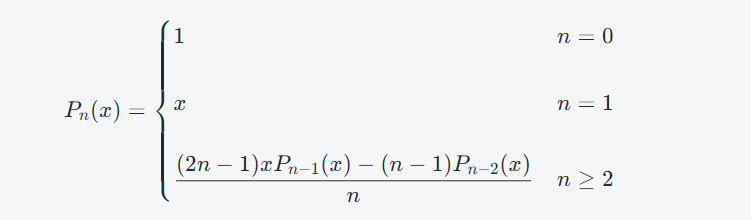./
是意思让解释器去引用当前目录下的内容
![![[Pasted image 20220418214825.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/91ea4b8874a44711ba574fc271c0a493.png)
../
是意思让解释器去引用上层目录下的内容
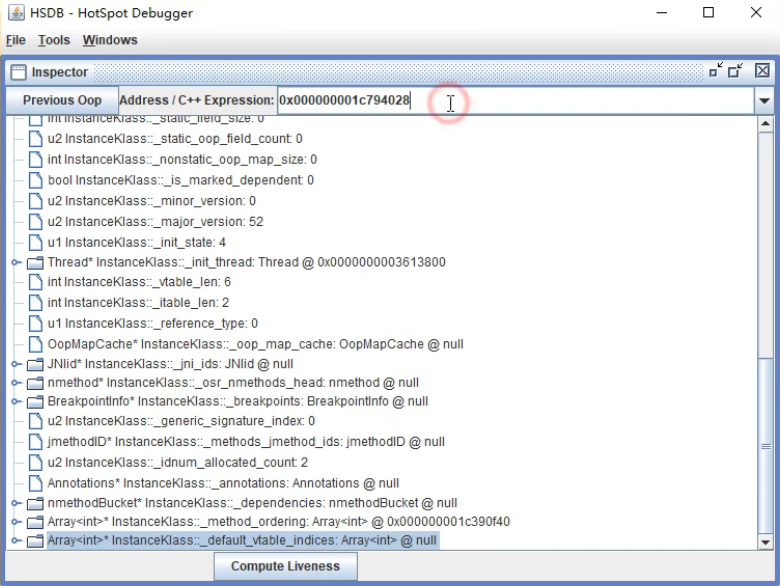
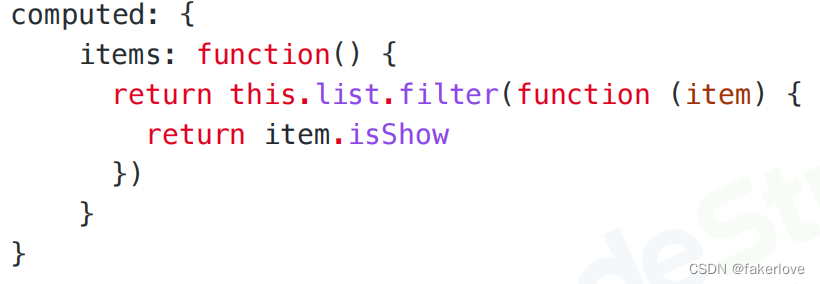
__all__
用来定义我们导出的内容可以有哪些的一个编码方式
![![[Pasted image 20220418214956.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/160c408df65544d4b2e784a7675fd36c.png)
flake8 可以检测代码的安全隐患,在python中
![![[Pasted image 20220418215149.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/49b59a6a5f9b4f2c8f3b908e8b6dd350.png)
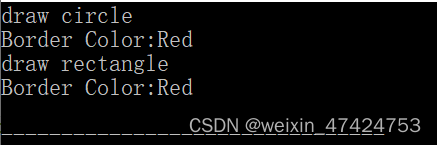
if __name__ == '__main__'
现在有两个文件,分别为:test1.py test2.py那么只有在分别以各自为启动主程的时候,才会执行 if __name__ == '__main__' 下的内容。
# -- test1.py
print('test still running')
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('here is main')
# -- test2.py
from test1 import *
print('here is test2 no main')
python test2.py的时候,不会打印here is main
__file__
用来获取到当前文件的所在路径:
可以结合python的os模块,得到当前文件所在的文件夹:
import os
current_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
print('current_dir:',current_dir)
![![[Pasted image 20220418220328.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/251f5e077da24ecb81522eb643acd651.png)