剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1
输入:head = [1,3,2]
输出:[2,3,1]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
}
}解题思路:
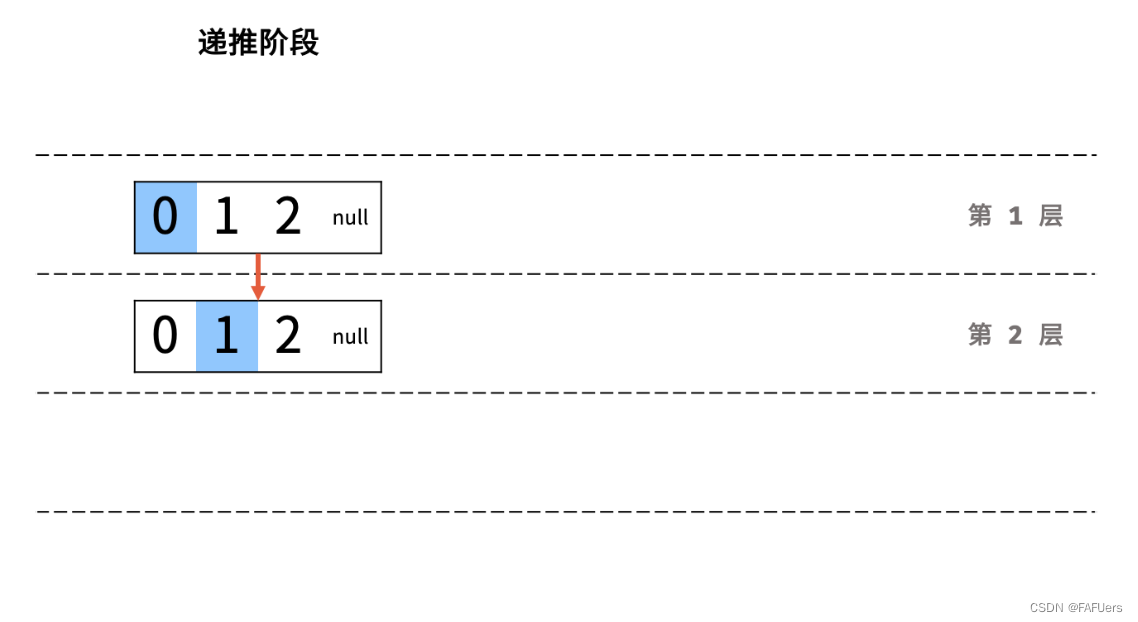
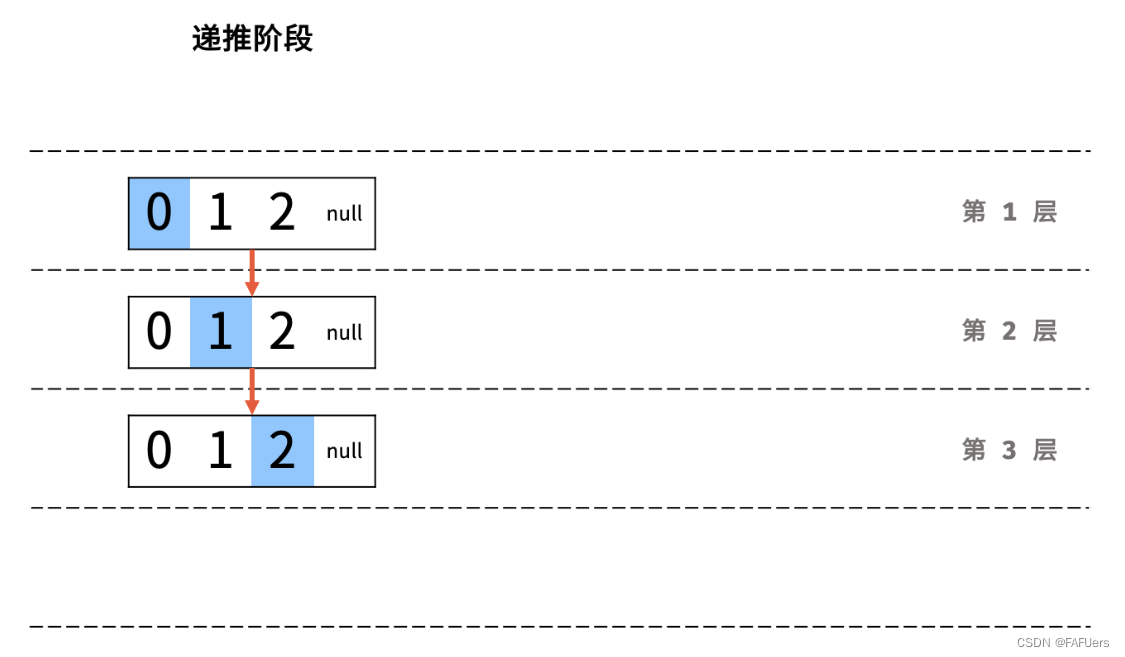
方法一:递归法
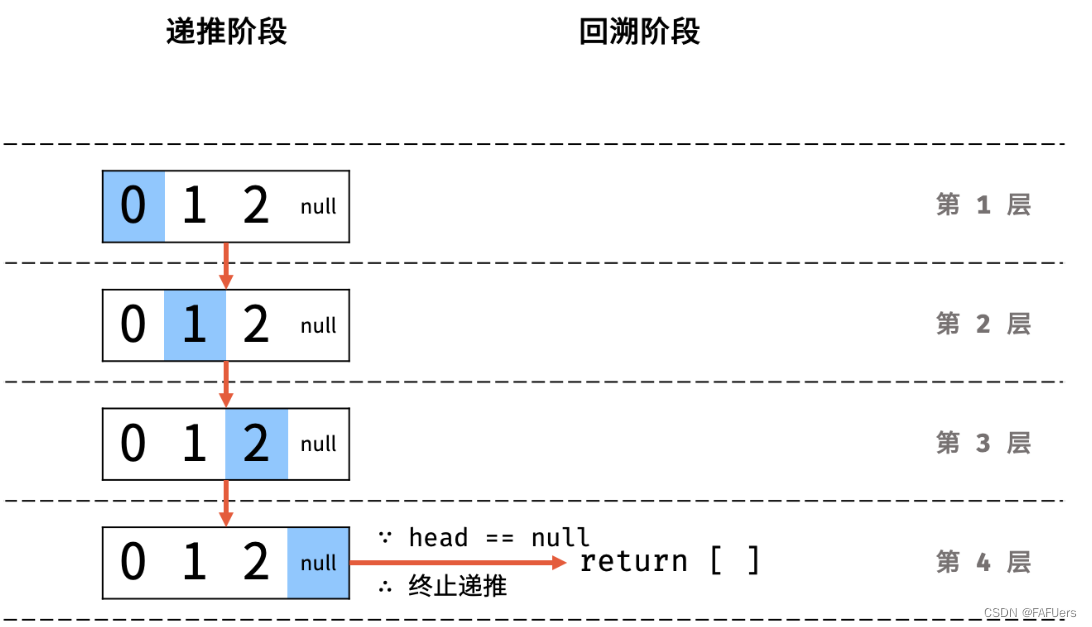
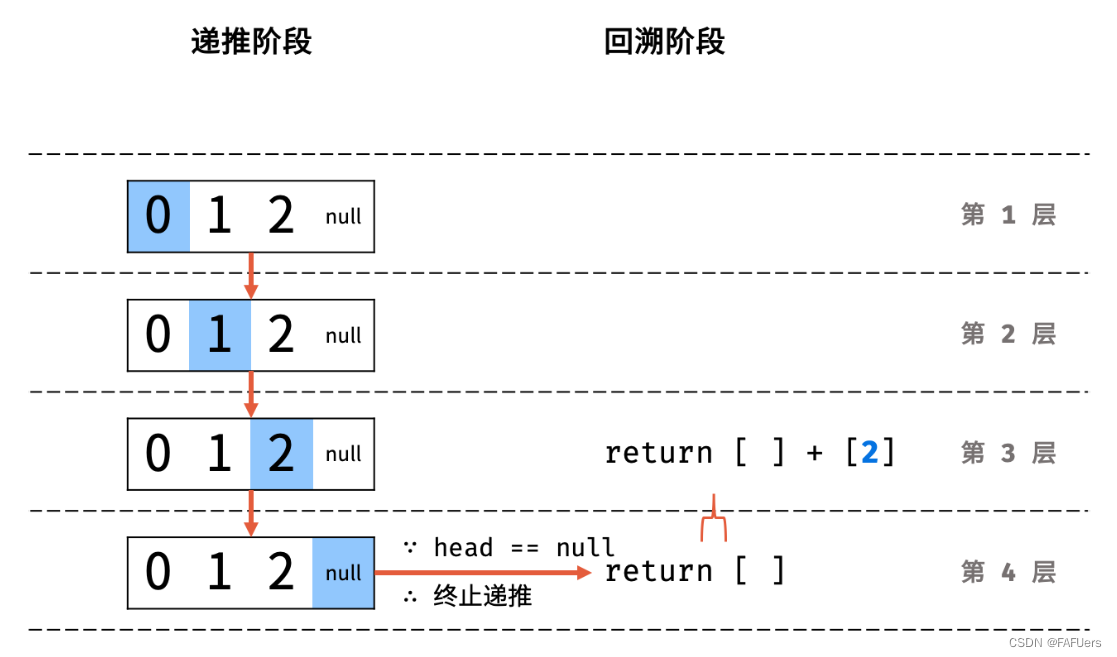
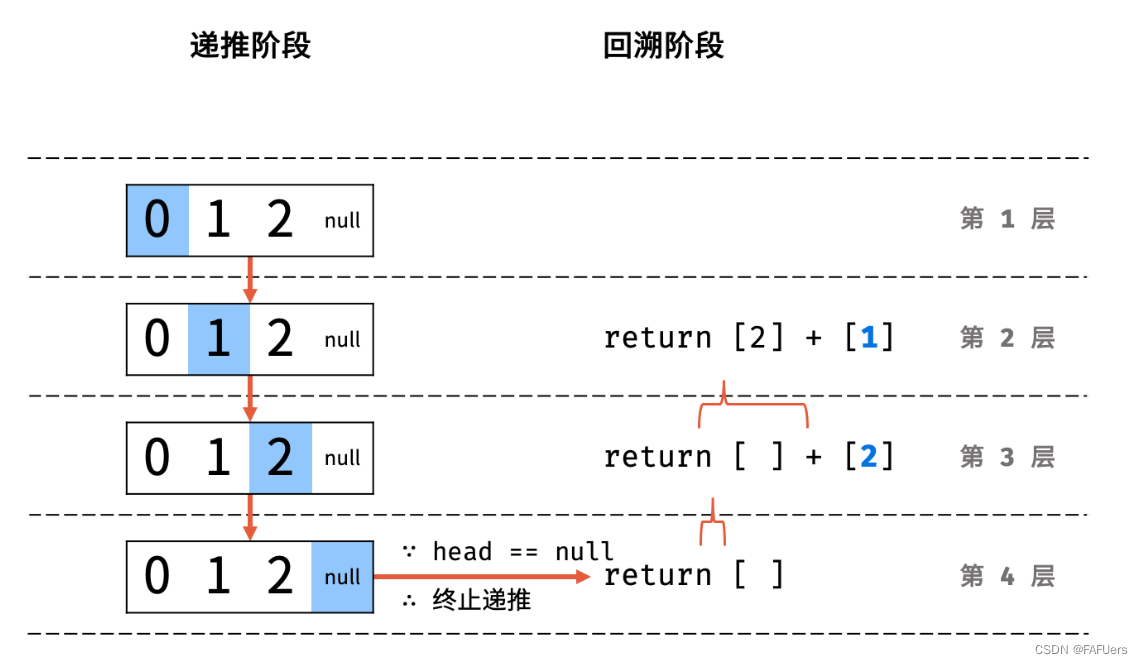
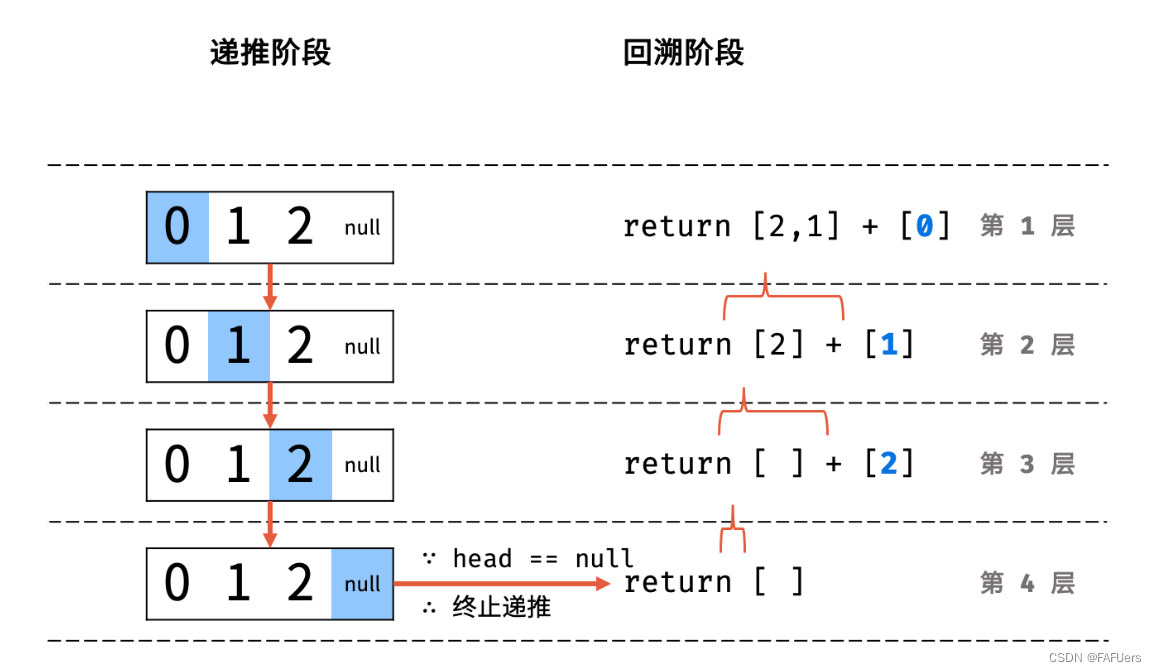
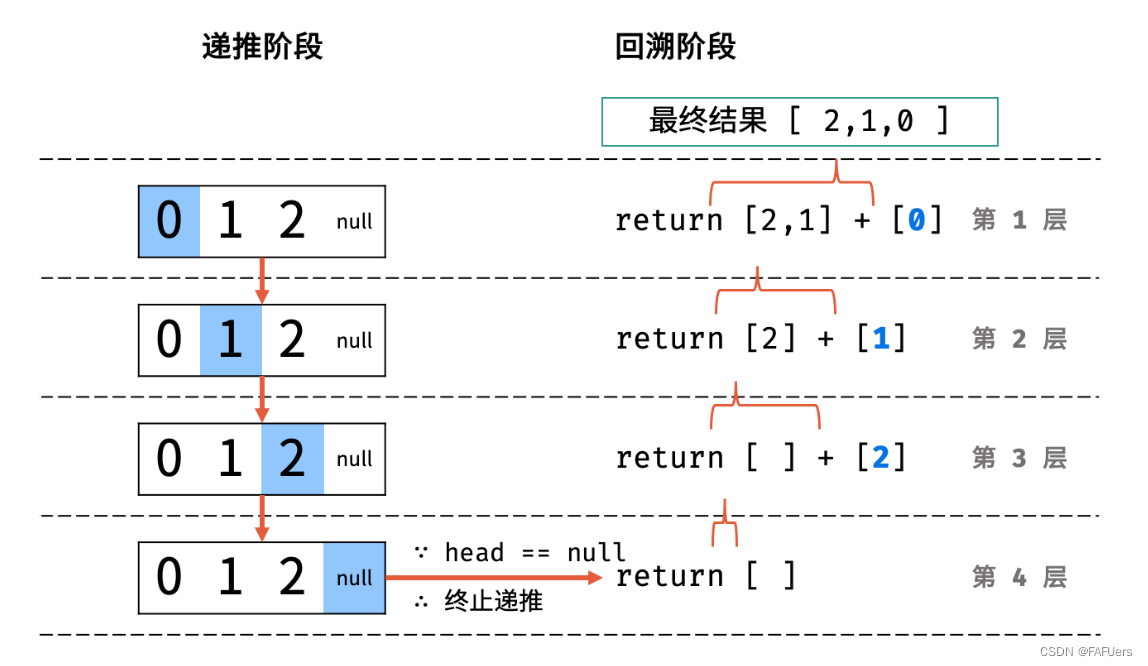
利用递归,先递推至链表末端;回溯时,依次将节点值加入列表,即可实现链表值的倒序输出。
递归解析:
终止条件: 当 head == None 时,代表越过了链表尾节点,则返回空列表;
递推工作: 访问下一节点 head.next ;
回溯阶段:将当前节点值 head.val 加入列表 tmp ;


代码如下:
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
recur(head);
int[] res = new int[tmp.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = tmp.get(i);
return res;
}
void recur(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return;
recur(head.next);
tmp.add(head.val);
}
}方法二:辅助栈法
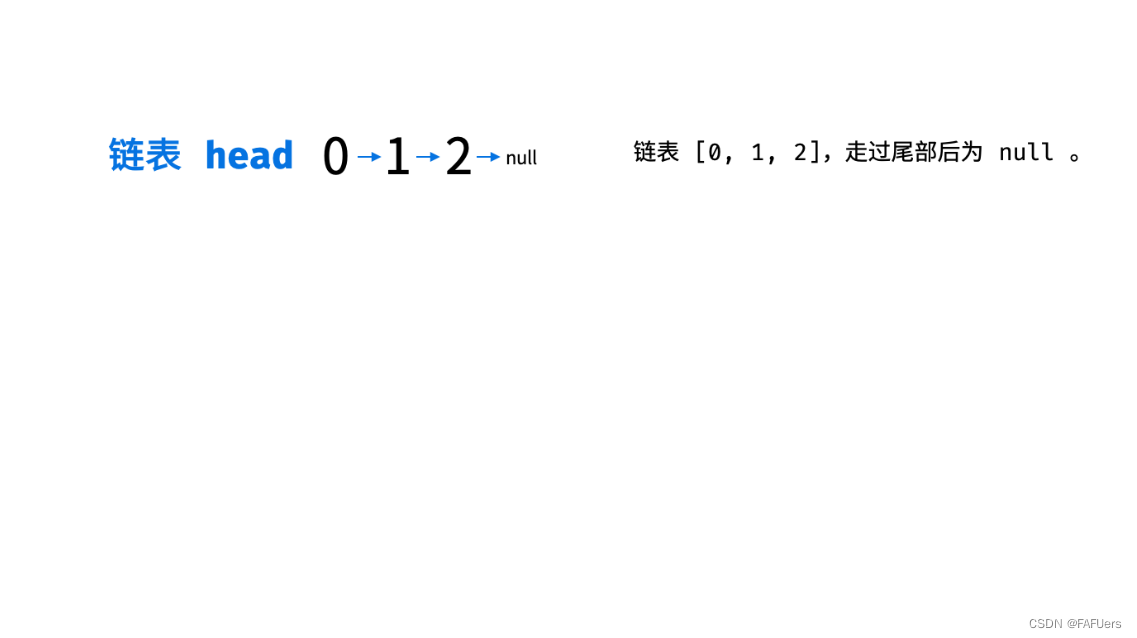
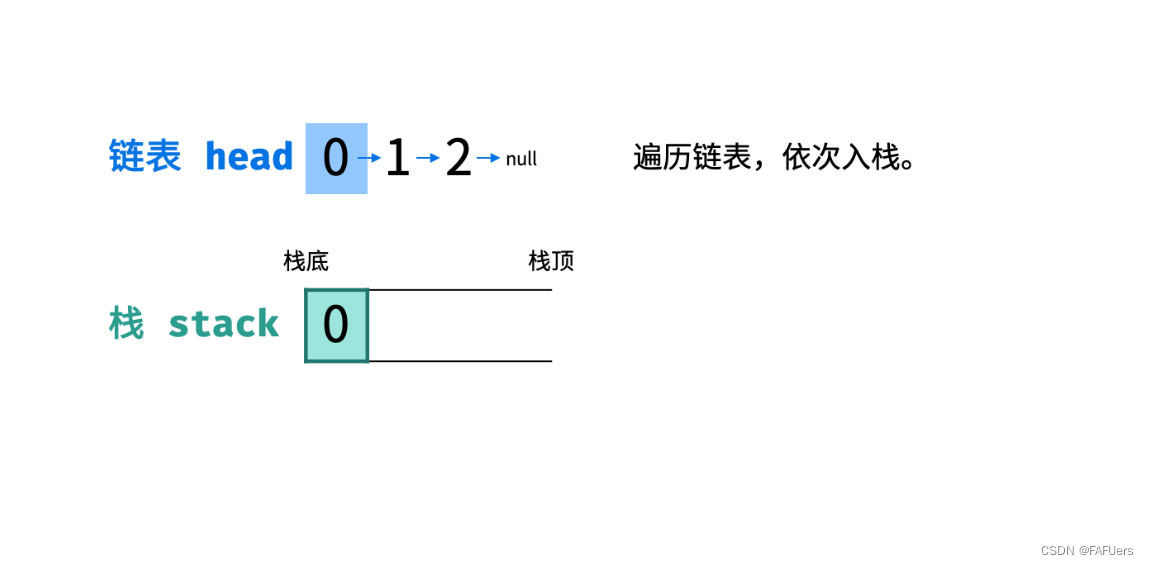
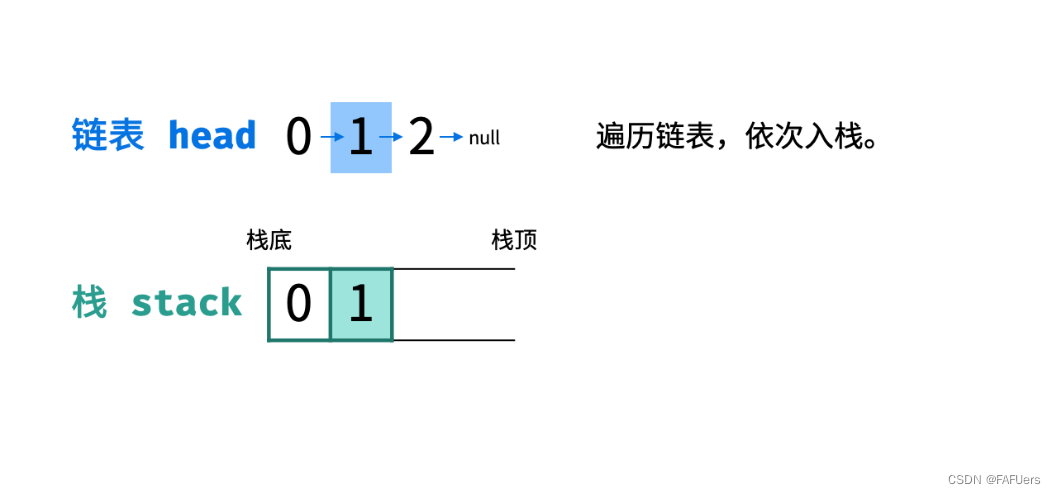
链表只能 从前至后 访问每个节点,而题目要求 倒序输出 各节点值,这种 先入后出 的需求可以借助 栈 来实现。
算法流程:
入栈: 遍历链表,将各节点值 push 入栈。
出栈: 将各节点值 pop 出栈,存储于数组并返回。
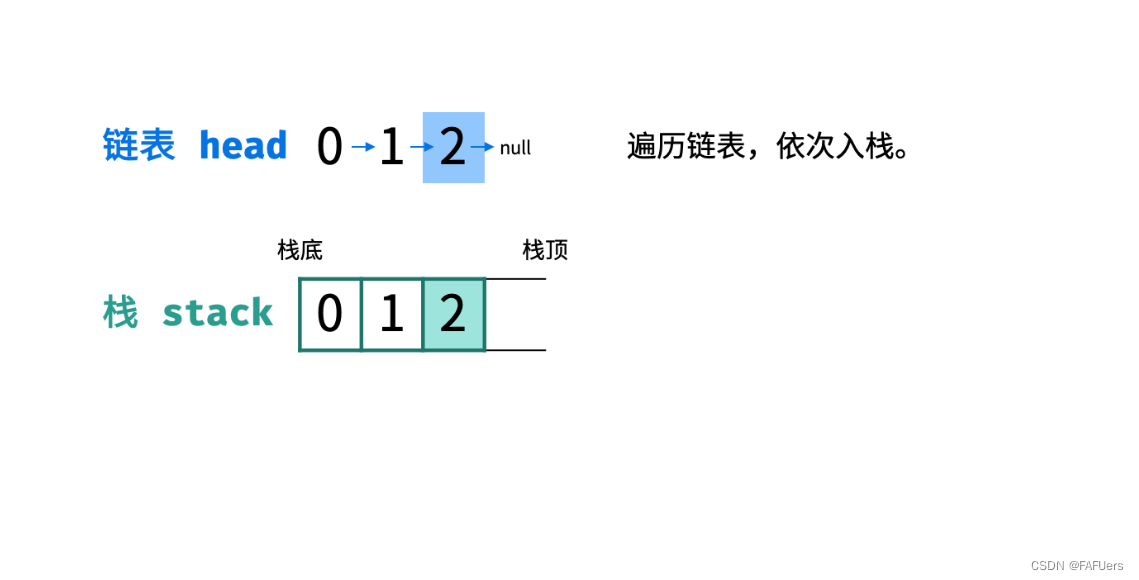
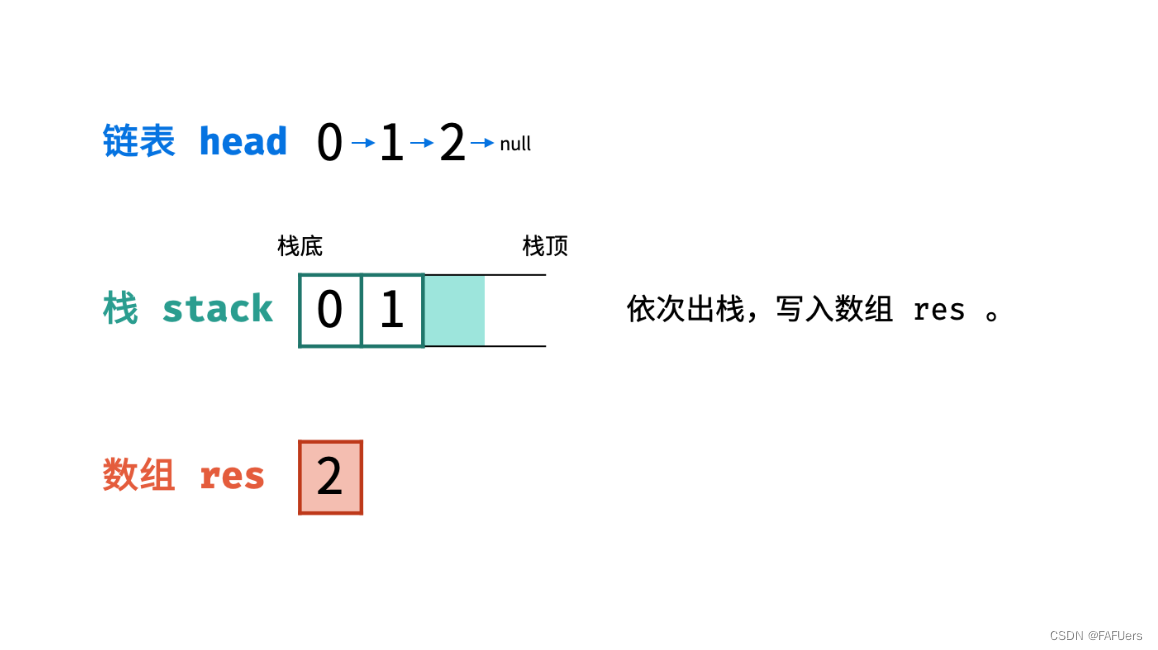
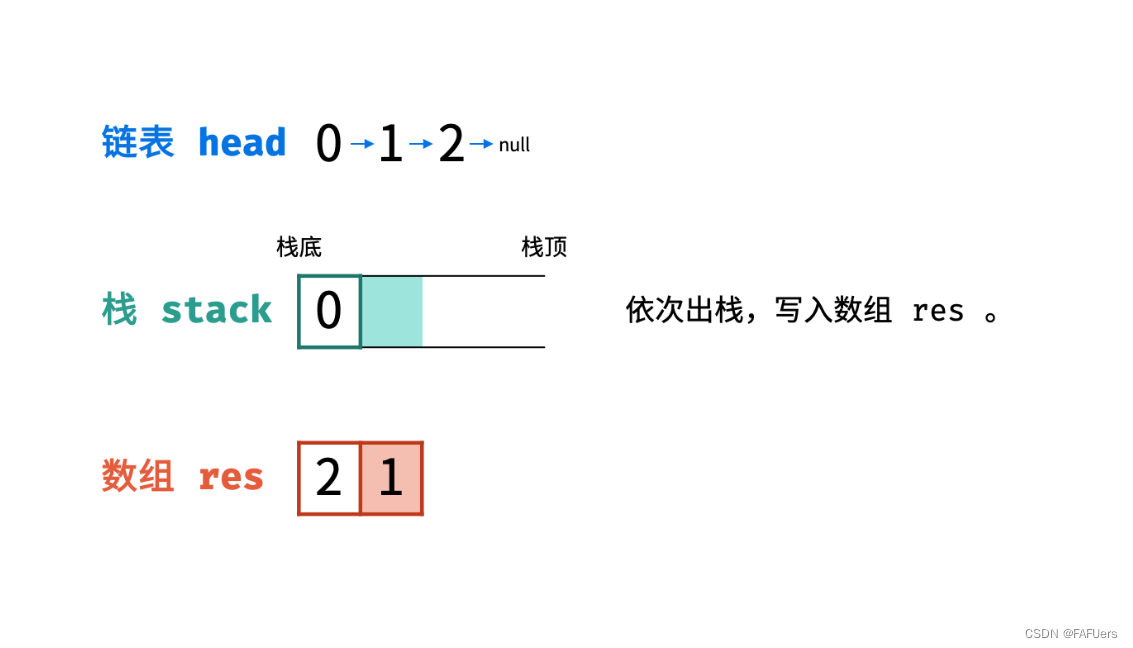


代码如下:
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while(head != null) {
stack.addLast(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int[] res = new int[stack.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = stack.removeLast();
return res;
}
}剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
}
}解题思路:
方法一:迭代(双指针)
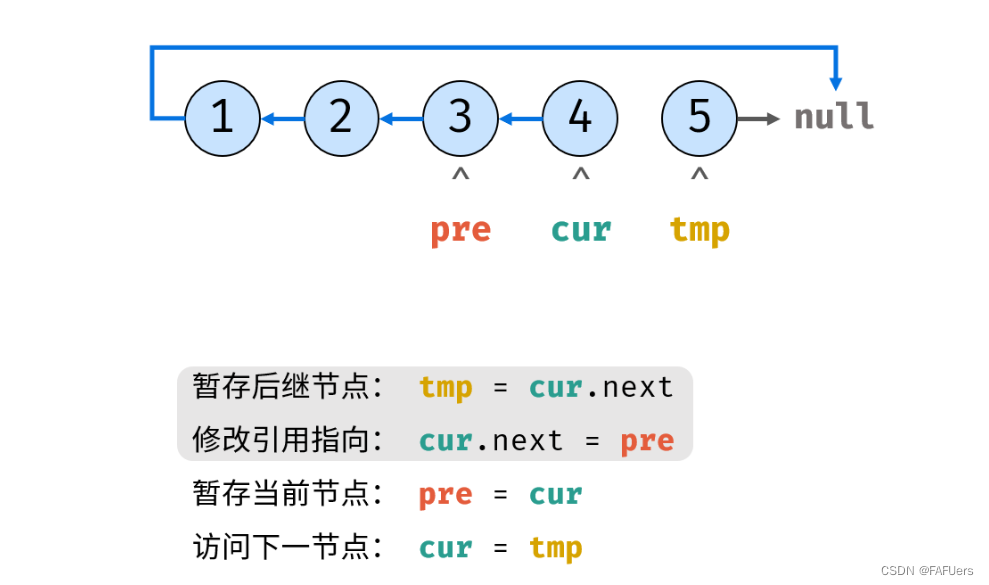
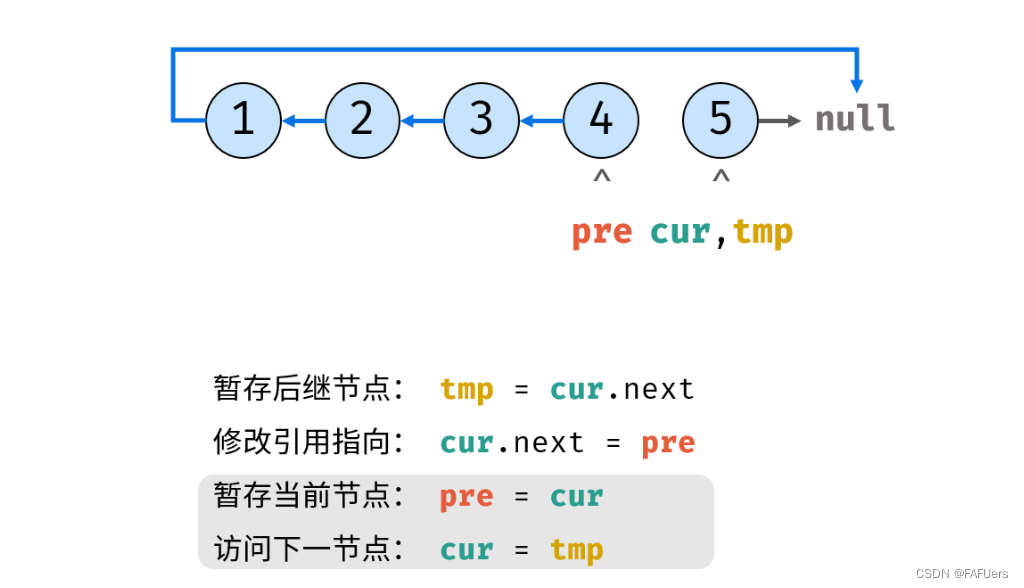
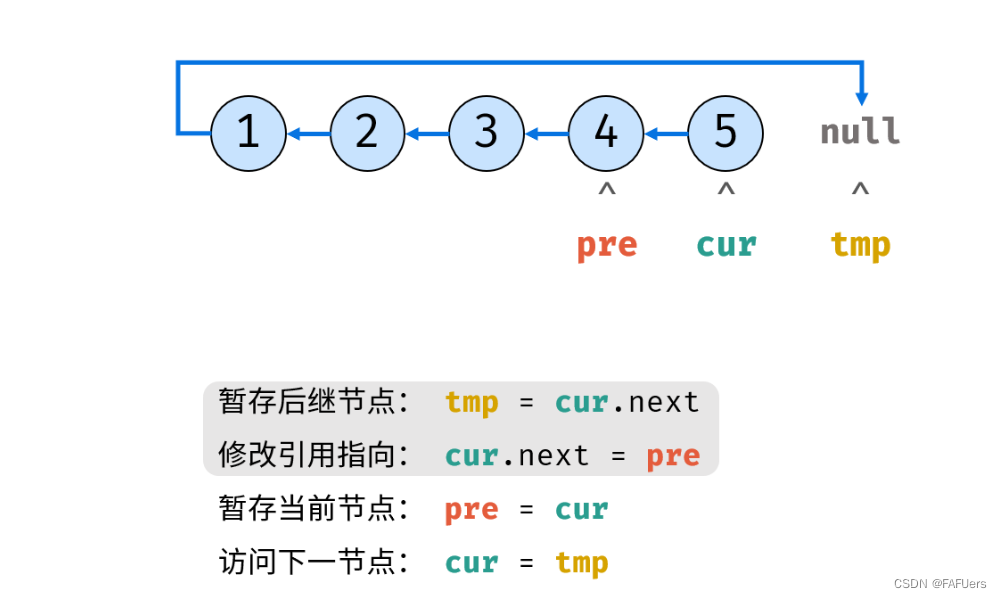
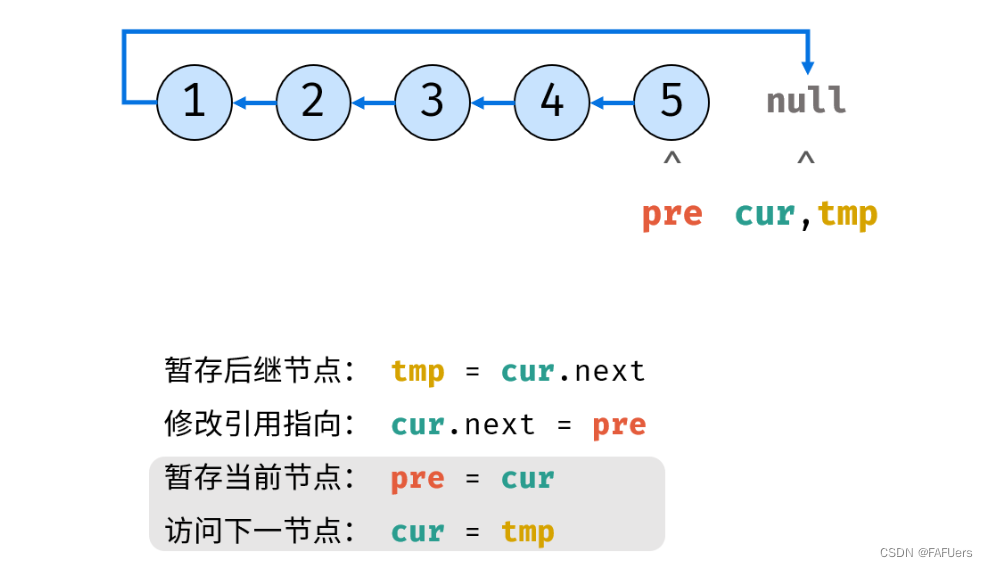
考虑遍历链表,并在访问各节点时修改 next 引用指向。
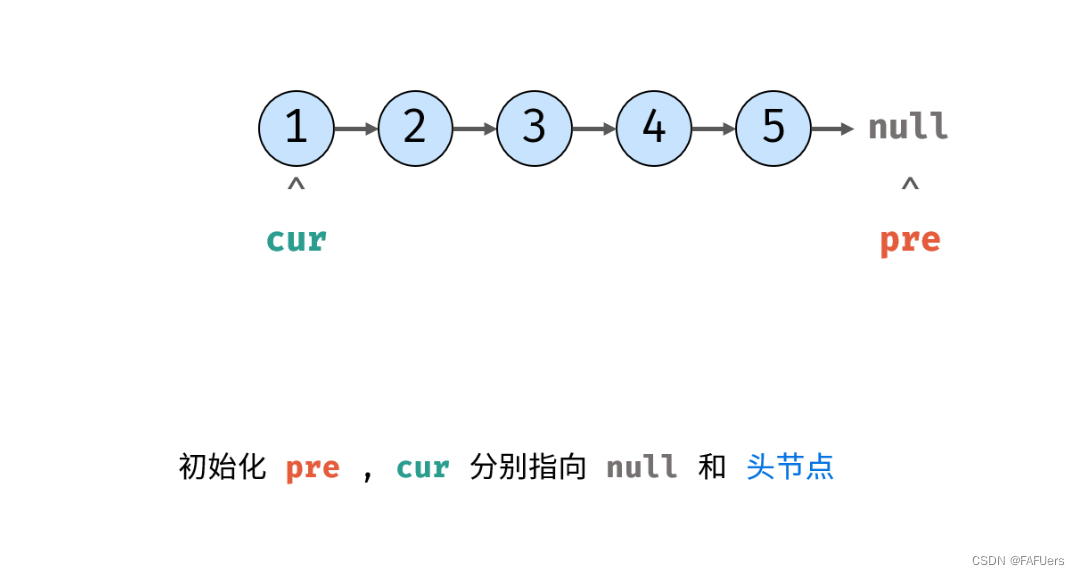

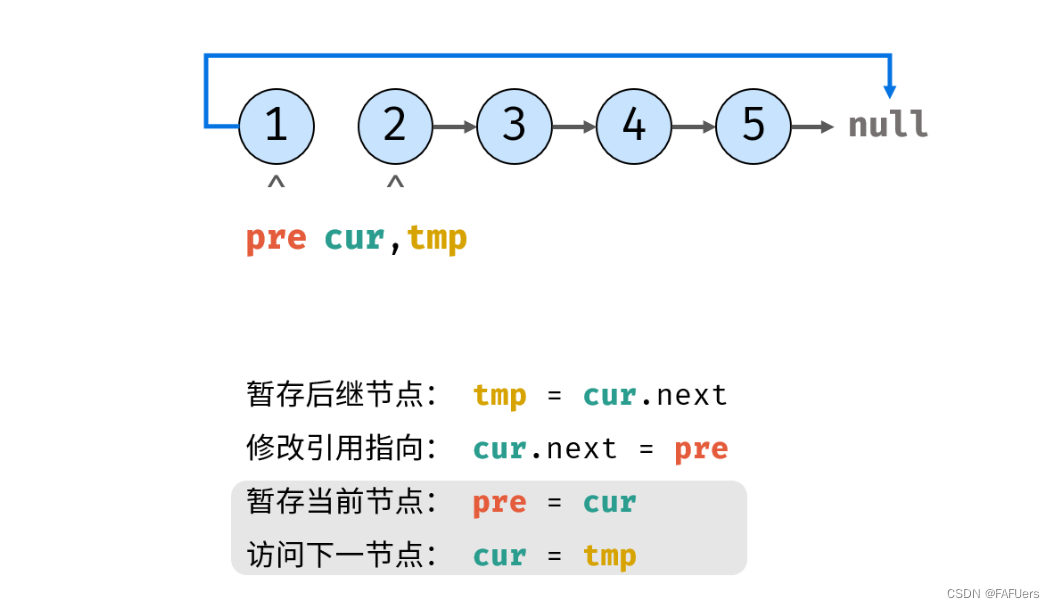
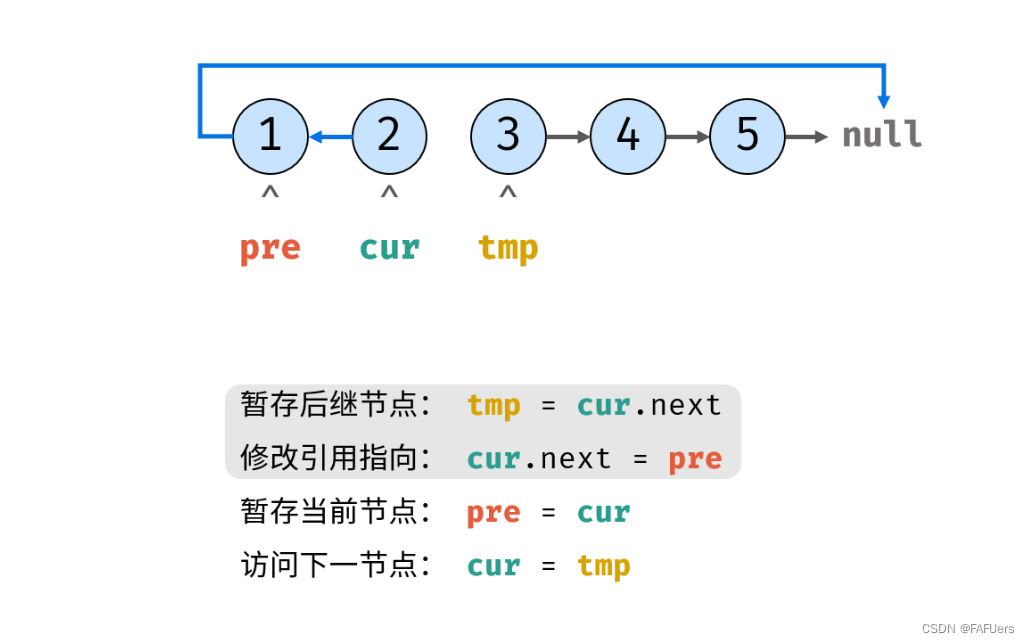
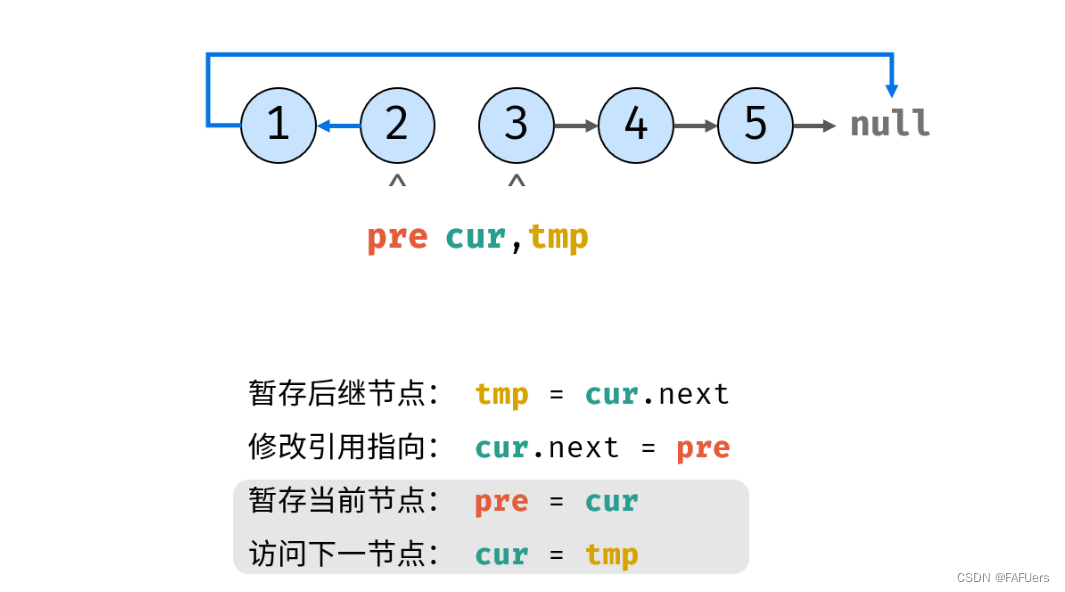
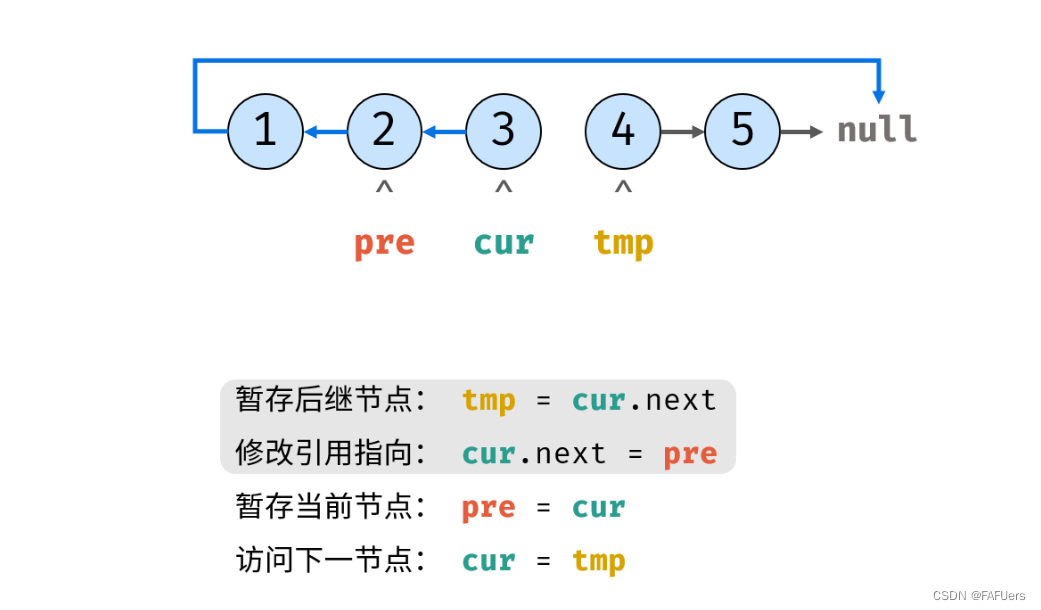

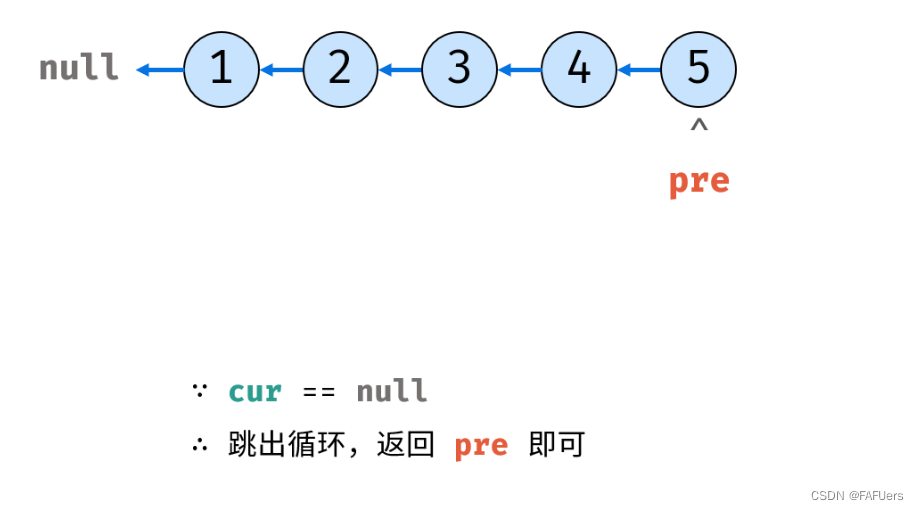
代码如下:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head, pre = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next; // 暂存后继节点 cur.next
cur.next = pre; // 修改 next 引用指向
pre = cur; // pre 暂存 cur
cur = tmp; // cur 访问下一节点
}
return pre;
}
}方法二:递归
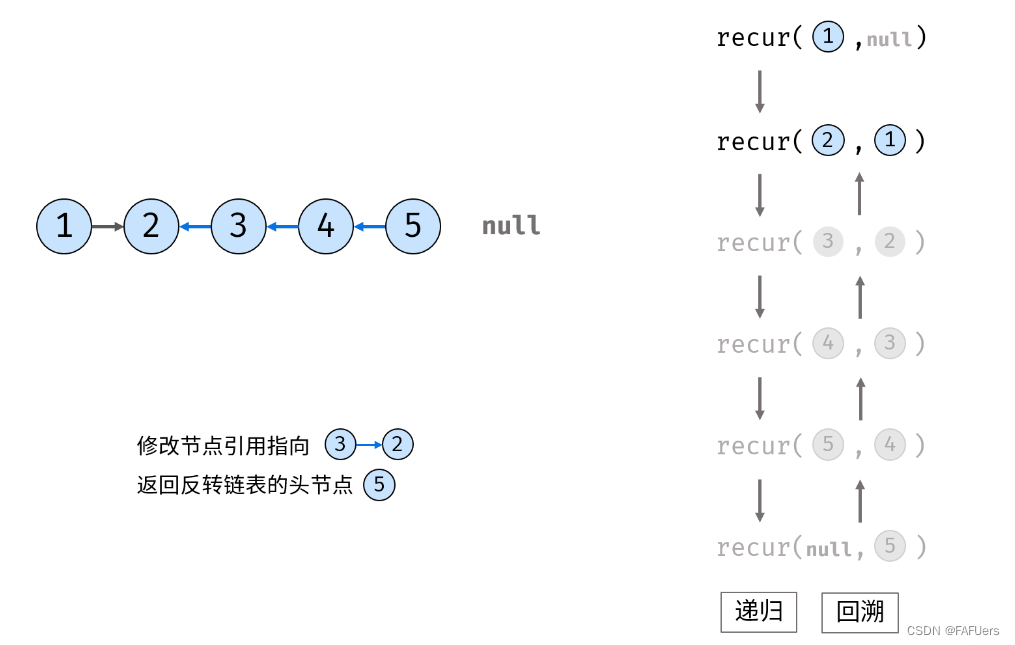
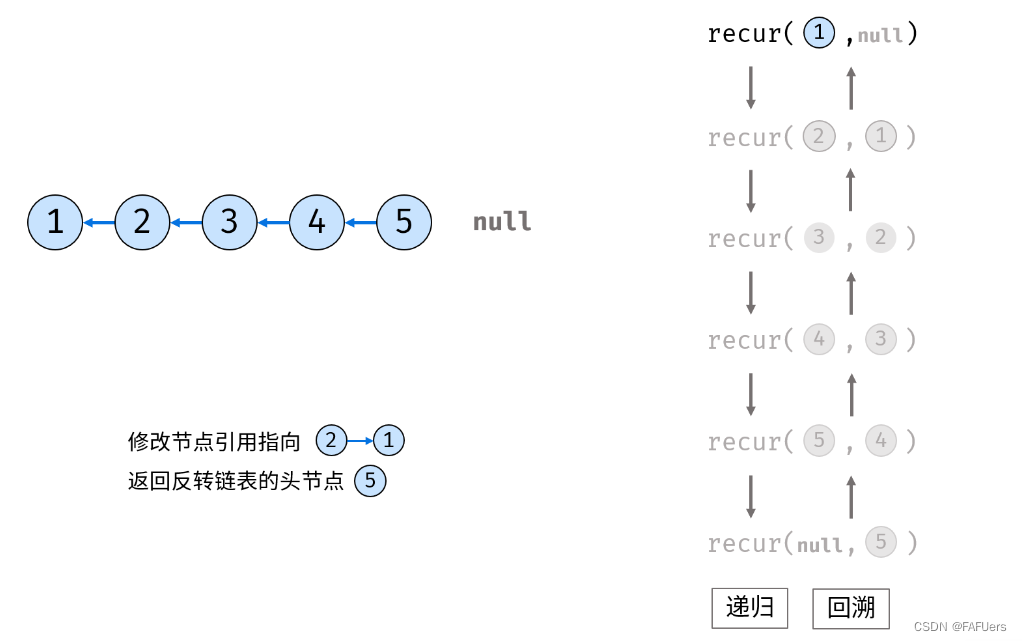
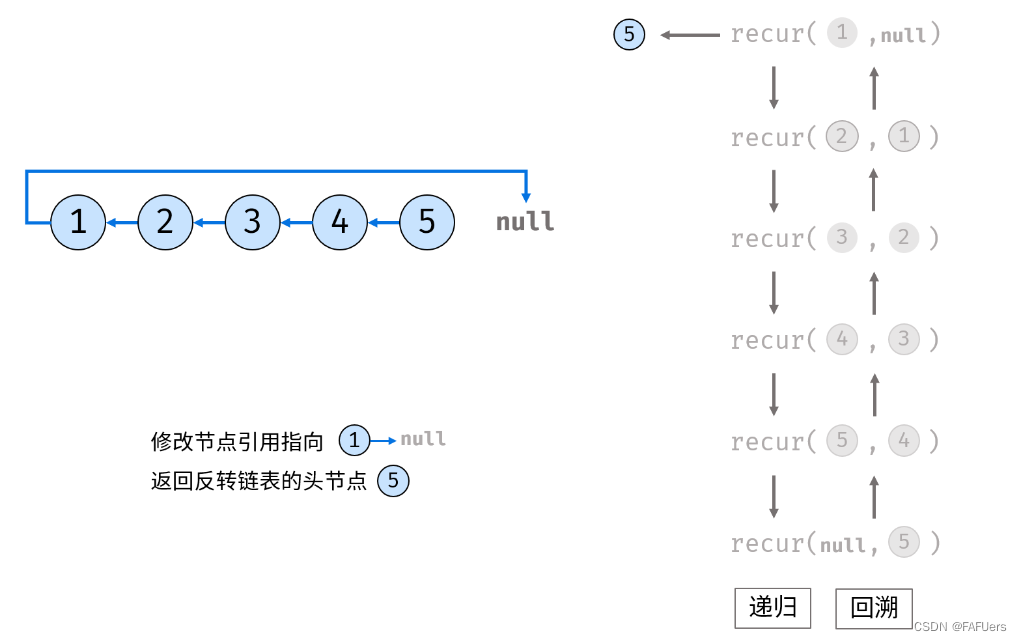
考虑使用递归法遍历链表,当越过尾节点后终止递归,在回溯时修改各节点的 next 引用指向。
recur(cur, pre) 递归函数:
终止条件:当 cur 为空,则返回尾节点 pre (即反转链表的头节点);
递归后继节点,记录返回值(即反转链表的头节点)为 res ;
修改当前节点 cur 引用指向前驱节点 pre ;
返回反转链表的头节点 res ;
reverseList(head) 函数:
调用并返回 recur(head, null) 。传入 null 是因为反转链表后, head 节点指向 null ;




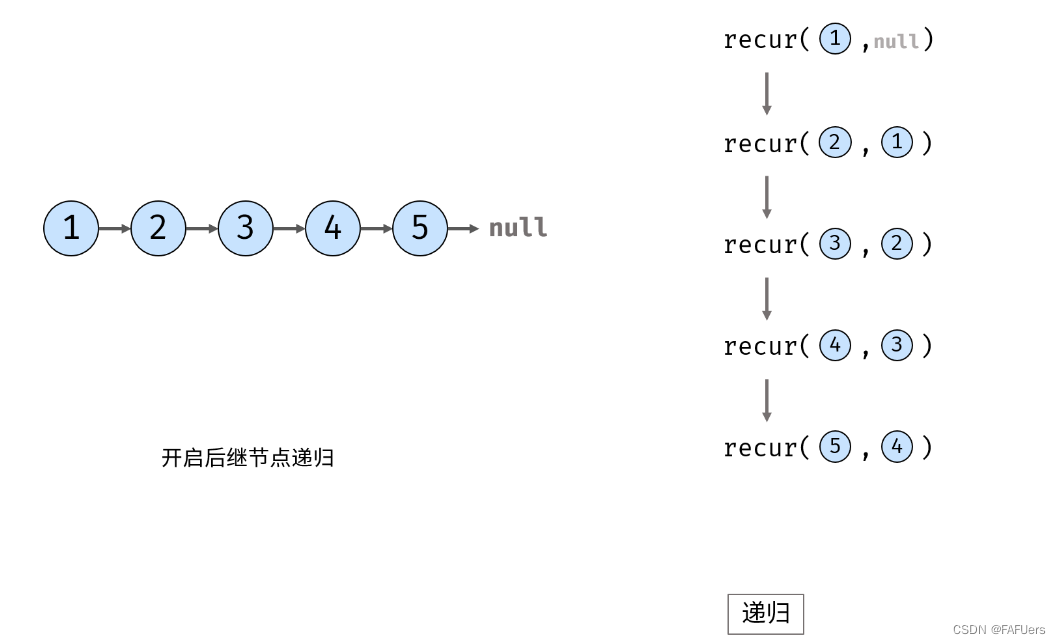

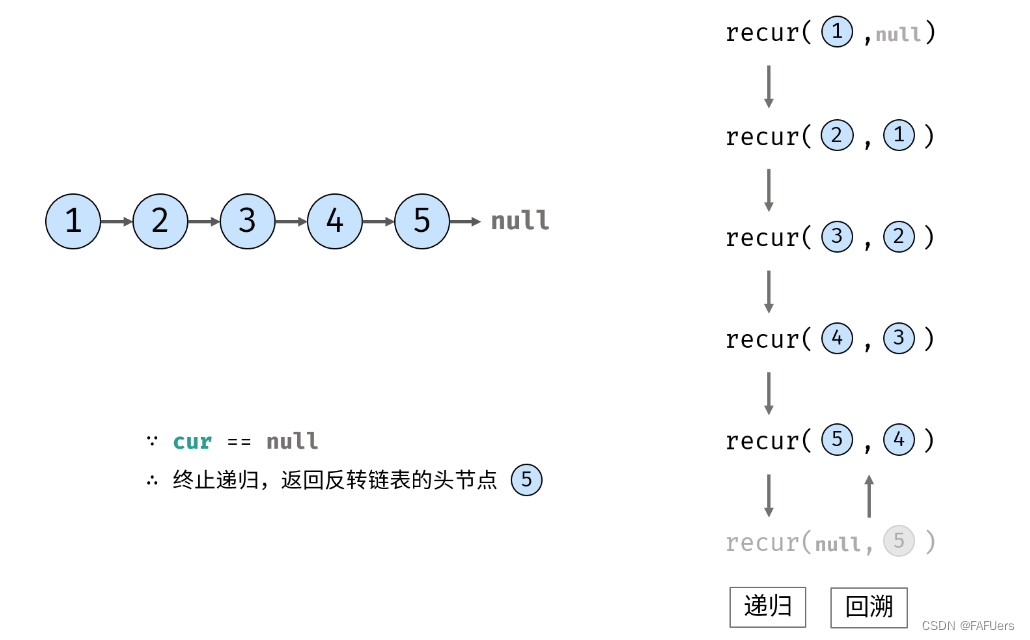

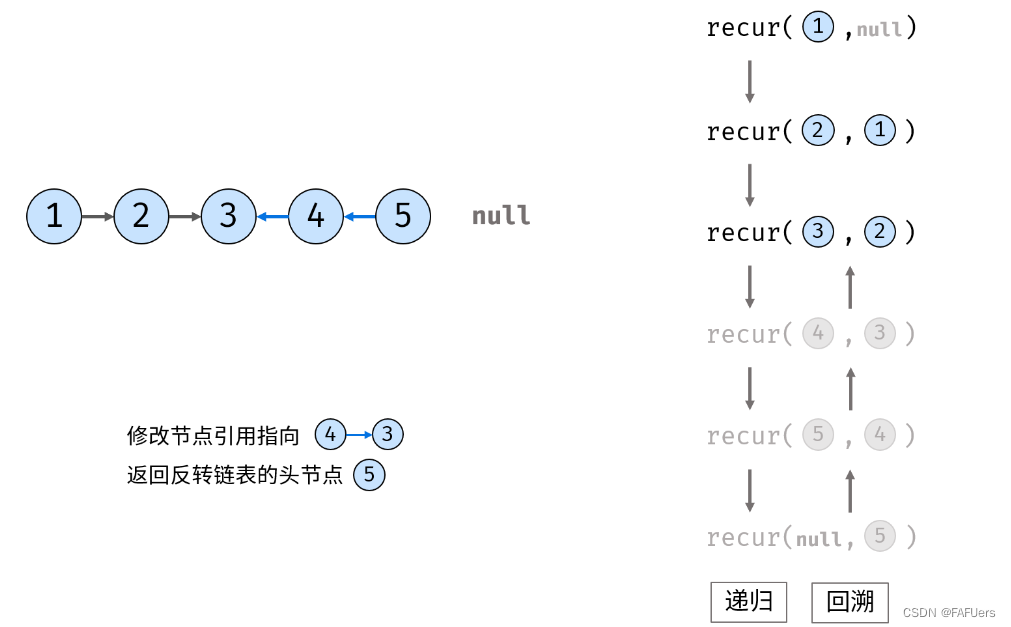
代码如下:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return recur(head, null); // 调用递归并返回
}
private ListNode recur(ListNode cur, ListNode pre) {
if (cur == null) return pre; // 终止条件
ListNode res = recur(cur.next, cur); // 递归后继节点
cur.next = pre; // 修改节点引用指向
return res; // 返回反转链表的头节点
}
}剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:
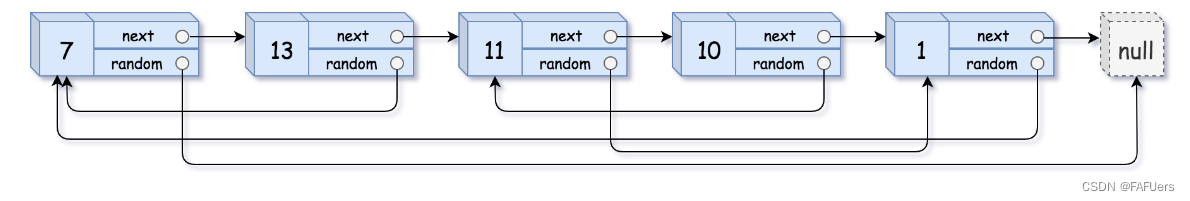 输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
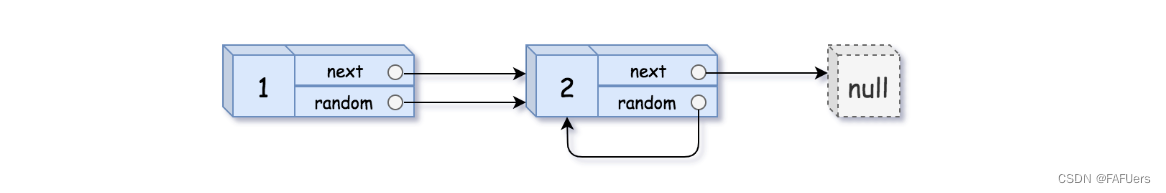 输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
}
}解题思路:
方法一:哈希表
利用哈希表的查询特点,考虑构建 原链表节点 和 新链表对应节点 的键值对映射关系,再遍历构建新链表各节点的 next 和 random 引用指向即可。
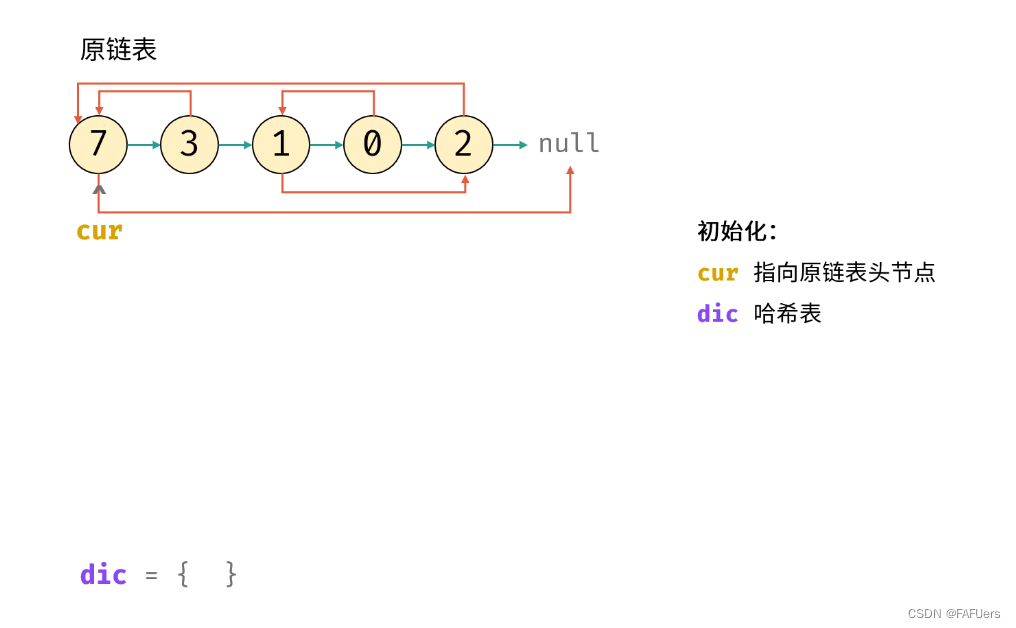
算法流程:
1.若头节点 head 为空节点,直接返回 null ;
2.初始化: 哈希表 dic , 节点 cur 指向头节点;
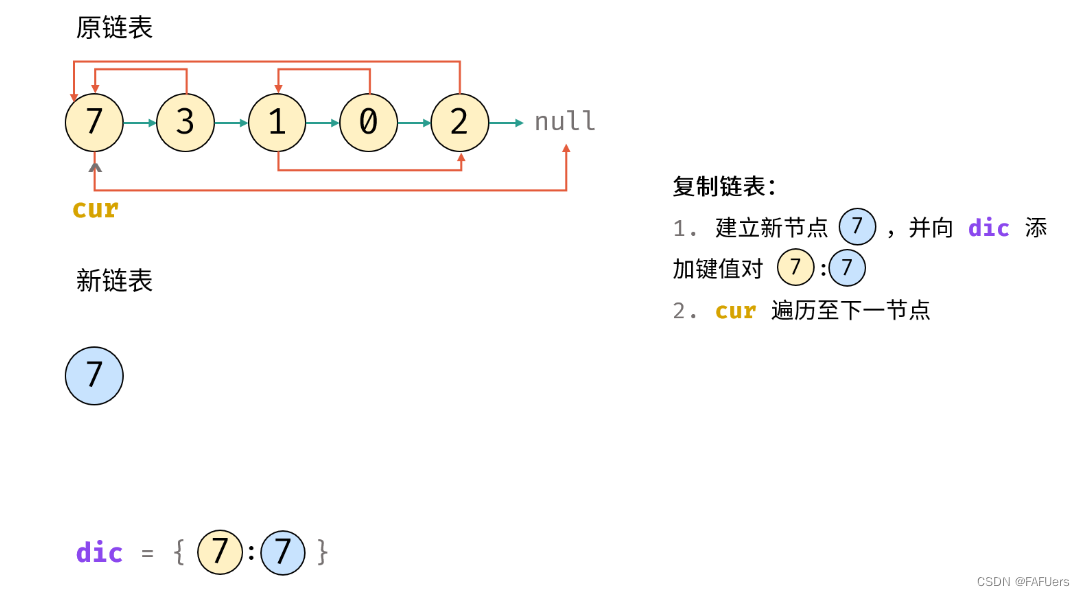
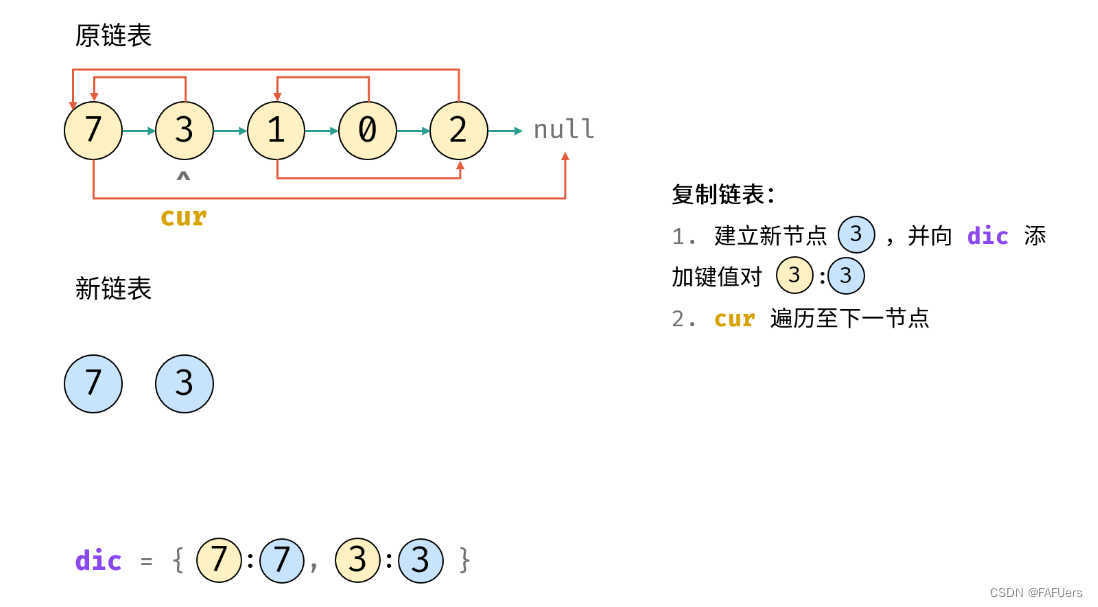
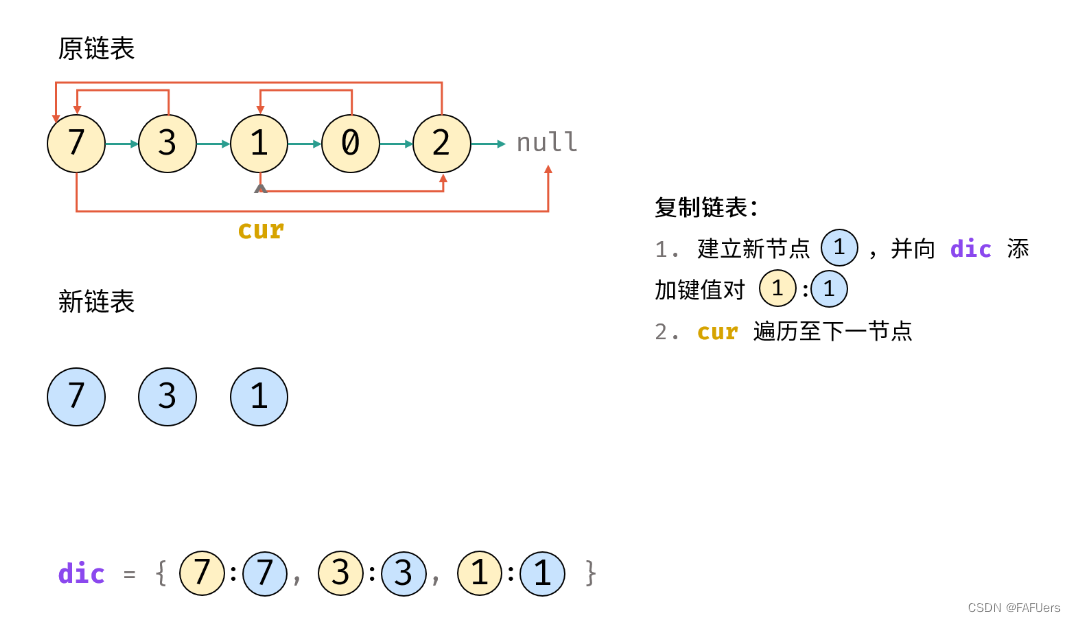
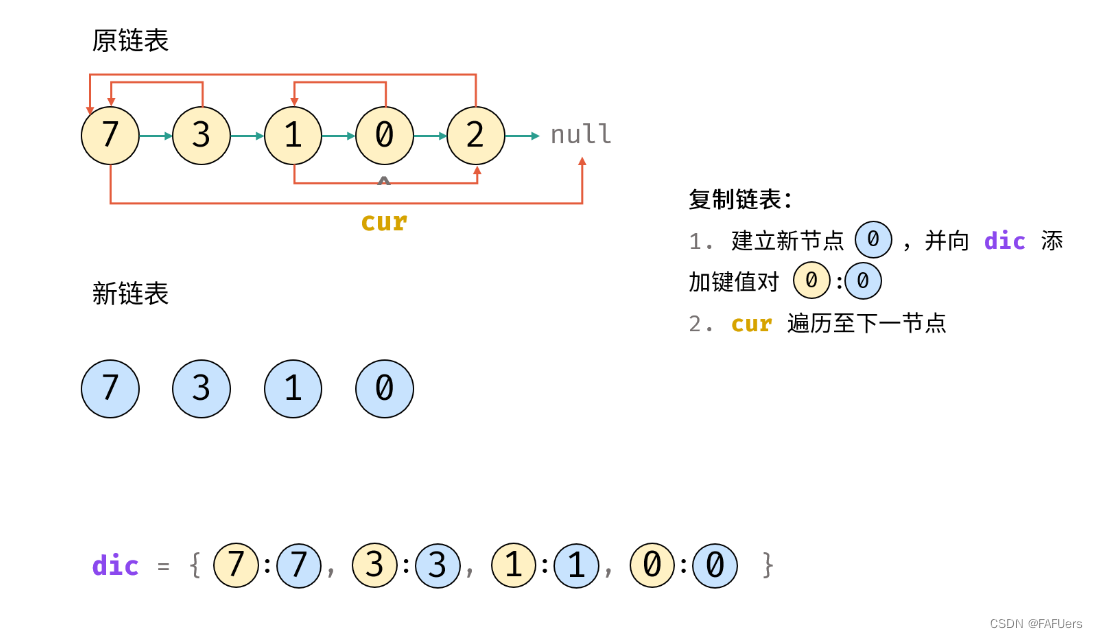
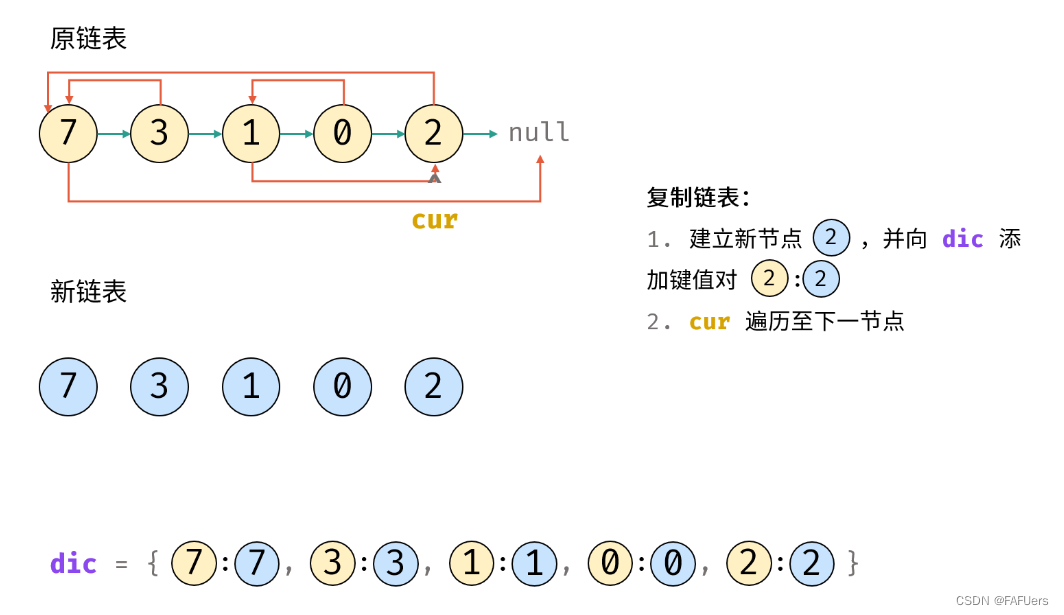
3.复制链表:
1.建立新节点,并向 dic 添加键值对 (原 cur 节点, 新 cur 节点) ;
2.cur 遍历至原链表下一节点;
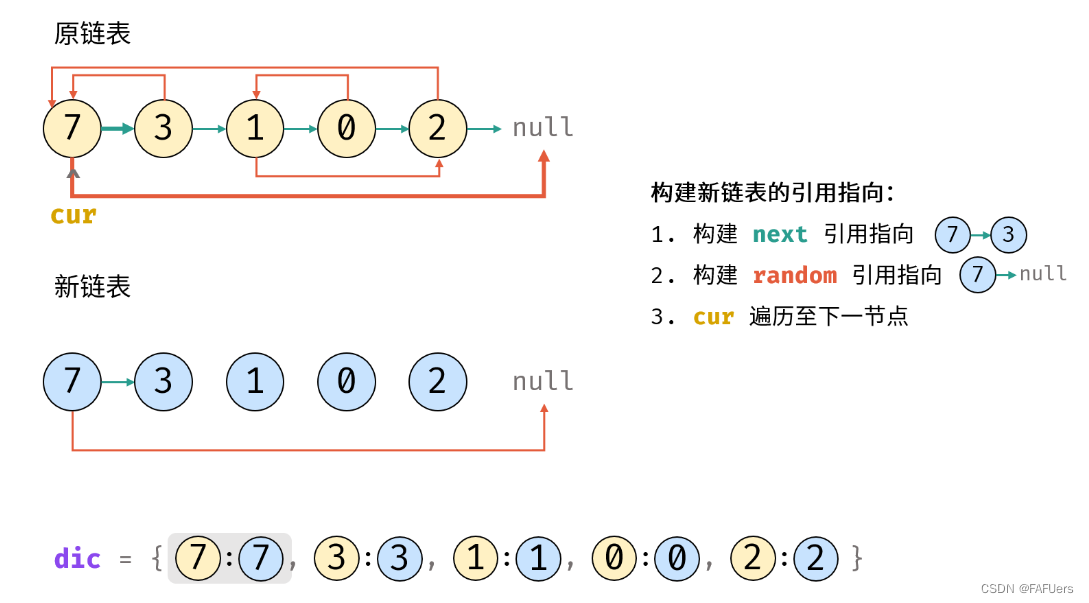
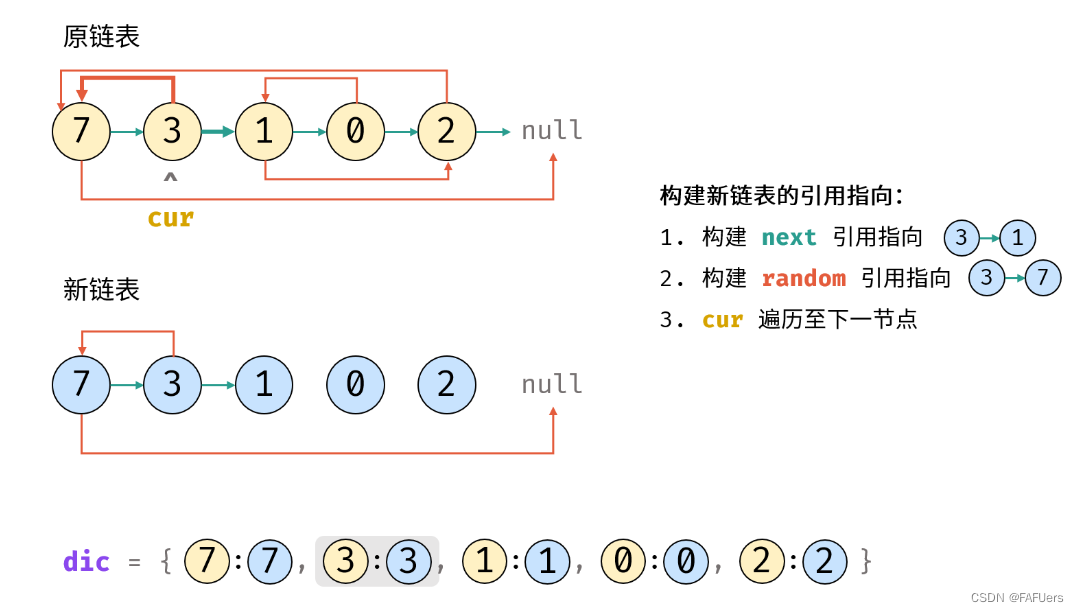
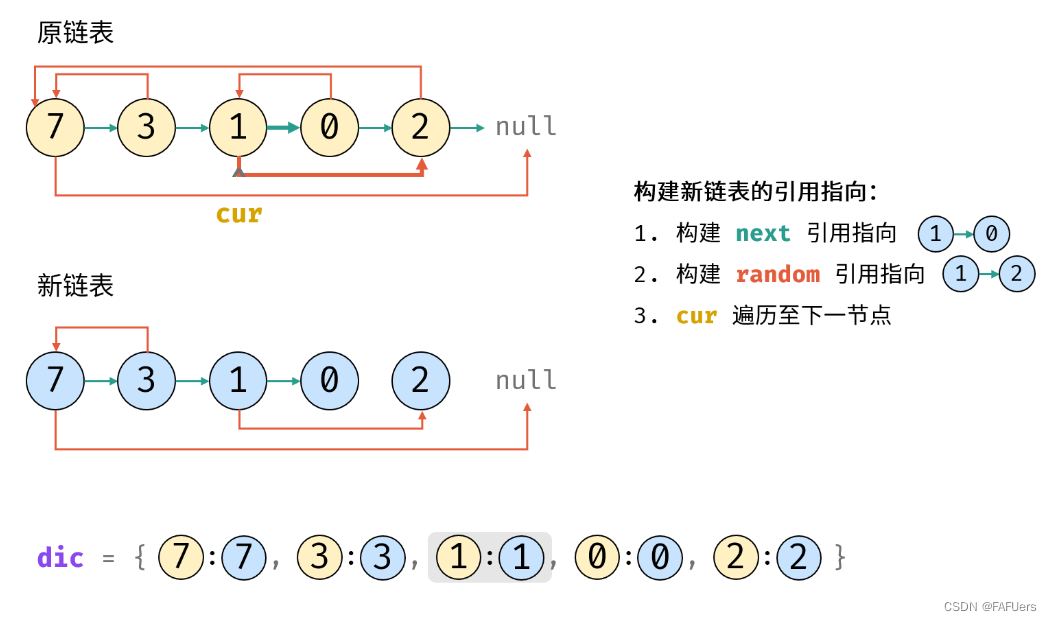
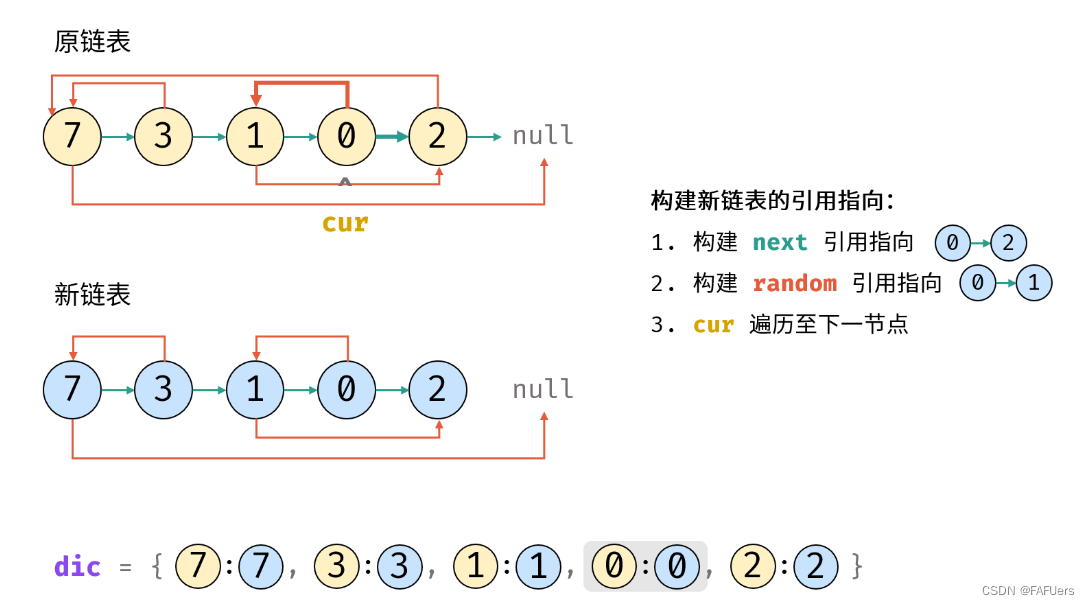
4.构建新链表的引用指向:
1.构建新节点的 next 和 random 引用指向;
2.cur 遍历至原链表下一节点;
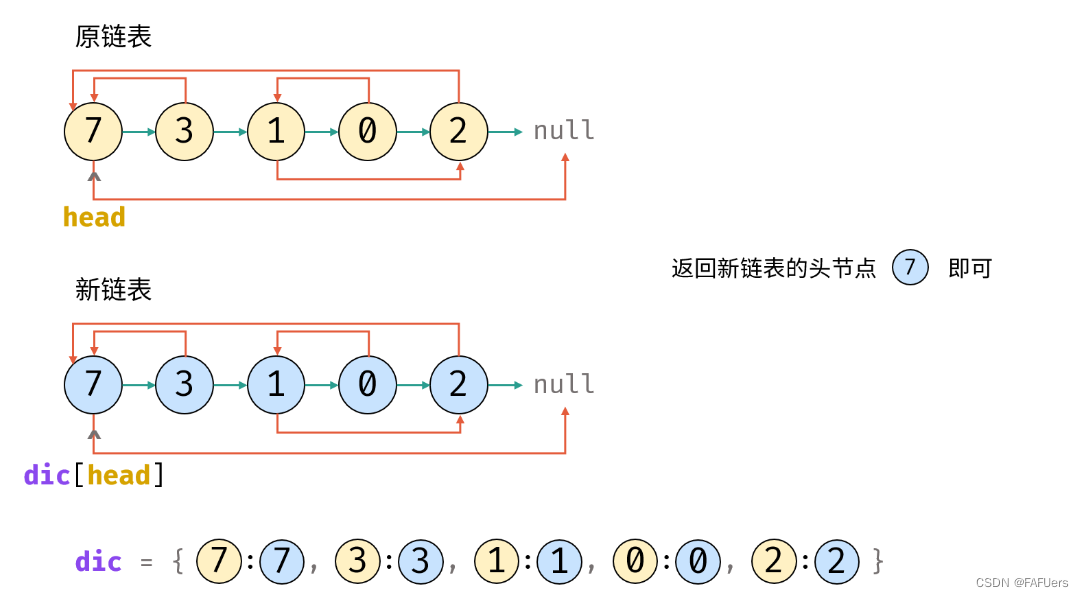
5.返回值: 新链表的头节点 dic[cur] ;

代码如下:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射
while(cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向
while(cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 5. 返回新链表的头节点
return map.get(head);
}
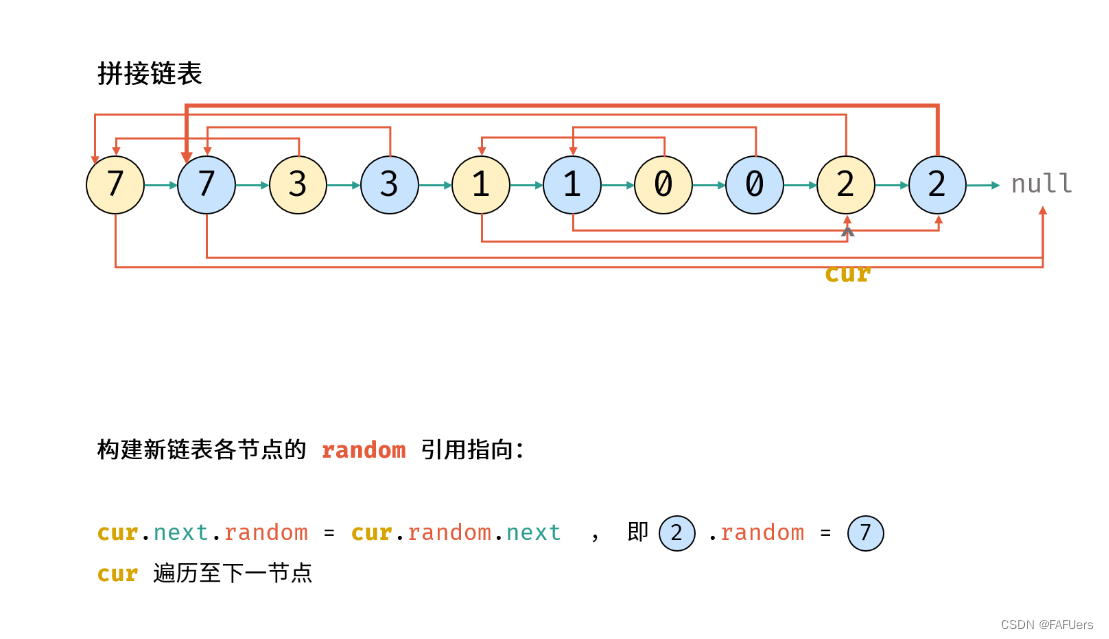
}方法二:拼接 + 拆分
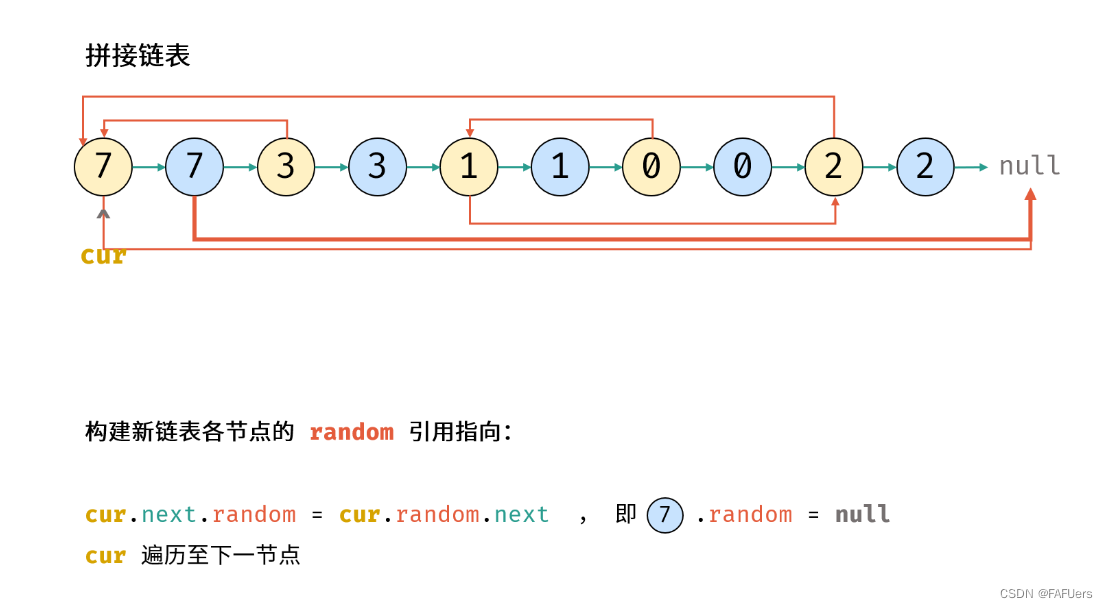
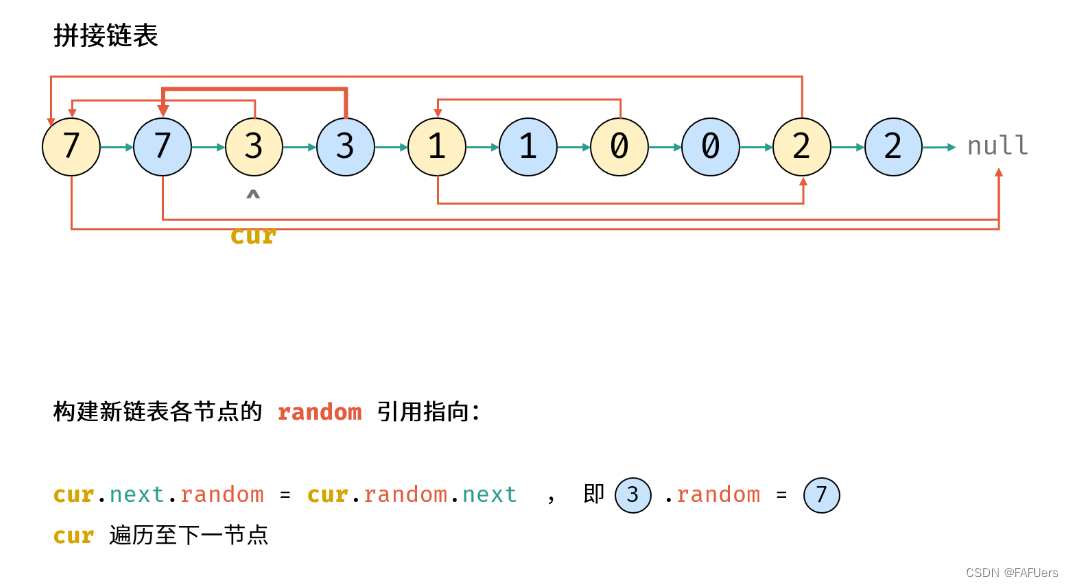
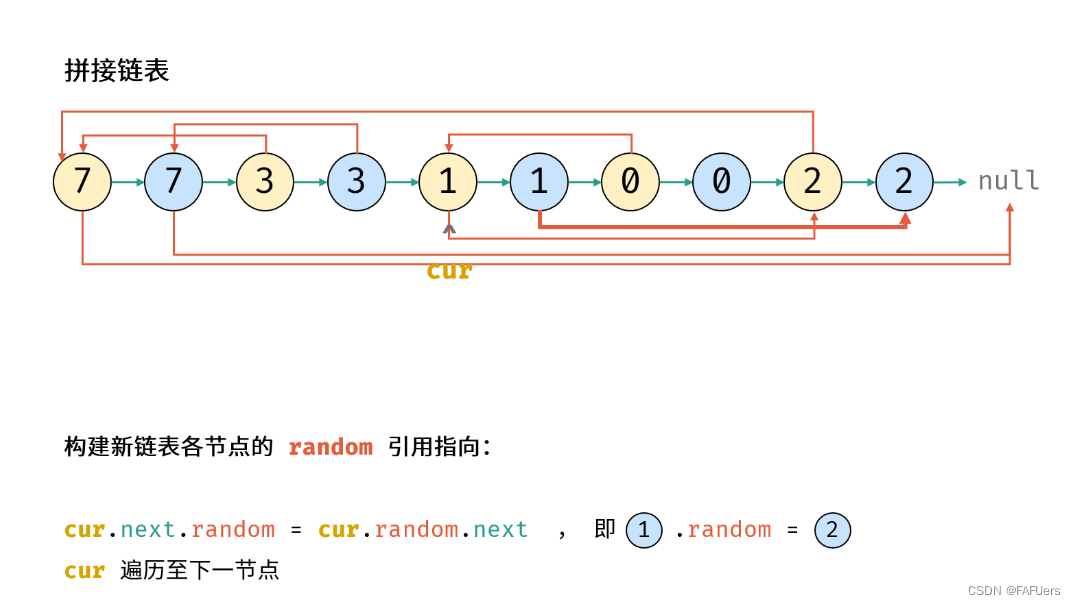
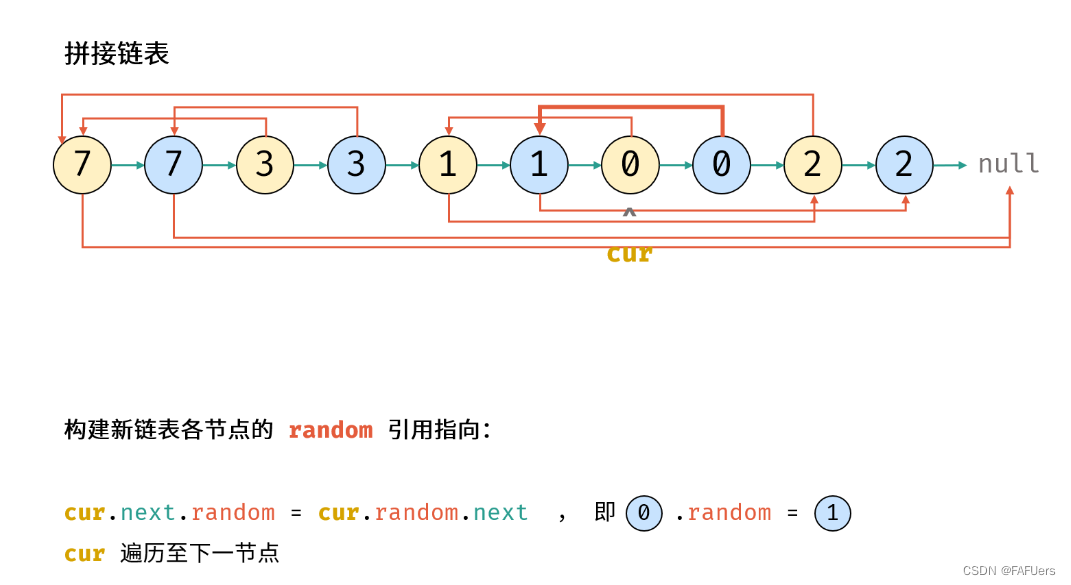
考虑构建 原节点 1 -> 新节点 1 -> 原节点 2 -> 新节点 2 -> …… 的拼接链表,如此便可在访问原节点的 random 指向节点的同时找到新对应新节点的 random 指向节点。
算法流程:
1.复制各节点,构建拼接链表
2.构建新链表各节点的 random 指向
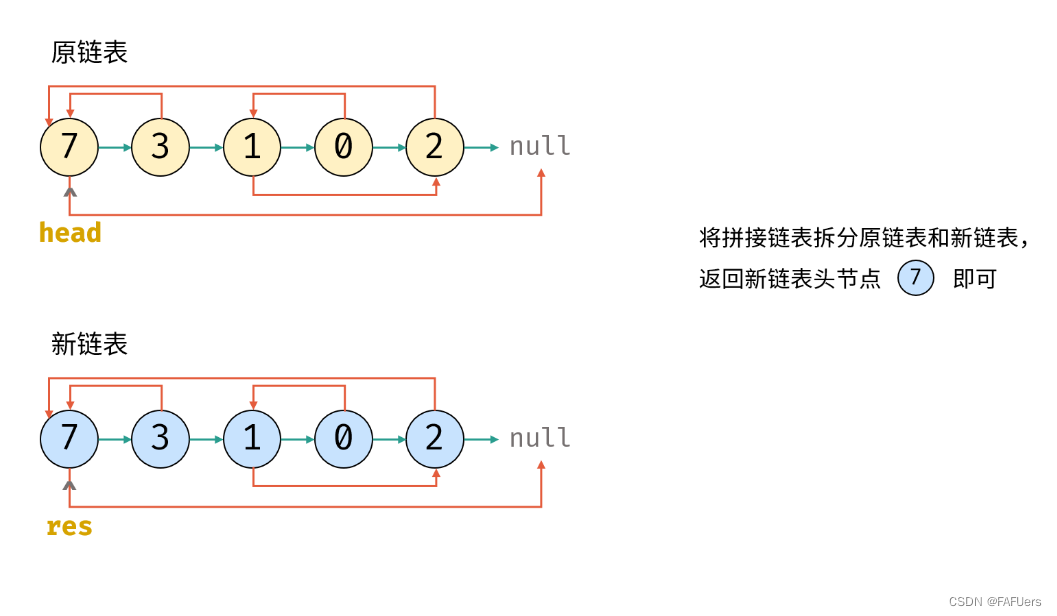
3.拆分原 / 新链表
4.返回新链表的头节点 res 即可

代码如下:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while(cur != null) {
Node tmp = new Node(cur.val);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
}
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null)
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3. 拆分两链表
cur = head.next;
Node pre = head, res = head.next;
while(cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null; // 单独处理原链表尾节点
return res; // 返回新链表头节点
}
}




![[操作系统笔记]连续分配管理方式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9bbadbfc7ebf438ca0f67a30fb3e69ff.png#pic_center)