文章目录
- 第一种:
- 第二种:
- 第三种:
以下是一个使用 JavaScript 和 DOM 编程实现的动态实时的时钟应用:
第一种:
HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>时钟</title>
<style>
#clock {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="clock">00:00:00</div>
<script src="clock.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript:
js代码在script标签内
function updateTime() {
var now = new Date();
var hours = now.getHours();
var minutes = now.getMinutes();
var seconds = now.getSeconds();
hours = (hours < 10 ? '0' : '') + hours;
minutes = (minutes < 10 ? '0' : '') + minutes;
seconds = (seconds < 10 ? '0' : '') + seconds;
var timeString = hours + ':' + minutes + ':' + seconds;
document.getElementById('clock').innerHTML = timeString;
}
setInterval(updateTime, 1000);
该 JavaScript 代码定期更新时钟显示,以显示当前时间。
函数 updateTime 获取当前时间,并将其格式化为 HH:MM:SS 的字符串。然后,该字符串被插入到具有 id="clock" 的 <div> 元素中。
setInterval 函数每隔 1000 毫秒(即一秒)调用一次 updateTime 函数,以使时钟保持同步。
最终HTML 中通过 <script> 标签引入该 JavaScript 文件。
第二种:
在 HTML 部分中,我们使用 <div> 元素来包含时钟元素,并使用 <span> 元素来分别显示小时、分钟和秒钟部分的值。
在 CSS 部分中,我们设置了一些样式来使页面看起来更加美观。设置了背景颜色、时钟的位置和样式,以及字体大小和颜色。
在 JavaScript 部分中,我们使用 window.setInterval() 函数每秒更新一次时钟的时间。首先使用 new Date() 获取当前的时间,并根据当前的时间设置每个时间部分的内容。使用三目运算符来将小时、分钟和秒钟的值转换为两位数的字符串。如果当前小时是 9,则我们会将其转换为字符串 “09”。
最后使用 document.getElementsByClassName() 和 document.querySelector() 函数来获取每个时间部分的元素,并将其内容更新为当前时间。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
/* 透明度 */
opacity: 0.6;
/* 固定定位 */
position: fixed;
top: 30px;
right: 20px;
/* 文字居中 弹性布局*/
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.time{
font-size: 40px;
font-weight: bold;
color: gold;
}
.second{
font-size: 25px;
color: brown;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span class="time">15</span>:
<span class="time">51</span>:
<span class="second">33</span>
</div>
</body>
<script>
window.setInterval(()=>{
let now = new Date()
let hours = now.getHours()
let minutes = now.getMinutes()
let seconds = now.getSeconds()
hours = hours<10?'0'+hours:hours
minutes = minutes<10?'0'+minutes:minutes
seconds = seconds<10?'0'+seconds:seconds
let h = document.getElementsByClassName('time')[0]
let m = document.getElementsByClassName('time')[1]
let s = document.querySelector('.second')
h.innerText = hours
m.innerText = minutes
s.innerText = seconds
},1000)
</script>
</html>

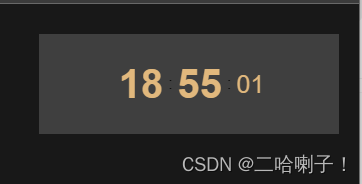
第三种:
这一种是对第二种代码的优化:
调整字体大小和颜色,使它们更加醒目。
背景色和文字颜色之间的对比度过低,将背景色更改为深色。
将 HTML 中的 元素替换为更具语义的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My Clock</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: #181818;
}
div {
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #444;
opacity: 0.9;
position: fixed;
top: 30px;
right: 20px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
.time {
font-size: 40px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #f7ca88;
margin: 0 5px;
}
.second {
font-size: 25px;
color: #f7ca88;
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<time class="time" datetime=""></time>:
<time class="time" datetime=""></time>:
<time class="second" datetime=""></time>
</div>
<script>
const [hour, minute, second] = document.querySelectorAll('time');
setInterval(() => {
const now = new Date();
hour.textContent = now.getHours().toString().padStart(2, '0');
minute.textContent = now.getMinutes().toString().padStart(2, '0');
second.textContent = now.getSeconds().toString().padStart(2, '0');
const isoTime = `${hour.textContent}:${minute.textContent}:${second.textContent}`;
hour.setAttribute('datetime', isoTime);
minute.setAttribute('datetime', isoTime);
second.setAttribute('datetime', isoTime);
}, 1000);
</script>
</body>
</html>