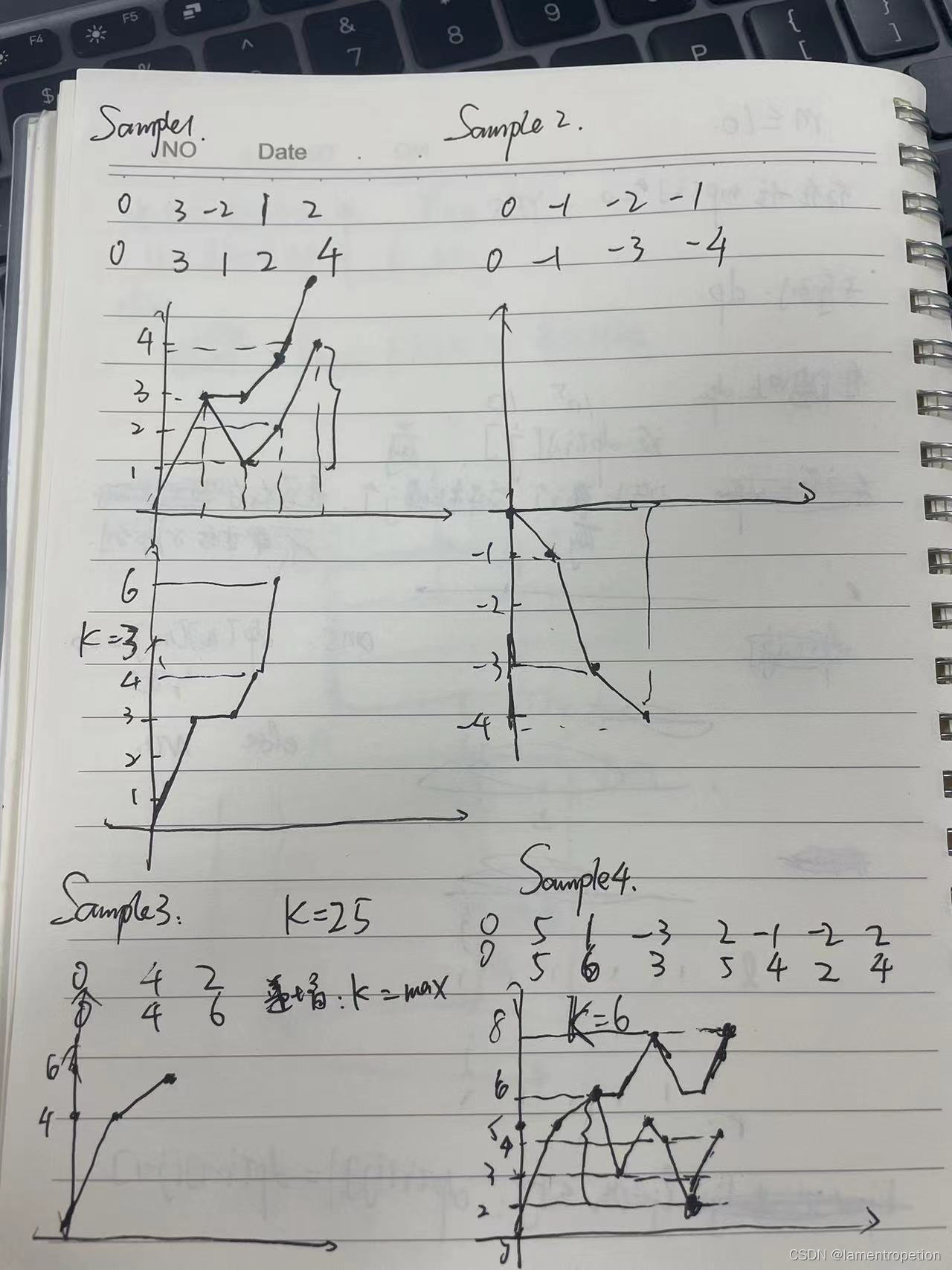
Java安全
数字签名
签名类
签名的jar文件可以通过Java的jarsigner工具进行管理。jarsigner工具使用密钥库中的信息来查找特定的实体,并使用这些信息对jar文件进行签名或验证签名。
要创建签名的jar文件,我们可以使用以下命令:
jarsigner xyz.jar sdo
这个命令会使用密钥库中的信息对xyz.jar文件进行签名。sdo是密钥库中的一个实体,通过它可以找到相应的私钥来进行签名。
要验证签名的jar文件,我们可以使用以下命令:
jarsigner -verify xyz.jar
这个命令会验证xyz.jar文件的签名是否有效。

签名的jar文件包含以下几个重要的部分:
- 一个
MANIFEST.MF声明文件,包含一组已签名的文件和相应的摘要。 - 一个签名文件,包含了签名信息。签名文件中的数据由声明文件中各项消息摘要组成。
- 一个块文件,其中包含实际的签名文件数据。
通过解析这些关键信息,我们可以验证签名的有效性。
java.security.Signature类的使用是实现数字签名的核心。我们可以通过调用类中的方法,例如initSign()、update()、sign()来实现签名的生成。同样,我们可以使用类中的initVerify()、update()、verify()方法来验证数字签名的有效性。
Signature类的实现
数字签名在Java中的实现是通过java.security.Signature类。该类提供了数字签名算法的功能,可以用于对数据进行签名和验证签名。
首先需要了解一些基本概念:
- 数字签名是一种用于验证数据完整性和认证发送方的技术。数字签名使用私钥对数据进行加密,生成签名。然后,使用相应的公钥对签名进行解密,验证数据的完整性和发送方的身份。
- 公钥密码是一种使用不同密钥进行加密和解密的密码系统。其中,公钥用于加密,私钥用于解密。公钥可以公开,私钥保密。
- 私钥是一种秘密密钥,只有拥有者可以使用。私钥用于生成数字签名。
- 公钥是一种公开密钥,任何人都可以使用。公钥用于验证数字签名。
java.security.Signature类提供了生成和验证数字签名的方法。以下是一些常用方法:
getInstance(String algorithm):通过提供的算法名称获取Signature对象的实例。initSign(PrivateKey privateKey):为进行数字签名初始化Signature对象,使用指定的私钥。initVerify(PublicKey publicKey):为进行数字签名验证初始化Signature对象,使用指定的公钥。update(byte[] data):更新要进行签名或验证的数据。sign():返回签名字节。verify(byte[] signature):验证给定的签名。
下面是一个使用Signature类进行数字签名的示例:
import java.security.*;
import java.security.spec.*;
import java.util.Base64;
public class DigitalSignatureExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 生成密钥对
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.genKeyPair();
// 创建 Signature 对象
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
// 使用私钥初始化 Signature 对象
signature.initSign(keyPair.getPrivate());
// 更新要签名的数据
signature.update("Hello, World!".getBytes());
// 生成签名
byte[] sign = signature.sign();
// 使用公钥验证签名
signature.initVerify(keyPair.getPublic());
signature.update("Hello, World!".getBytes());
boolean isVerified = signature.verify(sign);
System.out.println("Signature verified: " + isVerified);
}
}
这是一个基本的使用Signature类进行数字签名的示例。在示例中,首先使用KeyPairGenerator生成了一个密钥对。然后,创建了一个Signature对象,并使用私钥初始化它。接下来,使用update方法更新要签名的数据,并使用sign方法生成签名。
最后,使用公钥验证签名。首先,使用公钥和签名初始化Signature对象,然后使用update方法更新要验证的数据,并使用verify方法验证签名的有效性。最后,输出验证结果。
Java Security - Digital Signatures
In the world of Java security, digital signatures play a crucial role in ensuring data integrity and authenticating the sender. Java provides the java.security.Signature class to implement digital signature functionality, which allows you to sign data and verify signatures.
Introduction to Digital Signatures
A digital signature is a cryptographic technique used to verify the integrity and authenticity of data. It utilizes a private key to encrypt the data and generate a signature. The corresponding public key is then used to decrypt the signature and verify the integrity of the data and the identity of the sender.
Using Signature Class
The java.security.Signature class in Java provides methods to generate and verify digital signatures. Here are some commonly used methods:
getInstance(String algorithm): Retrieves an instance of theSignatureclass using the specified algorithm.initSign(PrivateKey privateKey): Initializes theSignatureobject for signing using the provided private key.initVerify(PublicKey publicKey): Initializes theSignatureobject for signature verification using the provided public key.update(byte[] data): Updates the data to be signed or verified.sign(): Returns the signature as an array of bytes.verify(byte[] signature): Verifies the given signature.
Let’s take a look at an example of using the Signature class to generate and verify a digital signature:
import java.security.*;
import java.security.spec.*;
import java.util.Base64;
public class DigitalSignatureExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Generate key pair
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.genKeyPair();
// Create Signature object
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
// Initialize Signature object for signing with private key
signature.initSign(keyPair.getPrivate());
// Update data to be signed
signature.update("Hello, World!".getBytes());
// Generate signature
byte[] sign = signature.sign();
// Initialize Signature object for verification with public key
signature.initVerify(keyPair.getPublic());
signature.update("Hello, World!".getBytes());
boolean isVerified = signature.verify(sign);
System.out.println("Signature verified: " + isVerified);
}
}
In this example, we first generate a key pair using the KeyPairGenerator class. Then, we create an instance of the Signature class and initialize it for signing using the private key from the generated key pair. We update the data to be signed using the update() method and generate the signature using the sign() method.
Finally, we initialize the Signature object for verification using the public key and update the data again. We verify the signature using the verify() method and output the result.
jarsigner Tool for Managing Signed JAR Files
To manage signed JAR files, Java provides the jarsigner tool. It utilizes the information from the keystore to find specific entities and sign or verify signatures of JAR files.
To create a signed JAR file, you can use the following command:
jarsigner xyz.jar sdo
This command signs the xyz.jar file using the information from the keystore. sdo is an entity in the keystore, which helps locate the corresponding private key for signing.
To verify the signatures of a JAR file, you can use the following command:
jarsigner -verify xyz.jar
This command verifies the signatures of the xyz.jar file.
A signed JAR file consists of the following key components:
- A
MANIFEST.MFdeclaration file that contains a set of signed files and their corresponding digests. - A signature file that contains signature information. The data in this file is composed of message digests from the declaration file.
- A block file that contains the actual data for the signature file.
By parsing these components, the validity of the signature can be verified.
In conclusion, the java.security.Signature class is an essential component in the realm of Java security for implementing digital signatures. By understanding the core concepts and utilizing the methods provided by this class, you can achieve secure digital signing in your Java applications.