文章目录
- 单值二叉树
- 检查两颗树是否相同
- 对称二叉树
- 二叉树的前序遍历
- 二叉树的中序遍历
- 二叉树的后序遍历
- 另一颗树的子树
- 通过前序遍历的数组构建二叉树
- 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
- 层序遍历
- k层节点数
- 二叉树的销毁
- 二叉树的整体
单值二叉树
单值二叉树,可以使用等式的传递性来解决,根的值和左右子树的值相比较,看是否相等。再比较左右子树。递归求出是否为单值二叉树。
代码如下:
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->left&&root->left->val!=root->val)
{
return false;
}
if(root->right&&root->right->val!=root->val)
{
return false;
}
return isUnivalTree(root->left)&&isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
检查两颗树是否相同
先比比较根,在比较左右子树。
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val!=q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
对称二叉树
先比较根的左右子树的根。在比较左子树的左和右子树的右,左子树的右和右子树的左
bool _isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* RootLeft,struct TreeNode* RootRight)
{
if(RootLeft == NULL&&RootRight == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(RootLeft == NULL ||RootRight == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(RootLeft->val != RootRight ->val)
{
return false;
}
return _isSymmetric(RootLeft->left,RootRight->right) &&
_isSymmetric(RootLeft->right,RootRight->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){
return _isSymmetric(root->left,root->right);
}
二叉树的前序遍历
前序遍历到数组中,注意下标的传值要使用传址调用
int BTreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int lcount = BTreeSize(root->left);
int rcount = BTreeSize(root-> right);
return lcount + rcount + 1;
}
void _preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* i)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
a[(*i)++] = root->val;
_preorderTraversal(root->left,a,i);
_preorderTraversal(root->right,a,i);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
*returnSize = BTreeSize(root);
//malloc一个数组
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
//执行前序遍历
//下标
int i = 0;
_preorderTraversal(root,a,&i);
return a;
}
二叉树的中序遍历
调换这几条语句的顺序
a[(*i)++] = root->val; _preorderTraversal(root->left,a,i); _preorderTraversal(root->right,a,i);
函数名要保证和对应的遍历相同
int BTreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int lcount = BTreeSize(root->left);
int rcount = BTreeSize(root-> right);
return lcount + rcount + 1;
}
void _inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* i)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
_inorderTraversal(root->left,a,i);
a[(*i)++] = root->val;
_inorderTraversal(root->right,a,i);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
*returnSize = BTreeSize(root);
//malloc一个数组
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
//执行前序遍历
//下标
int i = 0;
_inorderTraversal(root,a,&i);
return a;
}
二叉树的后序遍历
与上题相同
int BTreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int lcount = BTreeSize(root->left);
int rcount = BTreeSize(root-> right);
return lcount + rcount + 1;
}
void _postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* i)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
_postorderTraversal(root->left,a,i);
_postorderTraversal(root->right,a,i);
a[(*i)++] = root->val;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
*returnSize = BTreeSize(root);
//malloc一个数组
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
//执行前序遍历
//下标
int i = 0;
_postorderTraversal(root,a,&i);
return a;
}
另一颗树的子树

bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val!=q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot){
if(root == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot))
{
return true;
}
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
通过前序遍历的数组构建二叉树
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct BTNode
{
char data;
struct BTNode* left;
struct BTNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(char x)
{
BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc failed!\n");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->right = NULL;
return newnode;
}
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(char* a,int* pi)
{
if(a[*pi] == '#')
{
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
//创建根节点
BTNode* root = BuyNode(a[*pi]);
(*pi)++;
root->left = BinaryTreeCreate(a,pi);
root->right = BinaryTreeCreate(a,pi);
return root;
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ",root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main() {
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*100);
scanf("%s",a);
int pi = 0;
BTNode* root = BinaryTreeCreate(a,&pi);
InOrder(root);
}
判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树

//判断是否为完全二叉树
bool BTreeComplete(BT* root)
{
//新建一个队列
Que q;
QueueInit(&q);
//把root入队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
//队列不为空时继续遍历
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//出队列
BT* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
//带入左右子树
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BT* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front != NULL) //遇到不为空证明不是完全二叉树
{
QueueDestory(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
return true; //程序执行到这一步时,证明为完全二叉树
}
层序遍历

//二叉树的层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BT* root)
{
//新建一个队列
Que q;
QueueInit(&q);
//把root入队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
//队列不为空时继续遍历
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//出队列
BT* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
//带入左右子树
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
}
k层节点数
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BTreeLevelKSize(BT* root, int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
int left = BTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1);
int right = BTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
return left + right;
}
二叉树的销毁
递归展开图
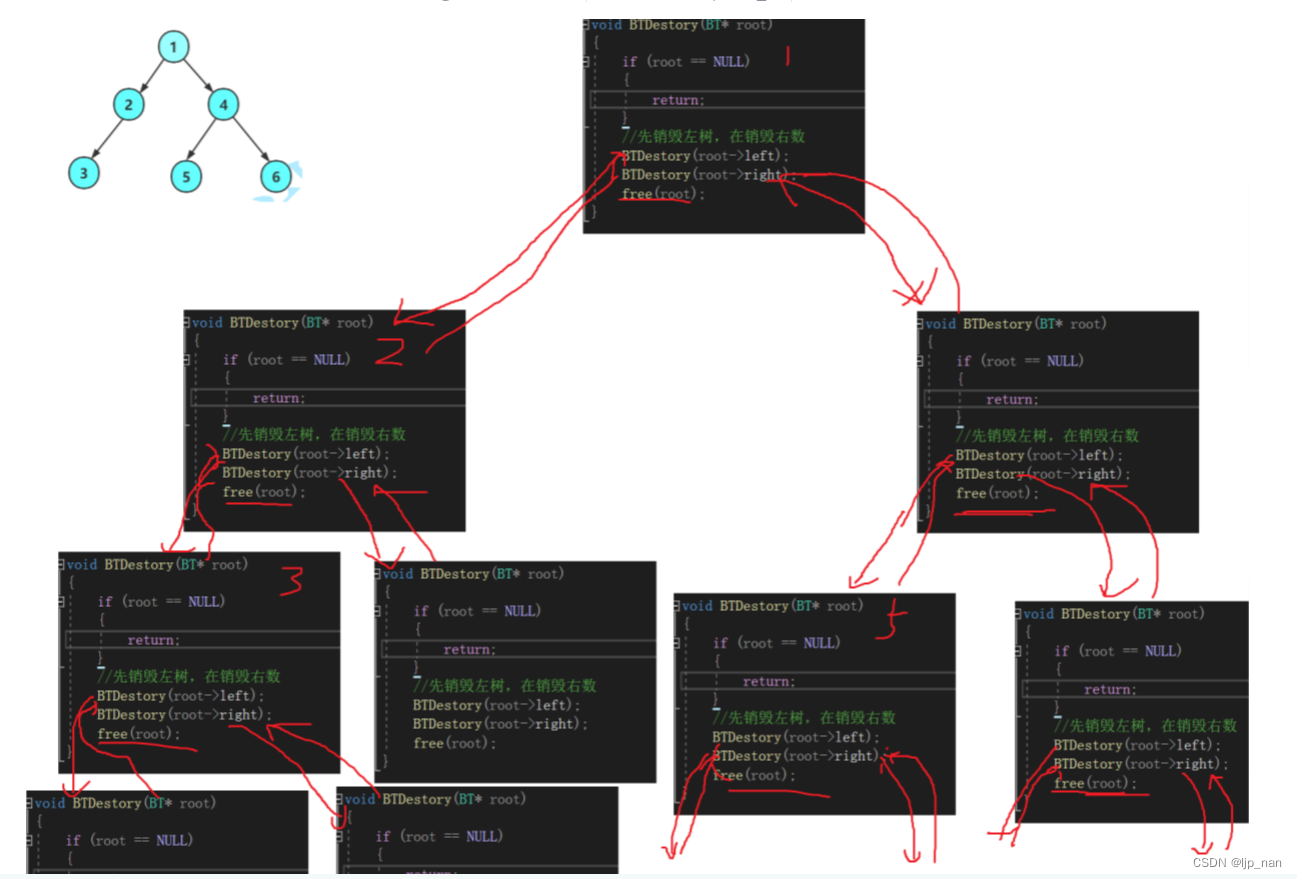
void BTDestory(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
//先销毁左树,然后销毁右树,然后再销毁根
BTDestory(root->left);
BTDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}
二叉树的整体
#include "Tree.h"
#include "Queue.h"
int BTreeLeafSize(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return BTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
int BTreeSize(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int lcount = BTreeSize(root->left);
int rcount = BTreeSize(root->right);
return lcount + rcount + 1;
}
int BTreeHeight(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int leftheight = BTreeHeight(root->left);
int rightheight = BTreeHeight(root->right);
//return leftheight > rightheight ? leftheight + 1: rightheight + 1;0
return 1 + (leftheight > rightheight ? leftheight : rightheight);
}
BT* BTreeFind(BT* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)
{
return root;
}
BT* left = BTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (left)
{
return left;
}
BT* right = BTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (right)
{
return right;
}
return NULL;
}
BT* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BT* node = (BT*)malloc(sizeof(BT));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc failed!\n");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BT* BTCreate()
{
BT* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BT* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BT* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BT* node4= BuyNode(4);
BT* node5= BuyNode(5);
BT* node6 = BuyNode(6);
//BT* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
//二叉树的遍历
//先序遍历
void Prevorder(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
Prevorder(root->left);
Prevorder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历
void Inorder(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
Inorder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
Inorder(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void Postorder(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
Postorder(root->left);
Postorder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BTreeLevelKSize(BT* root, int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
int left = BTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1);
int right = BTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
return left + right;
}
//二叉树的层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BT* root)
{
//新建一个队列
Que q;
QueueInit(&q);
//把root入队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
//队列不为空时继续遍历
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//出队列
BT* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
//带入左右子树
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
}
//判断是否为完全二叉树
bool BTreeComplete(BT* root)
{
//新建一个队列
Que q;
QueueInit(&q);
//把root入队列
QueuePush(&q, root);
//队列不为空时继续遍历
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//出队列
BT* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
//带入左右子树
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BT* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front != NULL) //遇到不为空证明不是完全二叉树
{
QueueDestory(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
return true; //程序执行到这一步时,证明为完全二叉树
}
void BTDestory(BT* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
//先销毁左树,然后销毁右树,然后再销毁根
BTDestory(root->left);
BTDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}







![[STC32F12K54入门第三步]USART1+Modbus RTU从机](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9264432e90cd4852ab11eff138936dab.png)
