Call
Call一般代表一个已经准备好的Request,Request的包装类,可执行,它一般有两个主要的方法:
- execute(立即执行,并阻塞线程,直到Response返回)
- enqueue(将Request放入队列,等待线程池调度执行),传入一个Callback。
需要注意的是:Response需要手动调用close方法。
一个Call只能调用一次execute或enqueue。
public interface Call extends Cloneable {
/** Returns the original request that initiated this call. */
Request request();
Response execute() throws IOException;
// 非立即执行,Dispatcher会决定这个Request什么时候可以执行
void enqueue(Callback responseCallback);
/** Cancels the request, if possible. Requests that are already complete cannot be canceled. */
void cancel();
/**
* Returns true if this call has been either {@linkplain #execute() executed} or {@linkplain
* #enqueue(Callback) enqueued}. It is an error to execute a call more than once.
*/
boolean isExecuted();
boolean isCanceled();
/**
* Create a new, identical call to this one which can be enqueued or executed even if this call
* has already been.
*/
Call clone();
interface Factory {
Call newCall(Request request);
}
}RealCall
Call只是一个基类,当调用OkhttpClient.newCall方法,实际返回的是RealCall(实现了Call接口)。
final class RealCall implements Call {}
new OkHttpClient().newCall(request)
public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false);
}
// 静态方法创建RealCall
static RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
RealCall call = new RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
call.eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call);
return call;
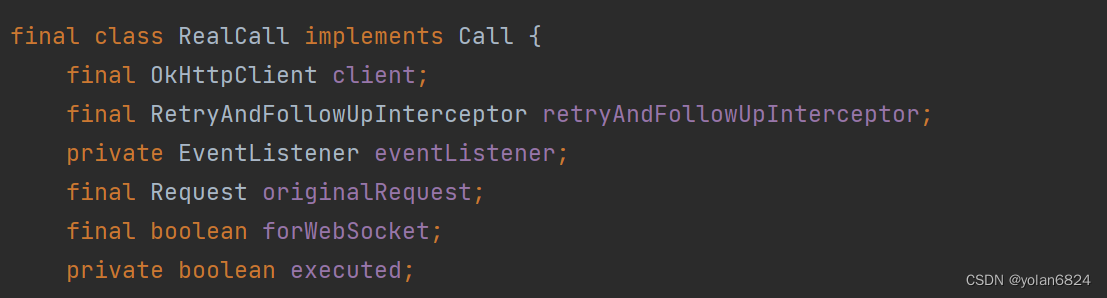
}RealCall持有的参数:
OkHttpClient,拦截器,EventListener,Request
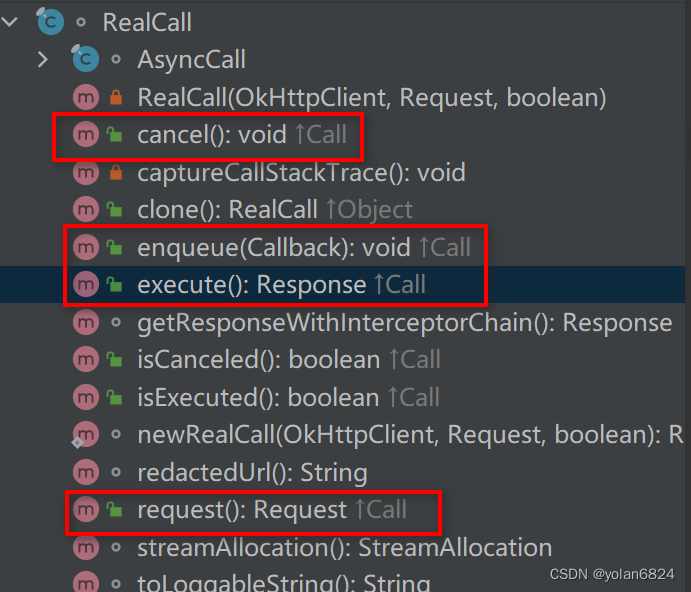
RealCall中比较重要的方法:
支持cancel,enqueue(入队),execute(立即执行)。
execute
execute代表同步执行call。
实际上,dispatcher的execute方法是由RealCall.execute方法调用的。
// RealCall.execute()
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);// 事件监听器
try {
client.dispatcher().executed(this);// 将自己加入Dispatcher的SyncCall队列中
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();// 同步通过拦截链获取结果
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
eventListener.callFailed(this, e);
throw e;
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);// 将自己从Dispatcher的SyncCall队列中移除
}
}execute方法主要做了三件事:
- 调用dispatcher().execute方法,将自己加入dispatcher的runningSyncCalls队列中。
- 同步调用getResponseWithInterceptorChain获取Response。
- 结束后,调用dispatcher().finished方法,将自己从dispatcher的runningSyncCalls中移除。
enqueue
public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized(this) {
if (this.executed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
}
this.executed = true;
}
this.captureCallStackTrace();
this.eventListener.callStart(this);
this.client.dispatcher().enqueue(new RealCall.AsyncCall(responseCallback));// 异步会需要一个CallBack传递结果,新建一个AsyncCall,AysncCall本质是一个Runnable
}enqueue方法只干了一件事:
将创建一个AsyncCall,并调用enqueue方法,将自己加入dispatcher的readyAsyncCalls或加入runningAsyncCalls,并加入线程池(具体机制看篇2:Dispatcher篇)。
看下AysncCall。
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {
private final Callback responseCallback;
AsyncCall(Callback responseCallback) {
super("OkHttp %s", new Object[]{RealCall.this.redactedUrl()});
this.responseCallback = responseCallback;
}
/****/
protected void execute() {// 被run()方法调用
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
Response response = RealCall.this.getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (RealCall.this.retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
this.responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
this.responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException var6) {
if (signalledCallback) {
Platform.get().log(4, "Callback failure for " + RealCall.this.toLoggableString(), var6);
} else {
RealCall.this.eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, var6);
this.responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, var6);
}
} finally {
RealCall.this.client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}AsyncCall实质是一个Runnable,它的run方法,调用了execute方法。
所以跟RealCall的区别只在于,AsyncCall是在一个线程里面调用了gettResponseWithInterceptorChain()来获取Response。
最后再通过业务方传入的responseCallback来回调这一次Call的执行结果。
AysncCall结束完成之后,再调用dispatcher.finished方法,将自己从dispatcher的runningAsyncCalls中移除,并安排新的AsyncCall进入线程池。
getResponseWithInterceptorChain
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}从RealCall的execute和enqueue方法都可以看出,获取Response的最主要方法就是getResponseWithInterceptorChain。
这个方法,通过添加一系列拦截器,封装到RealInterceptorChain中,最后调用chain.proceed方法得到Response。
所以说okhttp的核心就是链式+递归。
总结
- okhttpclient.newCall() 实际返回的是RealCall。
- RealCall的execute方法是一个同步阻塞获取Response的方法。execute方法会调用Dispatcher.execute方法,将自己加入到Dispatcher的runningSyncCalls队列中,并在获取到Response之后,调用Dispatcher.finished方法,将自己从队列中移除。
- RealCall的enqueue方法,实际是创建了一个实现了Runnable接口的AsyncCall,调用Dispatcher.enqueue方法,将自己加入线程池和Dispatcher的runningAysncCalls或只加入Dispatcher.readyAsyncCalls,等待Dispatcher的调度。并在AsyncCall运行完成后,调用Dispatcher.finished方法,将自己从队列中移除。
- 无论是execute方法还是enqueue方法,最终都是通过getResponseWithInterceptorChain获取Response的。这个方法里预定义了一系列拦截器,并最终将拦截器放入调用链中(RealInterceptorChain),顺序执行intercept方法。是一个典型的链式+递归结构。
因此下一篇,要讲解的就是拦截器篇啦。