文章目录
- Python远程ssh登录机器检查机器信息
- check_env.sh和hosts.yaml文件如下
- 演示
Python远程ssh登录机器检查机器信息
- 需要在hosts.yaml文件中中输入ssh主机名,端口,用户名,密码
- 使用python3环境,执行
python3 check_env.py - 为了简单,这里python脚本要和hosts.yaml在同级目录下
- 整个框架已经定义好了,想要检查其他信息只需要在display_check_result函数上扩展即可
check_env.sh和hosts.yaml文件如下
check_env.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import paramiko ## pip install paramiko
import yaml ## pip install pyyaml
ssh_client = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy)
class Display:
@staticmethod
def green(info: str):
return ("\033[92m" + info + "\033[0m").format()
@staticmethod
def red(err: str):
return ("\033[91m" + err + "\033[0m").format()
@staticmethod
def yellow(warn: str):
return ("\033[93m" + warn + "\033[0m").format()
@staticmethod
def blue(info: str):
return ("\033[94m" + info + "\033[0m").format()
class Host:
def __init__(self, host, password, port=22, username='root'):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.username = username
self.password = password
def get_password(self):
return self.password
def get_host(self):
return self.host
def get_username(self):
return self.username
def get_port(self):
return self.port
def diskusage(ssh: paramiko.SSHClient):
_, stdout, _ = ssh.exec_command('lsblk')
result = stdout.read().decode()
return result
def memory_usage(ssh: paramiko.SSHClient):
_, stdout, _ = ssh.exec_command('free -h')
result = stdout.read().decode()
return result
def hostname_info(ssh: paramiko.SSHClient):
_, stdout, _ = ssh.exec_command('hostname -f')
result = stdout.read().decode()
return result
def ip_info(ssh: paramiko.SSHClient):
_, stdout, _ = ssh.exec_command('hostname -i')
result = stdout.read().decode()
return result
def os_info(ssh:paramiko.SSHClient):
_, stdout, _ = ssh.exec_command('cat /etc/redhat-release')
result = stdout.read().decode()
return result
def display_check_result():
print(Display.green('Environment Statistics'))
print()
## print disk info
print("======== " + Display.blue('Disk Info: ') +"========")
print(diskusage(ssh_client))
## print memory info
print("======== " + Display.blue('Memory Info: ') + "========")
print(memory_usage(ssh_client))
## print hostname info
print(Display.green('Hostname: ') + hostname_info(ssh_client))
## print ip
print(Display.green('IP: ') + ip_info(ssh_client))
## os info
print(Display.green('OS: ') + os_info(ssh_client))
def read_yaml(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f:
hosts = yaml.safe_load(f)
return hosts
host_list = []
def construct_hosts():
hosts = read_yaml('./hosts.yaml')
for h in hosts:
host = Host(h.get('host'), h.get('password'), h.get('port'), h.get('username'))
host_list.append(host)
ssh_client.connect
if __name__ == "__main__":
construct_hosts()
for host in host_list:
try:
ssh_client.connect(host.host, host.port, host.username, host.password)
print("SSH connect to {} successfuly!", host.get_host())
display_check_result()
except Exception as e:
print("SSH connect to {} failed: {}".format(host.get_host(), e))
finally:
ssh_client.close()
hosts.yaml
### yaml定义样式如下:
# - host: 192.168.0.33
# port: 22
# username: root
# password: xwp12345
#
# - host: 192.168.0.34
# port: 22
# username: xwp
# password: xwphs123
- host: 192.168.0.33
port: 22
username: xwp
password: xwphs123
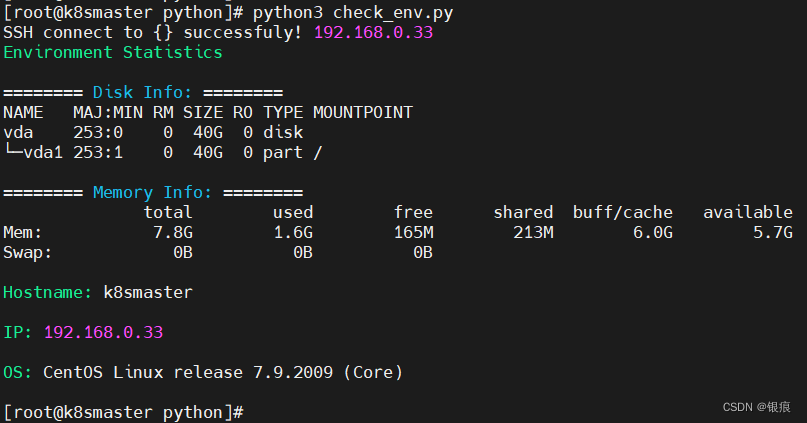
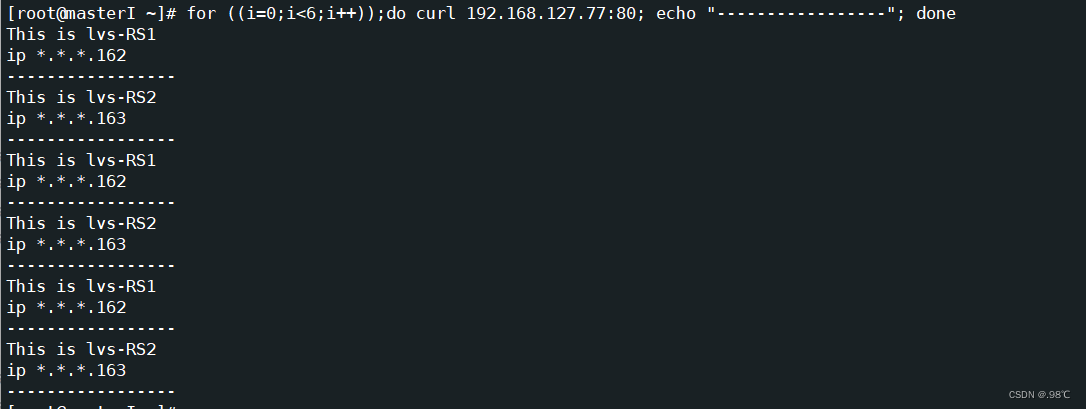
演示