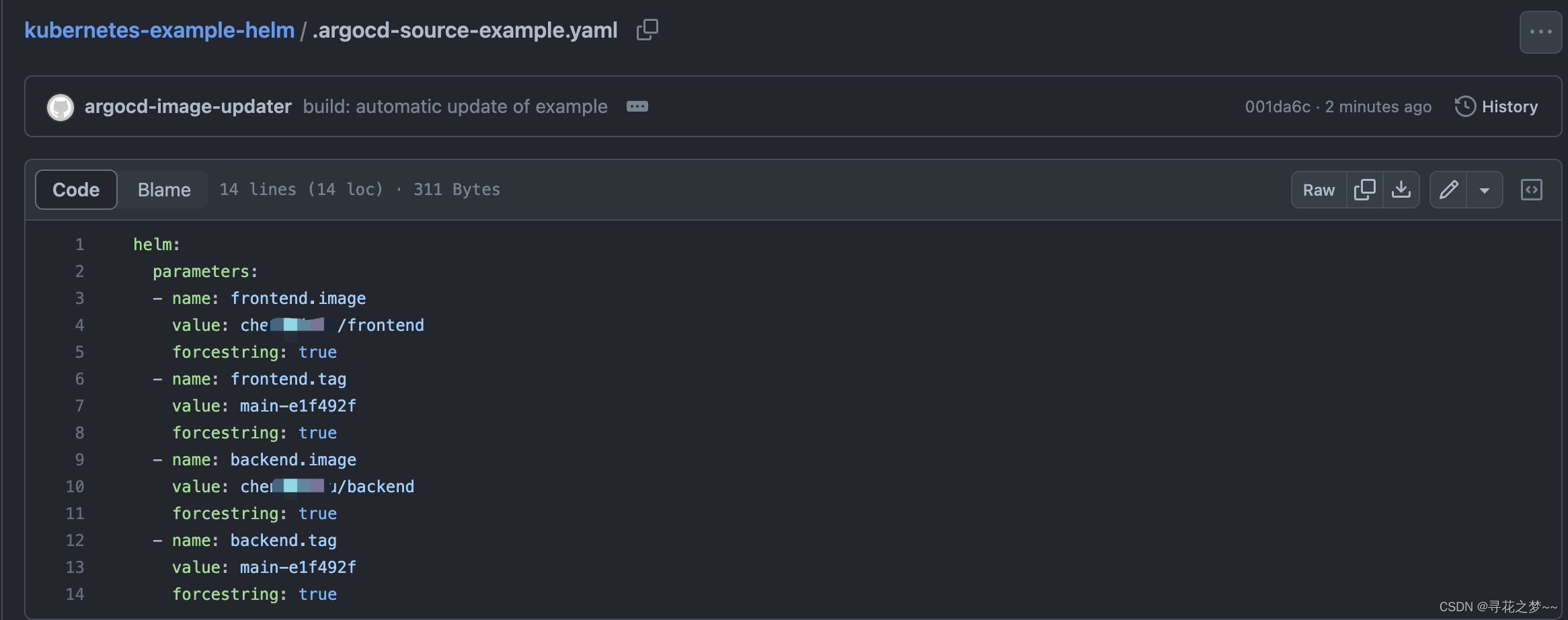
一、需求
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
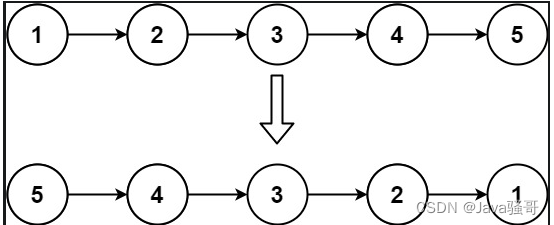
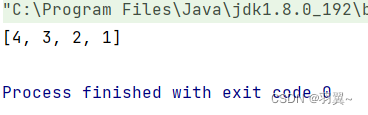
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
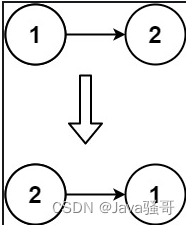
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
进阶:
链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
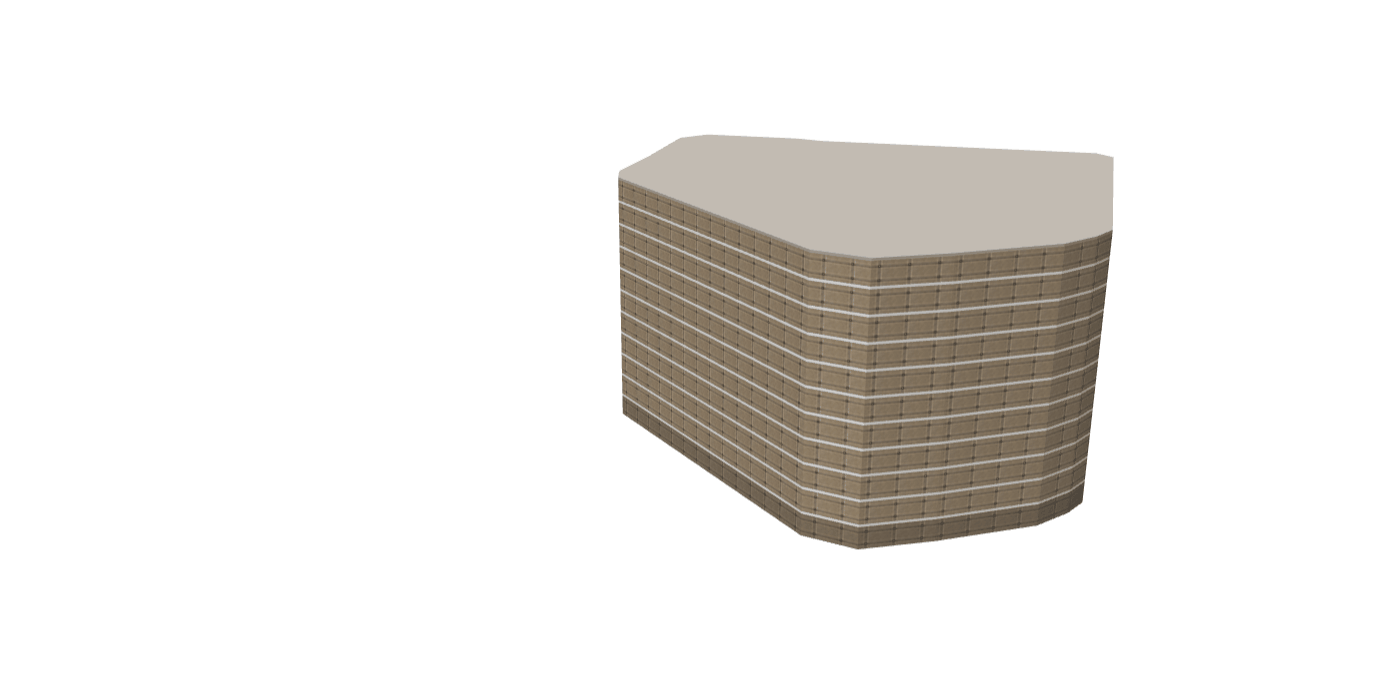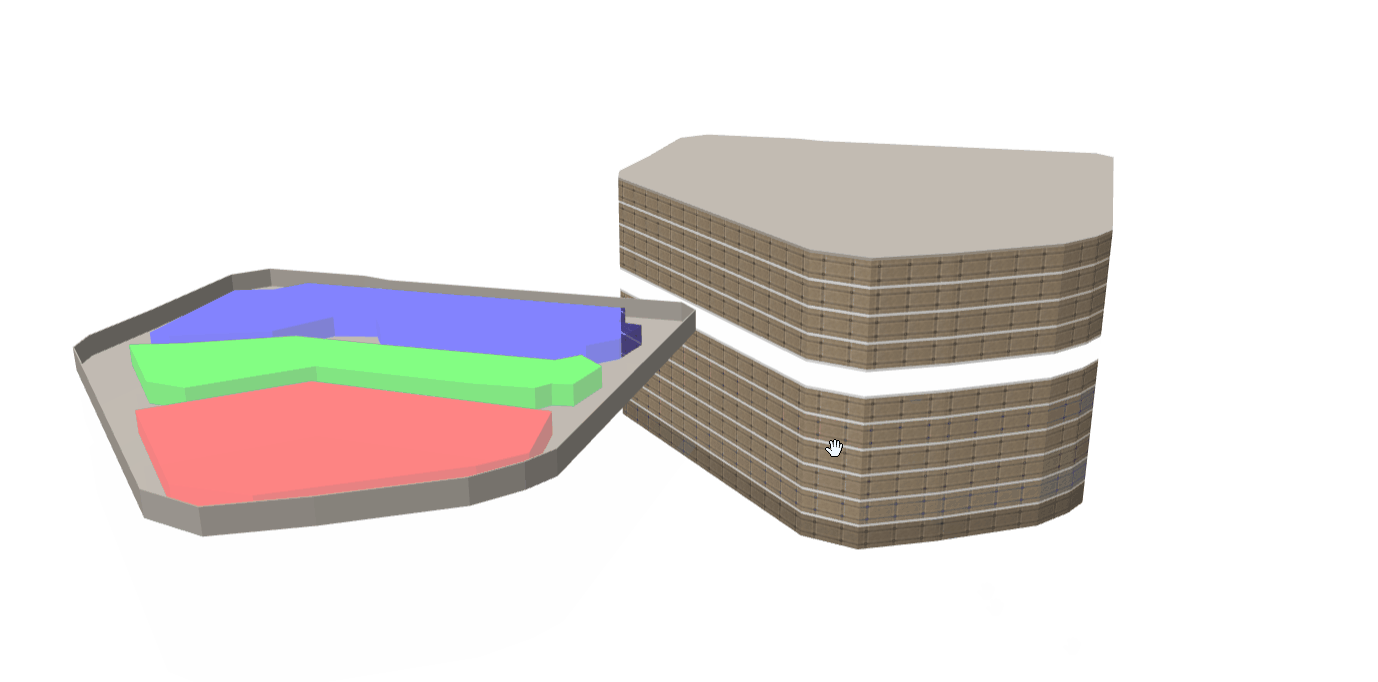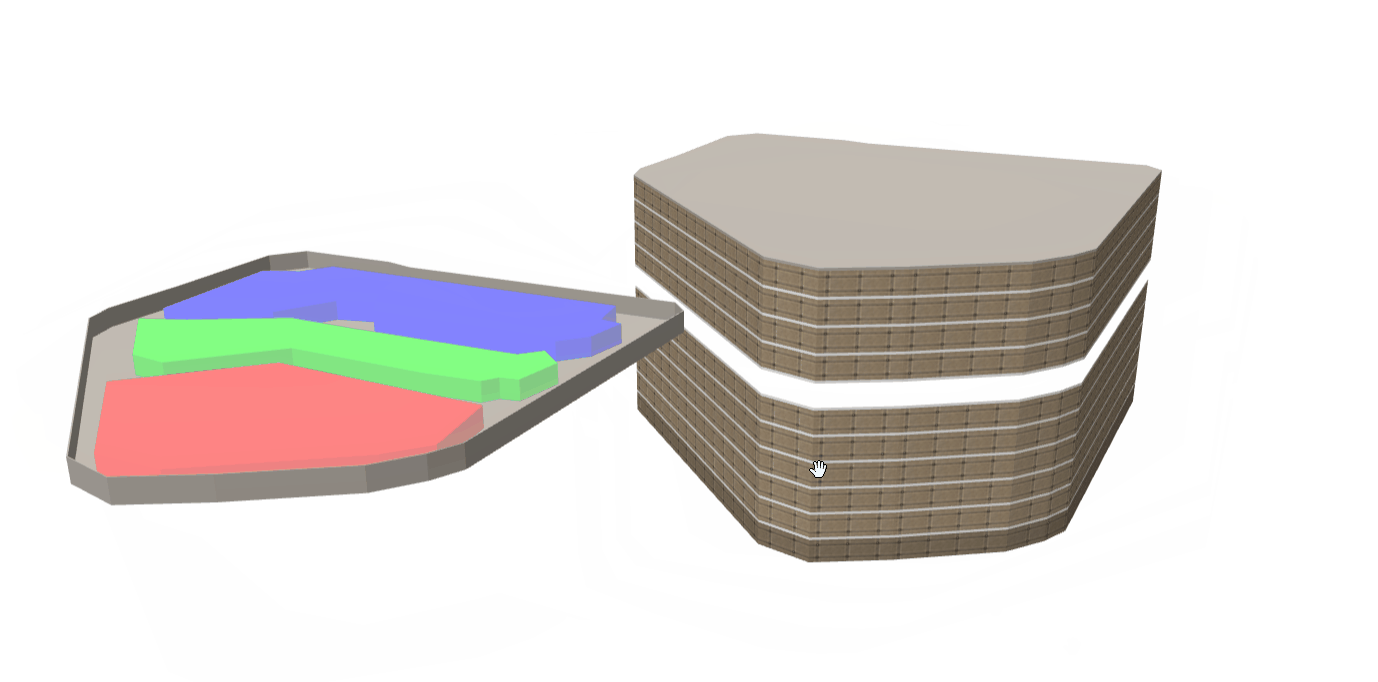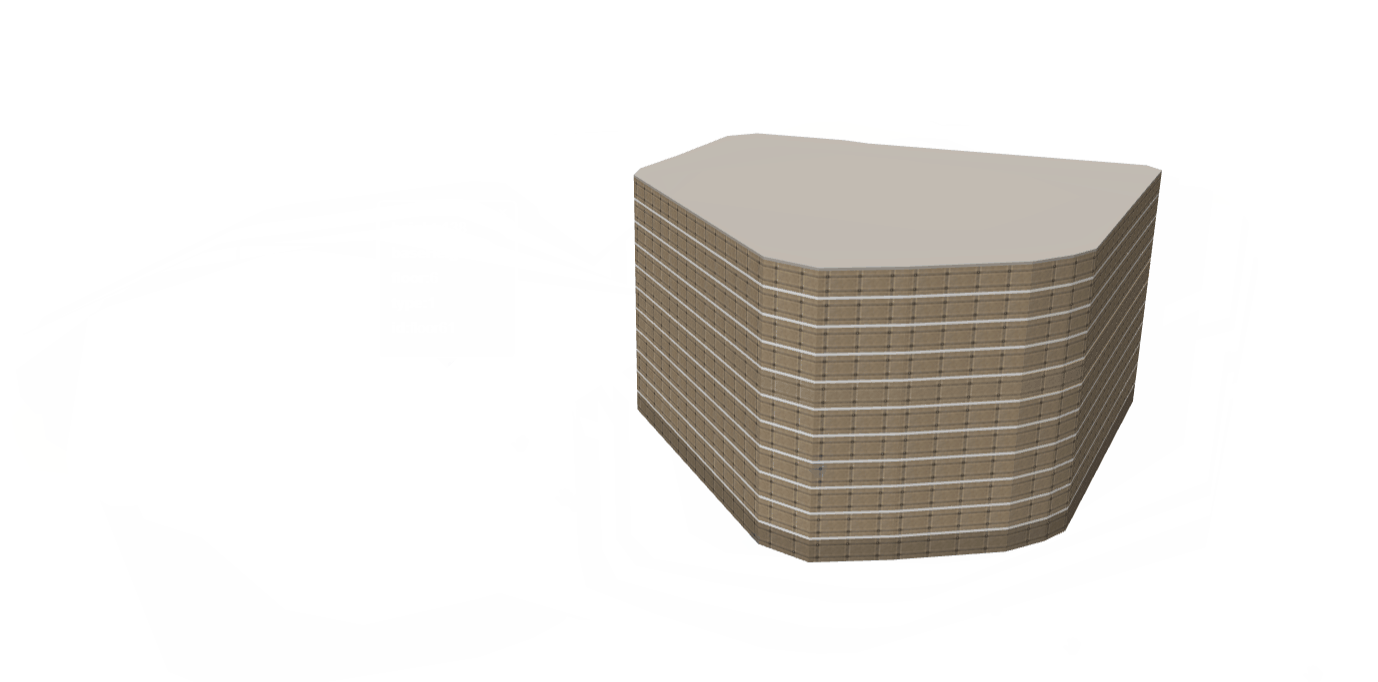
二、思路分析图
(一)递归方案



三、代码
(一)公共代码(链表类)
package com.bessky.pss.wzw.SuanFa;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
/**
* 链表类
*
* @author 王子威
* @date 2021/4/21
*/
public class ListNode
{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
@Override
public String toString()
{
ListNode ln = this;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(ln != null){
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(sb))
{
sb.append("[" + ln.val);
}
else
{
sb.append("," + ln.val);
}
ln = ln.next;
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}
(二)数据初始化
/**
* 入口
* 206、反转链表
* 输入:
* head1 = [1,2,3,4,5]
* head2 = [1,2,3,4,5]
* 输出:
* result1 = [5,4,3,2,1]
* result2 = [5,4,3,2,1]
* 解释:
* 1.递归方案
* 2.O(n)方案
*/
@Test
public void suanfa38()
{
// 初始化
ListNode head1 = new ListNode(1, new ListNode(2, new ListNode(3, new ListNode(4, new ListNode(5)))));
ListNode head2 = new ListNode(1, new ListNode(2, new ListNode(3, new ListNode(4, new ListNode(5)))));
// 打印
// 递归方案
ListNode result1 = this.recursionReverseList(head1);
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1.toString());
// O(n)方案【迭代方案】
ListNode result2 = this.forReverseList(head2);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2.toString());
}
(三)递归方案
/**
* 递归方案
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
private ListNode recursionReverseList(ListNode head)
{
// 如果head为null 说明这个链表就没有数据
// 如果下一个head为null,说明这个链表到最后一个值【节点】了【5到这里就直接返回了】
if (head == null || head.next == null)
{
return head;
}
// 递归调用:不到最后一个节点,递归下一个head节点
// head.next=2->head.next=3->head.next=4->head.next=5
ListNode nextNode = this.recursionReverseList(head.next);
// 5节点到不了,只有5节点以下的值才能来,因为5节点就是最后一个值
// 5 -> 4 : 5节点指向4节点【4下一个节点5,5下一个节点指向4】
// 4 -> 3 : 4节点指向3节点
// 3 -> 2 : 3节点指向2节点
// 2 -> 1 : 2节点指向1节点
head.next.next = head;
// 把4 -> 5 的指向删除【4的下一个节点】
// 把3 -> 4 的指向删除
// 把2 -> 3 的指向删除
// 把1 -> 2 的指向删除
head.next = null;
// nextNode[5,4]->nextNode[5,4,3]->nextNode[5,4,3,2]->nextNode[5,4,3,2,1]->结束递归
return nextNode;
}
(四) O(n)方案【迭代方案】
/**
* O(n)方案【迭代方案】
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
private ListNode forReverseList(ListNode head)
{
ListNode node = null;
for (ListNode temp = head;temp != null; temp = temp.next)
{
//node[1] -> node[2,1] -> node[3,2,1] -> node[4,3,2,1] -> node[5,4,3,2,1]
node = new ListNode(temp.val, node);
}
return node;
}
(五)结果图

作者:王子威
四、总结
- 学习了反转链表算法
- 有点久没有些算法了,看的两眼冒金星,参考了网络解法,感觉O(n)方案很精妙
- 算法兴趣+1 总:38
- 加强了对算法的分析能力