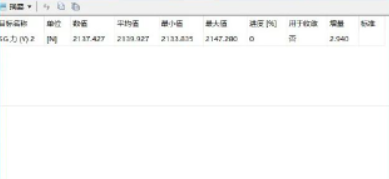
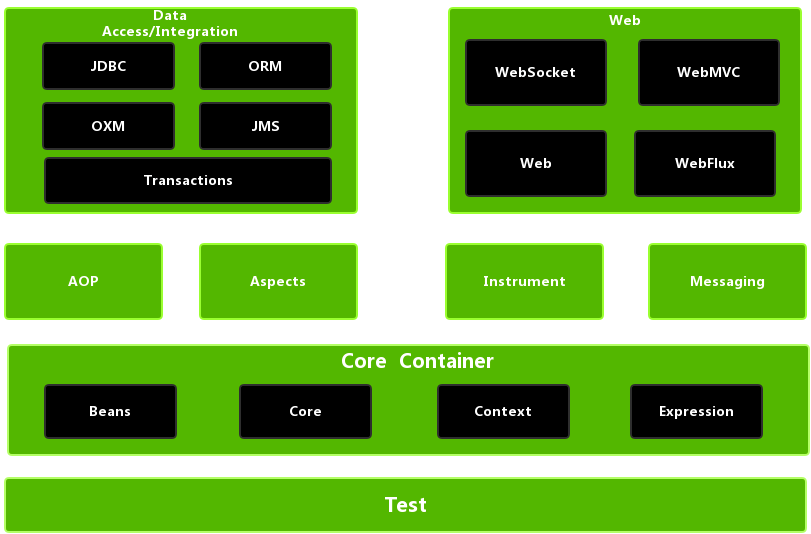
管道,通常指无名管道,是 UNIX 系统IPC(InterProcess Communication)最古老的形式。
1、特点:
1.它是半双工的(即数据只能在一个方向上流动) ,具有固定的读端和写端
2.它只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程之间的通信(也是子进程或者兄弟进程之间)。
3.它可以看成是一种特殊的文件,对于它的读写也可以使用普通的read、write 等函数。但是它不是普通的文件,并不属于其他任文件系统,并且只存在于内存中。
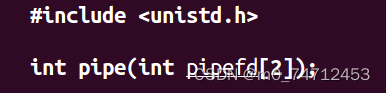

管道编程实例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
int main()
{
int fd[2];
int pid;
char buf[128];
if(pipe(fd) == -1){
printf("creat pipe failed\n");
}
pid = fork();
if(pid<0){
printf("creat child failed\n");
}
else if(pid > 0){
sleep(3);
printf("this is father\n");
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1],"hello from father",strlen("hello form father"));
wait();
}else{
printf("this is child\n");
close(fd[1]);
read(fd[0],buf,128);
printf("read from father: %s\n",buf);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}