文章目录
- 思考迭代器模式
- 1.迭代器模式的本质
- 2.何时选用迭代器模式
- 3.优缺点
- 4.实现
- 手动实现迭代器模式
- java迭代器模式
思考迭代器模式
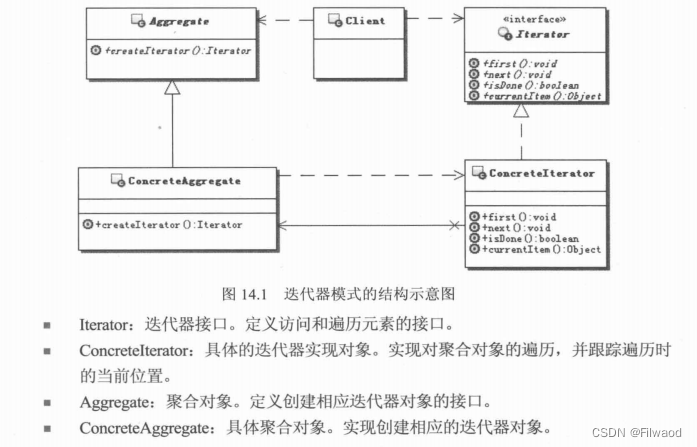
迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)是常用的设计模式,属于行为型模式。如果我们的集合元素是用不同的方式实现的,有数组,还有java的集合类,或者还有其他方式,当客户端要遍历这些集合元素的时候就要使用多种遍历方式,而且还会暴露元素的内部结构,可以考虑使用迭代器模式解决。
迭代器模式,提供一种遍历集合元素的统一接口,用一致的方法遍历集合元素,不需要知道集合对象的底层表示,即不暴露其内部的结构。
1.迭代器模式的本质
迭代器模式的本质:控制访问聚合对象中的元素。
迭代器模式的功能主要在于提供对聚合对象的迭代访问。迭代器就围绕着这个“访问”做文章,延伸出很多的功能来。比如:
- 以不同的方式遍历聚合对象,比如向前、向后等。对同一个聚合同时进行多个遍历。
- 以不同的遍历策略来遍历聚合,比如是否需要过滤等。
- 多态迭代,含义是:为不同的聚合结构提供统一的迭代接口,也就是说通过一个迭代接口可以访问不同的聚合结构,这就叫做多态迭代。上面的示例就已经实现了多态迭代。事实上,标准的迭代模式实现基本上都是支持多态迭代的。
聚合对象的类型很多,如果对聚合对象的迭代访问跟聚合对象本身融合在一起的话,会严重影响到聚合对象的可扩展性和可维护性。
因此迭代器模式的关键思想就是把对聚合对象的遍历和访问从聚合对象中分离出来,放入单独的迭代器中,这样聚合对象会变得简单一些;而且迭代器和聚合对象可以独立地变化和发展,会大大加强系统的灵活性。
2.何时选用迭代器模式
建议在以下情况中选用迭代器模式。
-
如果你希望提供访问一个聚合对象的内容,但是又不想暴露它的内部表示的时候,可以使用迭代器模式来提供迭代器接口,从而让客户端只是通过迭代器的接口来访问聚合对象,而无须关心聚合对象的内部实现。
-
如果你希望有多种遍历方式可以访问聚合对象,可以使用迭代器模式。
-
如果你希望为遍历不同的聚合对象提供一个统一的接口,可以使用迭代器模式。
3.优缺点
迭代器模式的优点。
- 更好的封装性
- 迭代器模式可以让你访问一个聚合对象的内容,而无须暴露该聚合对象的内部表示,从而提高聚合对象的封装性。
- 可以以不同的遍历方式来遍历一个聚合
- 使用迭代器模式,使得聚合对象的内容和具体的迭代算法分离开。这样就可以通过使用不同的迭代器的实例、不同的遍历方式来遍历一个聚合对象了,比如上面示例的带迭代策略的迭代器。
- 迭代器简化了聚合的接口
- 有了迭代器的接口,则聚合本身就不需要再定义这些接口了,从而简化了聚合的接口定义。
- 简化客户端调用
- 迭代器为遍历不同的聚合对象提供了一个统一的接口,使得客户端遍历聚合对象的内容变得更简单。
- 同一个聚合上可以有多个遍历
- 每个迭代器保持它自己的遍历状态,比如前面实现中的迭代索引位置,因此可以对同一个聚合对象同时进行多个遍历。
4.实现
手动实现迭代器模式
一个学院有多个系,计算机学院用数组存的,数学学院用集合存的,其他学院也是有的用数组存,有的用集合存,因为遍历集合和遍历数组的代码不同,遍历所有学院很困难,可以用迭代器模式实现这个效果
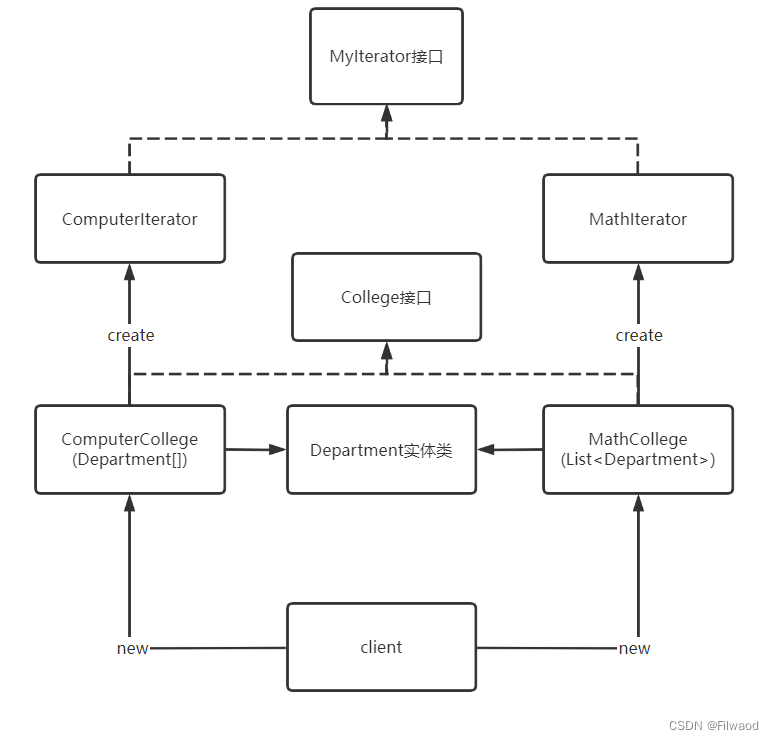
1.迭代器类
/**
* @description:自己实现的迭代器接口
*/
public interface MyIterator {
/**
* 移动到第一个元素
*/
void first();
/**
* 移动到下一个元素
*/
void next();
/**
* 判断是否是最后一个元素
* @return
*/
boolean isDone();
/**
* 获取当前元素
* @return
*/
Object currentItem();
}
/**
* @description:计算机学院迭代器
*/
public class ComputerIterator implements MyIterator{
/**
* 计算机学院对象
*/
private ComputerCollege computerCollege=null;
/**
* 记录索引位置
*/
private int index=-1;
public ComputerIterator(ComputerCollege computerCollege) {
this.computerCollege = computerCollege;
}
@Override
public void first() {
index=0;
}
@Override
public void next() {
if (index<this.computerCollege.size()){
index++;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
if (index==this.computerCollege.size()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Object currentItem() {
return this.computerCollege.get(index);
}
}
/**
* @description:计算机学院迭代器
*/
public class MathIterator implements MyIterator{
private MathCollege mathCollege;
private int index=-1;
public MathIterator(MathCollege mathCollege) {
this.mathCollege = mathCollege;
}
@Override
public void first() {
index=0;
}
@Override
public void next() {
if (index<this.mathCollege.size()){
index++;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
if (index==this.mathCollege.size()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Object currentItem() {
return this.mathCollege.get(index);
}
}
2.学院类
/**
* @description:学院接口
*/
public interface College {
/**
* 创建迭代器
* @return
*/
MyIterator createIterator();
}
/**
* @description:计算机学院类
*/
public class ComputerCollege implements College{
private Department[] departments=null;
@Override
public MyIterator createIterator() {
//初始化数据
departments=new Department[3];
departments[0]=new Department(1,"软件");
departments[1]=new Department(2,"通信");
departments[2]=new Department(3,"电子");
return new ComputerIterator(this);
}
/**
* 获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
public Object get(int index){
Object obj=null;
if (index<this.departments.length){
obj=departments[index];
}
return obj;
}
/**
* 返回学院下系的数量
* @return
*/
public int size(){
return this.departments.length;
}
}
/**
* @description:数学学院类
*/
public class MathCollege implements College{
private List<Department> departmentList=null;
@Override
public MyIterator createIterator() {
//初始化数据
departmentList=new ArrayList<>();
departmentList.add(new Department(1,"数学系"));
departmentList.add(new Department(2,"概率系"));
departmentList.add(new Department(3,"统计系"));
return new MathIterator(this);
}
/**
* 获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
public Object get(int index){
Object obj=null;
if (index<this.departmentList.size()){
obj=departmentList.get(index);
}
return obj;
}
/**
* 返回学院下系的数量
* @return
*/
public int size(){
return this.departmentList.size();
}
}
3.实体类
/**
* @description:系
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Department {
/**
* 系id
*/
private Integer id;
/**
* 系名
*/
private String name;
}
.测试类
/**
* @description:TODO
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//计算机学院
MyIterator citerator = new ComputerCollege().createIterator();
citerator.first();
while (!citerator.isDone()){
Object o = citerator.currentItem();
System.out.println(o);
citerator.next();
}
System.out.println("==========================================");
//数学学院
MyIterator miterator = new MathCollege().createIterator();
miterator.first();
while (!miterator.isDone()){
Object o = miterator.currentItem();
System.out.println(o);
miterator.next();
}
}
}
java迭代器模式
以计算机学院举例修改
1.修改学院接口,返回为java的Iterator对象
/**
* @description:学院接口
*/
public interface College {
/**
* 创建迭代器
* @return
*/
Iterator createIterator();
}
/**
* @description:计算机学院类
*/
public class ComputerCollege implements College {
private Department[] departments=null;
@Override
public Iterator createIterator() {
//初始化数据
departments=new Department[3];
departments[0]=new Department(1,"软件");
departments[1]=new Department(2,"通信");
departments[2]=new Department(3,"电子");
return new ComputerIterator(this);
}
/**
* 获取元素
* @param index
* @return
*/
public Object get(int index){
Object obj=null;
if (index<this.departments.length){
obj=departments[index];
}
return obj;
}
/**
* 返回学院下系的数量
* @return
*/
public int size(){
return this.departments.length;
}
}
2.迭代器类实现java的Iterator,重写方法
/**
* @description:计算机学院迭代器
*/
public class ComputerIterator implements Iterator {
/**
* 计算机学院对象
*/
private ComputerCollege computerCollege=null;
/**
* 记录索引位置
*/
private int index=0;
public ComputerIterator(ComputerCollege computerCollege) {
this.computerCollege = computerCollege;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(computerCollege!=null&&index<computerCollege.size()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
Object obj=null;
if (hasNext()){
obj=computerCollege.get(index);
index++;
}
return obj;
}
}
3.测试,可以看到比自己手动实现简单一些
public class Client2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Iterator iterator = new ComputerCollege().createIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}