智能合约
Remix IDE
是开发以太坊智能合约的在线IDE工具,部署简单的智能合约非常方便。
http://remix.ethereum.org
truffle
一个世界级的智能合约开发框架,专为智能合约而生。
- 管理智能合约的生命周期
- 自动化合约测试
- 可编程,可部署,可发布智能合约
- 不用过多的关注网络管理
- 强大的交互式控制台
安装truffle:
npm i truffle -g在指定文件夹下初始化合约:
truffle init合约目录结构:
- contracts/ :存放solidity智能合约文件
- migrations/ :truffle使用migration system来控制合约的部署
- test/ :测试文件存放位置
- truffle-config.js:配置文件
配置truffle-config.js文件:
打开开发配置,下方advance高级配置可以指定扣钱的账户,如不指定,默认是第一个登录的账号扣钱,这里我们是account2,导入的ganache账户。打开优化配置。
/**
* Use this file to configure your truffle project. It's seeded with some
* common settings for different networks and features like migrations,
* compilation, and testing. Uncomment the ones you need or modify
* them to suit your project as necessary.
*
* More information about configuration can be found at:
*
* https://trufflesuite.com/docs/truffle/reference/configuration
*
* Hands-off deployment with Infura
* --------------------------------
*
* Do you have a complex application that requires lots of transactions to deploy?
* Use this approach to make deployment a breeze 🏖️:
*
* Infura deployment needs a wallet provider (like @truffle/hdwallet-provider)
* to sign transactions before they're sent to a remote public node.
* Infura accounts are available for free at 🔍: https://infura.io/register
*
* You'll need a mnemonic - the twelve word phrase the wallet uses to generate
* public/private key pairs. You can store your secrets 🤐 in a .env file.
* In your project root, run `$ npm install dotenv`.
* Create .env (which should be .gitignored) and declare your MNEMONIC
* and Infura PROJECT_ID variables inside.
* For example, your .env file will have the following structure:
*
* MNEMONIC = <Your 12 phrase mnemonic>
* PROJECT_ID = <Your Infura project id>
*
* Deployment with Truffle Dashboard (Recommended for best security practice)
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
*
* Are you concerned about security and minimizing rekt status 🤔?
* Use this method for best security:
*
* Truffle Dashboard lets you review transactions in detail, and leverages
* MetaMask for signing, so there's no need to copy-paste your mnemonic.
* More details can be found at 🔎:
*
* https://trufflesuite.com/docs/truffle/getting-started/using-the-truffle-dashboard/
*/
// require('dotenv').config();
// const { MNEMONIC, PROJECT_ID } = process.env;
// const HDWalletProvider = require('@truffle/hdwallet-provider');
module.exports = {
/**
* Networks define how you connect to your ethereum client and let you set the
* defaults web3 uses to send transactions. If you don't specify one truffle
* will spin up a managed Ganache instance for you on port 9545 when you
* run `develop` or `test`. You can ask a truffle command to use a specific
* network from the command line, e.g
*
* $ truffle test --network <network-name>
*/
networks: {
// Useful for testing. The `development` name is special - truffle uses it by default
// if it's defined here and no other network is specified at the command line.
// You should run a client (like ganache, geth, or parity) in a separate terminal
// tab if you use this network and you must also set the `host`, `port` and `network_id`
// options below to some value.
//
development: {
host: "127.0.0.1", // Localhost (default: none)
port: 8545, // Standard Ethereum port (default: none)
network_id: "*", // Any network (default: none)
},
//
// An additional network, but with some advanced options…
// advanced: {
// port: 8777, // Custom port
// network_id: 1342, // Custom network
// gas: 8500000, // Gas sent with each transaction (default: ~6700000)
// gasPrice: 20000000000, // 20 gwei (in wei) (default: 100 gwei)
// from: <address>, // Account to send transactions from (default: accounts[0])
// websocket: true // Enable EventEmitter interface for web3 (default: false)
// },
//
// Useful for deploying to a public network.
// Note: It's important to wrap the provider as a function to ensure truffle uses a new provider every time.
// goerli: {
// provider: () => new HDWalletProvider(MNEMONIC, `https://goerli.infura.io/v3/${PROJECT_ID}`),
// network_id: 5, // Goerli's id
// confirmations: 2, // # of confirmations to wait between deployments. (default: 0)
// timeoutBlocks: 200, // # of blocks before a deployment times out (minimum/default: 50)
// skipDryRun: true // Skip dry run before migrations? (default: false for public nets )
// },
//
// Useful for private networks
// private: {
// provider: () => new HDWalletProvider(MNEMONIC, `https://network.io`),
// network_id: 2111, // This network is yours, in the cloud.
// production: true // Treats this network as if it was a public net. (default: false)
// }
},
// Set default mocha options here, use special reporters, etc.
mocha: {
// timeout: 100000
},
// Configure your compilers
compilers: {
solc: {
version: "0.8.18", // Fetch exact version from solc-bin (default: truffle's version)
// docker: true, // Use "0.5.1" you've installed locally with docker (default: false)
settings: { // See the solidity docs for advice about optimization and evmVersion
optimizer: {
enabled: false,
runs: 200
},
evmVersion: "byzantium"
}
}
},
// Truffle DB is currently disabled by default; to enable it, change enabled:
// false to enabled: true. The default storage location can also be
// overridden by specifying the adapter settings, as shown in the commented code below.
//
// NOTE: It is not possible to migrate your contracts to truffle DB and you should
// make a backup of your artifacts to a safe location before enabling this feature.
//
// After you backed up your artifacts you can utilize db by running migrate as follows:
// $ truffle migrate --reset --compile-all
//
// db: {
// enabled: false,
// host: "127.0.0.1",
// adapter: {
// name: "indexeddb",
// settings: {
// directory: ".db"
// }
// }
// }
};
在contracts下建立StudentStorage.sol文件。
solidity
数据位置
solidity数据存储位置有三类:storage,memory,calldata。不同存储位置的gas成本不同。storage类型的数据存在链上,类似计算机的硬盘,消耗gas多,memory和calldata类型的临时存储在内存里,消耗gas少。
- storage:合约里的状态变量默认都是storage,存储在链上。
- memory:函数里的参数和临时变量一般用memory。存储在内存中,不上链。
- calldata:和memory类似,存储在内存中,不上链。与memory不通点在于calldata不能修改,一般用于函数的参数。
作用域:
变量的作用域:Solidity中变量按作用域划分有三种:
状态变量:状态变量是数据存储在链上的变量,所有合约内函数都可以访问,gas消耗高。状态变量在合约内,函数外声明。可以在函数里更改状态变量的值。
局部变量:局部变量是仅在函数执行过程中有效的变量,函数脱出后,变量无效。局部变量的素具存储在内存,不上链,gas低,声明在函数内。
和全局变量:全局变量是全局范围工作的变量,都是solidity预留关键字。他们可以在函数内不声明直接使用(类似于msg.sender,block.number)
作用域类型
- public 公共状态变量可以在内部访问,也可以通过消息访问。对于公共状态变量,将生成一个自动getter函数。
- internal 内部状态变量只能从当前合约或其派生合约内访问,类似于继承。
- private:私有状态变量只能从当前合约内部访问,派生合约也不能访问。
函数可以指定为以下:
external:外部合约函数是合约接口的一部分,这意味着可以从其他合约或通过事务调用他们,但是内部无法调用。
public:外部和内部都可以调用。
internal:只能从当前合约或当前合约的派生合约中访问,外部无法访问,由于它们没有通过合约的ABI向外部公开,所以他们可以接受内部类型的参数,比如映射或存储引用。
private:私有函数类似于内部函数,但在派生合约中不可见。
智能合约脚本:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
//源码遵循协议,MIT...
pragma solidity >=0.4.16 <0.9.0; //限定solidity编译器版本
contract StudentStorage{ //名称与文件名一致
//创建两个状态变量,存储在链上,默认storage类型
uint age; //默认uint256
string name;
//函数形参使用memory/calldata类型,临时内存,基本类型可以不用设置,uint不用设置了
function setData(string memory _name,uint _age) public{
//string memory a; //局部变量
name=_name;
age=_age;
}
//view视图函数,只访问不修改状态变量,pure纯函数,不访问也不修改,两者可以节省gas,如果不加会花很多gas
function getData() public view returns (string memory,uint) {
return (name,age);
}
}必须写分号,不然报错
执行编译:
truffle compile编译结束,会出现一个build文件夹生成StudentStorage.json。
在migration文件夹下创建并编写部署脚本1_deploy.js:
const Contracts = artifacts.require("StudentStorage.sol")//引入合约
module.exports=function(deployer){
deployer.deploy(Contracts)
}部署合约,会先执行truffle compile,然后再部署:
truffle migrate与此同时,对应的account2消耗了gas。
下面我们可以测试一下,一次在终端输入:
truffle console
const object = await StudentStorage.deployed()object能够看到部署的智能合约对象,下面设置值
object.setData("xiaoming",18)读取值:
object.getData()此时我们如果直接通过object.name,或者object.age直接访问,是不能读取到的,改为公共属性即可。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
//源码遵循协议,MIT...
pragma solidity >=0.4.16 <0.9.0; //限定solidity编译器版本
contract StudentStorage{ //名称与文件名一致
//创建两个状态变量,存储在链上,默认storage类型
uint public age; //默认uint256
string public name;
//函数形参使用memory/calldata类型,临时内存,基本类型可以不用设置,uint不用设置了
function setData(string memory _name,uint _age) public{
//string memory a; //局部变量
name=_name;
age=_age;
}
//view视图函数,只访问不修改状态变量,pure纯函数,不访问也不修改,两者可以节省gas,如果不加会花很多gas
function getData() public view returns (string memory,uint) {
return (name,age);
}
}按照上述重新部署,再次访问obj.age,发现会返回一个函数,所有设置了public的变量,都会自动生成一个对应的getter方法
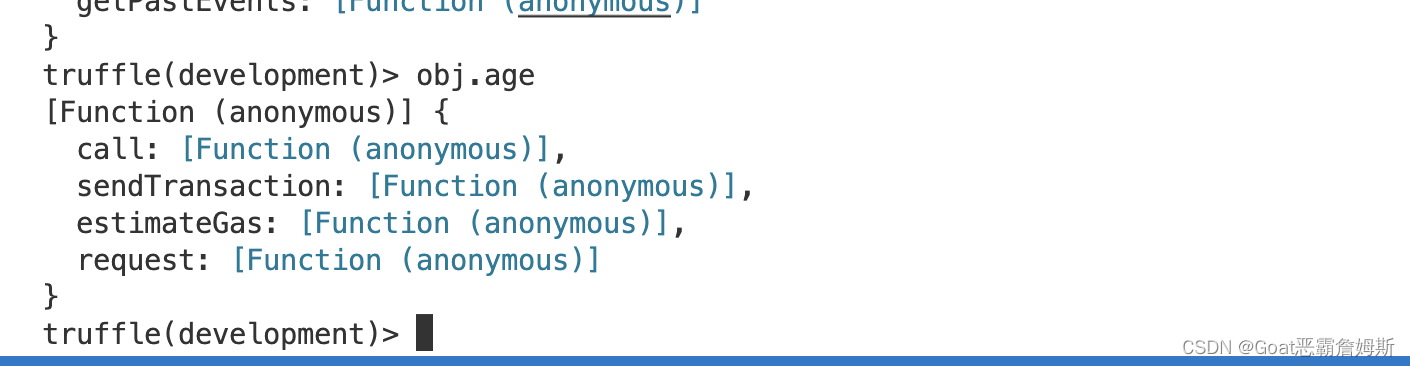
我们重新设值,然后访问使用obj.age()或obj.name()方法访问,就可以访问到了。所以想要外部调用使用public/external,不想的话就internal/private。