Collection集合的遍历
Iterator:迭代器是集合的专用的遍历的方式,使用时也需要导包
- Iterator iterator():返回集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合的iterator()方法得到
- 迭代器使用过集合的iterator()方法得到的,所以说它是依赖于集合而存在的
Iterator的常用方法:
-
E next():返回迭代中的下一个元素
package com.gather.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; public class IteratorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> c=new ArrayList<String>(); c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); //Iterator<E> iterator():返回此集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合的iterator()方法得到 Iterator<String> it = c.iterator(); //E next():返回迭代中的下一个元素 System.out.println(it.next()); System.out.println(it.next()); System.out.println(it.next()); //System.out.println(it.next());NoSuchElementException } }NoSuchElementException:表示请求的元素不存在,我们在集合中只存了三个元素,当请求第四个时就会报异常
-
boolean hasNext():如果迭代具有更多元素,则返回true
package com.gather.collection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; public class IteratorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> c=new ArrayList<String>(); c.add("hello"); c.add("world"); c.add("java"); Iterator<String> it = c.iterator(); //boolean hasNext():如果迭代器中具有更多元素,则返回true /*if (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } if (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } if (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); }*/ //用while循环改进判断 while (it.hasNext()){ String s = it.next(); System.out.println(s); } } }
案例:Collection集合存储学生对象并遍历
需求:创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储3个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
思路:
1.定义学生类
2.创建Collection集合对象
3.创建学生对象
4.把学生添加到集合
5.遍历集合(迭代器方式)
学生类:
package com.gather.collection.example;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
实现类:
package com.gather.collection.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Student> c = new ArrayList<Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("郝佳乐", 20);
Student s2 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student s3 = new Student("李四", 22);
//把学生添加到集合
c.add(s1);
c.add(s2);
c.add(s3);
//遍历集合(迭代器方式)
Iterator<Student> it = c.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Student s = it.next();
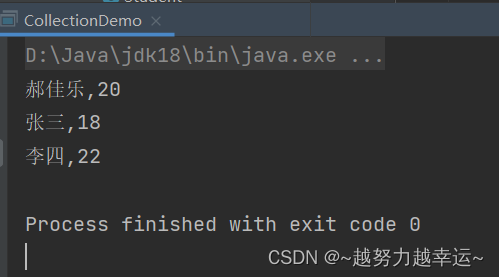
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}