面向对象的三大特征
封装 继承 多态
封装
该隐藏的数据私有化,该公开的数据设计为公有的接口
private public
目的为了更好地分工合作,有助于数据的安全性和使用的方便性,也防止不必要的扩展。
继承(inherite)
作用
实现了代码的复用,复用的实现是在已有代码的基础上进行扩展。继承发生在类与类之间
只有符合A is a B的情形,A与B就可以存在继承关系 比如: 动物 ------> 狗 猫 猪 鸡 狗 --------> 金毛 马犬 萨摩耶 汽车 ------> SUV 货车 轿车 电话 ------> 手机 座机 //电视 XXX 冰箱
语法实现
class A{…}; class B:继承方式 A{/新增的内容/};//B类中会包含A类中的所有内容 继承方式包括: 公有继承 ----- class B:public A{…}; 保护继承 ----- class B:protected A{…}; 私有继承 ----- class B:private A{…}; //B类继承A类,A就叫B的父类,B是A的子类(派生类) //如果不写继承方式,默认是私有继承
继承方式影响的是父类成员在子类中的访问权限。
公有继承
父类的公有成员在子类中仍然是公有的 父类中的保护成员在子类中仍然是保护的 父类的私有成员在子类中是隐藏的
保护继承
父类的公有成员在子类中变为保护的 父类中的保护成员在子类中仍然是保护的 父类的私有成员在子类中是隐藏的
私有继承
父类的公有成员在子类中变为私有的 父类中的保护成员在子类中变为私有的 父类的私有成员在子类中是隐藏的
注意:父类成员在子类中的访问权限只会收缩不会扩大,在子类中的访问全不会超过继承方式。
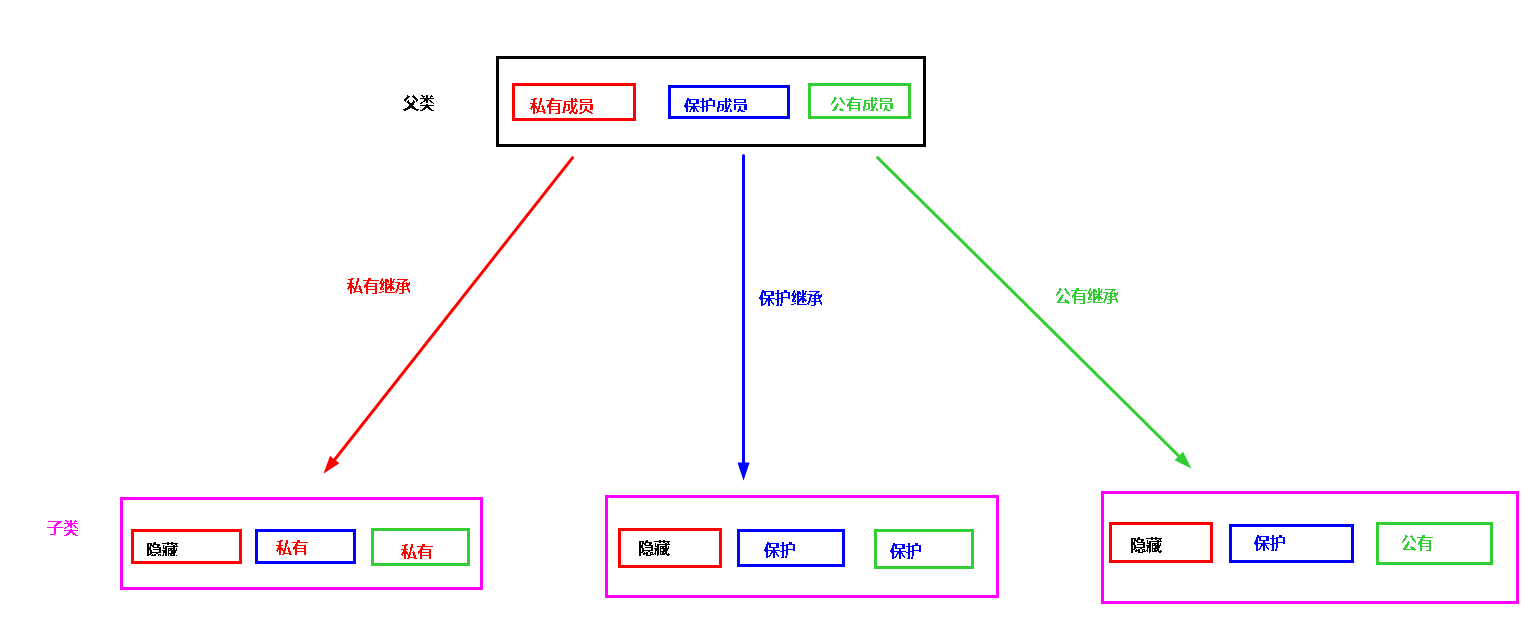
所谓继承方式就是父类成员能够提供给子类的最大访问权限,实际权限小于等于继承方式,私有数据在子类中总是隐藏的(隐藏不代表不存在)。
继承中的构造函数和析构函数
构造子类时,会自动调用父类的构造函数,析构子类时,自动调用父类的析构函数。调用构造函数和析构函数的顺序是相反的,先构造父类再构造子类,先析构子类再析构父类。
继承父类的数据由父类构造和析构,子类新增的数据由子类构造析构。
子类默认调用时父类的无参构造函数,如果需要给父类构造函数传参,可以通过子类构造函数的初始化参数列表传参。
/*03-继承中的构造函数和析构函数*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() { cout << "A()" << endl; }
A(int a, int b) { cout << "A(int,int)" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()" << endl; }
private:
int x;
int y;
};
class B : public A {
public:
B() { cout << "B()" << endl; }
B(int a, int b, int c) : A(a, b)/*给父类的构造函数传参*/, z(c) { cout << "B(int,int,int)" << endl; };
~B() { cout << "~B()" << endl; }
private:
int z;
};
int main() {
B b;
cout << "-----" << endl;
B b1(1, 2, 3);
return 0;
}
练习:
设计一个Dog类继承Animal,新增体重的属性成员(double weight)和看门的功能(dogfunc — 打印)。LiHuaCat继承Cat类,新增产地国家属性成员(string country)和吃鱼的功能(LiHuafunc — 打印)。
实现这两个类的构造函数。
/*02-继承*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
Animal(string name = "小飞飞", int age = 5) : name(name), age(age) {
}
void show() {
cout << this->name << ":" << this->age << endl;
}
protected:
string name;//可以在子类和类内访问
private:
int age;
};
//Dog继承Animal
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
Dog(string name = "妞妞", int age = 5, double weight = 23.4) :
Animal(name, age), weight(weight) {
}
void dogfunc() {
this->show();
cout << this->weight << " 看门!" << endl;
}
private:
double weight;
};
//Cat公有继承Animal ----- 得到Animal的所有内容
class Cat : public Animal {
public:
Cat(string name = "汤圆", int age = 3, string color = "yellow") : Animal(name, age), color(color) {
}
//新增的功能
void catfunc() {
this->show();
cout << this->color << "抓老鼠!" << endl;
}
private:
//新增属性
string color;
};
//LiHuaCat继承Cat
class LiHuaCat : public Cat {
public:
LiHuaCat(string name = "西红柿", int age = 3, string color = "豹纹", string country = "中国") :
Cat(name, age, color), country(country) {
}
//-----------------
//子类的构造函数的参数要看父类的构造函数的参数,让子类构造函数参数向父类的构造函数参数,
//调用父类的方法
//-----------------
void LiHuafunc() {
this->catfunc();
cout << "产地:" << this->country << " 吃鱼" << endl;
}
private:
string country;
};
int main() {
//Cat ct("端午",7,"白色");
//ct.catfunc();
//继承父类的成员函数
//ct.show();
Dog dg("阿黄", 2, 32.1);
dg.dogfunc();
cout << endl;
LiHuaCat lhc("桂兰", 7, "黑色", "美国");
lhc.LiHuafunc();
return 0;
}
继承中的拷贝构造
子类使用默认的拷贝构造,会自动调用父类的拷贝构造。但是重写子类的拷贝构造,默认不调用父类的拷贝构造,需要在子类的拷贝构造函数中使用初始化参数列表去调用父类的拷贝构造函数(使用子类的引用去代替父类的引用作为参数)。
/*04-继承中的拷贝构造和名字隐藏*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
A()
{
cout<<"A()"<<endl;
this->pdata = new char[10];
memset(this->pdata, 0, 10);
}
//拷贝构造
A(const A &a)
{
cout<<"A(const A &a)"<<endl;
this->pdata = new char[10];
memcpy(this->pdata,a.pdata,10);
}
~A()
{
cout<<"~A()"<<endl;
delete[] this->pdata;
}
void show()
{
cout<<"show A"<<endl;
}
private:
char *pdata;
};
class B:public A{
public:
B()
{
cout<<"B()"<<endl;
this->abc = new char[10];
memset(this->abc, 0, 10);
}
//子类拷贝构造 --- 通过初始化参数列表调用父类的拷贝构造!!!!
B(const B &b):A(b)
//---------------------------------------
{
cout<<"B(const B &b)"<<endl;
this->abc = new char[10];
memcpy(this->abc,b.abc,10);
}
~B()
{
cout<<"~B()"<<endl;
delete[] this->abc;
}
void show()
{
cout<<"show B"<<endl;
//this->A::show();
}
private:
char *abc;
};
int main()
{
B b1;
B b2 = b1;
//父类同名成员被隐藏,默认访问子类的同名成员
b2.show(); //show B 是B 里的方法
//访问父类的隐藏成员
b2.A::show(); //show A 是A 里的方法
return 0;
}
名字隐藏
如果子类中出现了和父类重名的成员,那么在子类中父类的同名成员将被隐藏。
如果想访问父类中被隐藏的成员,可以使用父类名+作用域符来访问
父类名::隐藏成员;

多重继承
概念
**C++允许一个子类继承多个父类,当一个类中包含多个类的属性和功能时,可以使用多重继承。
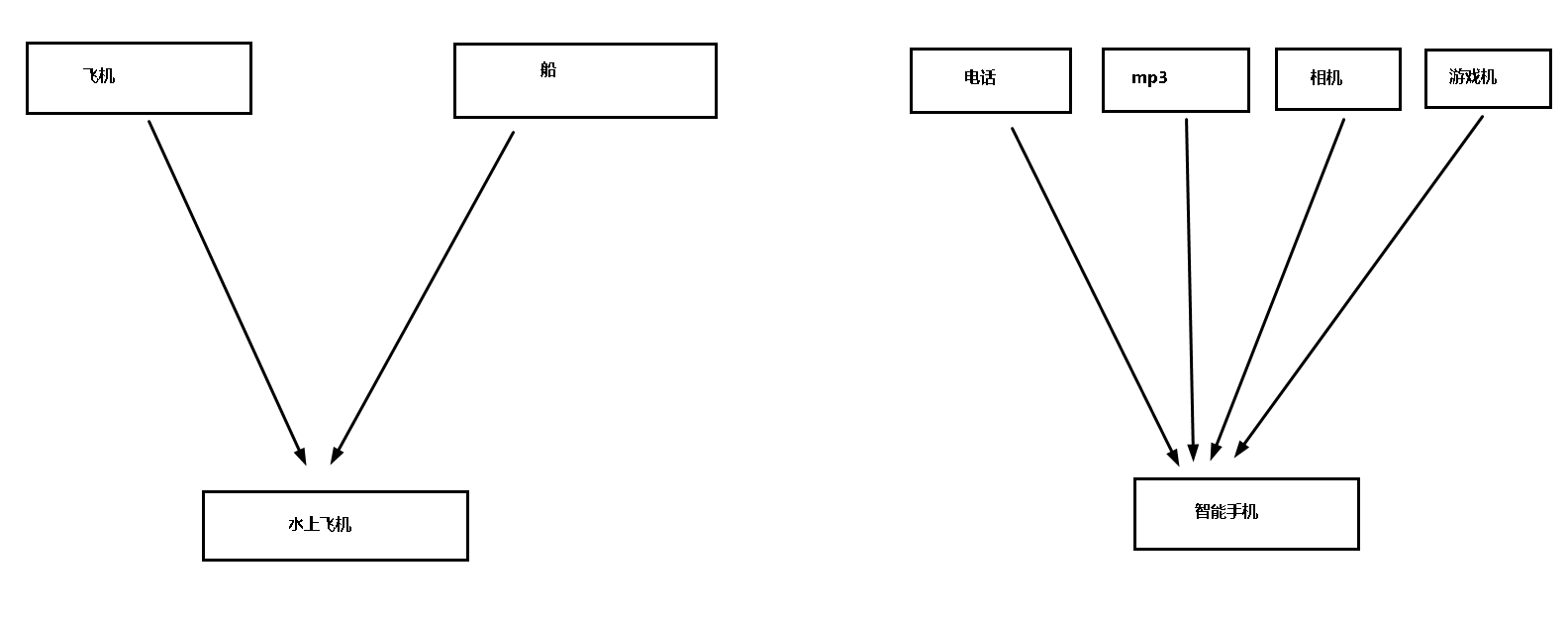
/*05-多重继承*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//电话类
class Phone {
public:
Phone(double p = 1000) : price(p) {
cout << "Phone()" << endl;
}
~Phone() {
cout << "~Phone()" << endl;
}
//读私有的成员的接口
double get_price() {
return this->price;
}
void call() {
cout << "打电话" << endl;
}
private:
double price;
};
//MP3类
class Mp3 {
public:
Mp3(double p = 300) : price(p) {
cout << "Mp3()" << endl;
}
~Mp3() {
cout << "~Mp3()" << endl;
}
//读私有的成员的接口
double get_price() {
return this->price;
}
void play(string song) {
cout << "播放" << song << endl;
}
private:
double price;
};
//相机类
class Camera {
public:
Camera(double p = 500) : price(p) {
cout << "Camera()" << endl;
}
~Camera() {
cout << "~Camera()" << endl;
}
//读私有的成员的接口
double get_price() {
return this->price;
}
void capture() {
cout << "拍照" << endl;
}
private:
double price;
};
//多重继承
class SmartPhone : public Phone, public Mp3, public Camera {
public:
double get_price() {
return Phone::get_price() + Mp3::get_price() + Camera::get_price() + 3000;
}
};
int main() {
SmartPhone iphone13;
cout << iphone13.get_price() << endl; // 本身子类的方法该方法调用父类
cout << iphone13.Camera::get_price() << endl; //Camera是多重继承里的
iphone13.play("蔡徐坤"); //继承的是mps里的方法
return 0;
}
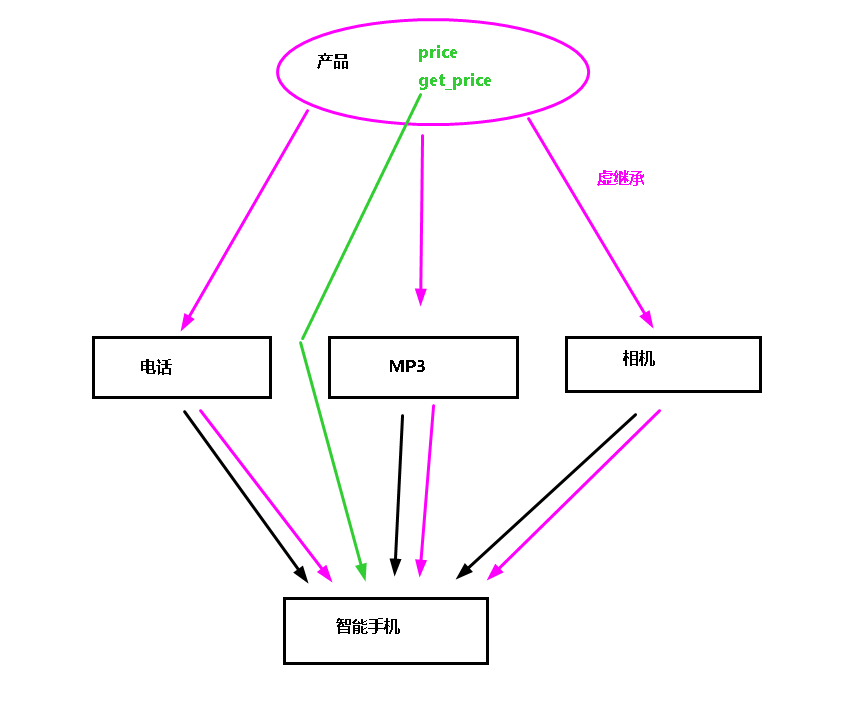
多继承的优化
多继承的子类中容易出现同名成员,造成代码冗余,可以使用以下方法进行优化
将父类中的同名成员提取出来
double price;
double get_price();
将这些同名成员放入一个更高层的父类
class Product{
double price; double get_price();
};
父类使用虚继承(virtual)继承最高层的父类(Product)
class 子类名:virtual 继承方式 父类名{
//...
};
对于单层继承来说,虚继承和普通继承完全一样,区别在于多层继承时,子类在拷贝数据时,如果该数据处于更高层的父类,子类不再从直接父类拷贝数据,而是从最高层的父类去拷贝。
(菱形继承)
/*06-多重继承的优化 ----- 虚继承*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//产品类
class Product {
public:
Product(int p = 0) : price(p) { //!!!!!!!!!!!!
}
double get_price() {
return this->price;
}
private:
double price;
};
//电话类 --- 虚继承
class Phone : virtual public Product { //!!!!!!!!!!!!
public:
Phone(double p = 1000) : Product(p) {
cout << "Phone()" << endl;
}
~Phone() {
cout << "~Phone()" << endl;
}
void call() {
cout << "打电话" << endl;
}
};
//MP3类-继承procduct
class Mp3 : virtual public Product { //!!!!!!!!!!!!
public:
Mp3(double p = 300) : Product(p) {
cout << "Mp3()" << endl;
}
~Mp3() {
cout << "~Mp3()" << endl;
}
void play(string song) {
cout << "播放" << song << endl;
}
};
//相机类
class Camera : virtual public Product { //!!!!!!!!!!!!
public:
Camera(double p = 500) : Product(p) { //这里要记得传入参数
cout << "Camera()" << endl;
}
~Camera() {
cout << "~Camera()" << endl;
}
void capture() {
cout << "拍照" << endl;
}
};
//多重继承
class SmartPhone : public Phone, public Mp3, public Camera {
public:
SmartPhone(double a = 0, double b = 0, double c = 0) : Product(a + b + c + 3000) {
}
};
int main() {
SmartPhone iphone13(1200, 500, 800);
cout << iphone13.get_price() << endl;
iphone13.play("蔡徐坤");
return 0;
}
练习:
实现一个Person类,有string p_name成员保存人名,char *p成员保存说明信息;实现一个Comp类,有string c_name的成员保存公司名,char *p成员保存说明信息;实现子类Employer继承Person和Comp,新增成员double salary,提供show成员函数打印成员信息。
实现虚继承,实现这这些类的构造函数,析构函数和拷贝构造函数。
/*06-多重继承实现员工类*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Object {
public:
Object(const char *s = NULL) {
cout << "Object()" << endl;
if (s) {
this->p = new char[strlen(s) + 1];
strcpy(this->p, s);
} else {
this->p = new char[10];
memset(this->p, 0, 10);
}
}
//拷贝构造 固定写法
Object(const Object &o) {
cout << "Object(const Object &o)" << endl;
if (strlen(o.p)) {
this->p = new char[strlen(o.p) + 1];
strcpy(this->p, o.p);
} else {//空串
this->p = new char[10];
memset(this->p, 0, 10);
}
}
~Object() {
cout << "~Object()" << endl;
delete[] this->p;
}
//获取
const char *get_p() {
return this->p;
}
private:
char *p;//说明信息
};
//虚继承
class Person : virtual public Object {
public:
Person(const char *s = NULL, string name = "xxx") : Object(s), p_name(name) {
cout << "Person()" << endl;
}
//获取
string get_pname() {
return this->p_name;
}
private:
string p_name;//人名
};
class Comp : virtual public Object {
public:
Comp(const char *s = NULL, string name = "xxx") : Object(s), c_name(name) {
cout << "Comp()" << endl;
}
//获取
string get_cname() {
return this->c_name;
}
private:
string c_name;//公司名
};
//员工类
class Employer : virtual public Person, virtual public Comp {
public:
Employer(const char *s = NULL, string pname = "xxx", string cname = "xxx", double salary = 1000.0) :
Object(s), Person(s, pname), Comp(s, cname), salary(salary) {
cout << "Employer()" << endl;
}
void show() {
cout << this->get_pname() << ":" << this->get_cname() << ":" <<
this->get_p() << ":" << this->salary << endl;
}
private:
double salary;
};
int main() {
Employer ep("五虎上将", "张飞", "蜀国", 300000.0);
ep.show();
Employer ep1 = ep;
return 0;
}
Object(const Object &o) { //拷贝构造函数固定写法
cout << "Object(const Object &o)" << endl;
if (strlen(o.p)) {
this->p = new char[strlen(o.p) + 1];
strcpy(this->p, o.p);
} else {//空串
this->p = new char[10];
memset(this->p, 0, 10);
}
}
作业:
实现一个农民工类继承工人类和农民类
工人类(Worker):
char *name; double salary;
农民类(Farmer):
char *name; double area;//地面积
农民工(FarmWorker):
新增show的成员函数打印所有的信息
要求使用虚继承实现多重继承,根据需要实现对应类的构造,析构和拷贝构造函数。
Work:
/*06-多重继承实现员工类*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
Person(const char *str = "xiaoyu") {
this->name = new char[strlen(str) + 1]; //strlen是有效字符的长度 ,结束符也要存起来,所以要加一
strcpy(this->name, str); //copy函数
}
Person(const Person &a) {
this->name = new char[strlen(a.name) + 1];
strcpy(this->name, a.name);
}
~Person() {
delete[] this->name;
}
char *show(void) {
return name;
}
private:
char *name;
};
class Worker : virtual public Person {
public:
Worker(double salary = 300, const char *name = "AAA") : Person(name) {
this->salary = salary;
}
double Salary() {
return this->salary;
}
private:
double salary;
};
//虚继承
class Farmer : virtual public Person {
public:
Farmer(double area = 300, const char *name = "aaa") : Person(name) {
this->area = area;
}
double Area() {
return this->area;
}
private:
double area;//地面积
};
class FarmWorker : virtual public Farmer, virtual public Worker {
public:
FarmWorker(const char *name = "haha", double area = 200, double salary = 40000) :
Person("name"), Farmer(area, name), Worker(salary, name) {
}
void All_info() {
cout << this->show() << " area " << this->Area() << " salary " << this->Salary() << endl;
}
};
int main() {
FarmWorker f1;
f1.All_info();
return 0;
}

相对固定的写法