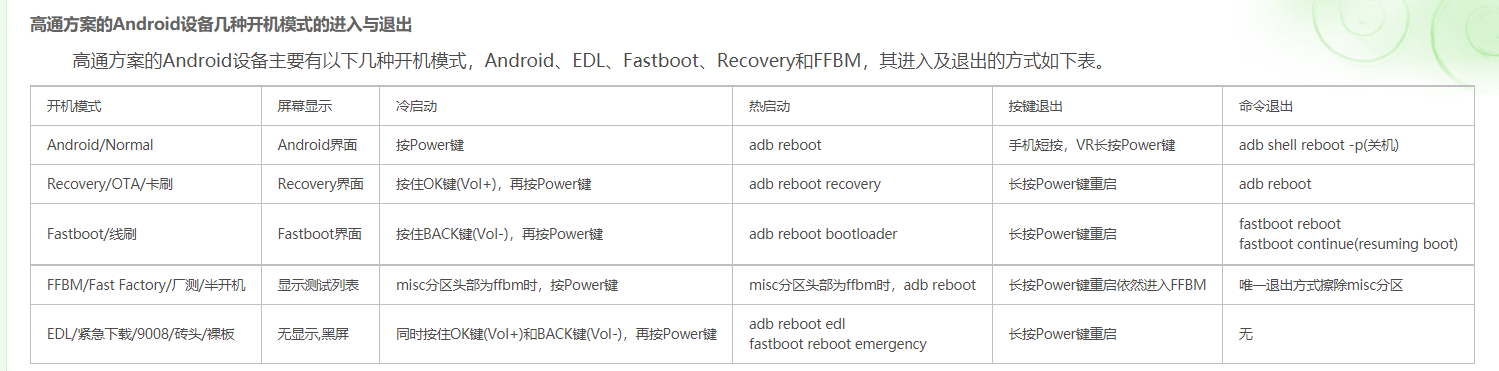
Trie字符串统计

思路:
Trie字符串就是把字符串像树一样存储下来
例子:
将如下字符串用trie存储
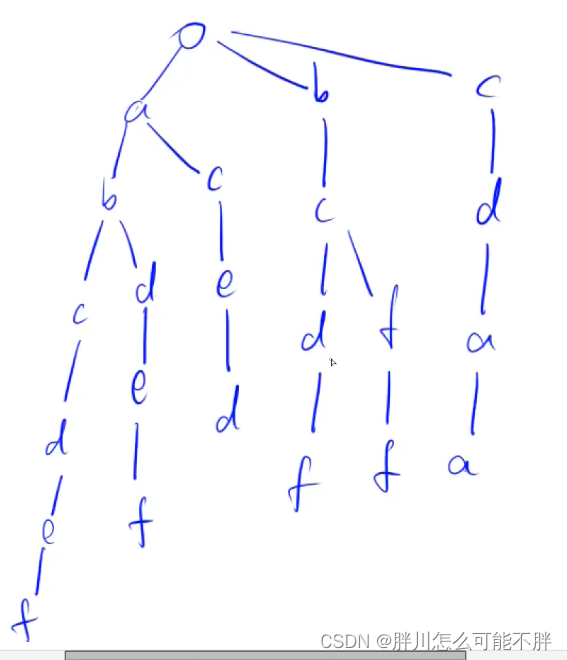
然后在查找字符串的时候就顺着树查找,但是要在每个字符串的结尾位置打上标记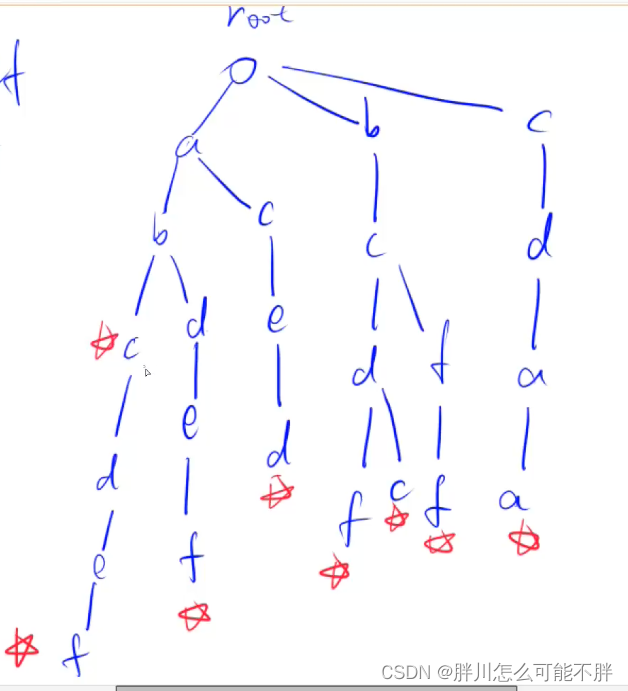
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
ll gcdd(ll a, ll b)
{
while(b^=a^=b^=a%=b);
return a;
}
// ll lcmm(ll a,ll b)
// {
// ll ans;
// ans=a/gcdd(a,b)*b;
// return ans;
// }
//ll idx;
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =998244353;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
ll book[N];
// ll ne[N],e[N],w[N];
// ll h[N],idx;
// void add(ll a,ll b, ll c)
// {
// e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
// }
int son[N][26],idx,cnt[N];
//son[][]存储子节点的位置,分支最多26条;
//cnt[]存储以某节点结尾的字符串个数(同时也起标记作用)
//idx表示当前要插入的节点是第几个,每创建一个节点值+1
void insert(string s)
{
int p = 0;
for(int i=0;s[i];i++)
{
int u = s[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = idx ++ ;//该节点不存在,创建节点
p = son[p][u];//使“p指针”指向下一个节点
}
cnt[p] ++;//结束时的标记,也是记录以此节点结束的字符串个数
}
int query(string s)
{
idx = 1;
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0;s[i]; i++)
{
int u = s[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]) return 0;//该节点不存在,即该字符串不存在
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];//返回字符串出现的次数
}
void fatchuan()
{
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
string op;
string s;
cin>>op>>s;
if(op == "I") insert(s);
else cout<<query(s)<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
//cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
fatchuan();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
好吧其实一个map容器解决
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
//#include<priority_queue>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define per(a,b,c) for(ll a=b;a>=c;a--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
#define endl "\n"
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
typedef pair<long double,long double> PDD;
ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
//const ll LINF=LLONG_MAX;
ll gcdd(ll a, ll b)
{
while(b^=a^=b^=a%=b);
return a;
}
// ll lcmm(ll a,ll b)
// {
// ll ans;
// ans=a/gcdd(a,b)*b;
// return ans;
// }
//ll idx;
const ll N = 2e6+ 10;
const ll mod =998244353;
ll t,n,m,x,y,ca;
ll arr[N],brr[N],crr[N];
ll book[N];
// ll ne[N],e[N],w[N];
// ll h[N],idx;
// void add(ll a,ll b, ll c)
// {
// e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
// }
void fatchuan()
{
cin>>n;
map<string ,int>mp;
while(n--)
{
string op;
string s;
cin>>op>>s;
if(op == "I") mp[s] ++;
else cout<<mp[s]<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
IOS;
t=1;
//scanf("%d",&t);
//cin>>t;
ca=1;
while(t--)
{
fatchuan();
ca++;
}
return 0;
}
n-皇后问题(dfs复习)

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=30;
int n;
char m[N][N];
int vis[N],dg[N],udg[N],ha[N];
void dfs(int x,int y ,int q)
{
if(y==n)y=0,x++;
if(x==n)
{
if(q==n)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cout<<m[i][j];
}cout<<endl;
}cout<<endl;
}
return;
}
dfs(x,y+1,q);
if(!vis[x] && !ha[y] && !dg[x+y] && !udg[n-x+y])
{
m[x][y]='Q';
ha[y]=dg[x+y]=udg[n-x+y]=vis[x]=1;
dfs(x,y+1,q+1);
m[x][y]='.';
ha[y]=dg[x+y]=udg[n-x+y]=vis[x]=0;
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
m[i][j]='.';
}
}
dfs(0,0,0);
};
八数码(bfs复习)
在一个 3×3 的网格中,1∼8 这 8 个数字和一个 x 恰好不重不漏地分布在这 3×3 的网格中。
例如:
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
在游戏过程中,可以把 x 与其上、下、左、右四个方向之一的数字交换(如果存在)。
我们的目的是通过交换,使得网格变为如下排列(称为正确排列):
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 x
例如,示例中图形就可以通过让 x 先后与右、下、右三个方向的数字交换成功得到正确排列。
交换过程如下:
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
x 4 6 4 x 6 4 5 6 4 5 6
7 5 8 7 5 8 7 x 8 7 8 x
现在,给你一个初始网格,请你求出得到正确排列至少需要进行多少次交换。
输入格式
输入占一行,将 3×3 的初始网格描绘出来。
例如,如果初始网格如下所示:
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
则输入为:1 2 3 x 4 6 7 5 8
输出格式
输出占一行,包含一个整数,表示最少交换次数。
如果不存在解决方案,则输出 −1。
输入样例:
2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8
输出样例
19题意:
得到一个输入之后,将“x”当作空格,可以与四周数字进行交换,最终使字符串变成“12345678x”,类似于小时候玩的益智游戏“华容道”,但这题神奇就神奇在,题目给的是一维的,要在换位过程中变成二维的。
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int nx[] = { 0,1,0,-1 };
int ny[] = { 1,0,-1,0 };
const int N = 35;
void bfs(string s)
{
int flag2 = 0;//标记能不能达到目的
queue<string>six;
unordered_map<string, int >d;//简单的来说是比map快的map(我是这么理解的有错误的话,希望大佬们能纠正我)
d[s] = 0;
six.push(s);
string end = "12345678x";//目的字符串
while (!six.empty())
{
string A;
A = six.front();
six.pop();
if (A == end)
{
cout << d[A];
flag2 =1;
break;
}
int step = d[A];
int flag = A.find("x");//找到x在字符串的位置
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++)
{
int x = flag / 3 + nx[i];//这里就是一维转二维了
int y = flag % 3 + ny[i];
if (x >= 0 && x < 3 && y >= 0 && y < 3)
{
swap(A[flag], A[x*3 + y]);
cout << A << endl;
if (!d.count(A))
{
d[A] = step + 1;
six.push(A);
}
swap(A[flag], A[x * 3 + y]);//交换完要交换回去,因为我没有额外定义专门用来交换的数组
cout << A << endl;
}
}
}
if(flag2==0)
cout << -1;
}
int main()
{
string s;
for (int i = 0;i < 9;i++)
{
char a;
cin >> a;
s += a;
}//由于输入数据带空格,所以这么输入的
//cout << s;
bfs(s);
}