目录
225. 用队列实现栈 Implement Stack Using Queues 🌟
232. 用栈实现队列 Implement Queue Using Stacks 🌟
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
Rust每日一练 专栏
Golang每日一练 专栏
Python每日一练 专栏
C/C++每日一练 专栏
Java每日一练 专栏
225. 用队列实现栈 Implement Stack Using Queues
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。int top()返回栈顶元素。boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false。
注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是
push to back、peek/pop from front、size和is empty这些操作。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例:
输入: ["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 2, 2, false] 解释: MyStack myStack = new MyStack(); myStack.push(1); myStack.push(2); myStack.top(); // 返回 2 myStack.pop(); // 返回 2 myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
提示:
1 <= x <= 9- 最多调用
100次push、pop、top和empty - 每次调用
pop和top都保证栈不为空
进阶:你能否仅用一个队列来实现栈。
代码:
package main
import "fmt"
type MyStack struct {
que1, que2 []int
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
func Constructor() MyStack {
return MyStack{}
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
func (this *MyStack) Push(x int) {
this.que2 = append(this.que2, x)
for len(this.que1) > 0 {
this.que2 = append(this.que2, this.que1[0])
this.que1 = this.que1[1:]
}
this.que1, this.que2 = this.que2, this.que1
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
func (this *MyStack) Pop() int {
x := this.que1[0]
this.que1 = this.que1[1:]
return x
}
/** Get the top element. */
func (this *MyStack) Top() int {
return this.que1[0]
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
func (this *MyStack) Empty() bool {
return len(this.que1) == 0
}
func main() {
myStack := Constructor()
myStack.Push(1)
myStack.Push(2)
fmt.Println(myStack.Top()) // 输出2
fmt.Println(myStack.Pop()) // 输出2
fmt.Println(myStack.Empty()) // 输出false
}
输出:
2
2
false
232. 用栈实现队列 Implement Queue Using Stacks
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
说明:
- 你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有
push to top,peek/pop from top,size, 和is empty操作是合法的。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
示例:
输入: ["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 1, 1, false] 解释: MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1] myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue) myQueue.peek(); // return 1 myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2] myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示:
1 <= x <= 9- 最多调用
100次push、pop、peek和empty - 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用
pop或者peek操作)
进阶:
- 你能否实现每个操作均摊时间复杂度为
O(1)的队列?换句话说,执行n个操作的总时间复杂度为O(n),即使其中一个操作可能花费较长时间。
代码:
package main
import "fmt"
type MyQueue struct {
inStack, outStack []int
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
func Constructor() MyQueue {
return MyQueue{}
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
func (this *MyQueue) Push(x int) {
this.inStack = append(this.inStack, x)
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
func (this *MyQueue) Pop() int {
this.move()
x := this.outStack[len(this.outStack)-1]
this.outStack = this.outStack[:len(this.outStack)-1]
return x
}
/** Get the front element. */
func (this *MyQueue) Peek() int {
this.move()
return this.outStack[len(this.outStack)-1]
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
func (this *MyQueue) Empty() bool {
return len(this.inStack) == 0 && len(this.outStack) == 0
}
func (this *MyQueue) move() {
if len(this.outStack) == 0 {
for len(this.inStack) > 0 {
this.outStack = append(this.outStack, this.inStack[len(this.inStack)-1])
this.inStack = this.inStack[:len(this.inStack)-1]
}
}
}
func main() {
myQueue := Constructor()
myQueue.Push(1) // 队列变成[1]
myQueue.Push(2) // 队列变成[1, 2]
fmt.Println(myQueue.Peek()) // 输出1
fmt.Println(myQueue.Pop()) // 输出1,队列变成[2]
fmt.Println(myQueue.Empty()) // 输出false
}
输出:
1
1
false
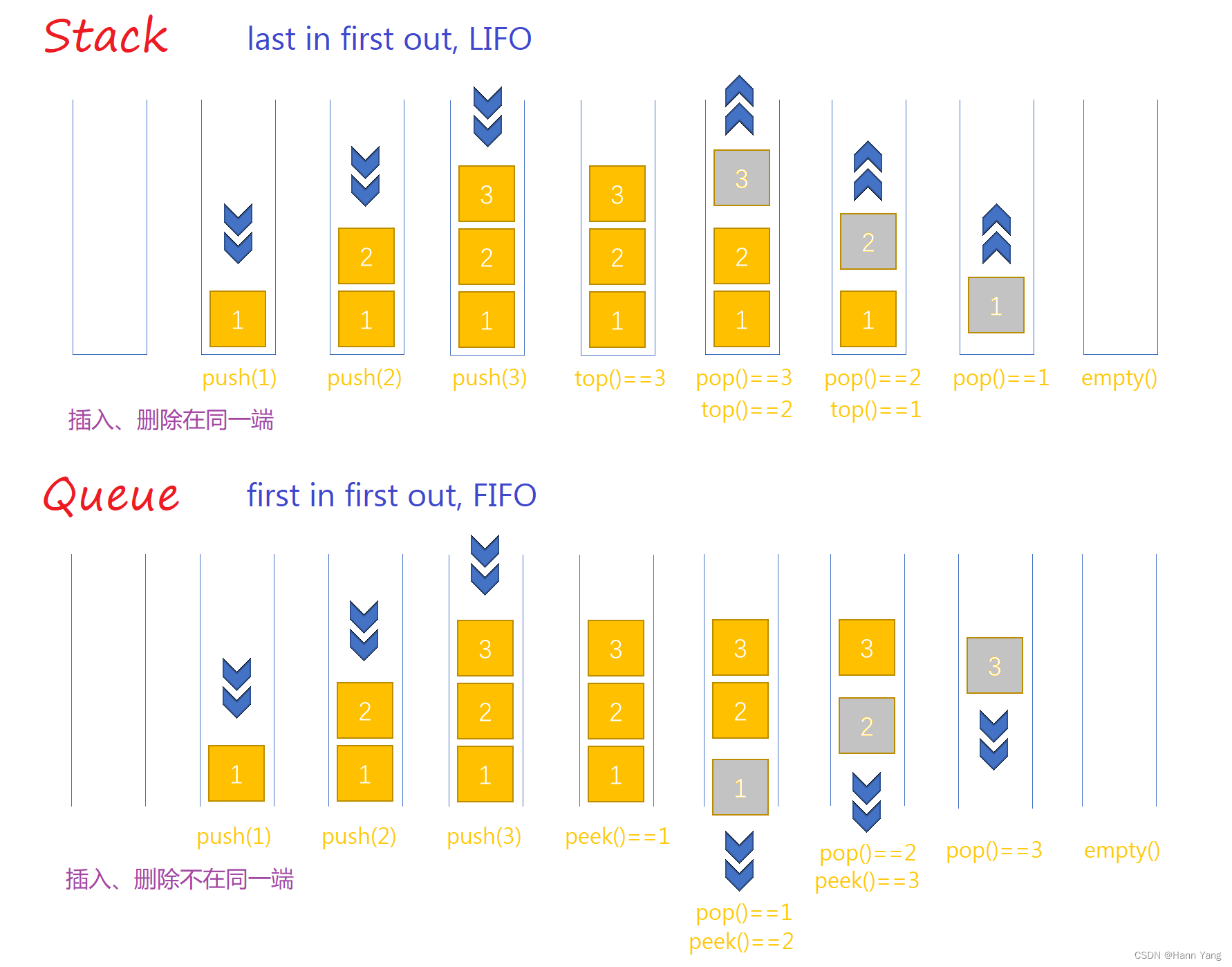
Stack和Queue
都是一种线性数据结构,其主要区别在于数据的操作方式。
Stack
是一种后进先出(Last In First Out,LIFO)的数据结构,即最后一个入栈的元素最先出栈,其操作包括压栈(push)和弹栈(pop)。
Queue
是一种先进先出(First In First Out,FIFO)的数据结构,即最先入队的元素最先出队,其操作包括入队(enqueue)和出队(dequeue)。
相同点
在于都可以使用数组或链表来实现,同时都是基于线性结构的数据类型。
不同点
在于其数据操作的方式不同,Stack的操作方式是LIFO,而Queue的操作方式是FIFO。
两种数据结构在不同的场景下有不同的应用,比如在计算机中的函数调用中常用Stack来实现函数调用栈,而在消息队列中则常用Queue来实现消息的异步处理。
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
✨ 持续,努力奋斗做强刷题搬运工!
👍 点赞,你的认可是我坚持的动力!
🌟 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✎ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!
☸ 主页:https://hannyang.blog.csdn.net/
|
| Rust每日一练 专栏(2023.5.16~)更新中... |
|
| Golang每日一练 专栏(2023.3.11~)更新中... |
|
| Python每日一练 专栏(2023.2.18~2023.5.18)暂停更 |
|
| C/C++每日一练 专栏(2023.2.18~2023.5.18)暂停更 |
|
| Java每日一练 专栏(2023.3.11~2023.5.18)暂停更 |