前言
其实,整合是一个循序渐进的学习,你肯定是要了解之前底层的相关知识,才能够具体知道现在框架方法api到底tm有什么作用,所以建议先看看我之前的redis博客。
可以不看,但是可以以我这个为目录,针对性得去了解相关知识(学习任何东西,都应该这样)。
(41条消息) Cenos7 --- Redis下载和安装(Linux版本)_本郡主是喵的博客-CSDN博客
(41条消息) redis学习 -- 常用指令_本郡主是喵的博客-CSDN博客
(41条消息) redis -- 持久化存储方案_本郡主是喵的博客-CSDN博客
(41条消息) redis的4种模式,单机,哨兵、主从复制、集群_本郡主是喵的博客-CSDN博客
1.快速入门
1.1导入相关依赖
<!--spring-data-redis组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--commons-pools连接池,lettuce没有内置的数据库连接池所以要用第三方的 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--web组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--test组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>1.2 配置文件
application.yml
server:
port: 8080
# redis配置
spring:
redis:
password: 123456
# 默认0库
database: 0
#连接超时时间
timeout: 10000ms
port: 6379
host: 192.168.88.135
lettuce:
pool:
# 设置最大连接数
max-active: 1024
# 最大阻塞时间
max-wait: 10000ms
# 最大空间连接,默认8
max-idle: 200
# 最小空间连接,默认5
min-idle: 5
1.3 核心代码
@SpringBootTest
class SpringDataRedisDemo1ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
// 这一种完全够用(与第二种,稍微一点差别,具体看下文)
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
// 转对redis的string类型的
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
void testDemo() {
ValueOperations value = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
value.set("qhx","name");
System.out.println(value.get("qhx"));
ValueOperations<String, String> stringValueOperations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
System.out.println(stringValueOperations.get("name"));
}
}
此处可以忽略。
我们在application.yml配置文件信息,按住ctrl + 单击点进去,发现是一个映射redis配置信息的类。

就是,假如有些配置你不知道,可以依托这个去相应的官网文档上去查找相应的用法。
1.4 自定义模版解决序列化问题
打开redis可视化客户端,发现我们成功存入数据,但是是java字节数据。如何解决?

先看下图。

RedisConfig.java
@Configuration
public class RedisConf {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory){
RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 为string 的key设置序列化
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 为string类型的value设置序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 为hash类型的value设置json序列化
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 为hash类型的key设置json序列化
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 设置数据库连接池
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(lettuceConnectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}
}
再次运行。
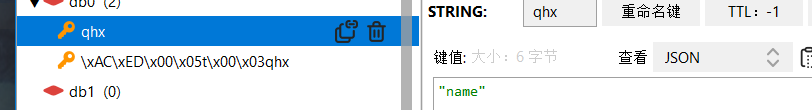
成功!
此处可以忽略。
可以看出,我们设置key先转成java字节数据,最后存入数据库中。
自定义后,我们设置key先转成java string数据,最后存入数据库中。
2.操作各种类型数据
此处可以忽略
其实,这些api如果你没有学过,需要跟着敲一遍,敲得途中你可能会发现这些api的意思(有基础的前提下)。
2.1 操作string类型数据
// 添加一条数据
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("name","zhangsan");
// 获取一条数据
String name = (String) ops.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
// 层级关系
ops.set("user:01","lisi");
// 添加多条数据
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("age","20");
hashMap.put("address","wei");
ops.multiSet(hashMap);
// 获取多条数据
ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("age");
list.add("address");
List listValue = ops.multiGet(list);
listValue.forEach(System.out::println);2.2 操作hash类型数据
HashOperations hashOps = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
// 添加hash单条数据
hashOps.put("user","name","qhx");
// 获取hash单条数据
String hash = (String) hashOps.get("user", "name");
// 添加hash多条数据
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("age","20");
hashMap.put("address","wei");
hashOps.putAll("user",hashMap);
// 获取hash类型的多条数据
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("age");
list.add("address");
List user = hashOps.multiGet("user", list);
user.forEach(System.out::println);
// 获取hash类型所有数据
Map entries = hashOps.entries("user");
entries.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key+"-->"+value);
});
// 删除Hash类型数据
hashOps.delete("user","age","name");2.3 操作list类型数据
ListOperations listOps = redisTemplate.opsForList();
// 左添加
listOps.leftPush("students","w1");
listOps.leftPushAll("students","w2","w3");
// 右添加
listOps.leftPush("students","w4");
// 在w1前面左添加w0
listOps.leftPush("students","w1","w0");
// 获取数据
List list = listOps.range("students", 0, 4);
System.out.println(list);
// 获取总条数
Long students = listOps.size("students");
// 删除1条数据
listOps.remove("students",1,"w0");
// 左弹出
listOps.leftPop("students");
listOps.rightPop("students");
2.4 操作set类型数据
SetOperations setOps = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
// 添加数据
setOps.add("ids","1","2");
// 获取数据
Set ids = setOps.members("ids");
ids.forEach(System.out::println);
// 删除数据
setOps.remove("ids","1","2");2.5 操作sorted-set类型数据
ZSetOperations zSetOps = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
// 添加多条数据(我自己也属实看不懂)将数据封装到hash里。
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> objectTypedTuple1 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("wls",1D);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> objectTypedTuple2 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("qhx",2D);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> objectTypedTuple3 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("zlx",3D);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple> tuples = new HashSet<>();
tuples.add(objectTypedTuple1);
tuples.add(objectTypedTuple2);
tuples.add(objectTypedTuple3);
zSetOps.add("names",tuples);
// 添加单条数据
zSetOps.add("names","qhx1",4D);
// 获取数据
Set names = zSetOps.range("names", 0, 3);
names.forEach(System.out::println);
// 删除数据
zSetOps.remove("names","qhx","wls");
2.6 获取所有的key和给key设置过期时间
// 获取所有的keys(当前数据库)
Set keys = redisTemplate.keys("*");
keys.forEach(System.out::println);
// 给已存在key设置失效时间
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("name","qhx",200, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 给key设置失效时间
redisTemplate.expire("age",30,TimeUnit.SECONDS);3.配置哨兵模式
先在redis中启用哨兵模式。
还有别忘了用Linux防火墙把相应的端口打开(或者,直接关闭防火墙)。
1.方式一,在aplication.yml文件中新加 spring.redis.sentinel
预览图:
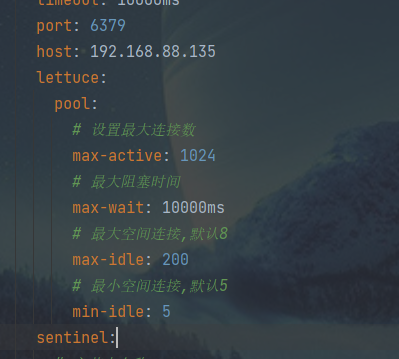
sentinel:
# 主节点名称
master: mysaster
# 主服务器密码
password: 123456
# 哨兵节点
nodes: 192.168.88.135:26379,192.168.88.135:26380,192.168.88.135:263812.方式二,
在上文RedisCong.java中添加
@Bean
public RedisSentinelConfiguration redisSentinelConfiguration(){
RedisSentinelConfiguration redisSentinelConfiguration = new RedisSentinelConfiguration()
// 主节点名称
.master("mymaster")
// 哨兵
.sentinel("192.168.88.135",26379)
.sentinel("192.168.88.135",26380)
.sentinel("192.168.88.135",26381);
// 密码
redisSentinelConfiguration.setPassword("123456");
return redisSentinelConfiguration;
}