Spring框架的概述和入门
目录
Spring框架的概述和入门
什么是Spring框架
Spring框架的特点
Spring框架的IOC核心功能快速入门
Spring框架中的工厂(了解)
Spring 创建Bean对象的三种方式
Spring框架的Bean管理的配置文件方式
Spring框架中标签的配置
依赖注入(DI)
Spring框架的属性注入
Spring的2.5版本中提供了一种:p名称空间的注入(了解)
Spring的3.0提供了一种:SpEL注入方式(了解)
数组,集合(List,Set,Map),Properties等的注入
Spring框架的配置文件分开管理(了解)
什么是Spring框架
1. Spring框架的概述
* Spring是一个开源框架
* Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java开发框架,由Rod Johnson在其著作Expert One-On-One J2EE Development and Design中阐述的部分理念和原型衍生而来。
* 它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许使用者选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 J2EE 应用程序开发提供集成的框架。
* Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。然而,Spring的用途不仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以 从Spring中受益。
* Spring的核心是控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EEfull-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
* EE开发分成三层结构
* WEB层 -- Spring MVC
* 业务层 -- Bean管理:(IOC) AOP 事务
* 持久层 -- Spring的JDBC模板.ORM模板用于整合其他的持久层框架
Spring框架的特点
1. 为什么要学习Spring的框架
* 方便解耦,简化开发
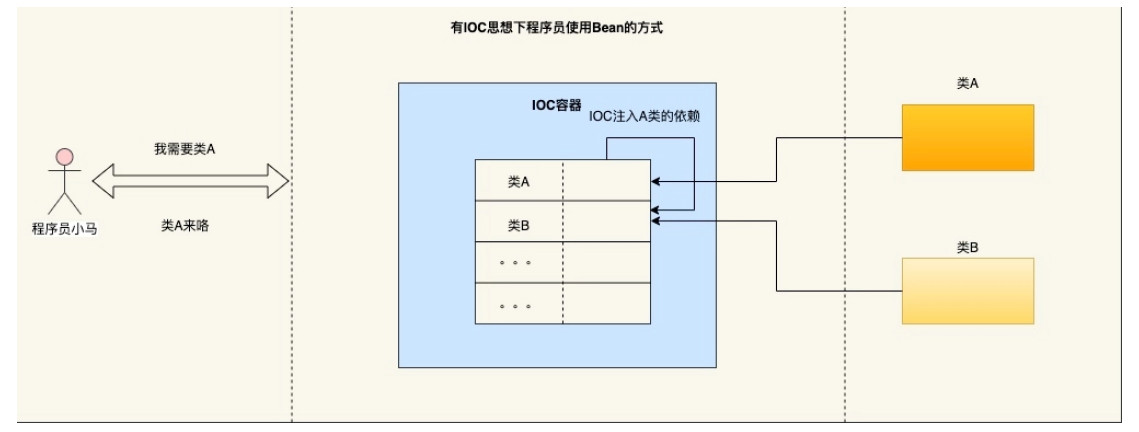
* Spring就是一个大工厂,可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理
* AOP编程的支持
* Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能
* 声明式事务的支持
* 只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程
* 方便程序的测试
* Spring对Junit4支持,可以通过注解方便的测试Spring程序
* 方便集成各种优秀框架
* Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts2、Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz等)的直接支持
* 降低JavaEE API的使用难度
* Spring 对JavaEE开发中非常难用的一些API(JDBC、JavaMail、远程调用等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低
2. Spring框架的版本
* Spring3.x和Spring4.x的版本,Spring5.x的版本
Spring框架的IOC核心功能快速入门
1. 什么是IOC的功能?
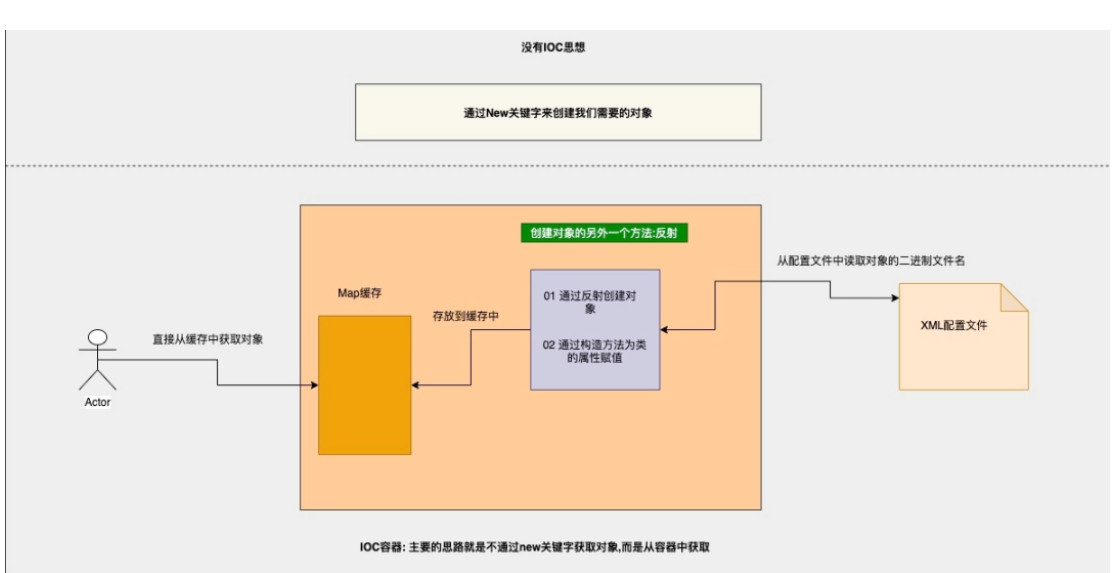
* IoC -- Inverse of Control,控制反转,将对象的创建权反转给Spring!!
* 使用IOC可以解决的程序耦合性高的问题!!
2. 步骤一:下载Spring框架的开发包
* 官网:https://spring.io/
* 下载地址:https://repo.springsource.org/libs-release-local/org/springframework/spring解压:(Spring目录结构:)
* docs -- API和开发规范
* libs -- jar包和源码
* schema -- 约束
3. 步骤二:创建JavaWEB项目,引入Spring的开发包
* 引入Spring框架IOC核心功能需要的具体的jar包
* Spring框架的IOC的功能,那么根据Spring框架的体系结构图能看到,只需要引入如下的jar包
• * Beans
• * Core
• * Context
• * Expression Language
• 导入这个四个jar包
• spring-beans-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
• spring-context-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
• spring-core-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
• spring-expression-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
如果使用的是Maven工程只需在pom.xml文件中添加Spring框架的坐标
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4. 步骤三:创建对应的包结构,编写Java的类,要注意:以后使用Spring框架做开发,都需要来编写接口与实现类!!
* org.westos.demo1
* UserService -- 接口 * UserServiceImpl -- 具体的实现类 5. 步骤四:想把UserServiceImpl实现类的创建交给Spring框架来管理,需要创建Spring框架的配置文件,完成配置 * 在resources目录下创建applicationContext.xml的配置文件,名称是可以任意的,但是一般都会使用默认名称!!注意如果时Maven工程就在resources
* 引入spring的约束,需要先找到具体的约束头信息!!
* spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html\xsd-config.html
* 具体的约束如下:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
* 完成UserService的配置
<!-- Spring的快速入门 -->
<bean id="userService" class="org.westos.demo1.UserServiceImpl"/>
6. 步骤五:编写测试程序,采用Spring框架的工厂方式来获取到UserService接口的具体实现类!!
public void demo2(){
// 使用Spring的工厂:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 通过配置的id名从工厂获得对象:
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.sayHello();
}
//方式2:获取bean对象,再传入一个参数接口的class类型,可以不用强转
UserService userService1 = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
Spring框架中的工厂(了解)
1. ApplicationContext接口
* 使用ApplicationContext工厂的接口,使用该接口可以获取到具体的Bean对象
* 该接口下有两个具体的实现类
* ClassPathXmlApplicationContext -- 加载src类路径下的Spring配置文件
* FileSystemXmlApplicationContext -- 加载本地磁盘下的Spring配置文件
* AnnotationConfigApplicationContext -- 读取注解创建容器的 后面讲解
2. BeanFactory工厂(是Spring框架早期的创建Bean对象的工厂接口)
* 使用BeanFactory接口也可以获取到Bean对象
public void run(){
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));
UserService us = (UserService) factory.getBean("us");
us.sayHello();
}
* BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别
* BeanFactory -- BeanFactory采取延迟加载,第一次getBean时才会初始化Bean
* ApplicationContext -- 在加载applicationContext.xml时候就会创建具体的Bean对象的实例,还提供了一些其他的功能
* 事件传递
* Bean自动装配
* 各种不同应用层的Context实现
Spring 创建Bean对象的三种方式
第一种方式:使用默认空参构造函数创建。
在spring的配置文件中使用bean标签,配以id和class属性之后,且没有其他属性和标签时。
采用的就是默认空参构造函数创建bean对象,此时如果类中没有默认构造函数,则对象无法创建。
例如:<bean class="org.westos.service.UserServiceImpl" id="userService"></bean>
第二种方式: 使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用某个类中的方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="org.westos.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
举例:第二种方式
我有一个工厂类 叫做 InstanceFactory 工厂类里面有一个方法 getAccountService() 返回一个 AccountService 对象,我想拿到这个 AccountService 对象
public class InstanceFactory { //工厂类
public AccountService getAccountService(){
return new AccountServiceImpl(); // AccountService是个接口 AccountServiceImpl是个实现类
}
}
我们现在不是想拿到工厂类对象,而是要拿到,工厂类种方法返回的那个AccountServiceImpl对象
那么我们就使用下面的配置
配置工厂类的
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="org.westos.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
/*
上面第二个bean的参数说明
配置工厂类返回的那个对象
id="accountService" 这个是工厂类的种返回的那个对象的id名等会我们可以通过这个名称来取
factory-bean="instanceFactory" 这个是工厂类的id名
factory-method="getAccountService" 这个是配置工厂类的方法名,是通过getAccountService这个方法返回的AccountServiceImpl对象 */
第三种方式:使用工厂中的静态方法创建对象(使用某个类中的静态方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)
<bean id="accountService" class="org.westos.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
举例:
public class StaticFactory { //这是个静态工厂
//这是给静态方法
public static AccountService getAccountService() {
return new AccountServiceImpl();
}
}
说明:如果这个工厂里面用的是一个静态方法来返回一个对象,那么配置就简化了
<bean id="accountService" class="org.westos.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>
我们可以通过 accountService 这个id名取出 AccountServiceImpl对象
Spring框架的Bean管理的配置文件方式
Spring框架中<bean>标签的配置
1. id属性和name属性的区别
* id -- Bean起个名字,在约束中采用ID的约束,唯一
* 取值要求:必须以字母开始,可以使用字母、数字、连字符、下划线、句话、冒号 id:不能出现特殊字符
* name -- Bean起个名字,没有采用ID的约束(了解)
* 取值要求:name:出现特殊字符.如果<bean>没有id的话 , name可以当做id使用
* Spring框架在整合Struts1的框架的时候,Struts1的框架的访问路径是以/开头的,例如:/bookAction
2. class属性 -- Bean对象的全路径
3. scope属性 -- scope属性代表Bean的作用范围
* singleton -- 单例(默认值)
* prototype -- 多例,在Spring框架整合Struts2框架的时候,Action类也需要交给Spring做管理,配置把Action类配置成多例!!
* request -- 应用在Web项目中,每次HTTP请求都会创建一个新的Bean 放到request域中,request销毁了,对象也就没了
* session -- 应用在Web项目中,同一个HTTP Session 共享一个Bean Session销毁了,里面的对象也就没了
* globalsession -- 应用在Web项目中,多服务器间的session
4. Bean对象的创建和销毁的两个属性配置(了解)
//Servlet init() service() destory()
* 说明:Spring初始化bean或销毁bean时,有时需要作一些处理工作,因此spring可以在创建和拆卸bean的时候调用bean的两个生命周期方法
* init-method -- 当bean被载入到容器的时候调用init-method属性指定的方法
* destroy-method -- 当bean从容器中删除的时候调用destroy-method属性指定的方法
* 想查看destroy-method的效果,有如下条件
* scope= singleton有效
* web容器中会自动调用,但是main函数或测试用例需要手动调用(需要使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的close()方法)
5. bean对象的生命周期
单例对象
出生:当容器创建时对象出生
活着:只要容器还在,对象一直活着
死亡:容器销毁,对象消亡
总结:单例对象的生命周期和容器相同
多例对象
出生:当我们使用对象时spring框架为我们创建 getBean()
活着:对象只要是在使用过程中就一直活着。
死亡:当对象长时间不用,且没有别的对象引用时,由Java的垃圾回收器回收
依赖注入(DI)
1. IOC和DI的概念
* IOC -- Inverse of Control,控制反转,将对象的创建权反转给Spring!!
* DI -- Dependency Injection,依赖注入,在Spring框架负责创建Bean对象时,动态的将依赖对象注入到Bean组件中!!
2. DI(依赖注入)
* 例如:如果UserServiceImpl的实现类中有一个属性,那么使用Spring框架的IOC功能时,可以通过依赖注入把该属性的值传入进来!!
* 具体的配置如下
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private String name; //提供属性
public void setName(String name) { //提供set方法
this.name = name;
}
}
<bean id="us" class="org.westos.demo1.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="uname" value="小风"/>
</bean>
依赖注入的演示
public class CustomerServiceImpl {
// 提供成员属性,提供set方法
private CustomerDaoImpl customerDao;
public void setCustomerDao(CustomerDaoImpl customerDao) {
this.customerDao = customerDao;
}
public void save(){
System.out.println("我是业务层service....");
// 原来编写方式
// new CustomerDaoImpl().save();
// Spring的方式
customerDao.save();
}
}
配置文件中 service中注入dao
<bean id="customerDao" class="org.westos.demo3.CustomerDaoImpl"/>
<bean id="customerService" class="org.westos.demo3.CustomerServiceImpl">
<property name="customerDao" ref="customerDao"/>
</bean>
Spring框架的属性注入
1. 对于类成员变量,常用的注入方式有两种
* 构造函数注入
* 属性setter方法注入
2. 在Spring框架中提供了前两种的属性注入的方式
1. 构造方法的注入方式,两步
* 编写Java的类,提供构造方法
public class Car {
private String name;
private double money;
public Car(String name, double money) {
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
}
* 编写配置文件
<bean id="car" class="org.westos.demo4.Car">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="大奔"/>
<constructor-arg name="money" value="100"/>
<!-- 用index 来写属性的编号也可以 从0开始数
<constructor-arg index="0" value="宝马"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="545000"/>
-->
</bean>
2. 属性的setter方法的注入方式
* 编写Java的类,提供属性和对应的set方法即可
* 编写配置文件
3. 如果Java类的属性是另一个Java的类,那么需要怎么来注入值呢?
* <property name="name" rel="具体的Bean的ID或者name的值"/>
* 例如:
<bean id="person" class="org.westos.demo4.Person">
<property name="pname" value="美美"/>
<property name="car2" ref="car2"/>
</bean>
Spring的2.5版本中提供了一种:p名称空间的注入(了解)
1. 步骤一:需要先引入 p 名称空间
* 在schema的名称空间中加入该行:xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
2. 步骤二:使用p名称空间的语法
* p:属性名 = ""
* p:属性名-ref = ""
3. 步骤三:测试
* <bean id="person" class="org.westos.demo4.Person" p:pname="老王" p:car2-ref="car2"/>
Spring的3.0提供了一种:SpEL注入方式(了解)
1. SpEL:Spring Expression Language是Spring的表达式语言,有一些自己的语法
2. 语法
* #{SpEL}
3. 例如如下的代码
<!-- SpEL的方式 -->
<bean id="person" class="org.westos.demo4.Person">
<property name="pname" value="#{'小风'}"/>
<property name="car2" value="#{car2}"/>
</bean>
4. 还支持调用类中的属性或者方法
* 定义类和方法,例如
public class CarInfo {
public String getCarname(){
return "奇瑞QQ";
}
}
数组,集合(List,Set,Map),Properties等的注入
1. 如果是数组或者List集合,注入配置文件的方式是一样的
private String [] arrs;
public void setArrs(String[] arrs) {
this.arrs = arrs;
}
//数组 或者 List集合 下面注入的方式都是一样的
<bean id="collectionBean" class="org.westos.demo5.CollectionBean">
<property name="arrs">
<array>
<value>美美</value>
<value>小风</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
//如果List集合中放的是对象就用
<bean id="collectionBean" class="org.westos.demo5.CollectionBean">
<property name="list">
<list>
<ref bean="car">
</list>
</property>
</bean>
2.如果是Set集合,注入的配置文件方式如下:
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>哈哈</value>
<value>呵呵</value>
</set>
</property>
3. 如果是Map集合,注入的配置方式如下:
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="老王2" value="38"/>
<entry key="凤姐" value="38"/>
<entry key="如花" value="29"/>
</map>
</property>
4. 如果是properties属性集合的方式,注入的配置如下:
<property name="pro">
<props>
<prop key="uname">root</prop>
<prop key="pass">123</prop>
</props>
</property>
5.其实: 用于给List结构集合注入的标签:
list array set 这三个标签可以互换
用于个Map结构集合注入的标签:
map props 这两个标签可以互换
结构相同,标签可以互换
Spring框架的配置文件分开管理(了解)
1. 例如:在src的目录下又多创建了一个配置文件,现在是两个核心的配置文件,那么加载这两个配置文件的方式有两种!
* 主配置文件中包含其他的配置文件:
<import resource="applicationContext2.xml"/>
* 工厂创建的时候直接加载多个配置文件:
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml","applicationContext2.xml");