说明
- 本文基于 kafka 2.7 编写。
- @author blog.jellyfishmix.com / JellyfishMIX - github
- LICENSE GPL-2.0
Sender 类属性
public class Sender implements Runnable {
private final Logger log;
/**
* Sender 具体用的是 KafkaClient 接口的实现类 NetworkClient, 为 Sender 提供了网络 IO 的能力
*/
/* the state of each nodes connection */
private final KafkaClient client;
/**
* RecordAccumulator, 可以获取待发送的 node 和此 node 对应待发送的消息
*/
/* the record accumulator that batches records */
private final RecordAccumulator accumulator;
/**
* MetaData 接口的实现类, 生产者元数据。存储着分区 leader 所在 node,node 的地址, topicPartition 等情况
*/
/* the metadata for the client */
private final ProducerMetadata metadata;
/**
* 是否保证消息在服务端的顺序性
*/
/* the flag indicating whether the producer should guarantee the message order on the broker or not. */
private final boolean guaranteeMessageOrder;
/**
* int 类型。请求的最大字节数,默认值是 1M
*/
/* the maximum request size to attempt to send to the server */
private final int maxRequestSize;
/**
* producer 的消息发送确认机制
* ack 有 3 个枚举值,分别是 1, 0 和 -1, 默认值是 -1。ack 枚举值的含义:
* 1) ack=1, producer 只要收到 leader 副本写入成功的响应就认为推送成功了。
* 2)ack=0,producer 发送请求了就认为推送成功,不管实际是否推送成功。
* 3)ack=-1,producer 只有收到 partition 内所有副本写入成功通知才认为推送消息成功了。
*/
/* the number of acknowledgements to request from the server */
private final short acks;
/**
* 生产者发送失败后的重试次数。默认是 0 次
*/
/* the number of times to retry a failed request before giving up */
private final int retries;
/* the clock instance used for getting the time */
private final Time time;
/**
* Sender 线程是否在运行中
*/
/* true while the sender thread is still running */
private volatile boolean running;
/* true when the caller wants to ignore all unsent/inflight messages and force close. */
private volatile boolean forceClose;
/* metrics */
private final SenderMetrics sensors;
/**
* producer 发送请求后等待 broker 响应的最大时间
* 过了最大响应时间如果配置了重试,生产者会再次发送这个请求。重试次数用完仍然请求超时, 则认为是请求失败
* 默认值 30,000,即 30 秒。
*/
/* the max time to wait for the server to respond to the request*/
private final int requestTimeoutMs;
/**
* 请求失败重发的间隔等待时间
* producer 发送请求失败后可能会引起重新发送失败的请求,间隔时间目的是防止重发过快造成服务端压力过大
* 默认是 100
*/
/* The max time to wait before retrying a request which has failed */
private final long retryBackoffMs;
/**
* ApiVersions,内部保存了每个 node 支持的 api 版本
*/
/* current request API versions supported by the known brokers */
private final ApiVersions apiVersions;
/* all the state related to transactions, in particular the producer id, producer epoch, and sequence numbers */
private final TransactionManager transactionManager;
/**
* 发送中的请求。key: TopicPartition,value: List<ProducerBatch>
*/
// A per-partition queue of batches ordered by creation time for tracking the in-flight batches
private final Map<TopicPartition, List<ProducerBatch>> inFlightBatches;
// ...
}
消息的发送
发送请求分为两步。
- 第一步是消息预发送,Sender 从 RecordAccumulator 拉取要发送的消息集合,封装成 ClientRequest,传递给 NetworkClient。
- NetworkClient 首先根据 ClientRequest 构造 InFlightRequest,InFlightRequest 表示已发送但还未收到响应的请求。然后根据收到的 ClientRequest 构造 NetworkSend 类对象,放入到 KafkaChannel 的缓存里,消息预发送结束。
- 第二步是真正的网络 IO,Sender 会调用 Selector#poll 方法, 把请求真正发送到 broker node。
run 方法
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#run
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#runOnce
实现了 Runnable 接口的 run 方法。run 方法会一直循环调用 runOnce 方法。
runOnce 方法主要逻辑:
- 把消息传递给 KafkaChanel 缓存。
- 执行网络 IO。
/**
* The main run loop for the sender thread
*/
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("Starting Kafka producer I/O thread.");
// main loop, runs until close is called
while (running) {
try {
runOnce();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in kafka producer I/O thread: ", e);
}
}
// ...
}
/**
* Run a single iteration of sending
*
*/
void runOnce() {
// ...
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
// 把消息传递给 KafkaChanel 缓存
long pollTimeout = sendProducerData(currentTimeMs);
// 执行网络 IO
client.poll(pollTimeout, currentTimeMs);
}
sendProducerData 方法 – 消息预发送
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#sendProducerData
- 获取元数据。
- 检查已经准备好的节点。
- 如果不存在任何 leaderPartition, 就更新元数据。
- 检查客户端和各 node 间连接是否正常。
- 把按分区聚合的请求集合, 转换为按节点聚合的请求集合(因为网络 IO 是按节点发请求)。
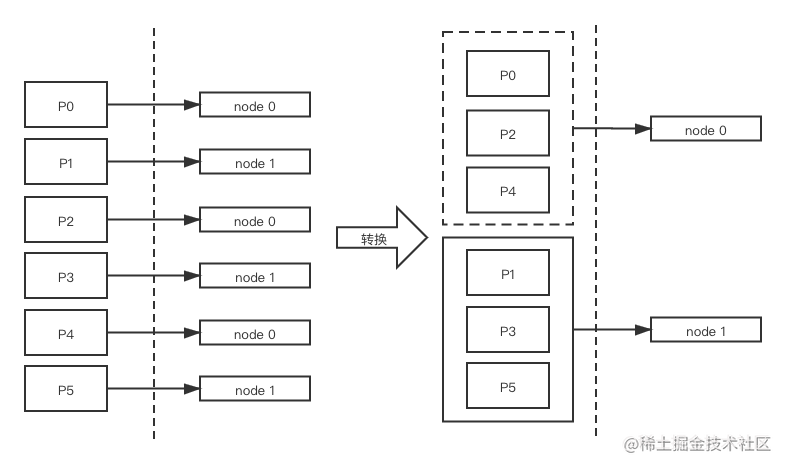
- 如图所示, 假设有两个 node(两台 broker 实例), 某个 topic 有 6 个 partition,每个 node 分配了 3 个 partition。如果按 partition 发送有 6 个请求,按 node 发送有 2 个请求。按 node 发送可以减小网络 IO 的开销。
- 收集过期的 batch, Sender#inflightBatches 发送中的请求集合里过期的 batch, RecordAccumulator#batches 集合里过期的 batch。处理过期 batch。
- 预发送消息。
/**
* 消息预发送, 把消息传递给 KafkaChanel 缓存
*/
private long sendProducerData(long now) {
// 获取元数据
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
// get the list of partitions with data ready to send
// 检查已经准备好的节点
RecordAccumulator.ReadyCheckResult result = this.accumulator.ready(cluster, now);
// 如果不存在任何 leaderPartition, 就更新元数据
// if there are any partitions whose leaders are not known yet, force metadata update
if (!result.unknownLeaderTopics.isEmpty()) {
// The set of topics with unknown leader contains topics with leader election pending as well as
// topics which may have expired. Add the topic again to metadata to ensure it is included
// and request metadata update, since there are messages to send to the topic.
for (String topic : result.unknownLeaderTopics)
this.metadata.add(topic, now);
log.debug("Requesting metadata update due to unknown leader topics from the batched records: {}",
result.unknownLeaderTopics);
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
}
// remove any nodes we aren't ready to send to
// 检查客户端和各 node 间连接是否可用
Iterator<Node> iter = result.readyNodes.iterator();
long notReadyTimeout = Long.MAX_VALUE;
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Node node = iter.next();
if (!this.client.ready(node, now)) {
iter.remove();
notReadyTimeout = Math.min(notReadyTimeout, this.client.pollDelayMs(node, now));
}
}
// create produce requests
// 把按分区聚合的请求集合, 转换为按节点聚合的请求集合(因为网络 IO 是按节点发请求)
Map<Integer, List<ProducerBatch>> batches = this.accumulator.drain(cluster, result.readyNodes, this.maxRequestSize, now);
addToInflightBatches(batches);
if (guaranteeMessageOrder) {
// Mute all the partitions drained
for (List<ProducerBatch> batchList : batches.values()) {
for (ProducerBatch batch : batchList)
this.accumulator.mutePartition(batch.topicPartition);
}
}
accumulator.resetNextBatchExpiryTime();
// 收集过期的 batch
// Sender#inflightBatches 发送中的请求集合里过期的 batch
List<ProducerBatch> expiredInflightBatches = getExpiredInflightBatches(now);
// RecordAccumulator#batches 集合里过期的 batch
List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = this.accumulator.expiredBatches(now);
expiredBatches.addAll(expiredInflightBatches);
// Reset the producer id if an expired batch has previously been sent to the broker. Also update the metrics
// for expired batches. see the documentation of @TransactionState.resetIdempotentProducerId to understand why
// we need to reset the producer id here.
// 处理过期 batch
if (!expiredBatches.isEmpty())
log.trace("Expired {} batches in accumulator", expiredBatches.size());
for (ProducerBatch expiredBatch : expiredBatches) {
String errorMessage = "Expiring " + expiredBatch.recordCount + " record(s) for " + expiredBatch.topicPartition
+ ":" + (now - expiredBatch.createdMs) + " ms has passed since batch creation";
failBatch(expiredBatch, -1, NO_TIMESTAMP, new TimeoutException(errorMessage), false);
if (transactionManager != null && expiredBatch.inRetry()) {
// This ensures that no new batches are drained until the current in flight batches are fully resolved.
transactionManager.markSequenceUnresolved(expiredBatch);
}
}
sensors.updateProduceRequestMetrics(batches);
// If we have any nodes that are ready to send + have sendable data, poll with 0 timeout so this can immediately
// loop and try sending more data. Otherwise, the timeout will be the smaller value between next batch expiry
// time, and the delay time for checking data availability. Note that the nodes may have data that isn't yet
// sendable due to lingering, backing off, etc. This specifically does not include nodes with sendable data
// that aren't ready to send since they would cause busy looping.
long pollTimeout = Math.min(result.nextReadyCheckDelayMs, notReadyTimeout);
pollTimeout = Math.min(pollTimeout, this.accumulator.nextExpiryTimeMs() - now);
pollTimeout = Math.max(pollTimeout, 0);
if (!result.readyNodes.isEmpty()) {
log.trace("Nodes with data ready to send: {}", result.readyNodes);
// if some partitions are already ready to be sent, the select time would be 0;
// otherwise if some partition already has some data accumulated but not ready yet,
// the select time will be the time difference between now and its linger expiry time;
// otherwise the select time will be the time difference between now and the metadata expiry time;
pollTimeout = 0;
}
// 预发送消息
sendProduceRequests(batches, now);
return pollTimeout;
}
getExpiredInflightBatches 方法 – 收集过期的 batch
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#getExpiredInflightBatches
- 遍历 inFlightBatches,遍历当前 partition 的 batches 列表。
- 判断 batch 是否投递超时。默认消息投递过期时间是 2 min。
- 如果 batch 超时且没有 done 的状态,就把 batch 加入到 expiredBatches 集合。
- 如果 batch 没有超时,则更新下一个 batch 的超时时间。
private List<ProducerBatch> getExpiredInflightBatches(long now) {
List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历 inFlightBatches
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<TopicPartition, List<ProducerBatch>>> batchIt = inFlightBatches.entrySet().iterator(); batchIt.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<TopicPartition, List<ProducerBatch>> entry = batchIt.next();
List<ProducerBatch> partitionInFlightBatches = entry.getValue();
if (partitionInFlightBatches != null) {
// 遍历当前 partition 的 batches 列表
Iterator<ProducerBatch> iter = partitionInFlightBatches.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
ProducerBatch batch = iter.next();
// 判断 batch 是否投递超时。默认消息投递过期时间是 2 min
if (batch.hasReachedDeliveryTimeout(accumulator.getDeliveryTimeoutMs(), now)) {
iter.remove();
// expireBatches is called in Sender.sendProducerData, before client.poll.
// The !batch.isDone() invariant should always hold. An IllegalStateException
// exception will be thrown if the invariant is violated.
// 如果 batch 没有 done 的状态,就把 batch 加入到 expiredBatches 集合
if (!batch.isDone()) {
expiredBatches.add(batch);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException(batch.topicPartition + " batch created at " +
batch.createdMs + " gets unexpected final state " + batch.finalState());
}
} else {
// 更新下一个 batch 的超时时间
accumulator.maybeUpdateNextBatchExpiryTime(batch);
break;
}
}
if (partitionInFlightBatches.isEmpty()) {
batchIt.remove();
}
}
}
return expiredBatches;
}
failBatch 方法 – 触发回调并改变 future 状态
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#failBatch(org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.ProducerBatch, long, long, java.lang.RuntimeException, boolean)
batch.done 调用了里面的回调方法,然后删除 batch 并释放 batch 占用的空间。
private void failBatch(ProducerBatch batch,
long baseOffset,
long logAppendTime,
RuntimeException exception,
boolean adjustSequenceNumbers) {
if (transactionManager != null) {
transactionManager.handleFailedBatch(batch, exception, adjustSequenceNumbers);
}
this.sensors.recordErrors(batch.topicPartition.topic(), batch.recordCount);
// batch.done 触发回调并改变 future 状态,然后删除 batch 并释放 batch 占用的空间
if (batch.done(baseOffset, logAppendTime, exception)) {
maybeRemoveAndDeallocateBatch(batch);
}
}
Sender#sendProduceRequest 方法 – 预发送消息
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#sendProduceRequest
预发送消息, 模型转换, 把 ProducerBatch 转换成 ClientRequest, 并把 ClientRequest 传递到 KafkaChannel 的缓存中。
- 初始化两个集合, produceRecordsByPartition 用于构建 ProducerRequest, recordsByPartition 用于构建 callback。
- 按分区填充 produceRecordsByPartition 和 recordsByPartition 两个集合。
- 构建 ProducerRequestBuilder, 构建 producerRequest 的 callback, 封装成 ClientRequest。
- 调用 NetworkClient#send 方法预发送消息, 把 ClientRequest 传递给 NetworkClient(传递到 KafkaChannel 的缓存中)。
/**
* Create a produce request from the given record batches
*
* 预发送消息
* 模型转换, 把 ProducerBatch 转换成 ClientRequest, 并把 ClientRequest 传递到 KafkaChannel 的缓存中
*/
private void sendProduceRequest(long now, int destination, short acks, int timeout, List<ProducerBatch> batches) {
if (batches.isEmpty())
return;
// 初始化两个集合, produceRecordsByPartition 用于构建 ProducerRequest, recordsByPartition 用于构建 callback
Map<TopicPartition, MemoryRecords> produceRecordsByPartition = new HashMap<>(batches.size());
final Map<TopicPartition, ProducerBatch> recordsByPartition = new HashMap<>(batches.size());
// find the minimum magic version used when creating the record sets
byte minUsedMagic = apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic();
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches) {
if (batch.magic() < minUsedMagic)
minUsedMagic = batch.magic();
}
// 按分区填充 produceRecordsByPartition 和 recordsByPartition 两个集合
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches) {
TopicPartition tp = batch.topicPartition;
MemoryRecords records = batch.records();
// down convert if necessary to the minimum magic used. In general, there can be a delay between the time
// that the producer starts building the batch and the time that we send the request, and we may have
// chosen the message format based on out-dated metadata. In the worst case, we optimistically chose to use
// the new message format, but found that the broker didn't support it, so we need to down-convert on the
// client before sending. This is intended to handle edge cases around cluster upgrades where brokers may
// not all support the same message format version. For example, if a partition migrates from a broker
// which is supporting the new magic version to one which doesn't, then we will need to convert.
if (!records.hasMatchingMagic(minUsedMagic))
records = batch.records().downConvert(minUsedMagic, 0, time).records();
produceRecordsByPartition.put(tp, records);
recordsByPartition.put(tp, batch);
}
String transactionalId = null;
if (transactionManager != null && transactionManager.isTransactional()) {
transactionalId = transactionManager.transactionalId();
}
// 构建 ProducerRequestBuilder
ProduceRequest.Builder requestBuilder = ProduceRequest.Builder.forMagic(minUsedMagic, acks, timeout,
produceRecordsByPartition, transactionalId);
// 构建 producerRequest 的 callback
RequestCompletionHandler callback = response -> handleProduceResponse(response, recordsByPartition, time.milliseconds());
String nodeId = Integer.toString(destination);
// 构建 ClientRequest
ClientRequest clientRequest = client.newClientRequest(nodeId, requestBuilder, now, acks != 0,
requestTimeoutMs, callback);
// 预发送消息, 把 ClientRequest 传递给 NetworkClient(传递到 KafkaChannel 的缓存中)
client.send(clientRequest, now);
log.trace("Sent produce request to {}: {}", nodeId, requestBuilder);
}
处理消息的响应
Sender#handleProduceResponse 方法 – 处理 ProduceRequest 的响应
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#handleProduceResponse
-
一个 response 是某一个 node 发给 client 的,一个 node 每次向 client 发送的 response 也是批量的,一个 response 有可能包含多个 partition 的响应信息。
-
Sender 收到 response 后会根据结果按情况处理, 处理方法是 completeBatch()。
-
Sender 需要触发 callback, callback 在构建 ClientRequest 时填充了。
/**
* Handle a produce response
*
* 处理 ClientResponse
*/
private void handleProduceResponse(ClientResponse response, Map<TopicPartition, ProducerBatch> batches, long now) {
RequestHeader requestHeader = response.requestHeader();
int correlationId = requestHeader.correlationId();
// 连接失败
if (response.wasDisconnected()) {
log.trace("Cancelled request with header {} due to node {} being disconnected",
requestHeader, response.destination());
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches.values())
completeBatch(batch, new ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse(Errors.NETWORK_EXCEPTION), correlationId, now);
// 处理版本不匹配
} else if (response.versionMismatch() != null) {
log.warn("Cancelled request {} due to a version mismatch with node {}",
response, response.destination(), response.versionMismatch());
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches.values())
completeBatch(batch, new ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse(Errors.UNSUPPORTED_VERSION), correlationId, now);
// 处理正常 response
} else {
log.trace("Received produce response from node {} with correlation id {}", response.destination(), correlationId);
// if we have a response, parse it
// 存在 response
if (response.hasResponse()) {
ProduceResponse produceResponse = (ProduceResponse) response.responseBody();
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse> entry : produceResponse.responses().entrySet()) {
TopicPartition tp = entry.getKey();
ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse partResp = entry.getValue();
ProducerBatch batch = batches.get(tp);
// 调用 completeBatch 方法处理
completeBatch(batch, partResp, correlationId, now);
}
this.sensors.recordLatency(response.destination(), response.requestLatencyMs());
} else {
// this is the acks = 0 case, just complete all requests
// response ack=0 时的处理
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches.values()) {
completeBatch(batch, new ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse(Errors.NONE), correlationId, now);
}
}
}
}
Sender#completeBatch 方法 – 处理 response 的状态
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#completeBatch(org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.ProducerBatch, org.apache.kafka.common.requests.ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse, long, long)
- 过长的单条消息,会把单条消息分成多个 batch 发送。
- 如果存在错误,能否再次发送, 可以的话则入队 batch。不能再次发送则进行不同错误情况的处理。
- 重复发送, 不用做任何处理。
- 授权失败等其他异常,统一调用 failBatch 处理。
- 没有错误正常执行回调方法, 并释放 accumulator 的空间。
private void completeBatch(ProducerBatch batch, ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse response, long correlationId,
long now) {
Errors error = response.error;
// 过长的单条消息,会把单条消息分成多个 batch 发送
if (error == Errors.MESSAGE_TOO_LARGE && batch.recordCount > 1 && !batch.isDone() &&
(batch.magic() >= RecordBatch.MAGIC_VALUE_V2 || batch.isCompressed())) {
// If the batch is too large, we split the batch and send the split batches again. We do not decrement
// the retry attempts in this case.
log.warn(
"Got error produce response in correlation id {} on topic-partition {}, splitting and retrying ({} attempts left). Error: {}",
correlationId,
batch.topicPartition,
this.retries - batch.attempts(),
error);
if (transactionManager != null)
transactionManager.removeInFlightBatch(batch);
this.accumulator.splitAndReenqueue(batch);
maybeRemoveAndDeallocateBatch(batch);
this.sensors.recordBatchSplit();
// 如果存在错误
} else if (error != Errors.NONE) {
// 能否再次发送, 可以的话则入队 batch
if (canRetry(batch, response, now)) {
log.warn(
"Got error produce response with correlation id {} on topic-partition {}, retrying ({} attempts left). Error: {}",
correlationId,
batch.topicPartition,
this.retries - batch.attempts() - 1,
error);
reenqueueBatch(batch, now);
// 重复发送, 不用做任何处理
} else if (error == Errors.DUPLICATE_SEQUENCE_NUMBER) {
// If we have received a duplicate sequence error, it means that the sequence number has advanced beyond
// the sequence of the current batch, and we haven't retained batch metadata on the broker to return
// the correct offset and timestamp.
//
// The only thing we can do is to return success to the user and not return a valid offset and timestamp.
completeBatch(batch, response);
} else {
final RuntimeException exception;
// topic 授权失败
if (error == Errors.TOPIC_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED)
exception = new TopicAuthorizationException(Collections.singleton(batch.topicPartition.topic()));
// cluster 授权失败
else if (error == Errors.CLUSTER_AUTHORIZATION_FAILED)
exception = new ClusterAuthorizationException("The producer is not authorized to do idempotent sends");
else
exception = error.exception(response.errorMessage);
// tell the user the result of their request. We only adjust sequence numbers if the batch didn't exhaust
// its retries -- if it did, we don't know whether the sequence number was accepted or not, and
// thus it is not safe to reassign the sequence.
// 授权失败等其他异常,统一调用 failBatch 处理
failBatch(batch, response, exception, batch.attempts() < this.retries);
}
// metadata 无效或错误, 更新 metadata
if (error.exception() instanceof InvalidMetadataException) {
if (error.exception() instanceof UnknownTopicOrPartitionException) {
log.warn("Received unknown topic or partition error in produce request on partition {}. The " +
"topic-partition may not exist or the user may not have Describe access to it",
batch.topicPartition);
} else {
log.warn("Received invalid metadata error in produce request on partition {} due to {}. Going " +
"to request metadata update now", batch.topicPartition, error.exception(response.errorMessage).toString());
}
metadata.requestUpdate();
}
} else {
// 正常执行回调方法
completeBatch(batch, response);
}
// Unmute the completed partition.
if (guaranteeMessageOrder)
this.accumulator.unmutePartition(batch.topicPartition);
}
private void completeBatch(ProducerBatch batch, ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse response) {
if (transactionManager != null) {
transactionManager.handleCompletedBatch(batch, response);
}
// 执行回调方法,并释放 accumulator 的空间
if (batch.done(response.baseOffset, response.logAppendTime, null)) {
maybeRemoveAndDeallocateBatch(batch);
}
}
Sender#canRetry 方法 – response 存在错误判断是否能再次发送
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.Sender#canRetry
response 存在错误判断是否能再次发送, 需要满足以下条件:
- 没有到投递的超时时间。
- batch 重试次数没有超过设定的次数。
- batch 状态未结束。
- 如果被事务管理器管理, 则调用事务管理器判断是否能重试。
private boolean canRetry(ProducerBatch batch, ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse response, long now) {
// 没有到投递的超时时间
return !batch.hasReachedDeliveryTimeout(accumulator.getDeliveryTimeoutMs(), now) &&
// batch 重试次数没有超过设定的次数
batch.attempts() < this.retries &&
// batch 状态未结束
!batch.isDone() &&
// 如果被事务管理器管理, 则调用事务管理器判断是否能重试
(transactionManager == null ?
response.error.exception() instanceof RetriableException :
transactionManager.canRetry(response, batch));
}

![[SUCTF 2018]GetShell](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e6fdca394c3b4763ab4085e4251202ac.png)