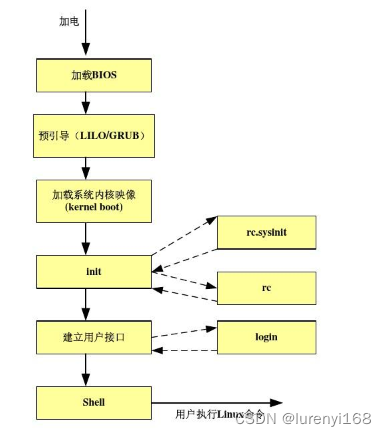
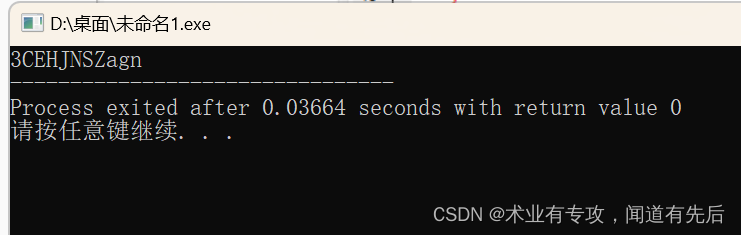
大家好哇,我是梦辛工作室的灵,在最近的开发中,有许多需要判断的分支处理,且处理内容较多且复杂,代码就容易越写越复杂,导致后期无法继续更新跌打,然后基于这个环境,我用责任链模式写了一个工具类用于解决这个问题,并将数据、判断、处理分隔开来,这样代码的重用性也增强了,下面来看下使用效果:
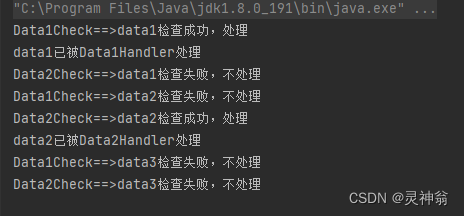
使用方法如下:
这里可自定义判断器和处理器,并自由组合,并链接起来,这里的判读器需实现一个检查方法,返回true 才会执行Handler的hand 方法,
而处理器返回true的话,就表示不在继续往后判断了,返回false表示,代码还是会下一个判断器进行判断
class Data1Check implements IfCheck{
@Override
public boolean check(Object[] args) {
if(args != null && args.length > 0 && "data1".equals(args[0])){
System.out.println("Data1Check==>" + args[0] + "检查成功,处理");
return true;
}
System.out.println("Data1Check==>" + args[0] + "检查失败,不处理");
return false;
}
}
class Data1Handler implements IfHandler{
@Override
public boolean hand(Object[] args) {
System.out.print(args[0]);
System.out.println("已被Data1Handler处理");
return false;
}
}
class Data2Check implements IfCheck{
@Override
public boolean check(Object[] args) {
if(args != null && args.length > 0 && "data2".equals(args[0])){
System.out.println("Data2Check==>" + args[0] + "检查成功,处理");
return true;
}
System.out.println("Data2Check==>" + args[0] + "检查失败,不处理");
return false;
}
}
class Data2Handler implements IfHandler{
@Override
public boolean hand(Object[] args) {
System.out.print(args[0]);
System.out.println("已被Data2Handler处理");
return true;
}
}
然后再来看下完整的代码:
IfChain
public class IfChain {
private IfChain nextChain;
private Object[] args;
private IfHandler handler;
private IfCheck ifCheck;
public IfChain(IfCheck ifCheck,IfHandler handler){
this.ifCheck = ifCheck;
this.handler = handler;
}
private boolean check(){
if (ifCheck.check(args)){
return handler.hand(args);
}
return false;
}
public IfCheck getIfCheck() {
return ifCheck;
}
public void setIfCheck(IfCheck ifCheck) {
this.ifCheck = ifCheck;
}
public IfChain getNextChain() {
return nextChain;
}
public void setNextChain(IfChain nextChain) {
this.nextChain = nextChain;
}
public Object[] getArgs() {
return args;
}
public void setArgs(Object[] args) {
this.args = args;
}
public IfHandler getHandler() {
return handler;
}
public void setHandler(IfHandler handler) {
this.handler = handler;
}
public void startCheck(){
if (!check() && nextChain != null){
nextChain.setArgs(args);
nextChain.startCheck();
}
}
}
IfHandler
public interface IfHandler {
boolean hand(Object[] args);
}
IfCheck
public interface IfCheck {
boolean check(Object[] args);
}
TestIfChain
public class TestIfChain {
class Data1Check implements IfCheck{
@Override
public boolean check(Object[] args) {
if(args != null && args.length > 0 && "data1".equals(args[0])){
System.out.println("Data1Check==>" + args[0] + "检查成功,处理");
return true;
}
System.out.println("Data1Check==>" + args[0] + "检查失败,不处理");
return false;
}
}
class Data1Handler implements IfHandler{
@Override
public boolean hand(Object[] args) {
System.out.print(args[0]);
System.out.println("已被Data1Handler处理");
return false;
}
}
class Data2Check implements IfCheck{
@Override
public boolean check(Object[] args) {
if(args != null && args.length > 0 && "data2".equals(args[0])){
System.out.println("Data2Check==>" + args[0] + "检查成功,处理");
return true;
}
System.out.println("Data2Check==>" + args[0] + "检查失败,不处理");
return false;
}
}
class Data2Handler implements IfHandler{
@Override
public boolean hand(Object[] args) {
System.out.print(args[0]);
System.out.println("已被Data2Handler处理");
return true;
}
}
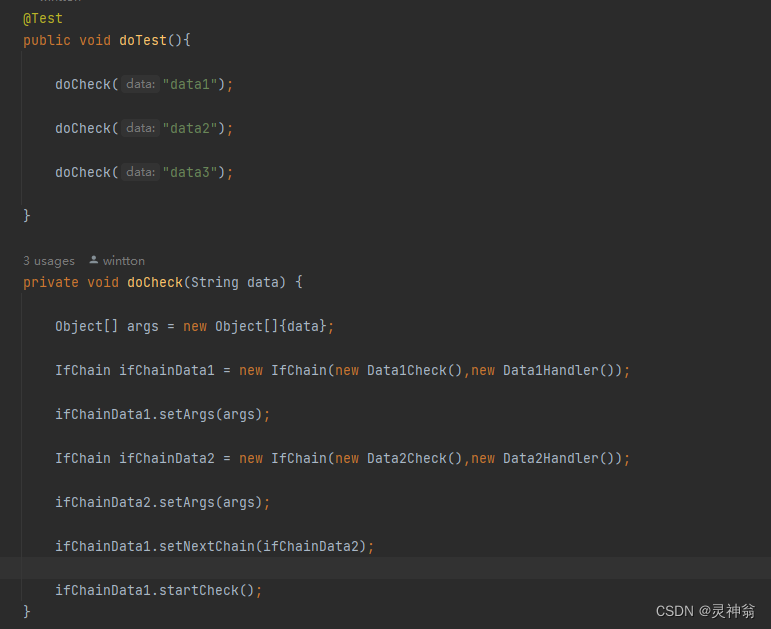
@Test
public void doTest(){
doCheck("data1");
doCheck("data2");
doCheck("data3");
}
private void doCheck(String data) {
Object[] args = new Object[]{data};
IfChain ifChainData1 = new IfChain(new Data1Check(),new Data1Handler());
ifChainData1.setArgs(args);
IfChain ifChainData2 = new IfChain(new Data2Check(),new Data2Handler());
ifChainData2.setArgs(args);
ifChainData1.setNextChain(ifChainData2);
ifChainData1.startCheck();
}
private void doCheck2(String data){
if("data1".equals(data)){
System.out.println("data1已被Data1Handler");
return;
}
if("data2".equals(data)){
System.out.println("data1已被Data2Handler");
return;
}
}
}
好了,今天的分享就到这里了
github连接 https://github.com/wintton/MxTestSql.git