损失函数
首先看下模型的输出结果:
output_cls:torch.Size([2, 900, 3])
output_box:torch.Size([2, 900, 4])
即设置batch-size=2,900个预测框
真值信息如下:第一张图片内有4个真值框,第二张图片亦然
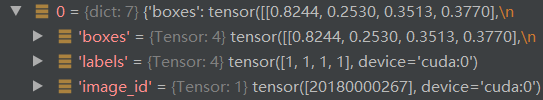
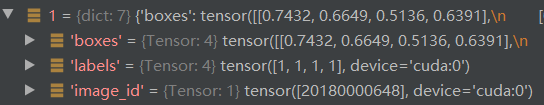
随后我们看看如何损失函数的计算,首先是进行匹配,即将预测框与真值框使用二分匹配的方式进行匹配。
outputs_without_aux 原本的output实际为6层的输出结果,我们只取最后一层即可。
outputs_without_aux = {k: v for k, v in outputs.items() if k != 'aux_outputs'}
device=next(iter(outputs.values())).device
indices = self.matcher(outputs_without_aux, targets)
通过indices = self.matcher(outputs_without_aux, targets)进行二分图匹配进入使预测框与真值框进行匹配。
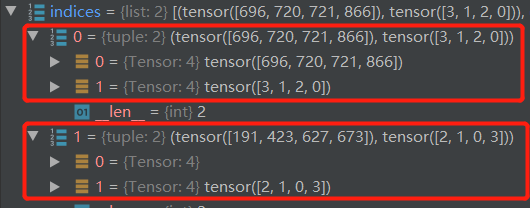
统计target数量,如果使用多显卡则进行平均分配
num_boxes = sum(len(t["labels"]) for t in targets)
num_boxes = torch.as_tensor([num_boxes], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
if is_dist_avail_and_initialized():
torch.distributed.all_reduce(num_boxes)
num_boxes = torch.clamp(num_boxes / get_world_size(), min=1).item()
开始计算损失:
首先是加噪损失,即DINO中使用添加噪声的方式来辅助匈牙利算法收敛,之后便是预测框与真值框的计算损失过程:
if 'interm_outputs' in outputs:
interm_outputs = outputs['interm_outputs']
indices = self.matcher(interm_outputs, targets)
if return_indices:
indices_list.append(indices)
for loss in self.losses:
if loss == 'masks':
# Intermediate masks losses are too costly to compute, we ignore them.
continue
kwargs = {}
if loss == 'labels':
# Logging is enabled only for the last layer
kwargs = {'log': False}
l_dict = self.get_loss(loss, interm_outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, **kwargs)
l_dict = {k + f'_interm': v for k, v in l_dict.items()}
losses.update(l_dict)
其损失包含类别损失与定位损失。
首先是通过匈牙利匹配算法来进行预测框与真值框的匹配,随后进行计算。获得匹配的编号

然后判断要计算哪些loss ,self.loss为 [‘labels’, ‘boxes’, ‘cardinality’]
调用get_loss方法计算损失值:
l_dict = self.get_loss(loss, interm_outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, **kwargs)
loss_map中保存loss_labels与loss_boxes等
def get_loss(self, loss, outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, **kwargs):
loss_map = {
'labels': self.loss_labels,
'cardinality': self.loss_cardinality,
'boxes': self.loss_boxes,
'masks': self.loss_masks,
}
assert loss in loss_map, f'do you really want to compute {loss} loss?'
return loss_map[loss](outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, **kwargs)
接下来我们看看labels损失与box损失是如何计算的
类别损失
首先是loss_labels :
def loss_labels(self, outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes, log=True):
传递的参数为:
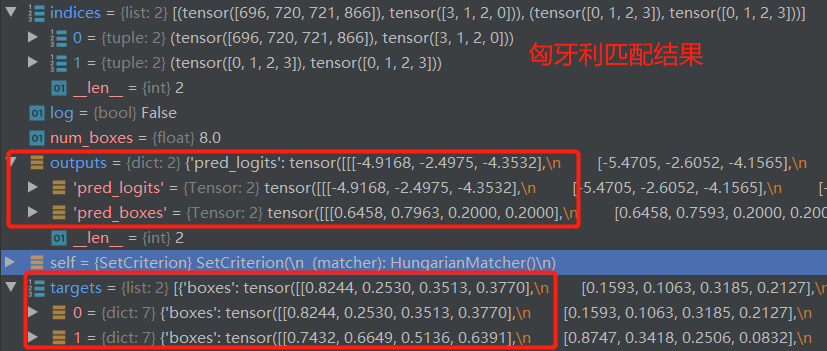
src_logits存储的是类别输出结果
src_logits = outputs['pred_logits'] torch.Size([2, 900, 3])
随后获取匹配结果的batch与编号
idx = self._get_src_permutation_idx(indices)
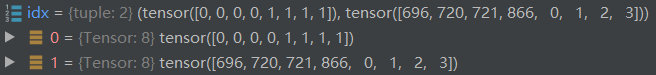
由_get_src_permutation_idx 方法的定义可知,其返回结果为所属batch与预测框的编号
def _get_src_permutation_idx(self, indices):
# permute predictions following indices
batch_idx = torch.cat([torch.full_like(src, i) for i, (src, _) in enumerate(indices)])
src_idx = torch.cat([src for (src, _) in indices])
return batch_idx, src_idx
进行类别编号赋值,target_classes_o值为tensor([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], device=‘cuda:0’),即这8个物体预测类别皆为1号类,随后是其余的全部划为背景类,即target_classes 为torch.Size([2, 900])
类目内容全为3,3为我们设定的背景类别
随后将对应编号的预测框设置为target_classes_o,即预测的类别
idx值为(tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]), tensor([696, 720, 721, 866, 0, 1, 2, 3]))
就相当于batch=0的696号置为target_classes_o设定的值,以次类推
target_classes_o = torch.cat([t["labels"][J] for t, (_, J) in zip(targets, indices)])
target_classes = torch.full(src_logits.shape[:2], self.num_classes,
dtype=torch.int64, device=src_logits.device)
target_classes[idx] = target_classes_o
随后进行one_hot编码
target_classes_onehot 为 torch.Size([2, 900, 4])

随后计算类别损失,使用的是交叉熵损失sigmoid_focal_loss ,值为:tensor(0.8650, device=‘cuda:0’, grad_fn=)
多分类任务采取的softmax loss,而是使用了多标签分类中的sigmoid
loss(即逐个判断属于每个类别的概率,不要求所有概率的和为1,一个检测框可以属于多个类别),原因是sigmoid的形式训练过程中会更稳定。
并将值保存在 losses = {'loss_ce': loss_ce} 中
同时class_error为:
losses['class_error'] = 100 - accuracy(src_logits[idx], target_classes_o)[0]
最终返回losses即可得到类别损失值。
接下来便是box回归损失的计算:
Box损失计算
box损失计算传入的参数与类别损失计算传入的参数相同,过程也即为类似,首先是通过匈牙利匹配获取预测框与真值框的匹配关系,紧接着进行L1损失与GIOU损失的计算。
idx值为:(tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]), tensor([696, 720, 721, 866, 0, 1, 2, 3]))
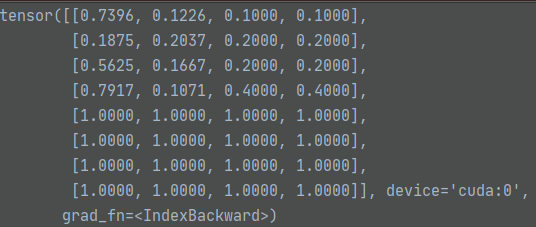
src_boxes值如下:
target_boxes值如下:
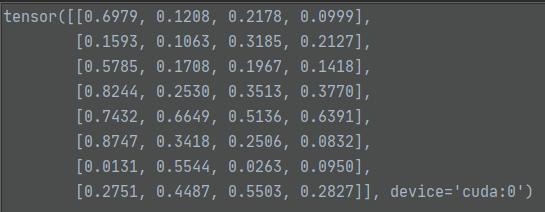
随后进行计算L1损失:
loss_bbox = F.l1_loss(src_boxes, target_boxes, reduction='none')
计算完成的损失值还要除以 num_boxes,值为 8.0
losses['loss_bbox'] = loss_bbox.sum() / num_boxes
紧接着计算GIOU损失值
loss_giou = 1 - torch.diag(box_ops.generalized_box_iou(
box_ops.box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(src_boxes),
box_ops.box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(target_boxes)))
losses['loss_giou'] = loss_giou.sum() / num_boxes
完整代码如下:
def loss_boxes(self, outputs, targets, indices, num_boxes):
assert 'pred_boxes' in outputs
idx = self._get_src_permutation_idx(indices)
src_boxes = outputs['pred_boxes'][idx]
target_boxes = torch.cat([t['boxes'][i] for t, (_, i) in zip(targets, indices)], dim=0)
loss_bbox = F.l1_loss(src_boxes, target_boxes, reduction='none')
losses = {}
losses['loss_bbox'] = loss_bbox.sum() / num_boxes
loss_giou = 1 - torch.diag(box_ops.generalized_box_iou(
box_ops.box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(src_boxes),
box_ops.box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(target_boxes)))
losses['loss_giou'] = loss_giou.sum() / num_boxes
# calculate the x,y and h,w loss
with torch.no_grad():
losses['loss_xy'] = loss_bbox[..., :2].sum() / num_boxes
losses['loss_hw'] = loss_bbox[..., 2:].sum() / num_boxes
return losses
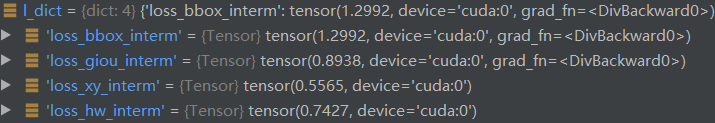
最终得到的loss_dict为,共有19个
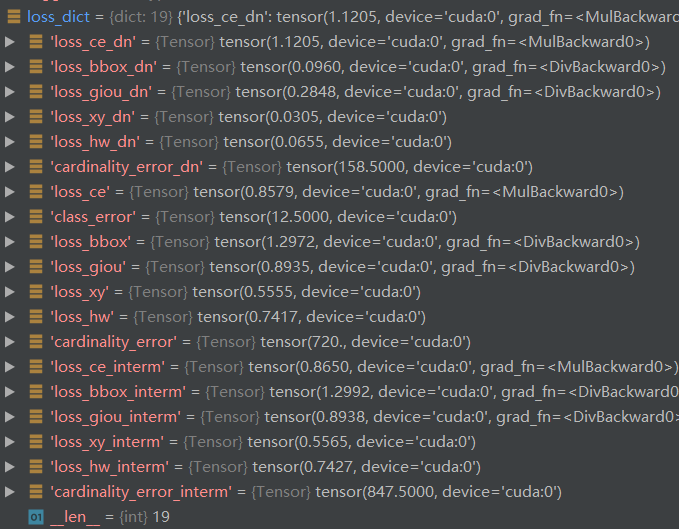
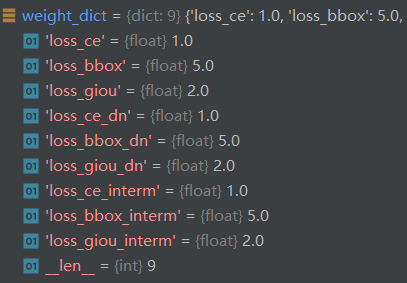
而真正计算损失的只有9个,这却决于是否给定weight值:







![【算法学习系列】03 - 由[1-5]等概率随机实现[2-10]等概率随机](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b38795eb6ab44f54afdd7e5fa6bbd2de.png)