算法基础第二章
第二章:数据结构 1、链表 1.1、单链表(写邻接表:存储图和树) 1.2、双链表(优化某些问题) 2、栈与队列 2.1、栈
2.2、队列 2.2.1、数组模拟队列 2.2.2、滑动窗口(单调队列的使用) 3、KMP(字符串匹配) 4、Trie树(高效地存储和查找字符串集合的数据结构) 5、并查集 6、堆 7、Hash表
8、STL常用容器(用的时候查一下就行了) 8.1、vector 8.3、pair<int,int> 8.2、string 8.3、queue(队尾进队头出,固定方向) 8.4、priority_queue(优先队列就是堆,默认是大根堆) 8.5、stack 8.6 deque(双端队列) 8.7 set、map、multiset、multimap(基于平衡二叉树(红黑树),动态维护有序序列) 8.8、unordered_set、unordered_map、unordered_multiset、unordered_multimap(哈希表) 8.9、bitset
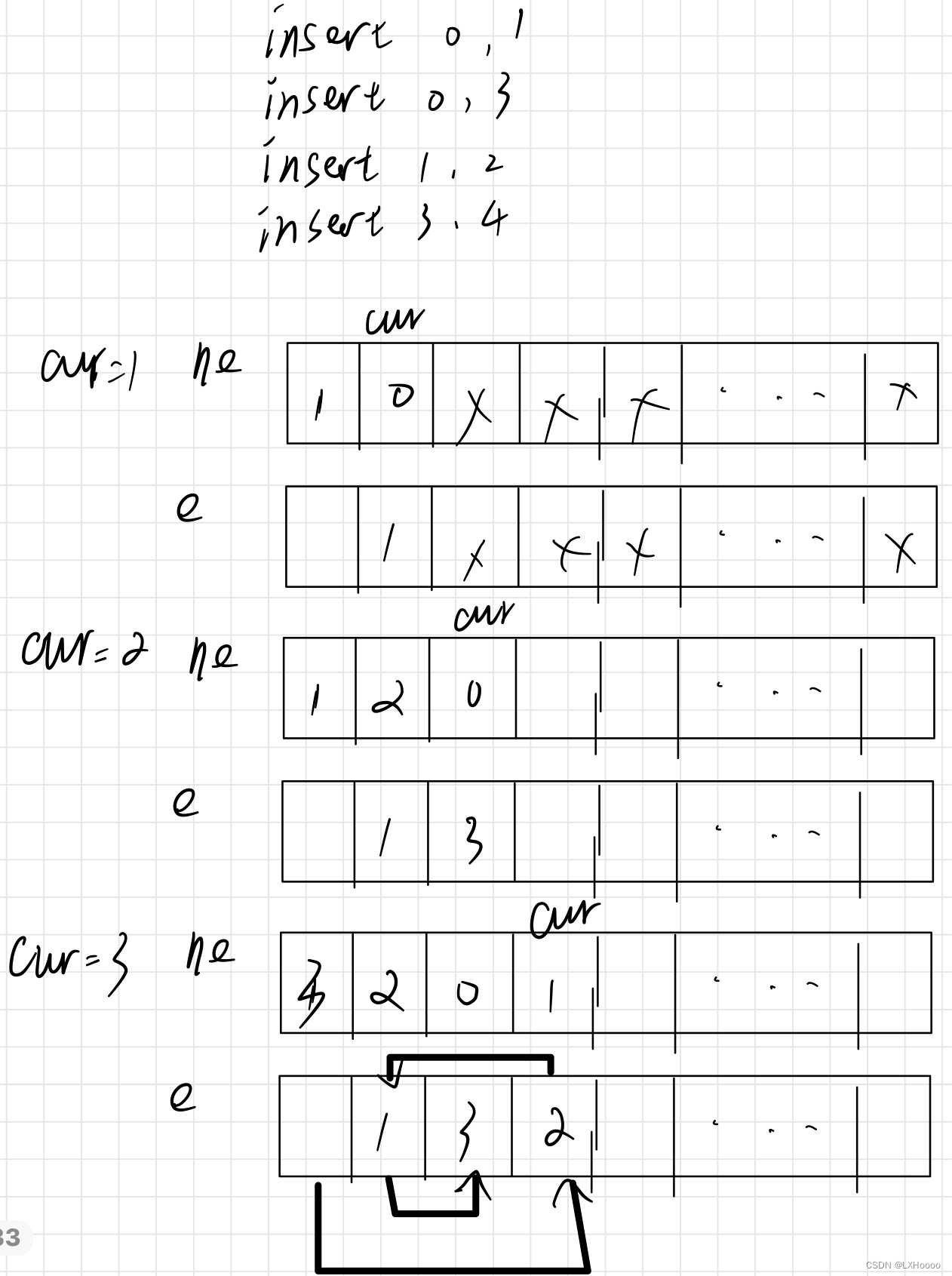
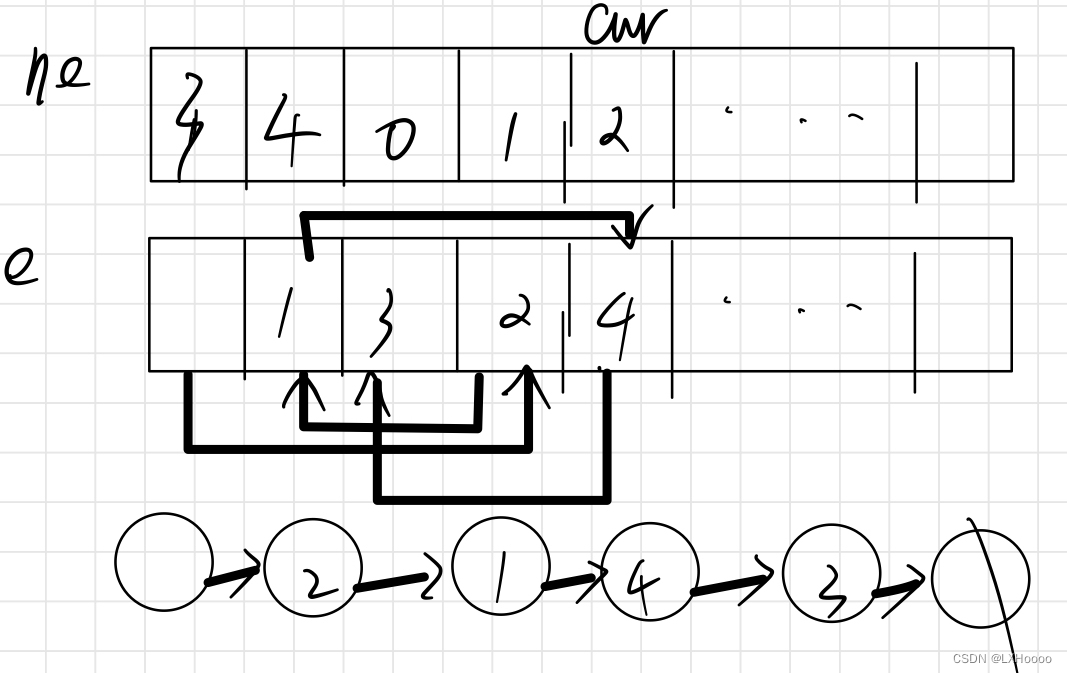
笔试中遇到需要链表写法解题的话尽量用数组替代,而不是用new创建节点,new非常的费时间 解析:如下四句输入,在0前面插入1的时候,0不是链表中的节点,插入链表尾,ne[0]是头指针,里面存着1,意思是头指针指向1节点,整个过程如下图所示。ne保存的是指向下一个元素的位置值,e保存的是自己本身的值。 题目链接:数组模拟链表 代码:这个代码使用了数组,并未使用stl,但并没有全a,后面输入数据过大不给调试,望路过的大佬能够补充 # include <iostream> # include <vector> # include <algorithm> # include <cstring> using namespace std;
const int N = 10010 ;
typedef pair< long long , int > PII;
int n;
PII tmp[ N] ;
long long e[ N] ;
int ne[ N] ;
int cur = 1 ;
void init ( )
{
memset ( tmp, 0x7fffffff , sizeof tmp) ;
}
int findx ( int cur, int x)
{
while ( cur>= 0 )
{
if ( tmp[ cur] . first== x)
{
return tmp[ cur] . second;
}
cur-- ;
}
return - 1 ;
}
int findy ( int cur, int x)
{
while ( cur>= 0 )
{
if ( e[ ne[ cur] ] == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur-- ;
}
return - 1 ;
}
void insert ( int x, int y)
{
auto t = findx ( cur, x) ;
auto u = findy ( cur, x) ;
if ( t != - 1 && u != - 1 )
{
e[ cur] = y;
ne[ cur] = t;
tmp[ cur] . first = y, tmp[ cur] . second = cur;
ne[ u] = cur, cur++ ;
}
else {
if ( ne[ 0 ] )
{
e[ cur] = y;
tmp[ cur] . first = y, tmp[ cur] . second = cur;
ne[ cur] = 0 ;
ne[ cur- 1 ] = cur, cur++ ;
}
else {
e[ cur] = y;
ne[ 0 ] = cur;
tmp[ cur] . first = y, tmp[ cur] . second = cur;
ne[ cur] = 0 ;
cur++ ;
}
}
}
void del ( int x)
{
auto t = findy ( cur, x) ;
auto u = findx ( cur, x) ;
if ( t != - 1 )
{
ne[ t] = ne[ u] ;
}
}
int main ( ) {
init ( ) ;
scanf ( "%d" , & n) ;
char str[ 7 ] ;
int x, y, z;
while ( n-- )
{
scanf ( "%s" , str) ;
if ( ! strcmp ( str, "insert" ) )
{
scanf ( "%d%d" , & x, & y) ;
insert ( x, y) ;
}
else {
scanf ( "%d" , & z) ;
del ( z) ;
}
}
if ( ne[ 0 ] )
{
for ( int i= ne[ 0 ] ; i; i= ne[ i] )
{
printf ( "%lld " , e[ i] ) ;
}
}
else {
printf ( "NULL" ) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
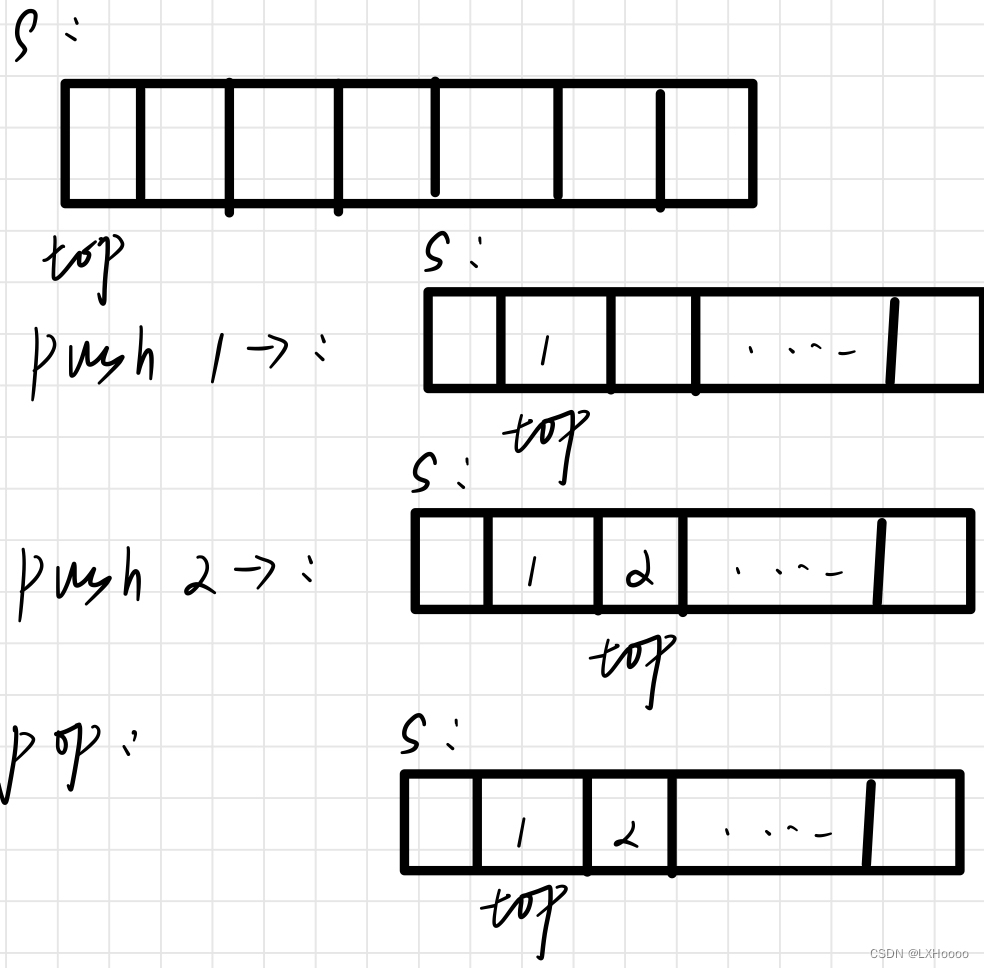
解析:用一个top指针来进行栈的弹出与压入,压栈top加,出栈top减 题目链接:数组模拟栈 代码 # include <iostream> # include <string> # include <algorithm> # include <cstring> using namespace std;
const int N = 100010 ;
int s[ N] ;
int n;
int top;
int main ( ) {
char opt[ 5 ] ;
int num;
scanf ( "%d" , & n) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++ )
{
scanf ( "%s" , opt) ;
if ( ! strcmp ( opt, "push" ) )
{
scanf ( "%d" , & num) ;
s[ ++ top] = num;
}
else if ( ! strcmp ( opt, "pop" ) )
{
if ( top)
{
printf ( "%d\n" , s[ top-- ] ) ;
}
else {
printf ( "error\n" ) ;
}
}
else {
if ( top)
{
printf ( "%d\n" , s[ top] ) ;
}
else {
printf ( "error\n" ) ;
}
}
}
return 0 ;
}
解析:在一个可能包含重复数字的序列中,找到每个数左边最近比它小的数,栈的压入和弹出如下图所示 题目链接:单调栈的应用 代码 # include <array> class Solution {
public :
vector< vector< int >> foundMonotoneStack ( vector< int > & nums) {
const int N = 100010 ;
int n = nums. size ( ) ;
int l[ N] , r[ N] , tl= 0 , tr= 0 ;
vector< vector< int >> arry ( n, vector < int > ( 2 ) ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++ )
{
while ( tl && nums[ l[ tl] ] >= nums[ i] )
tl-- ;
if ( tl)
arry[ i] [ 0 ] = l[ tl] ;
else
arry[ i] [ 0 ] = - 1 ;
l[ ++ tl] = i;
}
for ( int i = n- 1 ; i >= 0 ; i-- )
{
while ( tr && nums[ r[ tr] ] >= nums[ i] )
tr-- ;
if ( tr)
arry[ i] [ 1 ] = r[ tr] ;
else
arry[ i] [ 1 ] = - 1 ;
r[ ++ tr] = i;
}
return arry;
}
} ;
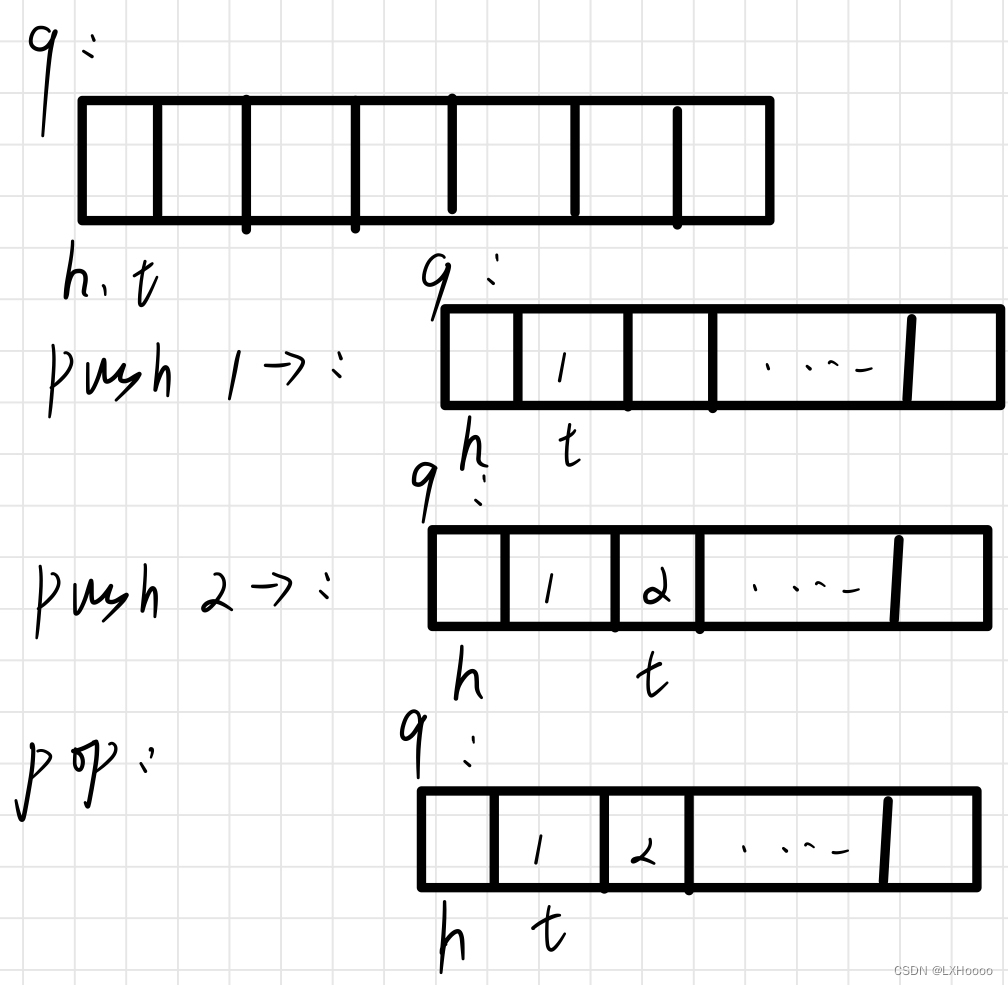
解析:通过一个头指针和尾指针来进行队列的压入与弹出,压入的时候队尾指针加,弹出的时候队头的指针加,front的位置是h+1 题目链接:数组模拟队列 代码 # include <iostream> # include <cstring> using namespace std;
const int N = 100010 ;
int q[ N] ;
int n;
int hh, tt;
int main ( ) {
scanf ( "%d" , & n) ;
char opt[ 5 ] ;
int num;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++ )
{
scanf ( "%s" , opt) ;
if ( ! strcmp ( opt, "push" ) )
{
scanf ( "%d" , & num) ;
q[ ++ tt] = num;
}
else if ( ! strcmp ( opt, "pop" ) )
{
if ( hh == tt)
{
printf ( "error\n" ) ;
}
else {
printf ( "%d\n" , q[ ++ hh] ) ;
}
}
else {
if ( hh != tt)
{
printf ( "%d\n" , q[ hh+ 1 ] ) ;
}
else {
printf ( "error\n" ) ;
}
}
}
}
解析:这个问题一般就三步:1、什么时候队头需要前进;2、队头的最大值或者最小值是否要更新;3、什么时候输出或者保存队头的最大或最小值 题目链接:滑动窗口 代码 class Solution {
public :
vector< int > maxInWindows ( const vector< int > & num, unsigned int size) {
const int N = 10010 ;
int n = num. size ( ) ;
int q[ N] , front= 0 , tail= - 1 ;
vector< int > ret;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++ ) {
int a = i - size + 1 ;
if ( front <= tail && a > q[ front] ) front++ ;
while ( front <= tail && num[ i] >= num[ q[ tail] ] ) tail-- ;
q[ ++ tail] = i;
if ( i >= size - 1 ) ret. push_back ( num[ q[ front] ] ) ;
}
return ret;
}
} ;
# include <iostream> # include <string> using namespace std;
const int N = 500010 ;
int main ( ) {
string str1, str2;
cin >> str1 >> str2;
char S[ N] , P[ N] ;
bool flag = false ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < str1. length ( ) ; i++ )
{
S[ i+ 1 ] = str1[ i] ;
}
for ( int i = 0 ; i < str2. length ( ) ; i++ )
{
P[ i+ 1 ] = str2[ i] ;
}
int ne[ N] ;
for ( int i = 2 , j = 0 ; i <= str2. length ( ) ; i++ )
{
while ( j && P[ i] != P[ j+ 1 ] ) j = ne[ j] ;
if ( P[ i] == P[ j+ 1 ] ) j++ ;
ne[ i] = j;
}
for ( int i = 1 , j = 0 ; i <= str1. length ( ) ; i++ )
{
while ( j && S[ i] != P[ j+ 1 ] ) j = ne[ j] ;
if ( S[ i] == P[ j+ 1 ] ) j++ ;
if ( j == str2. length ( ) )
{
flag = true ;
cout << i- str2. length ( ) << " " ;
j = ne[ j] ;
}
}
if ( flag)
return 0 ;
else
cout << - 1 ;
}
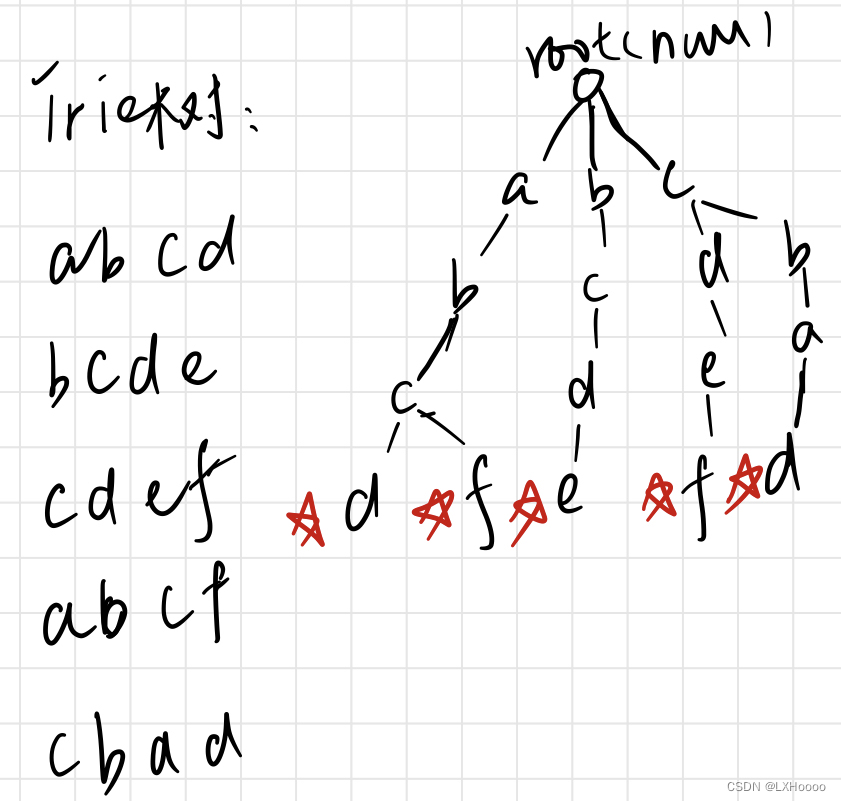
解析:trie树的存储方式如下所示,从根节点开始,依次找子节点,没有就新创建一个,并在每个单词的末尾打上一个标记,表示这是一个完整的单词 题目链接:字典树的实现 代码 解析:每个集合的根节点就是这个集合的编号,初始每个节点各自为一个集合,合并1,2这两个集合只需要让2作为1的父节点,节点1里面存的就是2这个父节点的值 题目链接:并查集的实现 代码:一下几次提交结果是使用cin和cout以及scanf和printf的结果,大数据量的时候使用cin读入和cout读出特别费时间,所以最好使用scanf和printf以节省时间。 # include <iostream> using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010 ;
int n, m;
int p[ N] ;
int find ( int x)
{
if ( p[ x] != x) p[ x] = find ( p[ x] ) ;
return p[ x] ;
}
int main ( ) {
scanf ( "%d%d" , & n, & m) ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++ )
{
p[ i] = i;
}
while ( m-- )
{
int opt, a, b;
scanf ( "%d%d%d" , & opt, & a, & b) ;
if ( opt == 1 )
{
if ( find ( a) == find ( b) ) printf ( "Yes\n" ) ;
else printf ( "No\n" ) ;
}
else if ( opt == 2 )
{
p[ find ( a) ] = find ( b) ;
}
}
}
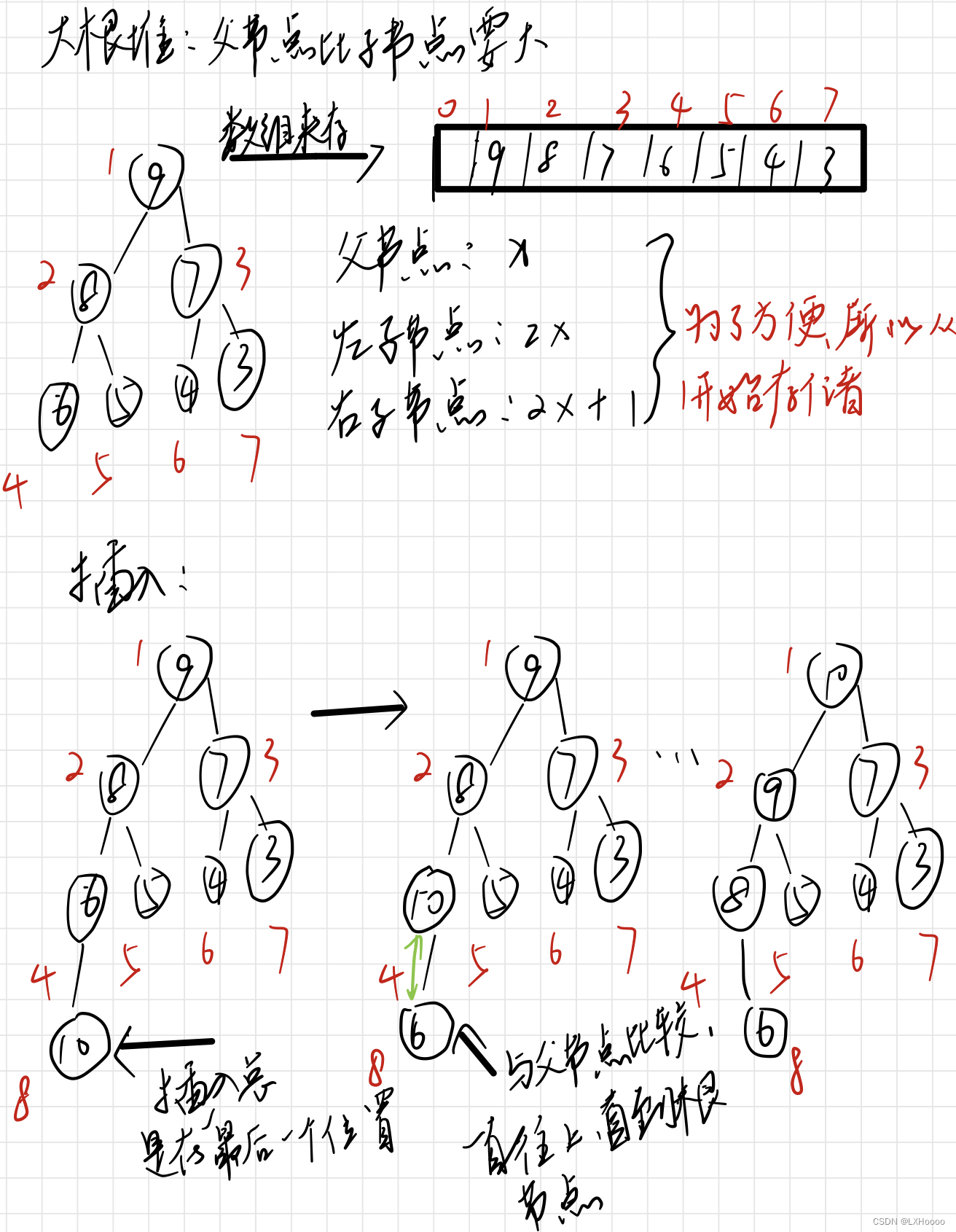
解析:整个的原理如下所示,堆本质是一颗完全二叉树,但可以通过数组来实现存储。不管是插入还是删除操作,做完之后都要针对该位置重新更新一下排序 题目链接:堆模板 代码 # include <iostream> # include <cstring> # include <algorithm> # include <vector> using namespace std;
const int N = 100010 ;
int arry[ N] , len;
void up ( int x)
{
while ( x/ 2 && arry[ x] > arry[ x/ 2 ] )
{
swap ( arry[ x] , arry[ x/ 2 ] ) ;
x >>= 1 ;
}
}
void down ( int x)
{
int t = x;
if ( x* 2 <= len && arry[ x* 2 ] > arry[ t] ) t = x * 2 ;
if ( x* 2 + 1 <= len && arry[ x* 2 + 1 ] > arry[ t] ) t = x * 2 + 1 ;
if ( t != x)
{
swap ( arry[ t] , arry[ x] ) ;
down ( t) ;
}
}
int main ( ) {
int n;
scanf ( "%d" , & n) ;
char opt[ 5 ] ;
int num;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++ )
{
scanf ( "%s" , opt) ;
if ( ! strcmp ( opt, "push" ) )
{
scanf ( "%d" , & num) ;
arry[ ++ len] = num;
up ( len) ;
}
else if ( ! strcmp ( opt, "pop" ) )
{
if ( len)
{
printf ( "%d\n" , arry[ 1 ] ) ;
arry[ 1 ] = arry[ len-- ] ;
down ( 1 ) ;
}
else {
printf ( "%s\n" , "empty" ) ;
}
}
else if ( ! strcmp ( opt, "top" ) ) {
if ( len)
printf ( "%d\n" , arry[ 1 ] ) ;
else
printf ( "%s\n" , "empty" ) ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
size和empty所有的都有这个,但clear有的没有
size():返回元素个数 empty():是否为空 clear():清空 front()/back() push_back()/pop_back() begin()/end() []:随机选址 支持比较运算(按字典序) first、second、支持比较运算(以first为第一关键字,second为第二关键字) 、p = make_pair(10,“lxh”); size()/length() empty()、clear() substr(a,b):返回a开始的长度为b的字串 c_str():返回string 的首地址 # include <stdio.h> # include <string.h> # include <iostream> # include <string> using namespace std;
int main ( )
{
string s = "lxh" ;
cout << s. substr ( 1 , 2 ) << endl;
printf ( "%s" , s. c_str ( ) ) ;
return 0 ;
}
**size()、empty()、没有clear() ** push():向队尾插入一个元素 front():返回队头元素 back():返回队尾元素 pop():弹出队头元素 push():插入一个元素 top():返回堆顶元素 pop():弹出堆顶元素 定义小根堆 priority_queue< int , vector< int > , greater< int >> hp;