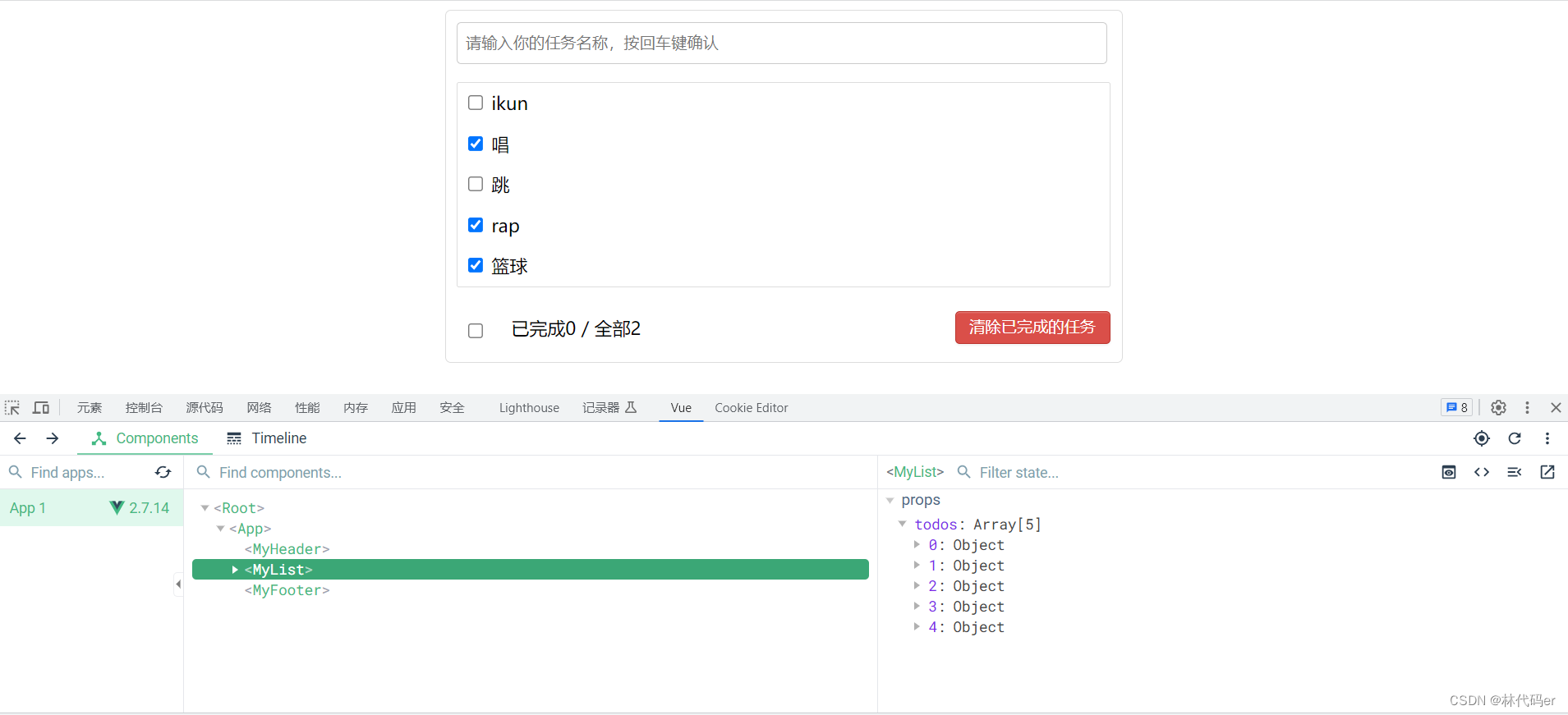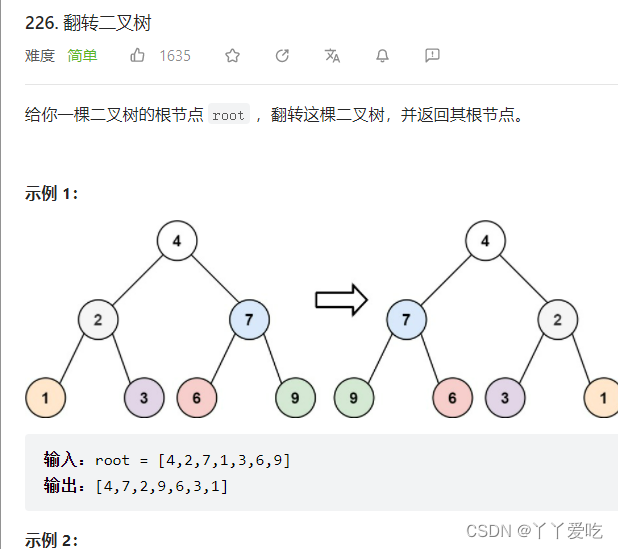
采用队列
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root==NULL) return root;
q.push(root);
int i=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
TreeNode *cur=q.front();
swap(cur->left,cur->right);
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
q.pop();
}
return root;
}
};
采用递归
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return root;
swap(root->left,root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};
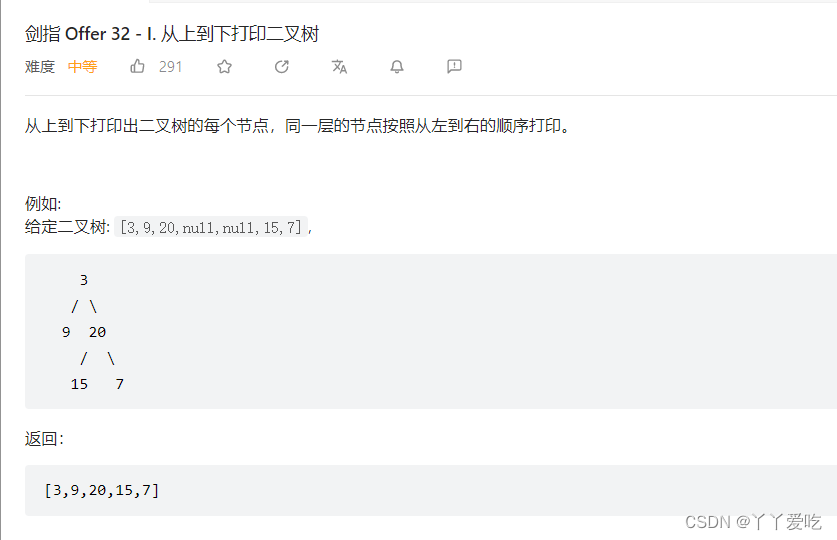
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> result;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root==NULL) return result;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
TreeNode *cur=q.front();
result.push_back(cur->val);
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
q.pop();
}
return result;
}
};
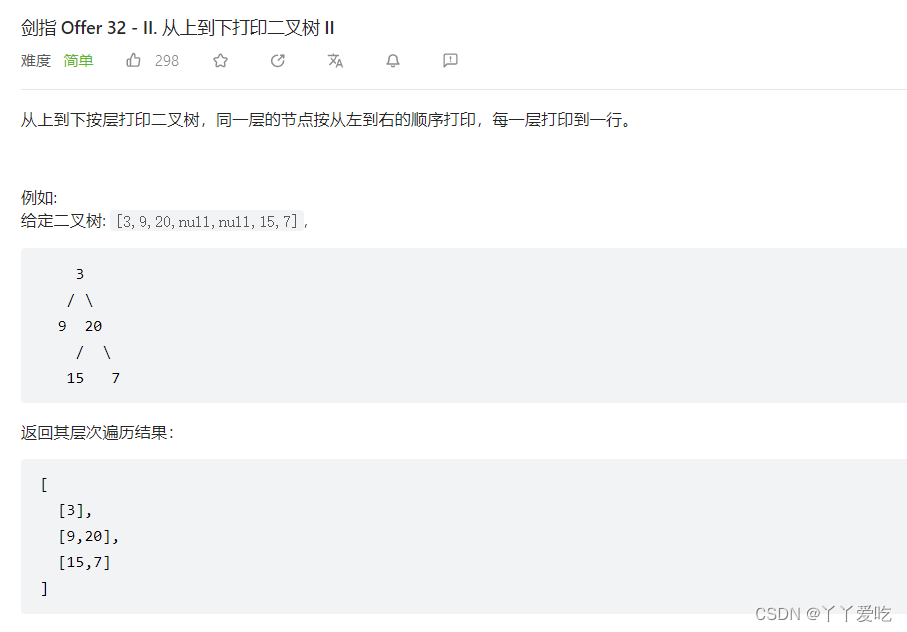
第一个需要考虑的问题是 二维数组怎样在不知道行和列的情况下进行插入 :先定义一维数组,然后将一维数组插入二维数组!
第二个需要考虑的问题是 BFS中队列进行遍历每一层的时候既需要把当前结点的左右孩子结点存到队列里,同时当前层结束后
原来的思路BFS队列
不为空就入队 取出来 放进vector里 然后左右孩子继续放进队列里
存在的问题即第二个问题 我怎么知道当前层是否遍历结束 ???反正下一层孩子都会在队里,继续push_back根本无法做到 每一层遍历后的结果放在一维数组里
原来的代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(root==NULL) return result;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
TreeNode* cur=root;
q.push(root);
int i=0;
while(cur||!q.empty())
{
vector<int> level;
while(!q.empty())
{
cur=q.front();
level.push_back(cur->val);
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
if(level.size()!=0) result.push_back(level);
}
return result;
}
};
这边就要对循环条件进行更改了
while(!q.empty())判断条件不对,更改成q.size()比如9,20在队列里,此时队列的size为2,那么只做两次,9一次,9没有孩子,20一次,20有孩子,当前走出循环,插入一维数组,
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(root==NULL) return result;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
TreeNode* cur=root;
q.push(root);
int i=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> level;
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cur=q.front();
level.push_back(cur->val);
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
if(level.size()!=0) result.push_back(level);
}
return result;
}
};
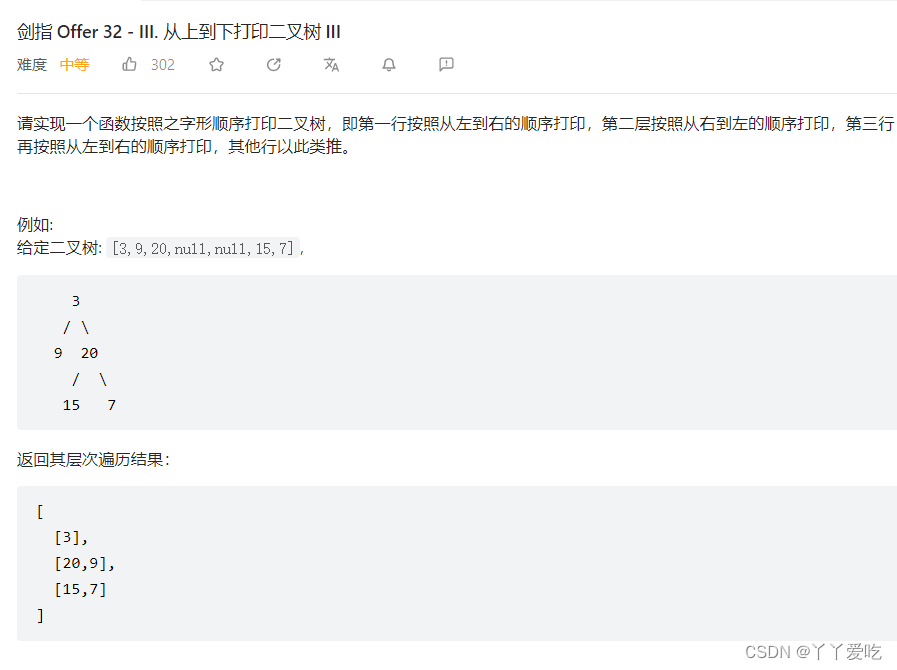
之字形打印
在上面的基础上,偶数层就不动,奇数就reverse
当然每次重中之重不要忘记判空了,root==NULL
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(root==NULL) return result;//不要忘记!
q.push(root);
int index=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> level;
int size=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
TreeNode* cur=q.front();
if(!cur) continue;//不加也可以通过 ,但是加了减少执行用时和内存消耗
level.push_back(cur->val);
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
if(index%2!=0) reverse(level.begin(),level.end());//奇数就得reverse
if(level.size()!=0) result.push_back(level);
index++;
}
return result;
}
};

![[Linux笔记]gcc/g++,动静态库,make/makefile/.PHONY](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1455489fda0b4d23a2e68a60b6dbdc67.png)




![[深度学习实战]基于PyTorch的深度学习实战(中)[线性回归、numpy矩阵的保存、模型的保存和导入、卷积层、池化层]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3f18404209c04aa8aa0e0ced0aec0b5c.png)