目录
- 8.1 线程池
- 2、==ThreadPoolExecutor(及其重要)==
- 1) 线程池状态
- ==2) 构造方法==
- 3) newFixedThreadPool
- 4) newCachedThreadPool
- 5) newSingleThreadExecutor
- 6) 提交任务
- 7) 关闭线程池
- 8) 任务调度线程池
8.1 线程池
2、ThreadPoolExecutor(及其重要)
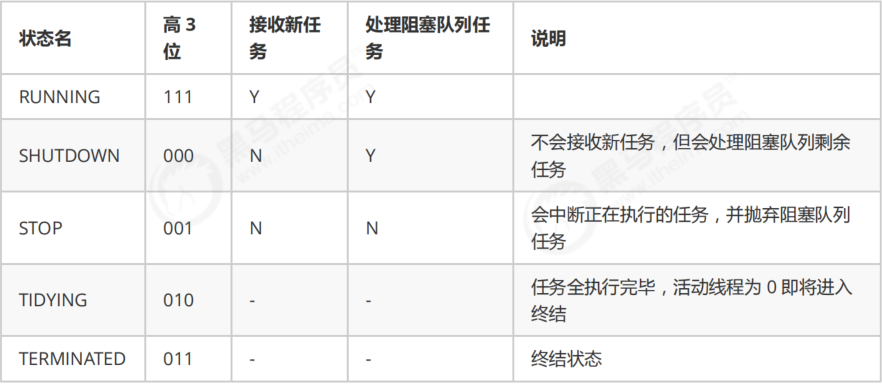
1) 线程池状态
ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的高 3 位来表示线程池状态,低 29 位表示线程数量
2) 构造方法
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize 核心线程数目 (最多保留的线程数,一直存活的线程数)
- maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目
- keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 针对救急线程
- unit 时间单位 - 针对救急线程
- workQueue 阻塞队列
- threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以为线程创建时起个好名字
- handler 拒绝策略
工作方式:
- 线程池中刚开始没有线程,当一个任务提交给线程池后,线程池会创建一个新线程来执行任务。
- 当线程数达到 corePoolSize 并没有线程空闲,这时再加入任务,新加的任务会被加入workQueue 队列排队,直到有空闲的线程,此时任务会从workQueue取出交给空闲线程执行
- 如果队列选择了有界队列,那么任务超过了队列大小时,会创建 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize 数目的线程来救急
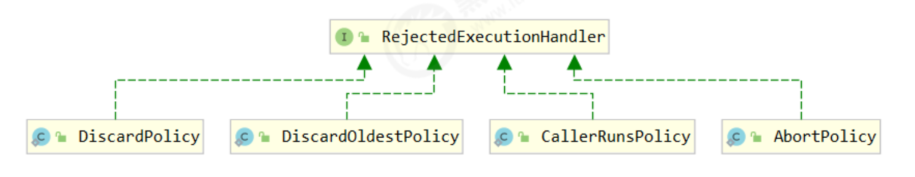
- 如果线程到达 maximumPoolSize 仍然有新任务这时会执行拒绝策略
- AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是默认策略
- CallerRunsPolicy 让调用者运行任务
- DiscardPolicy 放弃本次任务
- DiscardOldestPolicy 放弃队列中最早的任务,本任务取而代之
- 当高峰过去后,超过corePoolSize 的救急线程如果空闲了keepAliveTime时间后,就会被销毁
3) newFixedThreadPool
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// Executors类中有静态方法 newFixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
特点:
- 核心线程数 == 最大线程数(没有救急线程被创建),因此也无需超时时间
- 阻塞队列是无界的,可以放任意数量的任务,所以也没有拒绝策略
4) newCachedThreadPool
ExecutorService service1 = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// Executors类中有静态方法 newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
特点:
- 核心线程数是 0, 最大线程数是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,救急线程的空闲生存时间是 60s,意味着
- 全部都是救急线程(60s 后可以回收)
- 救急线程可以无限创建
- 队列采用了 SynchronousQueue 实现特点是,它没有容量,没有线程来取是放不进去的
SynchronousQueue的使用
5) newSingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
使用场景:
希望多个任务排队执行。线程数固定为 1,任务数多于 1 时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这唯一的线程也不会被释放。
newSingleThreadExecutor和newFixedThreadPool的区别:
- 自己创建一个单线程串行执行任务,如果任务执行失败而终止那么没有任何补救措施,而线程池还会新建一个线程,保证池的正常工作
- Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 线程个数始终为1,不能修改
- FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是装饰器模式,只对外暴露了 ExecutorService 接口,因此不能调用 ThreadPoolExecutor 中特有的方法
- Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1) 初始时为1,以后还可以修改
- 对外暴露的是 ThreadPoolExecutor 对象,可以强转后调用 setCorePoolSize 等方法进行修改
6) 提交任务
线程池提交任务
execute
// 执行任务
void execute(Runnable command);
submit
// 提交任务 task,用返回值 Future 获得任务执行结果
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
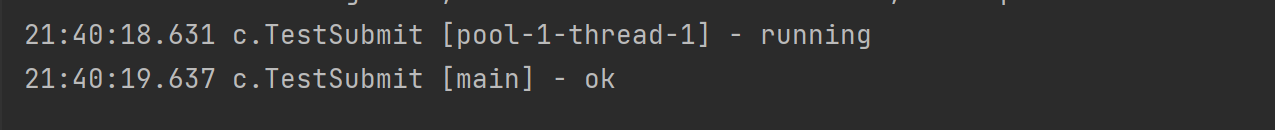
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit")
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
TestSubmit.method1(pool);
}
private static void method1(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Future<String> future = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("running");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "ok";
});
log.debug("{}", future.get());
}
}
invokeAll
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间,List<Future<T>>接收返回结果
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
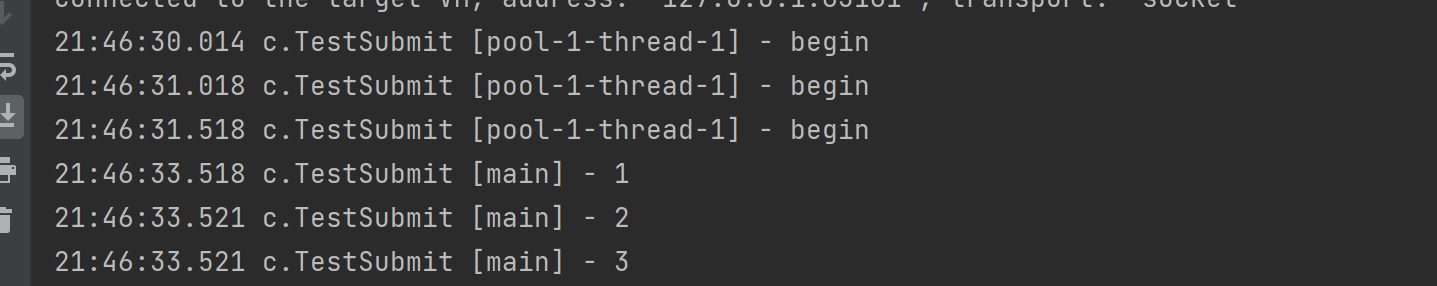
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
TestSubmit.method2(pool);
}
private static void method2(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException {
List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
));
futures.forEach( f -> {
try {
log.debug("{}", f.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
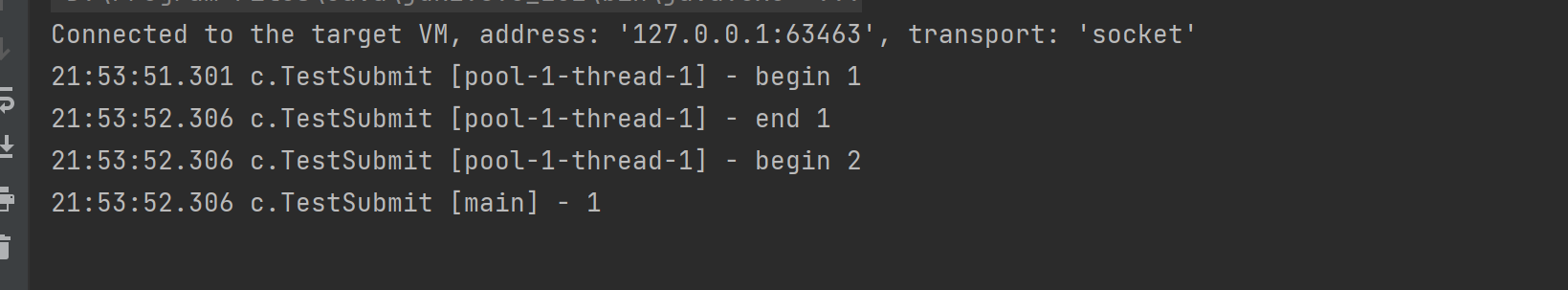
invokeAny
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
public class TestSubmit {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
TestSubmit.method3(pool);
}
private static void method3(ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
String result = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin 1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end 1");
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin 2");
Thread.sleep(500);
log.debug("end 2");
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin 3");
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.debug("end 3");
return "3";
}
));
log.debug("{}", result);
}
}
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消,带超时时间
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
7) 关闭线程池
shutdown()
线程池状态变为 SHUTDOWN
- 不会接收新任务
- 已提交的任务会执行完
- 此方法不会阻塞调用线程的执行
shutdownNow()
线程池状态变为 STOP
- 不会接收新任务
- 会将队列中的任务返回
- 并用 interrupt 的方式中断正在执行的任务



![[n00bzCTF 2023] CPR 全](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9984f416418e43e7837cde50f299679b.png)