概述
经常会在业务中遇到需要在项目启动后刷新/预热一些数据的要求。
常见可以监听ApplicationReadyEvent和ContextRefreshedEvent.
但是因为常见的springboot项目都依赖的springmvc,所以实际上有2个容器,spring的ioc容器是springmvc的父容器。
而且ContextRefreshedEvent实际中会发布多次,如果业务只需要执行一次的情况话是不太适合监听这个的。
发布多次的原因是每加载完一次context,就会执行一次ContextRefreshedEvent而且每次执行,都会再执行一次parent的ContextRefreshedEvent.上面提到父子容器都会触发这个事件
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#publishEvent(java.lang.Object, org.springframework.core.ResolvableType)
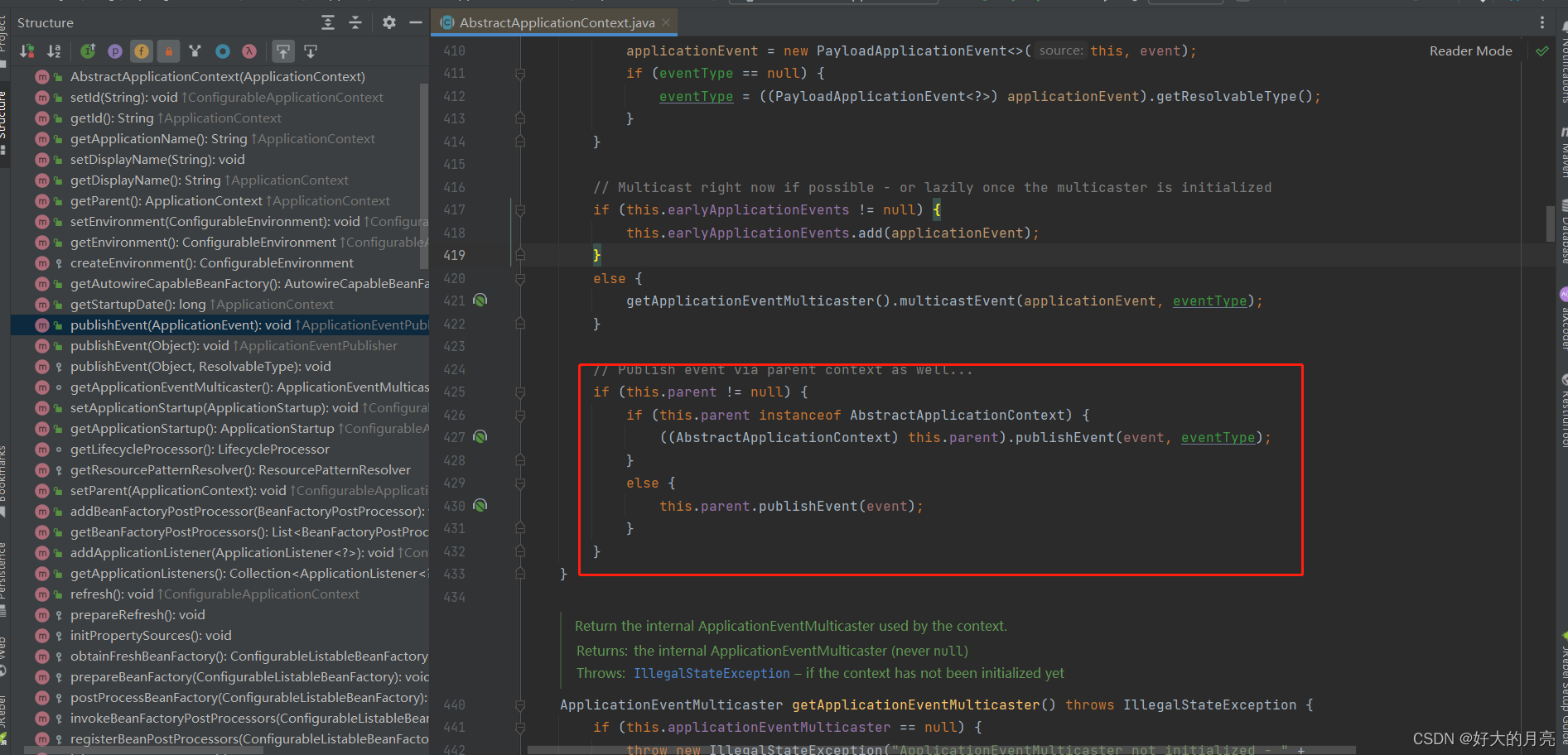
只想在启动后执行一次demo
可以监听ApplicationReadyEvent事件
package com.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx;
import cn.hutool.extra.spring.SpringUtil;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class xxxRefreshEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationReadyEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
//刷新配置
refreshTargetProperties();
}
private <T> T refreshObjProperties(Class<T> objClass){
try {
T bean = SpringUtil.getBean(objClass);
BusinessProperties annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(objClass, BusinessProperties.class);
if(Objects.isNull(annotation)){
return bean;
}
//配置前缀
String prefix = annotation.prefix();
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass());
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors()) {
String name = propertyDescriptor.getName();
Class<?> propertyType = propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType();
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
//完成的config key
String configKey = String.join(".", prefix, name);
//获取数据
xxx info = xxx.xxx(configKey);
if(Objects.isNull(info )){
continue;
}
//db中存放的值
String configValue = info.getConfigValue();
//给属性填充值
if(Objects.equals(propertyType, String.class)){
writeMethod.invoke(bean, configValue);
}else {
Object propertyValue = objectMapper.readValue(configValue, propertyType);
writeMethod.invoke(bean, propertyValue);
}
}
return bean;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("刷新配置异常,class:{}", objClass, e);
return null;
}
}
}
spring关键的几个事件
ContextClosedEventspring容器关闭事件ContextRefreshedEventspring容器的初始化后或者刷新完成事件;ContextStoppedEventspring容器停止事件ContextStartedEventspring容器初始化开始事件
3和4其实是spring生命周期相关的事件,1是整个spring容器销毁的事件。
springboot对spring容器周期事件的扩展
springboot对于spring的事件又有自己的扩展.
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent容器环境对象初始化后的事件ApplicationPreparedEvent容器初始化前的事件,主要是在做refresh动作之前做触发的事件ApplicationStartedEvent容器已经完成 refresh 动作后所触发的事件ApplicationReadyEvent容器已经运行中的事件ApplicationFailedEvent容器初始化失败所触发的事件ApplicationStartingEvent容器开始时所触发的事件
触发顺序如下
ApplicationStartingEvent ->
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent ->
ApplicationPreparedEvent ->
ContextStartedEvent ->
ContextRefreshedEvent ->
ApplicationStartedEvent ->
ApplicationReadyEvent