原题链接
原题链接

相关算法概念介绍
前缀和(Prefix Sum)
前缀和是指将数组中从开头位置到当前位置的所有元素累加得到的新数组。通常,我们使用一个额外的数组来保存这些累加和,这个数组被称为前缀和数组。对于原始数组A,前缀和数组P的第i个元素P[i]表示A[0]到A[i]之间所有元素的和。
前缀和的应用:
- 区间和的快速计算:通过预先计算前缀和数组,可以在O(1)的时间复杂度内快速得到任意区间 [l, r] 的和,即 P[r] - P[l-1]。这在需要多次查询区间和的情况下,可以大大加速计算过程。
- 子数组问题:前缀和在解决一些子数组相关问题时非常有用,例如找到和最大的子数组、和为特定值的子数组等。
- 优化计算:有时候某些问题的计算过程中,存在大量重复计算的情况。通过预先计算前缀和,可以减少重复计算,从而提高算法的效率。
单调栈
博主上篇文章
本题分析
思路:
题目中的
F
(
B
,
L
,
R
)
F(B,L,R)
F(B,L,R)定义为整数数组 B的索引从 L到 R(包括两者)的子数组的各个元素之和。
那么,一个
F
(
B
,
L
,
R
)
F(B,L,R)
F(B,L,R)便是一次前缀和。
如果一个长度为 K的整数数组 C满足其所有前缀和均为非负整数,则称数组 C为快乐数组。
这句话的意思便是由F组成的数组长度为K的前缀和为非负整数,则为快乐数组。
那么便是要求前缀和的前缀和。
最后计算所有快乐连续子数组的元素和相加的结果。
对于计算连续子数组的元素和,可以先设定义r[l]为
p
l
p_l
pl的最长快乐数组的右端点。
当1=<j<=l时,r[j]均为快乐数组。

(当时在做这道题的时候没有分析出来这部分,因此直接引用原作者所写)
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
long long a[N], b[N], st[N];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int _ = 1; _ <= t; _++) {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[i]=a[i-1]+x;
b[i]=b[i-1]+a[i];
}
int top =-1;
st[++top] = 0;
long long ans =0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
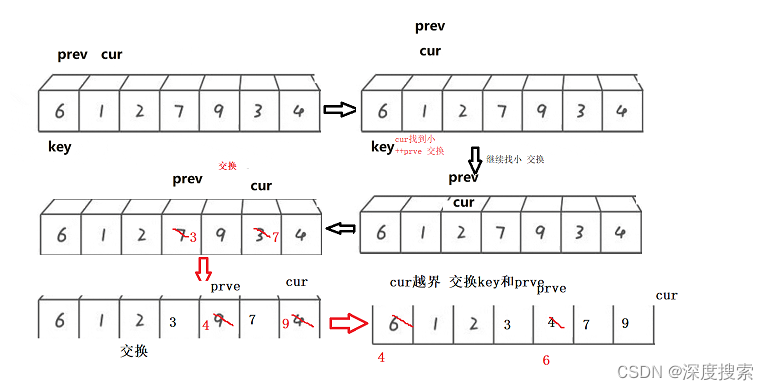
while(top!=-1&&a[st[top]]>a[i])
{
int l =st[top--]+1,r=i;
ans+=b[r-1]-b[l-1]-a[l-1]*(r-l);
}
st[++top]=i;
}
while(top!=-1)
{
int l = st[top--]+1,r=n+1;
ans+=b[r-1]-b[l-1]-a[l-1]*(r-l);
}
cout << "Case #" << _ << ": " << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}