-
Ansible Loops是什么?以及实际例子
就是循环语句。让我们看看这个创建Playbook的示例。要使用用户模块在系统中创建用户,在本例中, 我们只创建一个用户。但是如果我们有多个用户呢?name: Create users hosts: localhost tasks: - user: name= george state=present一种方法是根据需要多次复制这些行
name: Create users hosts: localhost tasks: - user: name= george state=present - user: name= ravi state=present - user: name= mani state=present - user: name= kiran state=present - user: name= jazlan state=present - user: name= emaan state=present - user: name= mazin state=present - user: name= izaan state=present - user: name=mike state=present - user: name= menaal state=present - user: name= shoeb state=present - user: name=rani state=present但这并不是很优雅,因为有很多重复。一个更好的方法是在所有用户上建立一个任务循环。这就是我们使用循环的地方。
Loop是一个循环指令,它多次执行相同的任务。每次运行时, 它都会将循环中每个项的值存储在名为“item”的变量中。因此, 可以简单地替换用户名,如下所示。这会使行动手册更有条理,并减少重复。
上面的写法,可以转换成下面的写法,方便理解loop,loop相当于创建了多个task,然后每个task都第一了变量item,如下。执行行动手册时, 它将以这种方式运行。这里只是方便理解loop,不建议这么写。

所以任何时候你遇到一本可能是别人写的Playbook,而loop部分很混乱, 我会建议你像这样可视化它。
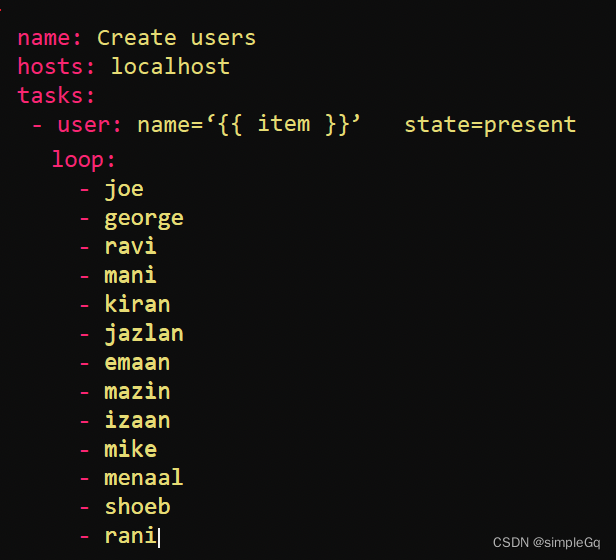
在上面的例子中, 循环是一个字符串值数组,只有用户名。但是如果我也想指定用户id呢?这意味着循环中的每一项都必须有两个值;用户名和用户ID。但是如何在一个数组中传递两个值,而不是通过循环传递一个字符串数组。
传入一个字典数组。每个字典将有两个键值对。键是name是每个用户的id。
循环中每个任务内的item变量都是一个字典,因此, 在每个任务中, 要获取用户名,我可以执行item.name。要获取用户ID, 我可以执行item.uid。
对于字典数组, 可以简单地使用字典中的item.属性名来获取列表中每个字典中的一个项。
上面的例子可以可视化为如下,没一个task都有一个item字典变量,里面包含name和uid两个属性。使用的时候可以使用item.属性名的方式
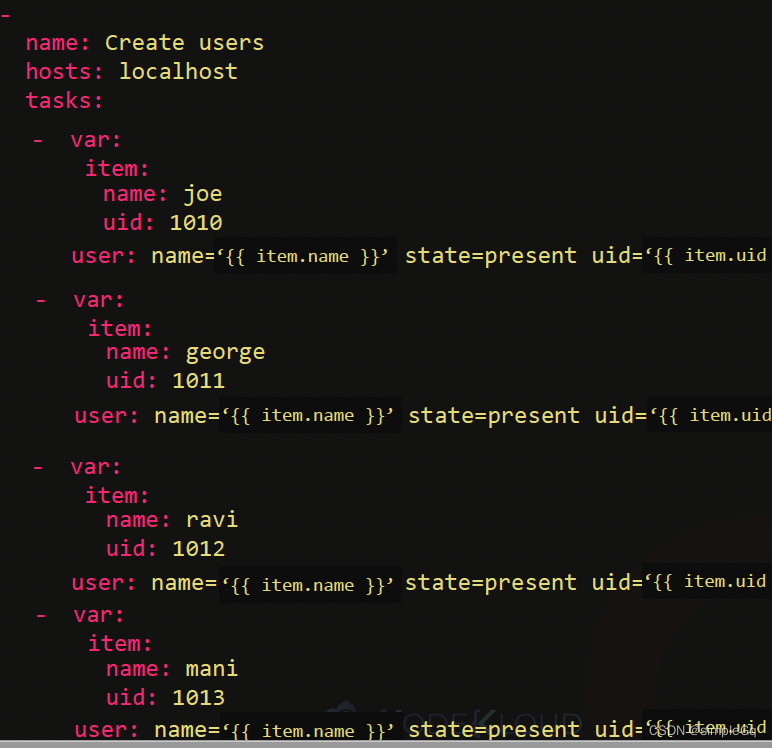
还要注意, 字典数组也可以用json格式表示,如上上图所示。 -
With_*
我们刚才看到的loop指令用于创建简单的循环,这些循环迭代许多项。在Playbook中创建循环还有另一种方法。这就是使用带下划线的指令。
我们开发的这个Playbook也可以像下面这样使用with_items指令来编写。
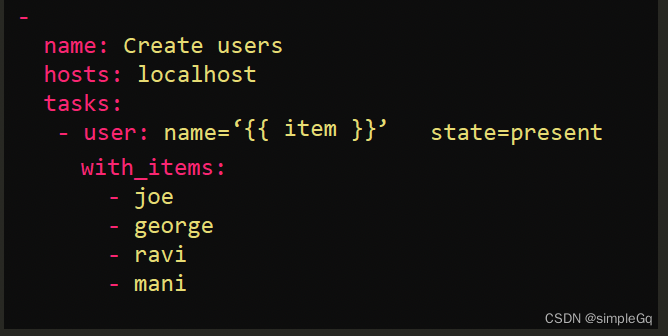
实际上,loop指令是Ansible中新添加的。在过去, 我们只有with_items指令。在这种情况下, 两个Playbook产生相同的结果,两者之间没有太大的区别。对于像我们正在处理的那些简单循环,建议使用loop指令本身。然而, 在一些较旧的剧本中,可能会遇到with_items指令, 因此当您看到它时, 您应该理解它的含义。现在, 让我们看看
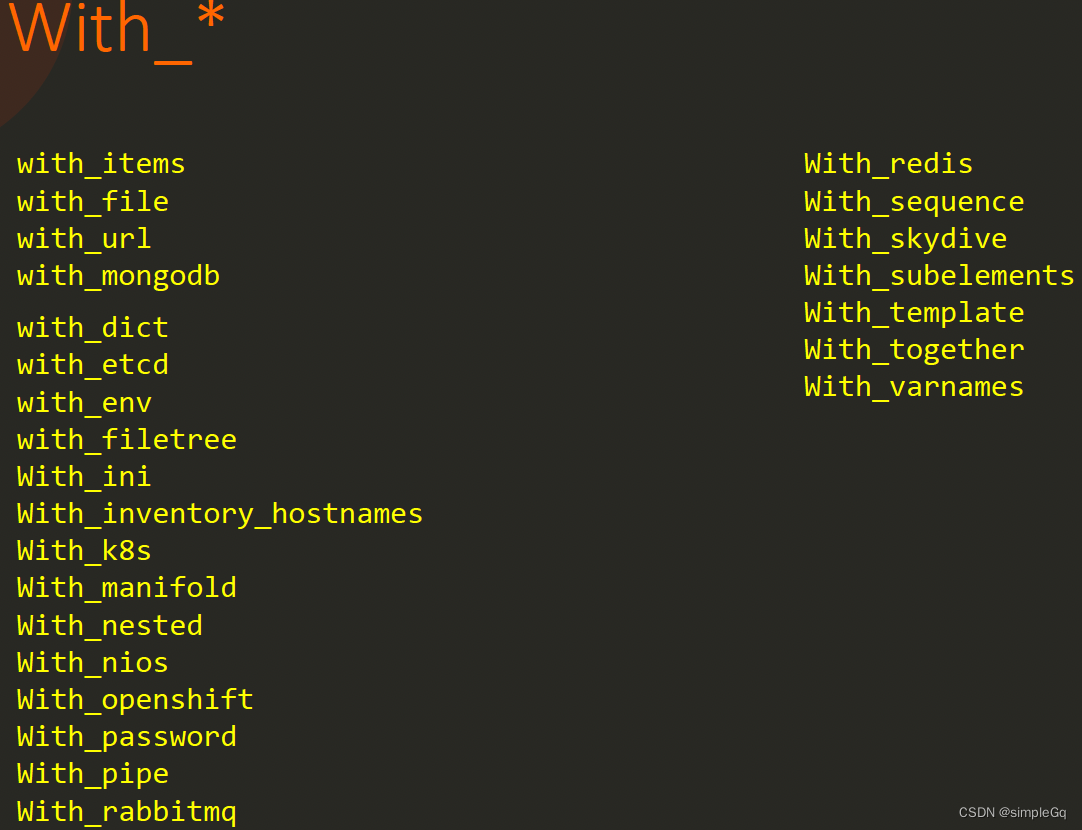
with指示词的优点。With_items只是遍历一个项目列表。我们还有其他的指令, 比如,with_files可以遍历多个文件,with_url可以连接多个url,with_mongodb可以连接多个mongodb数据库。这些只是其中的一部分。
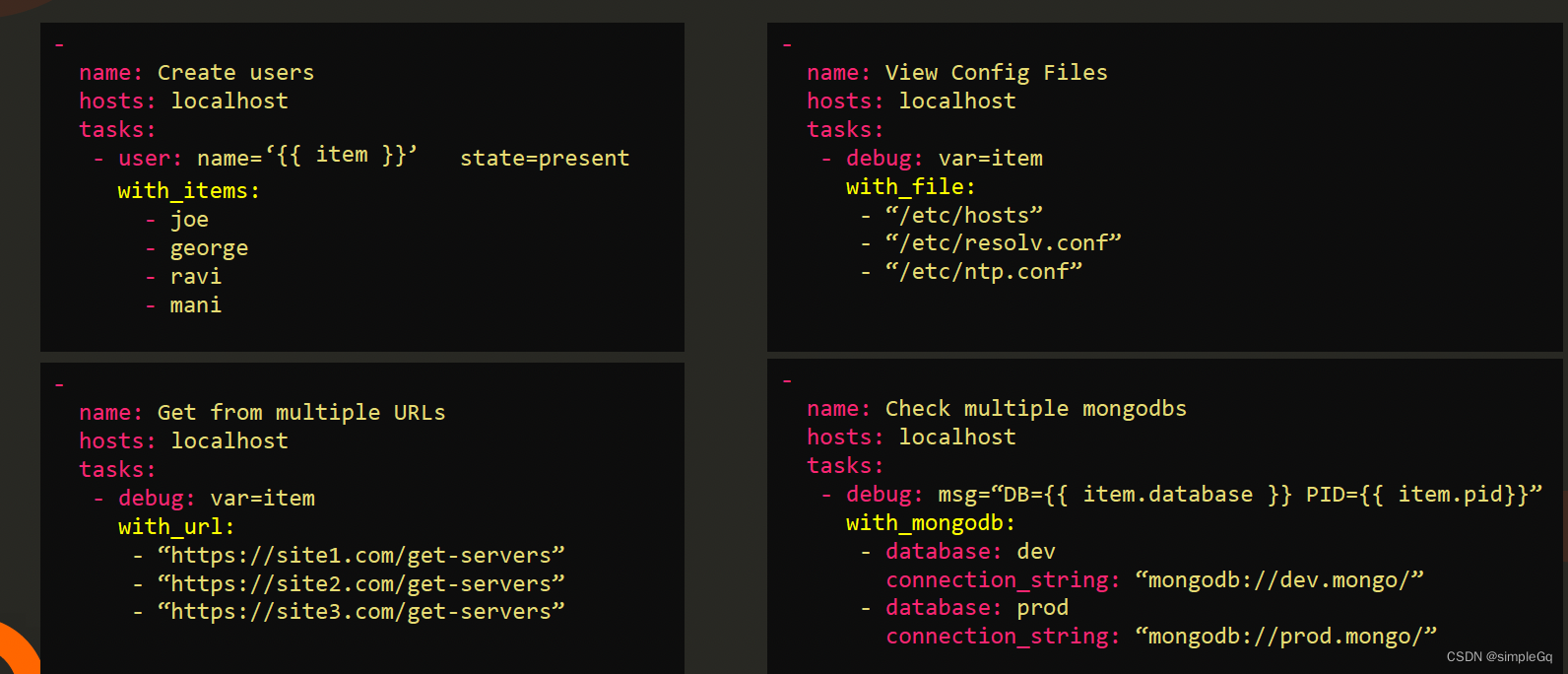
with_*指令有很多。类型属于查找插件(lookup)
-
例子:下面的例子只会输出一个
Apple,请使用with_items让它输出所有的fruits?- name: 'Print list of fruits' hosts: localhost vars: fruits: - Apple - Banana - Grapes - Orange tasks: - command: 'echo "{{ item }}"'答案:
- name: 'Print list of fruits' hosts: localhost vars: fruits: - Apple - Banana - Grapes - Orange tasks: - command: 'echo "{{ item }}"' with_items: '{{ fruits }}'还可以不使用变量,如下:
- name: 'Print list of fruits' hosts: localhost tasks: - command: 'echo "{{ item }}"' with_items: - Apple - Banana - Grapes - Orange下面的例子,只会安装一个
package,改写它,让它能安装所有的package: - name: 'Install required packages' hosts: localhost become: yes vars: packages: - httpd - make - vim tasks: - yum: name: vim state: present答案:
- name: 'Install required packages' hosts: localhost become: yes vars: packages: - httpd - make - vim tasks: - yum: name: '{{ item }}' state: present with_items: '{{ packages }}'更多关于
Ansible的文章,请参考我的Ansible专栏:https://blog.csdn.net/u011069294/category_12331290.html
10.Ansible Loops介绍
news2025/12/13 2:07:36
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.coloradmin.cn/o/598584.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系多彩编程网进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!相关文章
城市二次供水设备远程监控解决方案
城市二次供水设备远程监控解决方案
一、项目背景
近年来,随着我国城市日新月异的发展,新建商场和小区高层逐渐的增多,需要二次供水的楼盘也在逐渐增多。二次供水模式成了城市普遍的供水模式,当前普遍采用传统供水方式存在着供水水源、加压供…
Sentinel怎么使用和控制台讲解
Sentinel 基础
官网
1 Github: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel
2 快速开始: https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html
3 中文: https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/介绍
4 使用手册: https://spring-cloud-alibaba-group.github.io/github-pag…
LNMP搭建过程详解,验证搭建论坛
LNMP搭建过程详解,验证搭建论坛 一、安装Nginx服务1、安装依赖包2、创建运行用户3、编译安装4、优化路径5、添加Nginx 系统服务 二、安装MySQL服务1、安装Mysql环境依赖包2、创建运行用户3、编译安装4、修改mysql配置文件5、更改mysql安装目录和配置文件的属主属组6…
【C/C++】基础知识之输入输出流
创作不易,本篇文章如果帮助到了你,还请点赞 关注支持一下♡>𖥦<)!! 主页专栏有更多知识,如有疑问欢迎大家指正讨论,共同进步! 🔥c系列专栏:C/C零基础到精通 🔥 给大…
改进YOLOv5系列:结合CVPR2021:多头注意力Efficient Multi-Head Self-Attention
Efficient Multi-Head Self-Attention Efficient注意力介绍代码common代码yaml文件参数结果论文:
ResT: An Efficient Transformer for Visual Recognition Efficient注意力介绍 本文提出了一个高效的多尺度视觉变换器,称为ResT,它可以作为图像识别的通用支柱。可以作为图像…
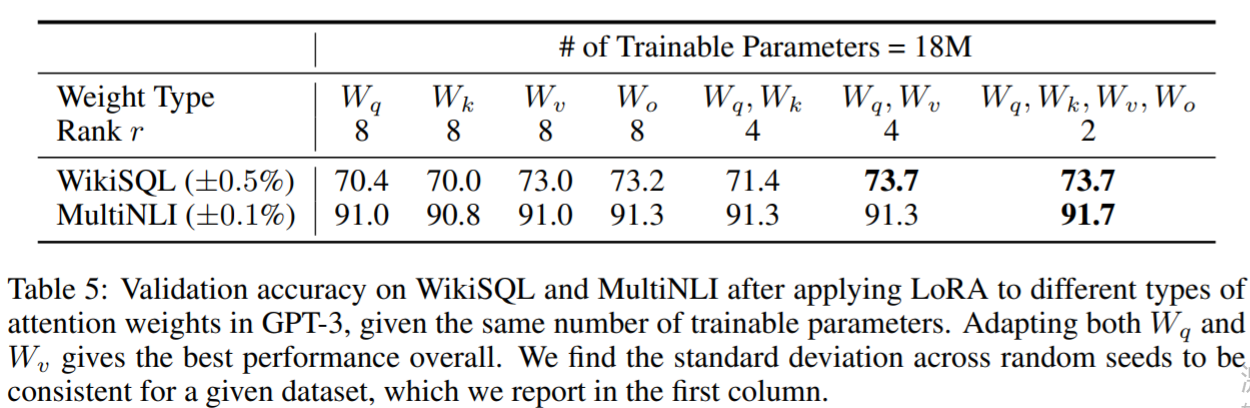
LORA: LOW-RANK ADAPTATION OF LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS
LORA: LOW-RANK ADAPTATION OF LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS (Paper reading)
Edward H, Microsoft, arXiv2021, Cited: 354, Code, Paper
1. 前言
自然语言处理的一个重要范式是在通用领域数据上进行大规模预训练,然后根据特定任务或领域进行适应性训练。随着我们对模…
Hightopo 使用心得(2)- 2D 图纸 GraphView,节点 Node, 连线 Edge,与基本动画 ht.Default.startAnim()
概括来说,用 HT for Web 做可视化主要分为两部分,也就是 2D 和 3D。这两部分需要单独创建。在它们被创建完成后,我们再把它们集成到一起。
HT for Web 的 2D 部分主要是指 ht.graph.GraphView (简称 GraphView,也就是 2D 图纸)。…
设计模式-访问者模式
访问者模式 问题背景解决方案:传统方案 访问者模式基本介绍原理UML类图 使用访问者模式解决问题UML类图示例代码运行结果 注意事项和细节 问题背景
我们来制作一台电脑,他的硬件有CPU和磁盘,CPU和磁盘类都有一个常量作为他们各自的数据&…
java企业级信息系统开发学习笔记10 利用MyBatis实现关联查询
文章目录 一、学习目标(一)针对三张表关联查询(二)按班级编号查询班级信息(三)查询全部班级信息 二、创建数据库(一)创建教师表(二)创建班级表(三…
Linux系统搭建Java的运行环境
目录 JDKTomcatMySQL JDK
对于Linux安装JDK有很多方法~ 这里就掌握最简单的办法—基于yum来进行安装~ yum是“包管理器”,相当于应用商店~
首先,先搜索一下,看看yum上关于jdk有没有,以及叫啥名字~
通过 yum list命令࿰…
六一亲子嘉年华 | 来迅镭激光过一个五彩缤纷的儿童节!
童年是梦,如七彩的画卷; 童年是诗,如璀璨的星空; 童年是歌,如跳跃的音符! 在“六一”儿童节到来之际 为给员工及子女创造一个难忘的亲子时光 迅镭激光开展了六一亲子嘉年华主题活动 让孩子们在迅镭大家庭的…
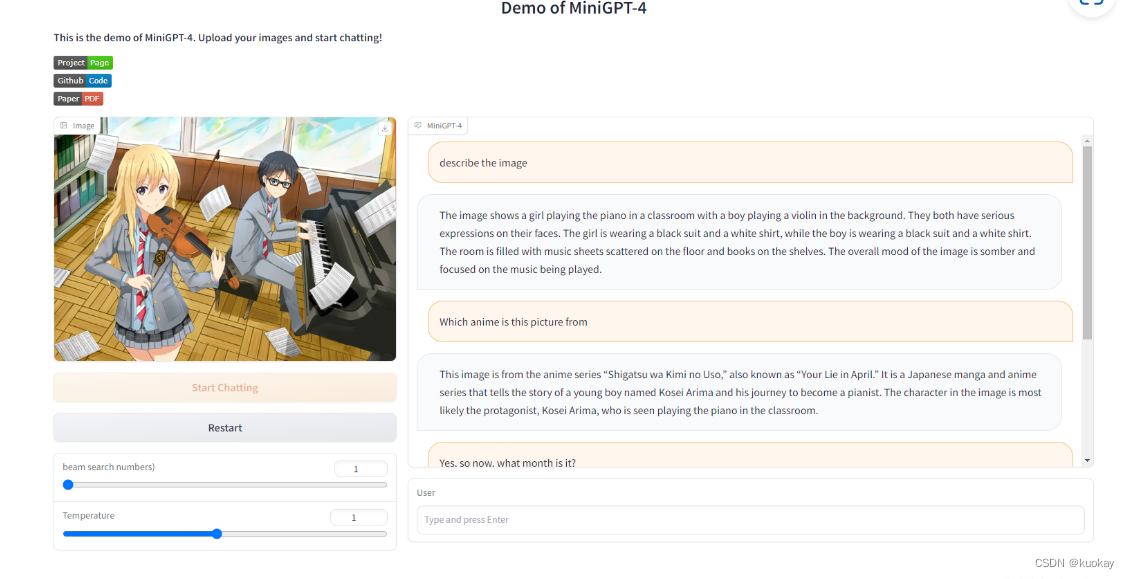
Minigpt4实战搭建
简介
Minigpt4虽然放出了网页版但是使用后发现网页体验的话,由于并发量比较大,很容易突然卡顿的现象,所以下面我主要讲解一下如何进行本地部署。
之前文章已经介绍过Minigpt4了这里就不重复赘述了,不了解的可以去看看https://bl…
使用python开发“魂斗罗”游戏
使用python开发“魂斗罗”游戏 开发完整的魂斗罗(Contra)游戏是一个庞大的任务,它涉及到图形渲染、物理碰撞、敌人AI、游戏关卡等多个方面。在这个简短的交互中,我将向你展示一个基本的魂斗罗风格的游戏框架,你可以在此…
结构化文档发布的故事和性能调优
前阵子一个TW朋友跟我抱怨他们的文档发布很慢。正常发布需要一个晚上才能完成发布。中间如果出点错,就得重新发布,那么中间是漫长的等待。
不像MS Word或者InDesign这样所见即所得的软件,结构化文档源文件是XML格式的,就像计算机…
C语言——数据在内存中的存储(下)
数据在内存中的存储(下)
1. 浮点数在内存中的存储
浮点数家族: float double long double 浮点数的表示范围:
这里要引用float.h头文件 【实例一】
//输出结果是什么?
int main()
{int n 9;float *pFloat (float…
【代码规范】Google开源项目风格指南
系列综述: 💞目的:本系列是个人整理为了秋招面试的,整理期间苛求每个知识点,平衡理解简易度与深入程度。 🥰来源:材料主要源于Google开源项目风格指南进行的,每个知识点的修正和深入…
基于卡尔曼滤波实现线性目标跟踪
文章目录 前言卡尔曼滤波基本推导运算 实现目标检测卡尔曼预测器ID分配器(跟踪器) 完整代码代码总结 前言
一个需求,在一个稳定的场景当中,实现目标检测计数算法。
任务点: 实现目标检测完成对不同类别的物品进行计数…
Three.js--》实现3d字体模型展示
目录
项目搭建
初始化three.js基础代码
设置环境纹理
加载字体模型 今天简单实现一个three.js的小Demo,加强自己对three知识的掌握与学习,只有在项目中才能灵活将所学知识运用起来,话不多说直接开始。
项目搭建
本案例还是借助框架书写…