存储框架封装:LruCacheUtils+DiskLruCacheUtils+责任链设计模式+DeepLink
- 一.存储框架实现思路?
- 1.缓存策略
- 2.LRU算法
- 3.LruCache内存缓存原理
- 4.DiskLruCache磁盘缓存原理
- 5.使用单例模式实现LRUCacheUtils
- 5.使用单例模式实现DiskLRUCacheUtils
- 二.什么是责任链设计模式?
一.存储框架实现思路?
思路来源与图片的三级缓存,即:内存->磁盘->网络
对于部分数据(如:静态数据或者配置信息)我们可能同样需要进行缓存来提升效率,
具体实现思路如下:
1、使用多级缓存完成资源的复用 如:内存 -> 磁盘 ->…
2、使用责任链设计模式,可以通过自定义添加链节点完成多级缓存
3、使用LruCache完成内存部分存储
4、使用DiskLruCache完成磁盘部分存储
1.缓存策略
缓存策略主要包含缓存的添加、获取和删除三类操作。删除缓存是因为不管是内存缓存还是硬盘缓存,它们的缓存大小都是有限的。当缓存满了之后,再想添加缓存就需要删除一些旧的缓存。
2.LRU算法
Android的三级缓存主要的就是内存缓存和硬盘缓存。这两种缓存机制的实现都应用到了LRU算法。
LRU(Least Recently Used)缓存算法是近期最少使用算法,它的核心思想是当缓存满时,会优先淘汰那些近期最少使用的缓存对象。
3.LruCache内存缓存原理
LruCache是Android 3.1提供的一个缓存类,在Android中可以直接使用LruCache实现内存缓存。而硬盘缓存DisLruCache目前还不是Android SDK的一部分,但Android官方文档推荐使用该算法来实现硬盘缓存。
LruCache的核心思想就是维护一个缓存对象列表,这个队列就是由LinkedHashMap维护的。列表的排列方式按照访问顺序实现,即一直没访问的对象,将放在队尾,即将被淘汰,而最近访问的对象将放在队头,最后被淘汰。
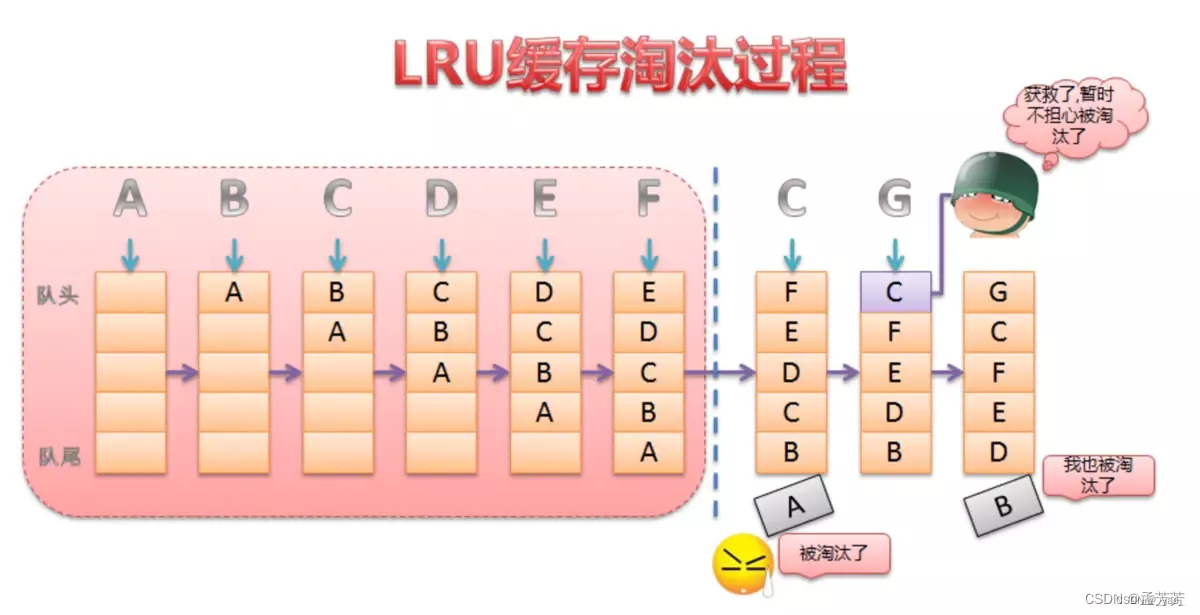
LinkedHashMap由数组+双向链表实现。其中双向链表的结构可以实现访问顺序和插入顺序,使得LinkedHashMap中的<key,value>对按照一定顺序排列起来。
LinkedHashMap通过构造函数来指定双向链表的结构是访问顺序还是插入顺序。
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
accessOrder为true是访问顺序,为false是插入顺序。
比如,当设置accessOrder为true时:
public static final void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(0, 0.75f, true);
map.put(0, 0);
map.put(1, 1);
map.put(2, 2);
map.put(3, 3);
map.put(4, 4);
map.put(5, 5);
map.put(6, 6);
map.get(1);
map.get(2);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
输出结果:
0:0
3:3
4:4
5:5
6:6
1:1
2:2
即最近访问的最后输出,这正好满足LRU缓存算法的思想。LruCache的实现就是利用了LinkedHashMap的这种数据结构
4.DiskLruCache磁盘缓存原理
磁盘读写也是用的LRU算法。但是这个和内存的LRU算法有一点小区别。为什么呢?因为内存缓存是我们运行的时候,程序加载内存里面的资源,可以直接通过一个LinkedHashMap去实现。但是磁盘不同,我总不可能吧所有磁盘的资源读出来然后加载在内存里面吧,这样的话,肯定会引发oom了。那么Glide是怎么做磁盘的LRU的呢?
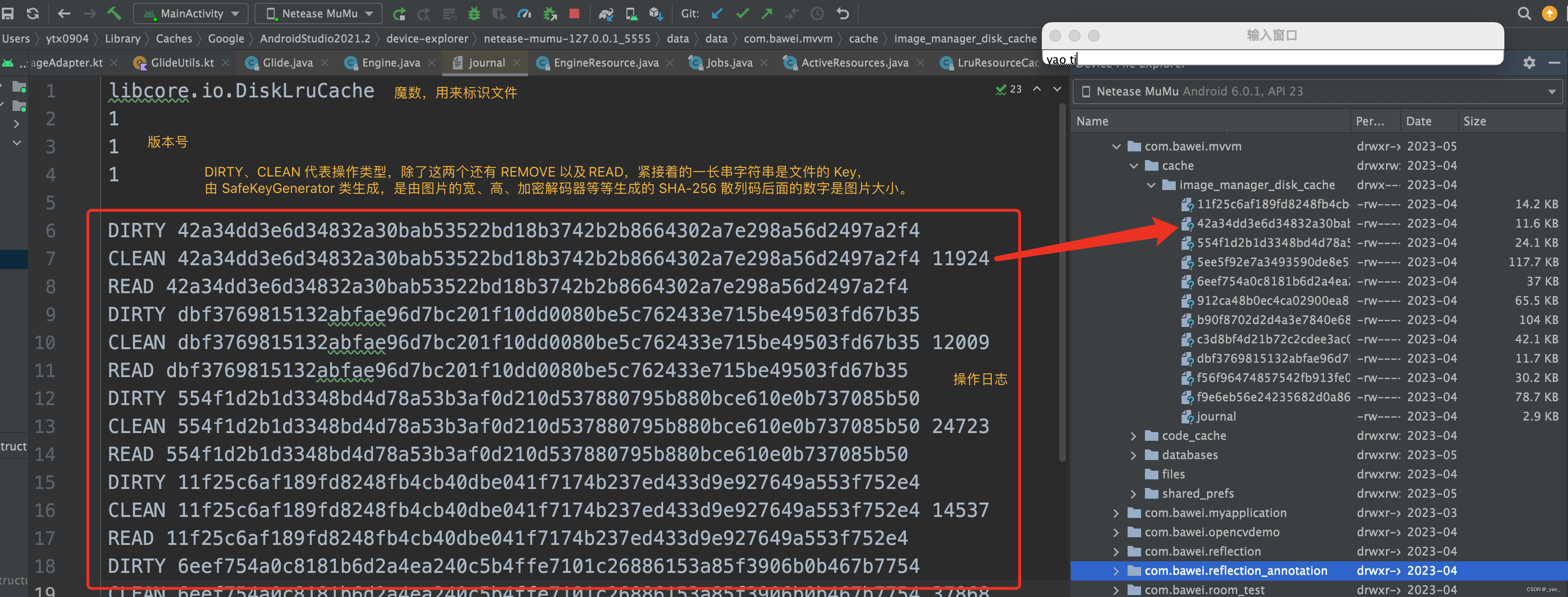
Glide 是使用一个日志清单文件来保存这种顺序,DiskLruCache 在 APP 第一次安装时会在缓存文件夹下创建一个 journal 日志文件来记录图片的添加、删除、读取等等操作,后面每次打开 APP 都会读取这个文件,把其中记录下来的缓存文件名读取到 LinkedHashMap 中,后面每次对图片的操作不仅是操作这个 LinkedHashMap 还要记录在 journal 文件中. journal 文件内容如下图:
data/data/应用包名/cache/。。。。。
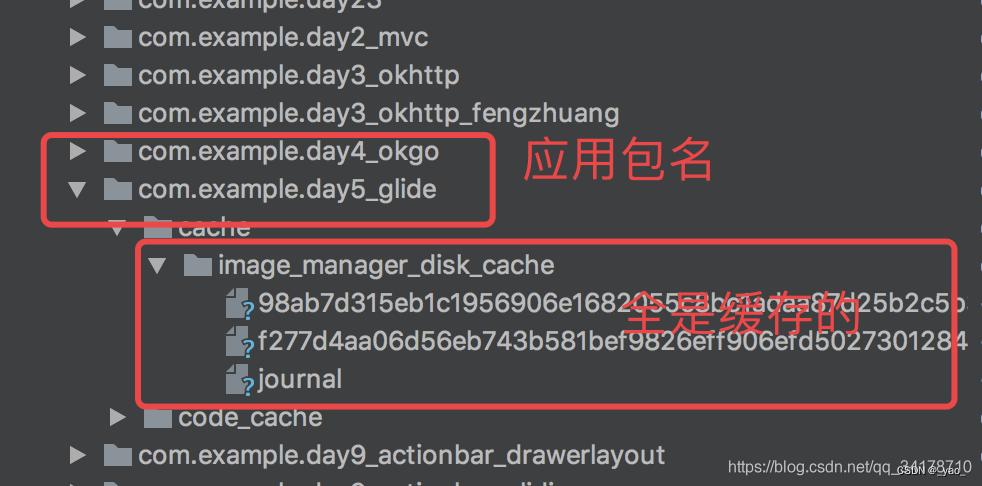
日志文件:
5.使用单例模式实现LRUCacheUtils
**********kotlin单例模式(掌握)
java版本
public class LRUCacheUtils<V> {
int maxSize= (int) (Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory()/8);
private LRUCacheUtils(){
lruCache=new LruCache<String, V>(maxSize);
}
private static volatile LRUCacheUtils instance=null;
public static LRUCacheUtils getInstance(){
if (null==instance){
synchronized (LRUCacheUtils.class){
if (null==instance){
instance=new LRUCacheUtils();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
LruCache<String,V> lruCache=null;
/**
* 按Key存储值
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void putValue(String key,V value){
lruCache.put(key,value);
}
/**
* 按Key获取值
* @param key
* @return
*/
public V getValue(String key){
return lruCache.get(key);
}
/**
* 按Key删除指定值
* @param key
*/
public void removeValue(String key){
lruCache.remove(key);
}
/**
* 清空
*/
public void clear(){
lruCache.evictAll();
}
}
kotlin版本
/**
* @Author : yaotianxue
* @Time : On 2023/5/23 07:59
* @Description : LRUCacheUtils
*/
class LRUCacheUtils<V> {
var maxSize = (Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory() / 8).toInt()//内存的1/8
var lruCache:LruCache<String,V> = LruCache<String,V>(maxSize)//lruCache
//双重锁单例模式
companion object{
val instance by lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode.SYNCHRONIZED) {
LRUCacheUtils<Any>()
}
}
/**
* 按Key存储值
*/
fun putValue(key:String,value:V){
lruCache.put(key,value)
}
/**
* 按Key获取值
*/
fun getValue(key:String): V? {
return lruCache.get(key)
}
/**
* 按key删除
*/
fun removeValue(key:String){
lruCache.remove(key)
}
/**
* 清空
*/
fun clear(){
lruCache.evictAll()
}
}
5.使用单例模式实现DiskLRUCacheUtils
java版本
public final class DiskLRUCacheUtils<V> {
private DiskLruCache diskLruCache;
private static DiskLRUCacheUtils instance=new DiskLRUCacheUtils();
/**
* 容量上限200M
*/
private static final int MAX_SIZE=200*1024*1024;
private DiskLRUCacheUtils(){
/**
* 如下 初始化DiskLruCache
*/
String diskCachePath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath()+ File.separator+"bawei6diskcache";
File file=new File(diskCachePath);
if (!file.exists()){
file.mkdirs();
}
try {
diskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(file, 1, 1, MAX_SIZE);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static DiskLRUCacheUtils getInstance(){
return instance;
}
public void putValue(String key, V data) {
String mKey= MD5.encrypt(key);
OutputStream outputStream = null;
DiskLruCache.Editor edit=null;
try {
edit = diskLruCache.edit(mKey);
if (edit!=null){
//对象转byte数组
byte[] bytes= ObjUtils.obj2ByteArray(data);
outputStream = edit.newOutputStream(0);
outputStream.write(bytes);
edit.commit();
diskLruCache.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (edit!=null){
try {
edit.abort();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}finally {
if (outputStream!=null){
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public V getValue(String key) {
InputStream is=null;
try {
List<Byte> data = new ArrayList<>();
String mKey = MD5.encrypt(key);
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapShot = diskLruCache.get(mKey);
if (snapShot != null) {
is = snapShot.getInputStream(0);
byte[] bytes = new byte[2048];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(bytes)) != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
data.add(bytes[i]);
}
}
bytes = new byte[data.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
bytes[i] = data.get(i);
}
return ObjUtils.byteArray2Object(bytes);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (is!=null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return null;
}
public void removeValue(String key) {
String mKey=MD5.encrypt(key);
try {
diskLruCache.remove(mKey);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void clear() {
try {
diskLruCache.delete();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
kotlin版本
/**
* @Author : yaotianxue
* @Time : On 2023/5/23 08:09
* @Description : DiskLRUCacheUtils
*/
class DiskLRUCacheUtils<V> {
//磁盘缓存路径
private var diskCachePath:String = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().absolutePath + File.separator +"2010baweidiskcache"
//磁盘缓存对象
var diskCache: DiskLruCache
//初始化
init {
var file = File(diskCachePath)
if(!file.exists()){//文件夹不存在
file.mkdirs()//创建文件夹
}
diskCache = DiskLruCache.open(file,1,1, MAX_SIZE.toLong())
}
companion object{
const val MAX_SIZE = 200*1024*1024
val instance by lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode.SYNCHRONIZED){
DiskLRUCacheUtils<Any>()
}
}
/**
* 按Key存储值
*/
fun putValue(key:String,data:V){
var mKey = MD5.encrypt(key)//使用工具类将keyMD5加密
var editor = diskCache.edit(mKey)
editor.let {
var arrays = ObjUtils.obj2ByteArray(data)//对象转数组
var outputStream = editor.newOutputStream(0)
outputStream.write(arrays)
editor.commit()
diskCache.flush()
outputStream.close()
}
}
/**
* 按Key获取值
*/
fun getValue(key:String): V? {
var mKey = MD5.encrypt(key)//使用工具类将keyMD5加密
var snapshot = diskCache.get(mKey)//根据键获得snapshot对象
var inputStream = snapshot.getInputStream(0)//获得输入流
var bytes = ByteArray(2048)
var outputStream = ByteArrayOutputStream()//字节数组输出流
var len = 0
//inputStream读取数据到outputStream
while ((inputStream.read(bytes).also { len = it })!=-1){
outputStream.write(bytes)
}
return ObjUtils.byteArray2Object(outputStream.toByteArray())
}
/**
* 按key删除
*/
fun removeValue(key:String){
var mKey = MD5.encrypt(key)//使用工具类将keyMD5加密
diskCache.remove(mKey)
}
/**
* 清空
*/
fun clear(){
diskCache.delete()
}
}
测试使用
//测试
var diskLRUCacheUtils = DiskLRUCacheUtils.instance.putValue("111","我是测试数据")
var str = DiskLRUCacheUtils.instance.getValue("111")
Toast.makeText(this,"$str",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
二.什么是责任链设计模式?
顾名思义,责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility
Pattern)为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链。这种模式给予请求的类型,对请求
的发送者和接收者进行解耦。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式。
在这种模式中,通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。如果一个对象不
能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下一个接收者,依此类推。
实现参考链接:https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/chain-of-responsibility-pattern.html