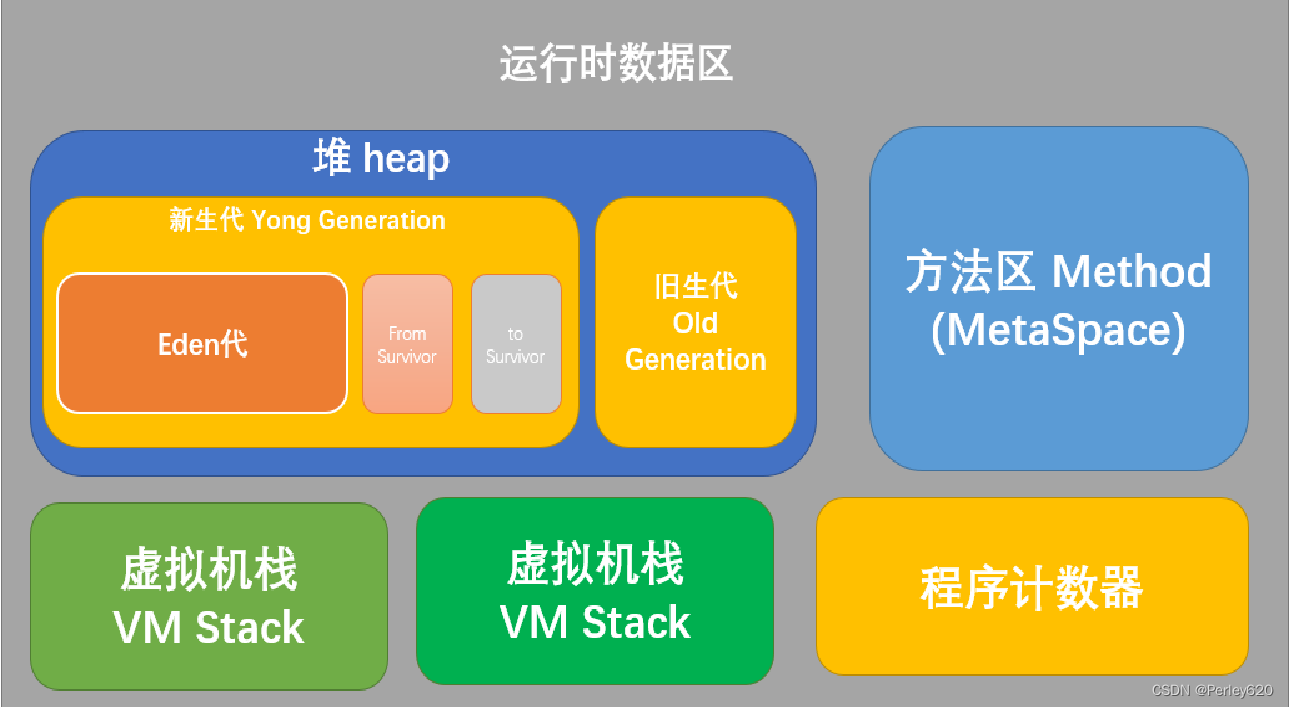
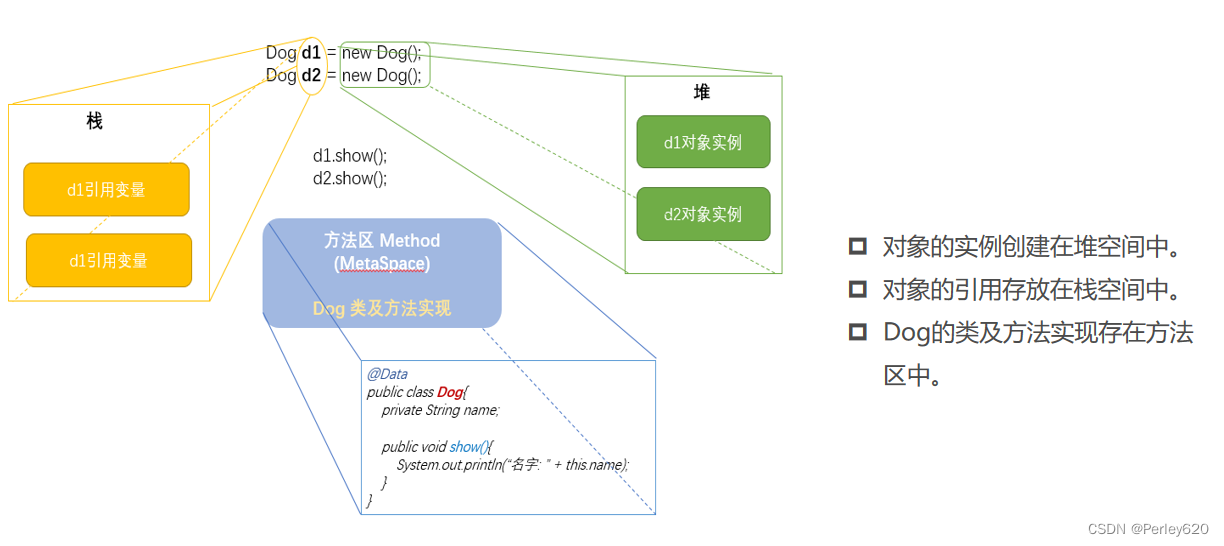
java内存分配
java内存分布概略图
堆
是Java虚拟机所管理的内存中最大的一块。Java堆是被所有线程共享的一块内存区域,在虚拟机启动时创建。此内存区域的唯一目的就是存放对象实例。
方法区
与Java堆一样,是各个线程共享的内存区域,它用于存储已被虚拟机加载的类信息、常量、静态变量、即时编译器编译后的代码等数据。虽然Java虚拟机规范把方法区描述为堆的一个逻辑部分,但是它却有一个别名叫做Non-Heap(非堆),目的应该是与Java堆区分开来。
常量池
运行时常量池(Runtime Constant Pool)是方法区的一部分。Class文件中除了有类的版本、字段、方法、接口等描述等信息外,还有一项信息是常量池(Constant Pool Table),用于存放编译期生成的各种字面量和符号引用,这部分内容将在类加载后存放到方法区的运行时常量池中
注:JDK1.8中JVM把String常量池移入了堆中,同时取消了“永久代”,改用元空间代替(Metaspace)。
创建对象内存分配
反射
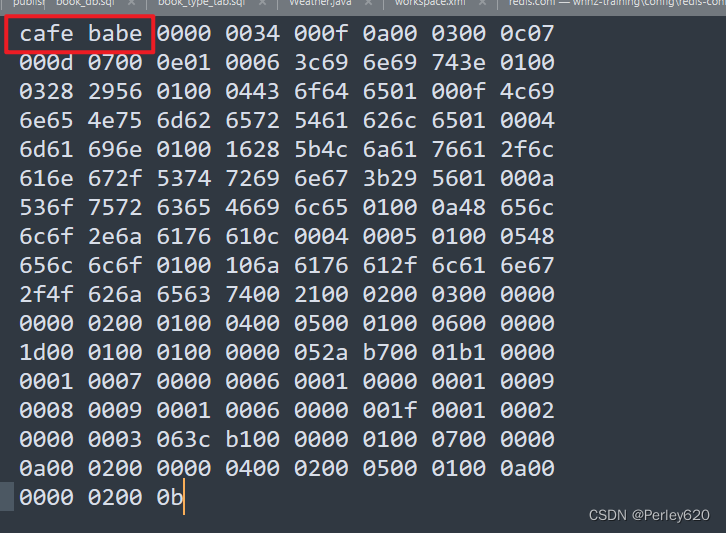
class文件的底层
cafe babe 魔术头
类加载顺序
将class文件加载如 jvm管控的内存中。
1.检查
检查代码是否有问题
2.开辟静态资源空间
3.常量池
4.其他…
5.创建一个唯一的类的对象
Class —-用来表示Hello这个类
获取Class对象的几种方式
- 类.class
- Class.forName(“包名.类名”)
- 对象.getClass()

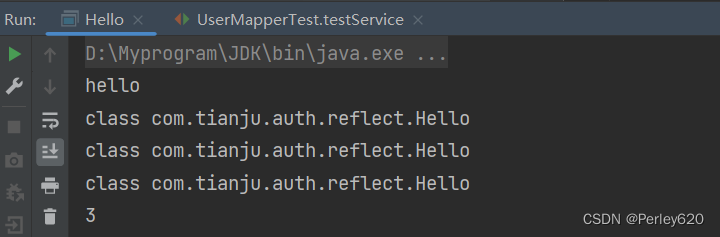
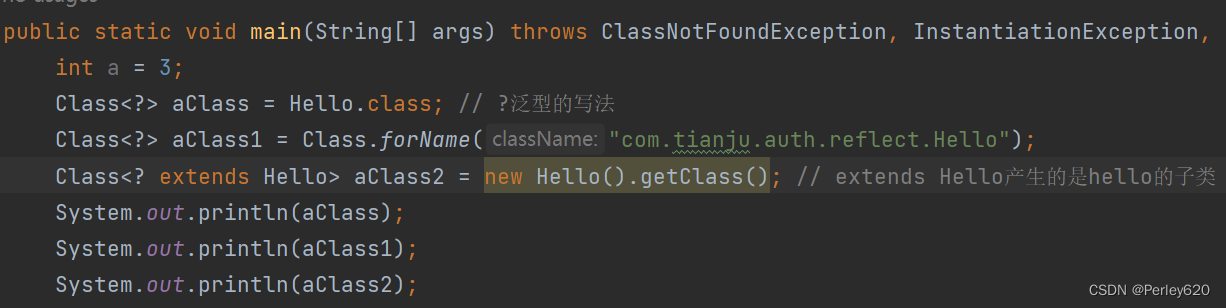
class com.tianju.auth.reflect.Hello
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
public class Hello {
public Integer count(Integer a,Integer b){
return a+b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
int a = 3;
Class<?> aClass = Hello.class; // ?泛型的写法,?未知类型
Class<?> aClass1 = Class.forName("com.tianju.auth.reflect.Hello");
Class<? extends Hello> aClass2 = new Hello().getClass(); // extends Hello 代表的hello的子集
System.out.println(aClass);
System.out.println(aClass1);
System.out.println(aClass2);
Hello o = (Hello) aClass.newInstance(); // 创建对象
int count = o.count(1, 2);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
创建对象几种方式
new 看到new : new Book()
反射 Class.forName(“包名.类名”)
克隆(拷贝)
- 继承的时候,可以将子类的访问控制符扩大,但不能缩小;子类不得比父类抛出更多,更大的异常。
- 浅拷贝、深拷贝问题:

浅拷贝

// protected:代表本包或者继承
// 继承的时候,可以将子类的访问控制符扩大,但不能缩小;
// 子类不能比父类抛出更多的异常
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
深拷贝
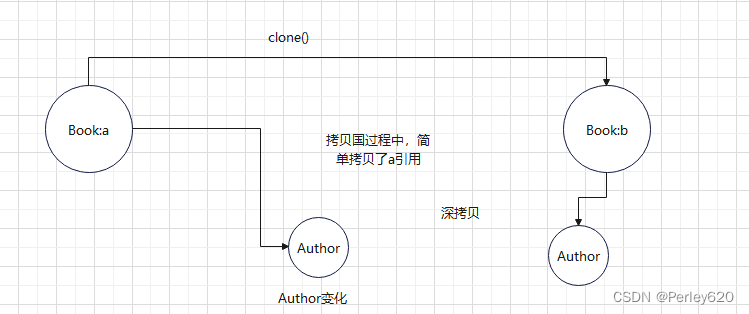
public Book deepClone(){
Book book = new Book();
Author au = new Author();
au.setName(author.getName());
book.setAuthor(au);
book.setTitle(this.title);
book.setPrice(this.price);
return book;
}
案例
Author.java实体类
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Author {
private String name;
}
Book.java实体类
implements Cloneable{ // 可以克隆的
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Book implements Cloneable{ // 可以克隆的
private String title;
private Author author;
public double price;
static {
System.out.println("book的静态代码块");
}
// protected:代表本包或者继承
// 继承的时候,可以将子类的访问控制符扩大,但不能缩小;
// 子类不能比父类抛出更多的异常
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
public Book deepClone(){
Book book = new Book();
Author au = new Author();
au.setName(author.getName());
book.setAuthor(au);
book.setTitle(this.title);
book.setPrice(this.price);
return book;
}
}
进行测试
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
public class TestDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Author author = new Author();
author.setName("吴承恩");
Book book = new Book("三国演义", author,12.56);
Book book1 = book;
System.out.println(book1==book);// == 两个引用是否指向同一个对象
// clone创建了一个新的对象,只是值一样
Book bookClone = (Book) book.clone();
// 深拷贝,创建了新的对象,上面的浅拷贝,只是拷贝了引用
Book deepClone = book.deepClone();
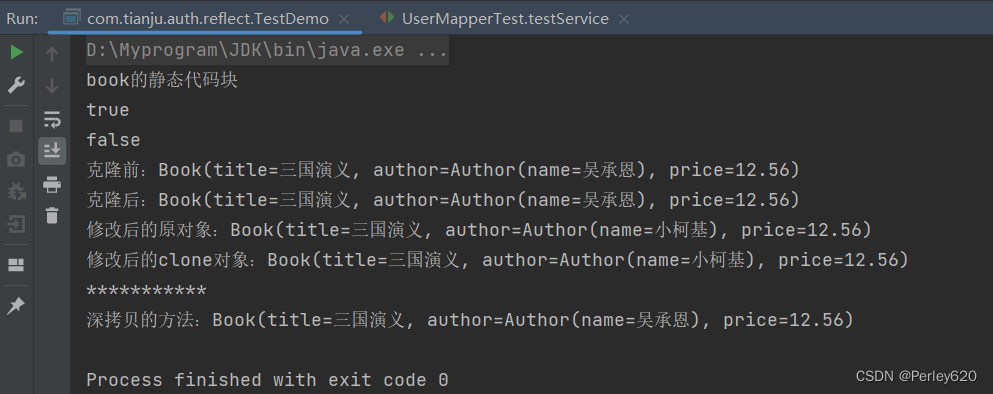
System.out.println(bookClone==book);
System.out.println("克隆前:"+book);
System.out.println("克隆后:"+bookClone);
author.setName("小柯基");
System.out.println("修改后的原对象:"+book);
System.out.println("修改后的clone对象:"+bookClone);
// 深拷贝
System.out.println("***********");
System.out.println("深拷贝的方法:"+deepClone);
}
}
序列化和反序列化
什么时候加载.class文件进入内存(JVM)
类的加载过程
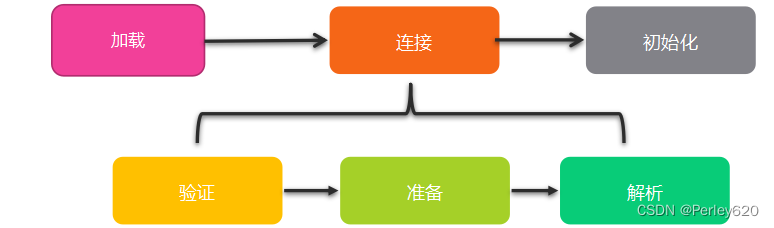
连接:
- 验证:格式检查->语义检查->字节码验证->符号引用验证
- 准备:为静态变量分配内存并设置默认的初始值
- 解析:符号引用替换为直接引用
cafe babe 魔术头
初始化:JVM对类进行初始化
- 则是为标记为常量值的字段赋值的过程。换句话说,只对static修饰的变量或语句块进行初始化。
- 如果类存在直接的父类并且这个类还没有被初始化,那么就先初始化父类。
- 如果类中存在初始化语句,就依次执行这些初始化语句。
每一个类产生了一个唯一的对象Class, Class对象记录了类的基本信息。
如何获取Class对象【反射的基础】
- 对象.getClass()
- 类.class
- Class.forName(“包名.类名”)
类什么时候被加载
Hello h; // 此时没有用Hello,jvm并没有进行类加载
- 看到new : new Book()
- Class.forName: Class.forName(“包名.类名”)
- 类加载器
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
public class HelloTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Hello h; // 此时没有用Hello,jvm并没有进行类加载
System.out.println("**********");
new Hello(); // new 的时候会加载到内存中
System.out.println("**********");
Class.forName("com.tianju.auth.reflect.Hello");
}
}
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
public class Hello {
static {
System.out.println("hello");
}
public Integer count(Integer a,Integer b){
return a+b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
int a = 3;
Class<?> aClass = Hello.class; // ?泛型的写法
Class<?> aClass1 = Class.forName("com.tianju.auth.reflect.Hello");
Class<? extends Hello> aClass2 = new Hello().getClass();
System.out.println(aClass);
System.out.println(aClass1);
System.out.println(aClass2);
Hello o = (Hello) aClass.newInstance();
int count = o.count(1, 2);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
怎么被加载?
双亲委托(派)机制
- AppClassLoader (自定义的类)
- ExtClassLoader
- BootstrapClassLoader
A$B: B是A的内部类
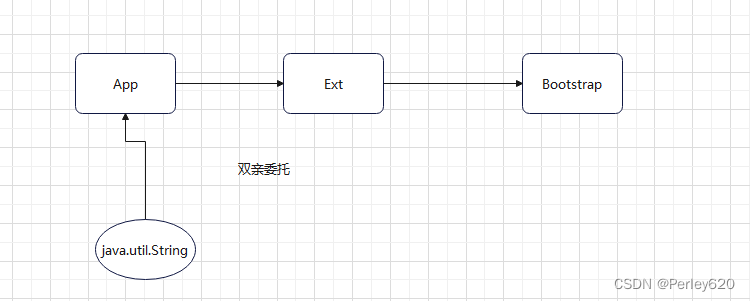
A$B: B是A的内部类

另一种情况
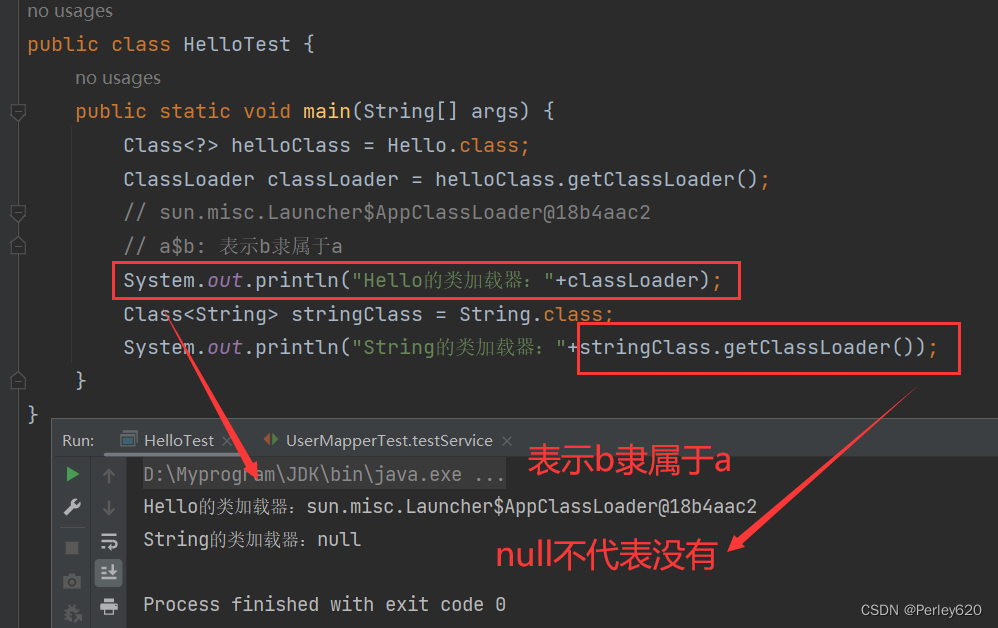
双亲委托(委派)机制
好处:安全
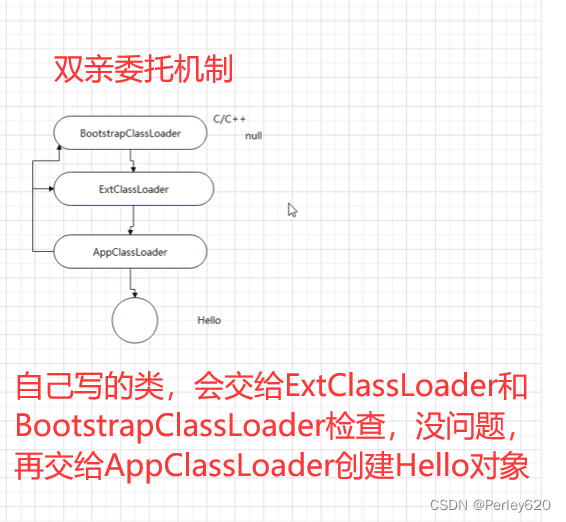
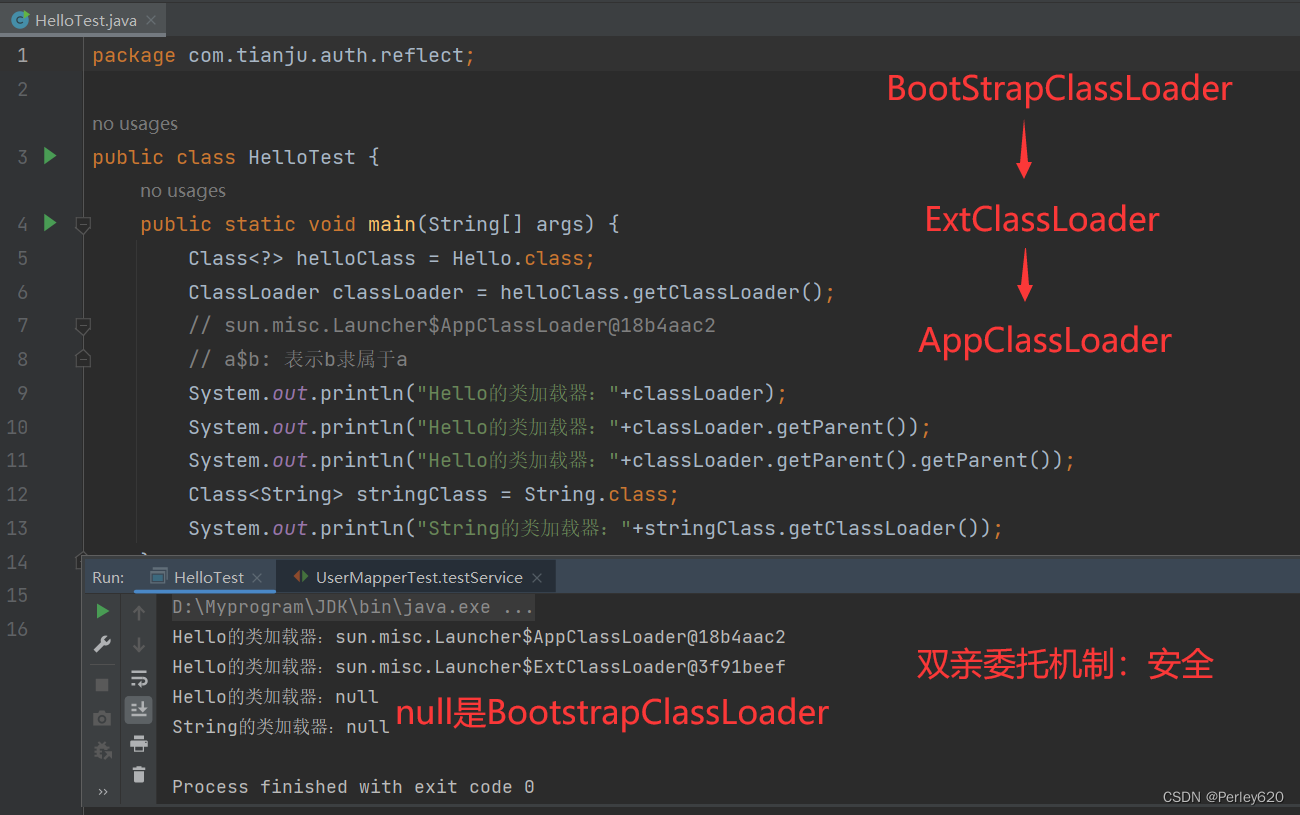
例子:创建了java.lang.String报错
实际是加载的时候BootstrapClassLoader拒接加载
能编译,不能运行
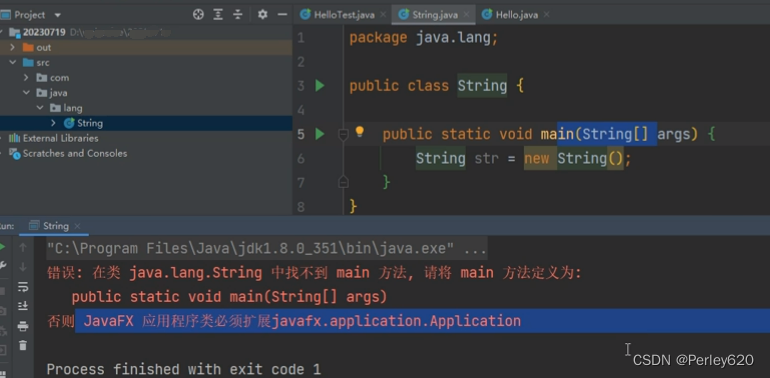
配置这个是因为类加载,lib表示下面包都可以加载;或者配置指向rt里面,常用的string能在里面
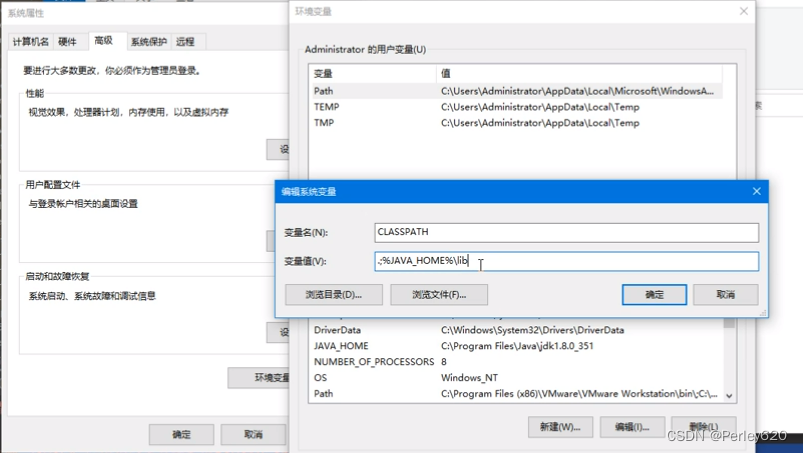
反射
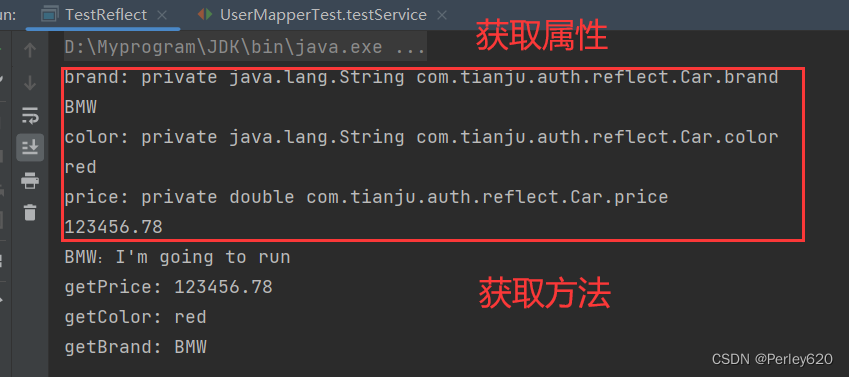
Class对象
Filed: 属性对象
Method: 方法对象
Car.java实体类
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
public class Car {
private String brand;
private String color;
private double price;
public void run(String carName){
System.out.println(carName+":I'm going to run");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
Method: 方法对象;
Filed: 属性对象
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class TestReflect {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
Car c = new Car();
c.setBrand("BMW");
c.setColor("red");
c.setPrice(123456.78);
/**
* 属性
*/
Class<Car> carClass = Car.class;
Field[] declaredFields = carClass.getDeclaredFields(); // 获得所有的属性
for(Field field:declaredFields){
System.out.println(field.getName() + ": "+field);
// Class com.tianju.auth.reflect.TestReflect can not access a member of
// class com.tianju.auth.reflect.Car with modifiers "private"
field.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(field.get(c));
}
/**
* 方法
*/
Method[] declaredMethods = carClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method:declaredMethods){
String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.startsWith("get")){
// method.invoke(c) 表示 Car c 调用这个方法
System.out.println(methodName+": "+method.invoke(c));
}
if (methodName.equals("run")){
method.invoke(c,"BMW");
}
}
}
}
注解
注解的本质
本质就是标记一下
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) // 作用在类上
@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) // 作用在属性上
@Target({ElementType.METHOD}) // 这个注解作用在方法上
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 自定义注解:能找到指定的方法,进行指定的操作
*/
//@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) // 作用在类上
//@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) // 作用在属性上
@Target({ElementType.METHOD}) // 这个注解作用在方法上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CarAnnotation {
String name() default "";
}
反射+自定义注解案例
1.执行某些方法,不执行某些方法
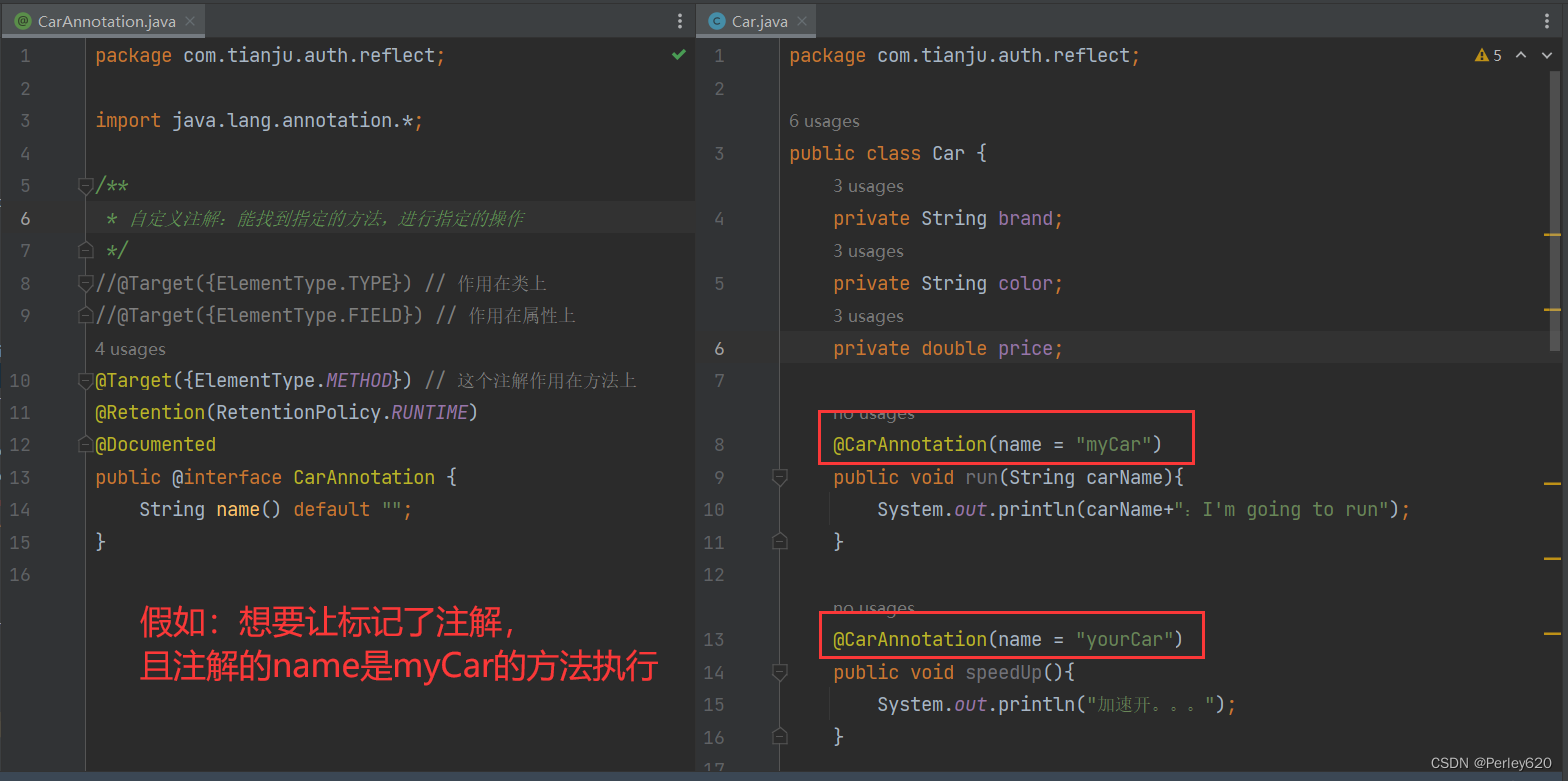
CarAnnotation.java注解文件
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 自定义注解:能找到指定的方法,进行指定的操作
*/
//@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) // 作用在类上
//@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) // 作用在属性上
@Target({ElementType.METHOD}) // 这个注解作用在方法上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CarAnnotation {
String name() default "";
}
Car.java文件
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
public class Car {
private String brand;
private String color;
private double price;
@CarAnnotation(name = "myCar")
public void run(String carName){
System.out.println(carName+":I'm going to run");
}
@CarAnnotation(name = "yourCar")
public void speedUp(){
System.out.println("加速开。。。");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
执行注解的name是myCar的方法
CarAnnotation annotation = method.getDeclaredAnnotation(CarAnnotation.class);
“myCar”.equals(annotation.name())
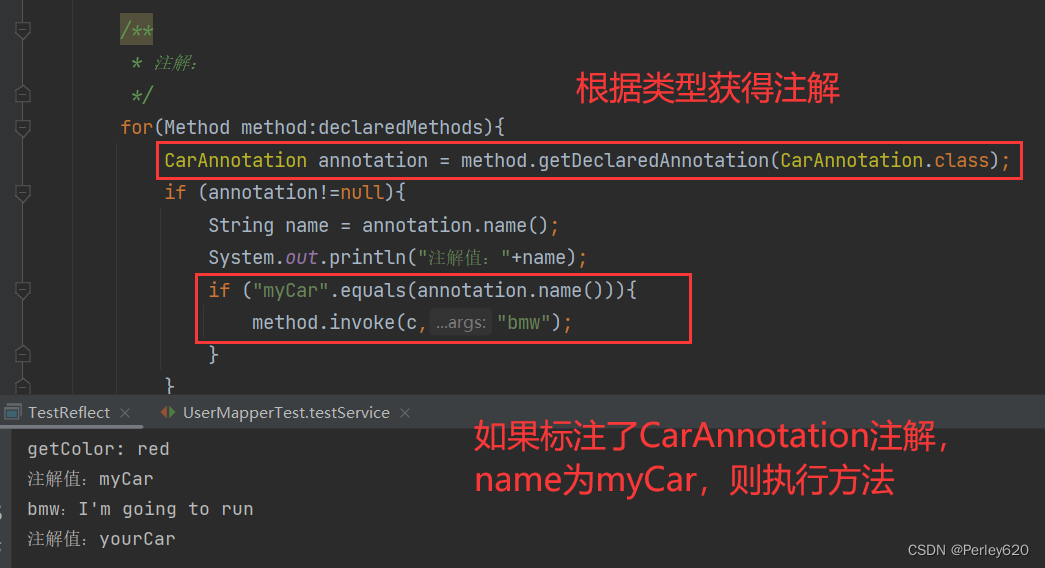
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class TestReflect {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
Car c = new Car();
c.setBrand("BMW");
c.setColor("red");
c.setPrice(123456.78);
/**
* 属性
*/
Class<Car> carClass = Car.class;
Field[] declaredFields = carClass.getDeclaredFields(); // 获得所有的属性
for(Field field:declaredFields){
System.out.println(field.getName() + ": "+field);
// Class com.tianju.auth.reflect.TestReflect can not access a member of
// class com.tianju.auth.reflect.Car with modifiers "private"
field.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(field.get(c));
}
/**
* 方法
*/
Method[] declaredMethods = carClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method:declaredMethods){
String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.startsWith("get")){
// method.invoke(c) 表示 Car c 调用这个方法
System.out.println(methodName+": "+method.invoke(c));
}
if (methodName.equals("run")){
method.invoke(c,"BMW");
}
}
/**
* 注解:
*/
for(Method method:declaredMethods){
CarAnnotation annotation = method.getDeclaredAnnotation(CarAnnotation.class);
if (annotation!=null){
String name = annotation.name();
System.out.println("注解值:"+name);
if ("myCar".equals(annotation.name())){
method.invoke(c,"bmw");
}
}
}
}
}
2.模拟springBoot的自动注入@Autowired
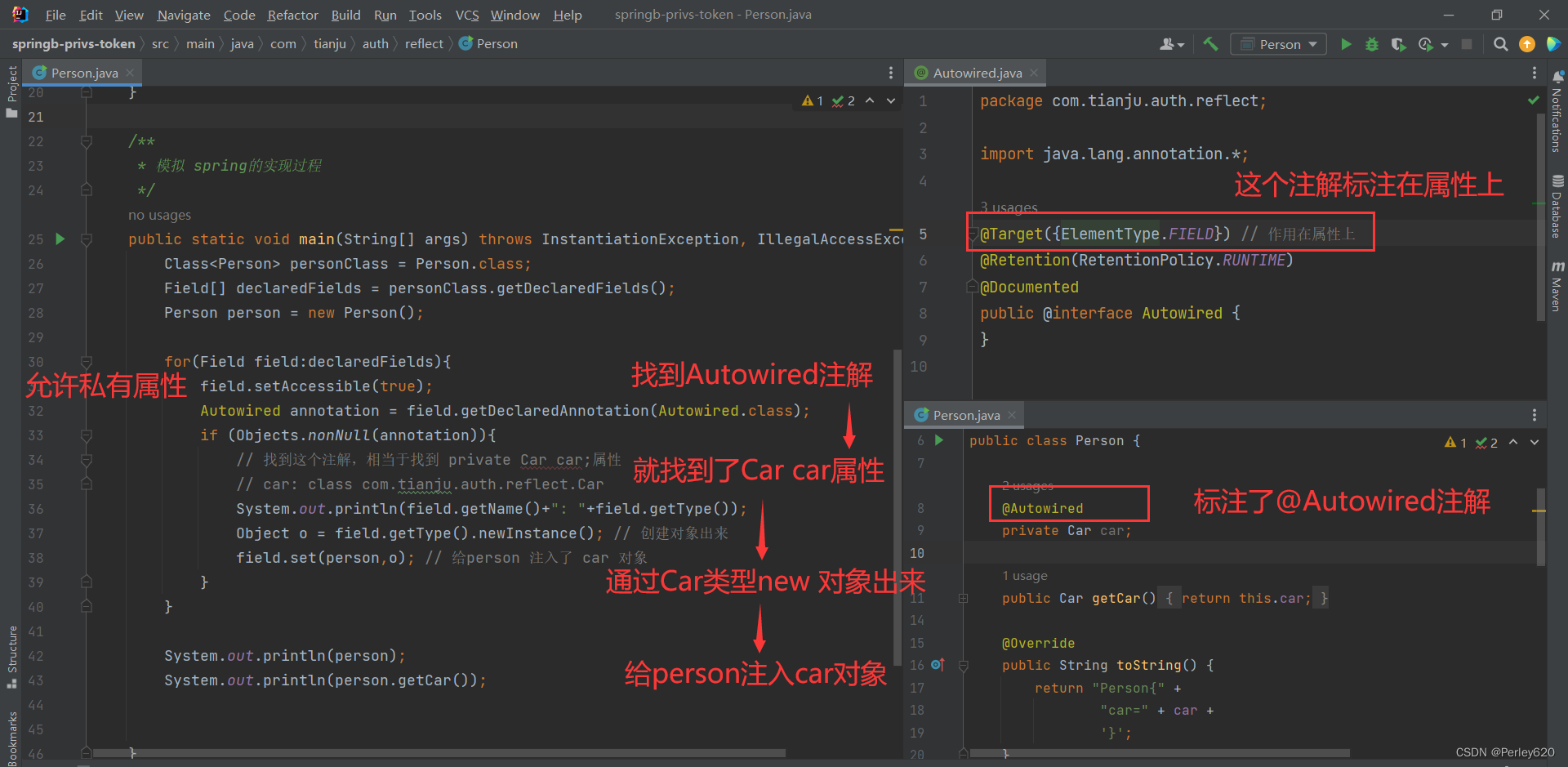
Autowired.java注解实体类
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) // 作用在属性上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
}
person.java实体类
field.set(person,o); // 给person 注入了 car 对象
package com.tianju.auth.reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Person {
@Autowired
private Car car;
public Car getCar(){
return this.car;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"car=" + car +
'}';
}
/**
* 模拟 spring的实现过程
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;
Field[] declaredFields = personClass.getDeclaredFields();
Person person = new Person();
for(Field field:declaredFields){
field.setAccessible(true);
Autowired annotation = field.getDeclaredAnnotation(Autowired.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(annotation)){
// 找到这个注解,相当于找到 private Car car;属性
// car: class com.tianju.auth.reflect.Car
System.out.println(field.getName()+": "+field.getType());
Object o = field.getType().newInstance(); // 创建对象出来
field.set(person,o); // 给person 注入了 car 对象
}
}
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(person.getCar());
}
}
3.简单模拟MybatisPLus工作流程
简单模拟MybatisPLus工作流程
核心: 对象
框架: 对象映射为SQL(数据库) ORM框架
数据库: sql
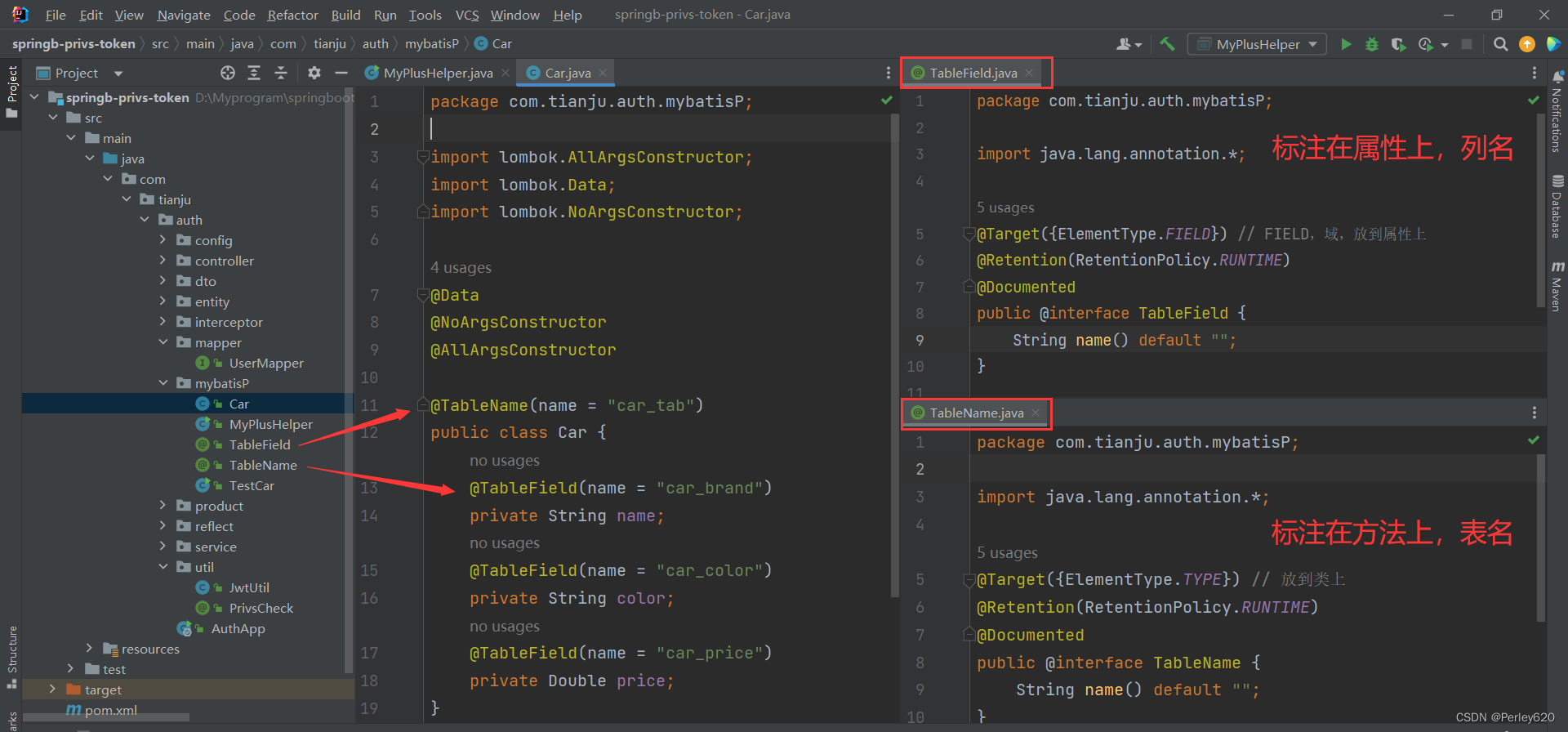
@TableName, @TableField注解
@TableName
package com.tianju.auth.mybatisP;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) // 放到类上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TableName {
String name() default "";
}
@TableField
package com.tianju.auth.mybatisP;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) // FIELD,域,放到属性上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TableField {
String name() default "";
}
实体类加入注解
package com.tianju.auth.mybatisP;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@TableName(name = "car_tab")
public class Car {
@TableField(name = "car_brand")
private String name;
@TableField(name = "car_color")
private String color;
@TableField(name = "car_price")
private Double price;
}
映射
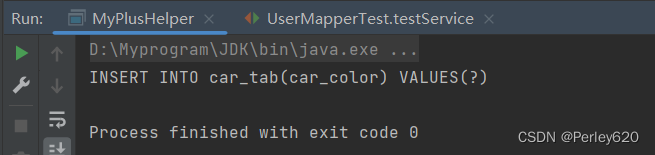
package com.tianju.auth.mybatisP;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
public class MyPlusHelper {
private StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
private List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 产生添加的SQL语句
* @param obj
* @return INSERT INTO car_tab(列名,) VALUES(?,)
*/
public String insert(Object obj) throws IllegalAccessException {
Class<?> aClass = obj.getClass();
// 获取表名
TableName tableNameAnn = aClass.getAnnotation(TableName.class);
String tableName = tableNameAnn.name();
sql.append("INSERT INTO ");
sql.append(tableName);
sql.append("(");
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field:declaredFields){
field.setAccessible(true);
TableField fieldAnnotation = field.getAnnotation(TableField.class);
String columName = fieldAnnotation.name();
Object fieldVal = field.get(obj);
if (Objects.nonNull(fieldVal)){
list.add(fieldVal); // 获取传进来的obj的属性的值
sql.append(columName+",");
}
}
sql.deleteCharAt(sql.length()-1);// 把最后的逗号,删掉
sql.append(")");
sql.append(" VALUES(");
for (int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
sql.append("?,");
}
sql.deleteCharAt(sql.length()-1);// 把最后的逗号,删掉
sql.append(")");
return sql.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
Car car = new Car();
car.setColor("red");
System.out.println(new MyPlusHelper().insert(car));
}
}
总结
1.java运行时的内存分配,创建对象时内存分配;
2.类加载的顺序,创建一个唯一的类的类对象;
3.创建对象的方式,new,Class.forName,clone;
4.什么时候加载.class文件进入JVM内存中,看到new,Class.forName;
5.如何加载?双亲委托(委派)机制:安全;AppClassLoader;
6.反射实质:能够获取属性,获取方法;
7.注解的本质:标记;注解+反射才能实现工作;



![[保研/考研机试] 约瑟夫问题No.2 C++实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a6f6e7f24e9244a9993053e684b781f4.png)