介绍
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类
- Key和Value都允许空
- 有序
- key可重复可覆盖,value可重复
- 非线程安全
- 可用于实现LRU
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
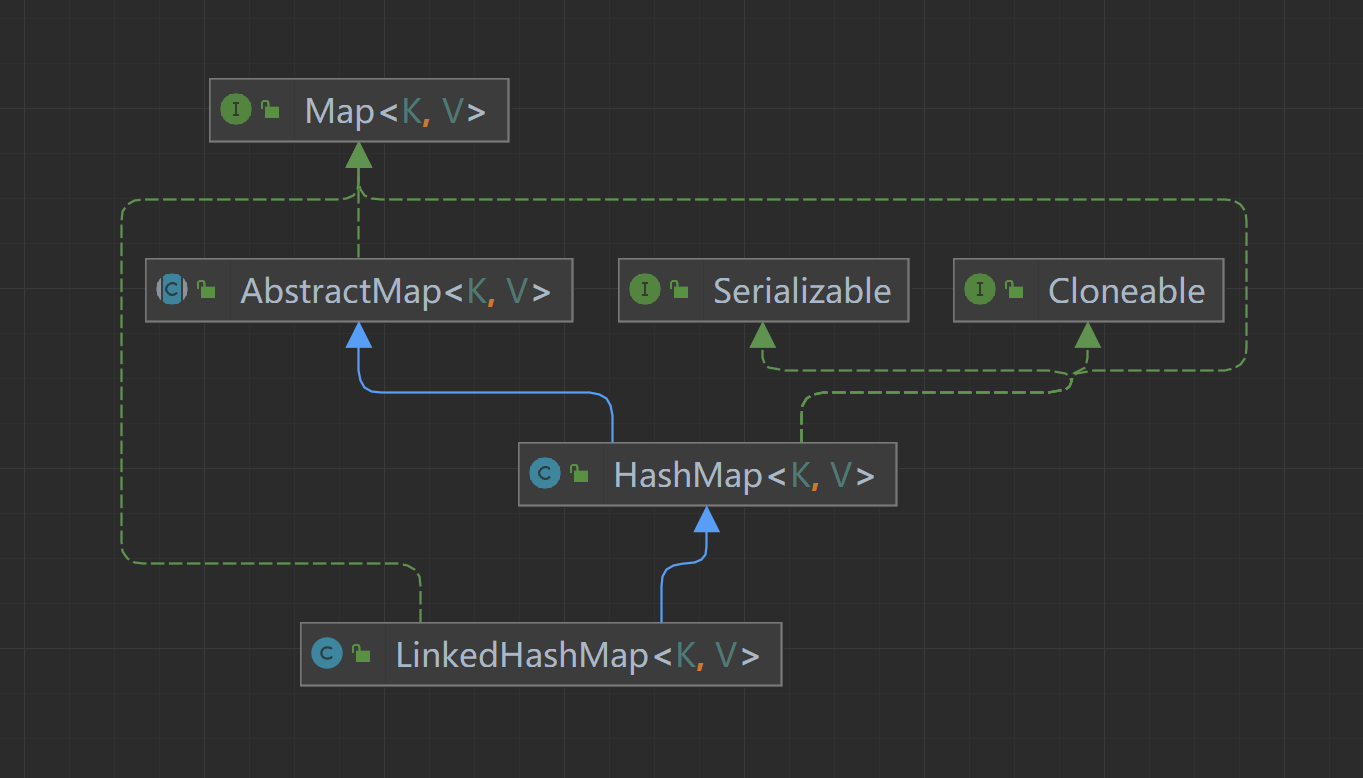
LinkedHashMap的原理图:
LinkedHashMap是HashMap和双向链表的合二为一,即一个将所有Entry节点链入一个双向链表的HashMap(LinkedHashMap = HashMap + 双向链表)
LinkedHashMap 在不对HashMap做任何改变的基础上,给HashMap的任意两个节点间加了两条连线before指针和after指针,使这些节点形成一个双向链表。在LinkedHashMapMap中,所有put进来的Entry都保存在HashMap中,但由于它又额外定义了一个以head为头结点的空的双向链表,因此对于每次put进来Entry还会将其插入到双向链表的尾部。
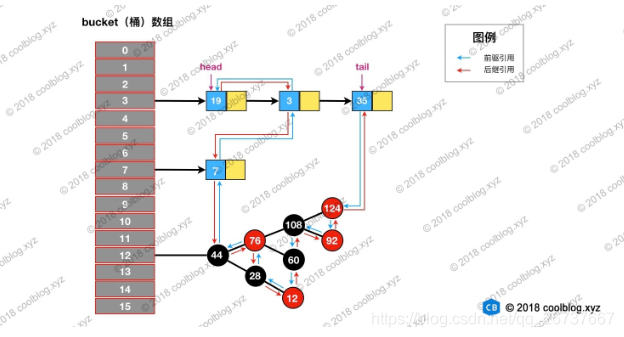
LinkedHashMap和HashMap的Entry结构图:
常量&变量
//序列化版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L;
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
* 头节点,最老的元素
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
* 尾节点,最新的元素
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
* 默认是false,则迭代时输出的顺序是插入节点的顺序。
* 若为true,则输出的顺序是按照访问节点的顺序。为true时,可以在这基础之上构建LRU
*
* @serial
*/
final boolean accessOrder;
- header是LinkedHashMap所维护的双向链表的头结点
- tail是尾节点
- accessOrder用于决定具体的迭代顺序
构造方法
详情查看hashmap源码
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with
* the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt>
* instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial
* capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
内部类
Entry
实际上是继承自HashMap.Node 静态内部类 ,我们知道HashMap.Node 实际上是一个单链表,因为它只有next 节点,但是这里LinkedHashMap.Entry保留了HashMap的数据结构,同时有before, after 两个节点,一个前驱节点一个后继节点,从而实现了双向链表
/**
* HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries.
* 双向链表
*/
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
//前后节点
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
LinkedKeySet、LinkedValues 、LinkedEntrySet
**LinkedKeySet:**LinkedHashMap 的 key 集合
**LinkedValues:**LinkedHashMap 的 value 集合
LinkedEntrySet: LinkedHashMap 的 set 集合
结构都类似
final class LinkedKeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
//元素个数
public final int size() { return size; }
//清空
public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap.this.clear(); }
//key的迭代器
public final Iterator<K> iterator() {
return new LinkedKeyIterator();
}
//是否包含指定的key
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsKey(o); }
//通过key移除
public final boolean remove(Object key) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null;
}
public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED |
Spliterator.ORDERED |
Spliterator.DISTINCT);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int mc = modCount;
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
action.accept(e.key);
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
LinkedHashIterator
LinkedHashMap 的元素遍历器
abstract class LinkedHashIterator {
//下个Node节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> next;
//当前节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> current;
//预期修改次数
int expectedModCount;
LinkedHashIterator() {
next = head;
expectedModCount = modCount;
current = null;
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> nextNode() {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
current = e;
next = e.after;
return e;
}
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
LinkedKeyIterator、LinkedValueIterator、LinkedEntryIterator
继承了 LinkedHashIterator,只重写 next() 方法
final class LinkedKeyIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().getKey(); }
}
final class LinkedValueIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
}
final class LinkedEntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
常用方法
newNode
LinkedHashMap并没有重写任何put相关的方法,但其重写了构建节点的newNode方法;newNode方法会在putVal方法中被调用;putVal方法会在向集合中插入数据的时候被调用(单条插入put(K key, V value),批量插入putMapEntries(Map m, boolean evict))。
在每次构建新节点时,通过LinkedNodeLast方法将新节点链接在双向链表的尾部。
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
//创建Entry节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
//添加到尾部
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
linkNodeLast
// link at the end of list
//将指定entry插入到双向链表末尾
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
//尾指针指向p
tail = p;
//如果原尾节点指向null,意味着双向循环链表为空,头尾指针都指向p
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
//p的前驱节点指向原尾节点
p.before = last;
//原尾节点的后继节点指向p
last.after = p;
}
}
clear
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* 清空map中元素
*/
public void clear() {
// 增加modcount,清除数组内元素
super.clear();
// 头等于尾等于null,代表链表为空
head = tail = null;
}
containsValue
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value.
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
* 查看是否包含某个元素
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
//从头到尾遍历双向链表
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) {
V v = e.value;
// 直接判断相等或者对象使用equals判断值相等时返回true
if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
keySet
/**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the keys contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation), the results of
* the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal,
* which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via the
* <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, <tt>Set.remove</tt>,
* <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt>, and <tt>clear</tt>
* operations. It does not support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt>
* operations.
* Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential
* performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of
* {@code HashMap}.
*
* @return a set view of the keys contained in this map
* 获取map的key值Set
*/
public Set<K> keySet() {
// 获取keySet
Set<K> ks = keySet;
if (ks == null) {
// 实例化LinkedKeySet
ks = new LinkedKeySet();
keySet = ks;
}
return ks;
}
values
/**
* Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map.
* The collection is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the collection, and vice-versa. If the map is
* modified while an iteration over the collection is in progress
* (except through the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation),
* the results of the iteration are undefined. The collection
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Collection.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>,
* <tt>retainAll</tt> and <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not
* support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
* Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential
* performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of
* {@code HashMap}.
*
* @return a view of the values contained in this map
* 获取map的value值的集合
*/
public Collection<V> values() {
// 获取集合元素
Collection<V> vs = values;
if (vs == null) {
// 实例化为LinkedValues
vs = new LinkedValues();
values = vs;
}
return vs;
}
get
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
// 调用HashMap方法判断元素是否已经存在
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
// 当设置accessOrder时,将当前获取的元素放入
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
afterNodeAccess
/**
* 第一种情况,插入节点是头节点
* a b c d e
* get(a),将a放到末尾
* b c d e a
* 第二种情况,插入节点不是头节点
* a b c d e
* get(b),将b放到末尾
* a c d e b
*
* 将元素移动到最后一个
* @param e
*/
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
// 当需要排序并且加入节点e不是尾节点时,进入逻辑(为尾节点时,无需操作,已经为最近访问过的元素)
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
// 首先暂存插入节点的当前节点,前节点,后节点
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
// 将插入节点的后节点设为null,代表尾节点
p.after = null;
// 如果p的前置节点为null,代表插入节点p为头节点,p的后节点a就变为头节点
// a ...
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
// 不为空时, b的后指针指向a节点 b a
// b -> a
b.after = a;
// 插入节点的后一个节点不为null时,插入节点的后一个节点的前一个节点设置为插入节点的前一个节点 b p a
if (a != null)
//a的上一个节点就变为b
// b <- a
a.before = b;
else
//b为尾结点
last = b;
// 尾节点为null,代表链表为空,头节点直接设置为插入节点
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
// 头节点的前置节点为尾节点
p.before = last;
// 尾节点的后一个节点为插入节点
last.after = p;
}
// 新的尾节点设置为插入节点
tail = p;
// 增加修改数量
++modCount;
}
}