目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
👨💻4 Matlab代码
💥1 概述
无线传感网络最早应用于军事领域,随着工业界和学术界的关注度提高和技术的成熟,现已广泛应用于军事侦查、环境监测和智能家居等领域。该网络由传感器节点组成,通过节点之间的相互协作将感知到的信息进行适当计算和融合,并最终传送到基站,是传感器技术、计算机技术和通信技术结合的产物。 与传统无线网络不同的是,无线传感网络的目的是收集被监测区域的环境信息,而不是点对点的通信。因此,各层的网络协议的设计都应以数据为中心。
由于无线传感器节点的能量、计算能力和通信范围有限,因此有效的利用节点能量,进而延长网络的生命周期是无线传感网络协议的关键课题之一。本文从路由协议出发,对现有的几种典型路由协议进行了分类和对比。
分簇路由协议思想简单,把节点分层的思想便于拓扑管理,加上数据融合技术使得网络负载小,能量利用高效等优点,成为无线传感网络发展最快的路由技术。LEACH协议是典型的分簇路由协议,之后许多的分簇路由协议思想都是基于这个协议。本文提出的分簇路由协议也是基于LEACH协议的,因此对LEACH协议进行了详述,并指出因为其同构节点的假设条件使其在异构节点组成的网络的情景中无法发挥很好的效果。SEP协议是针对二级异构网络提出的分簇路由协议,它考虑了节点的初始能量信息,和LEACH不同的是它不是基于节点个数的轮转算法,而是基于能量均衡的。
📚2 运行结果
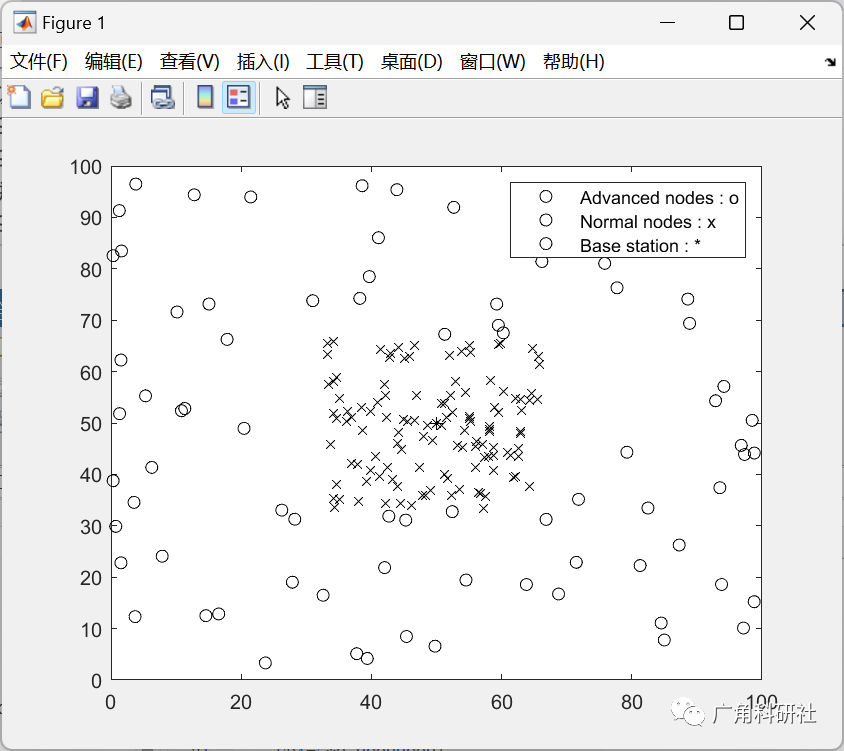
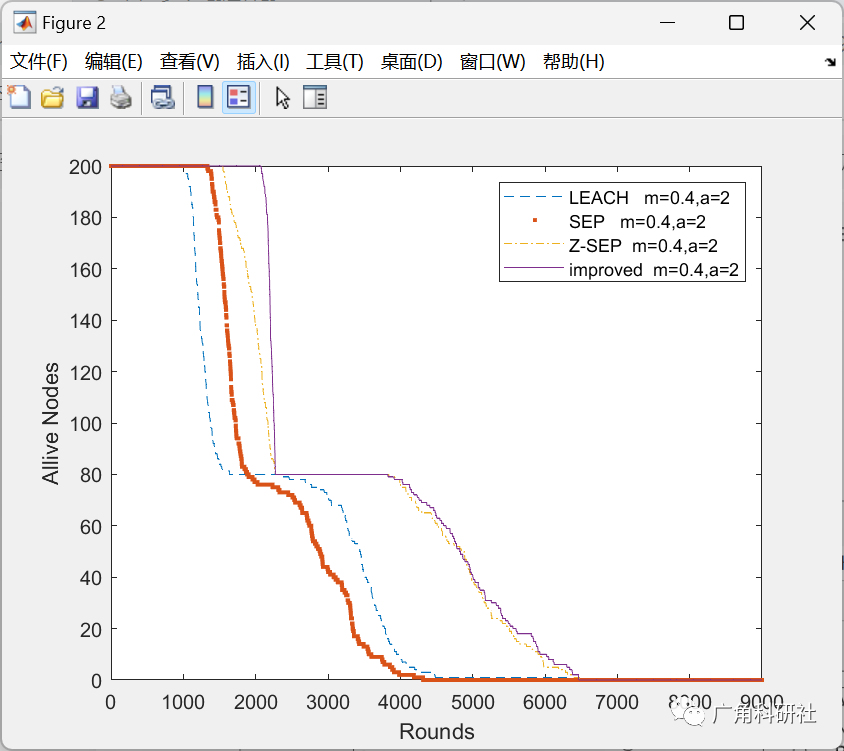
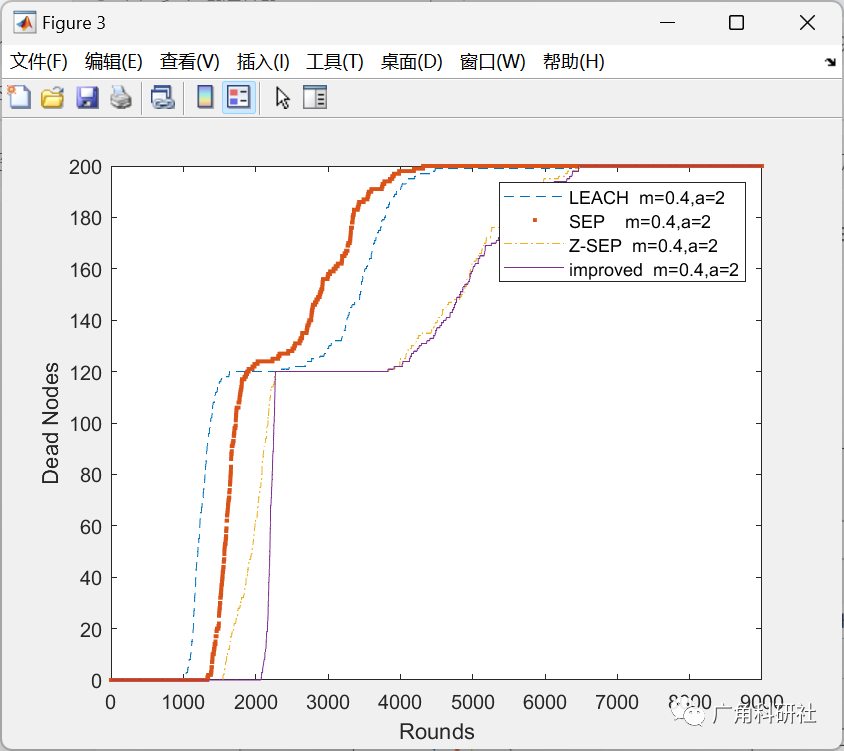
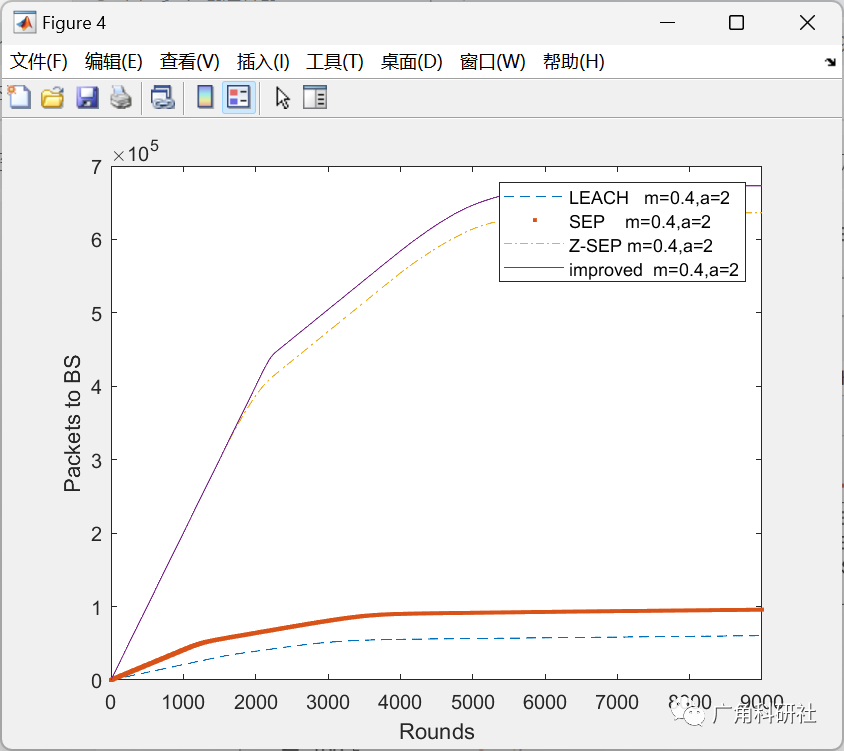
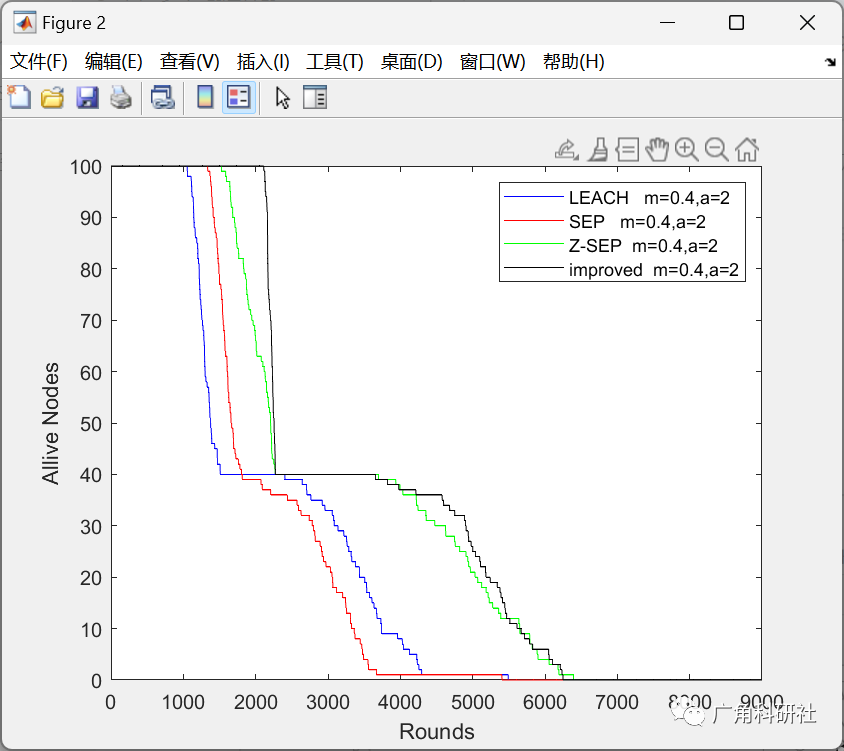
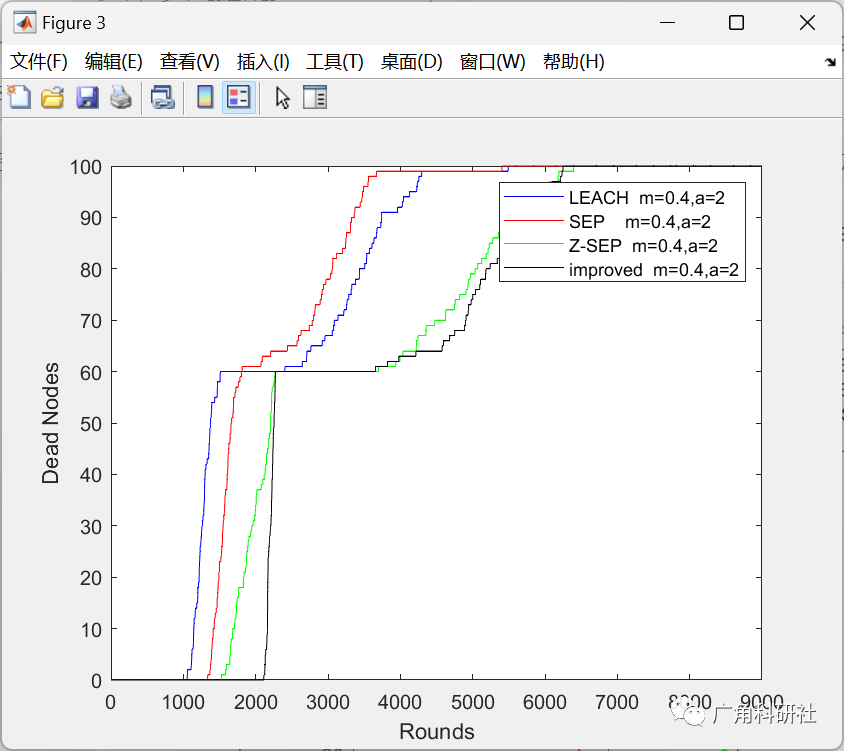
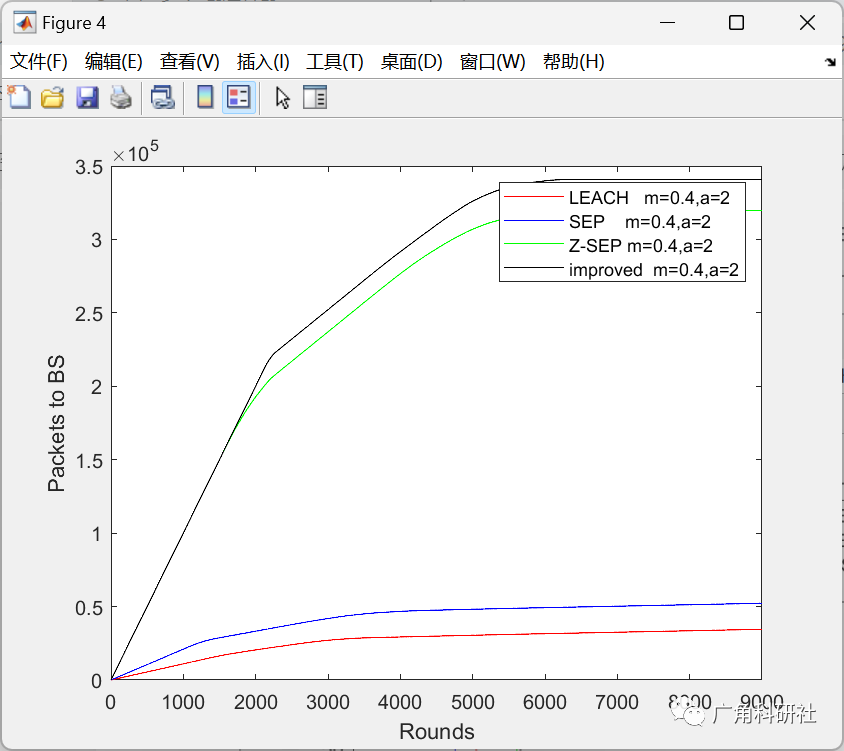
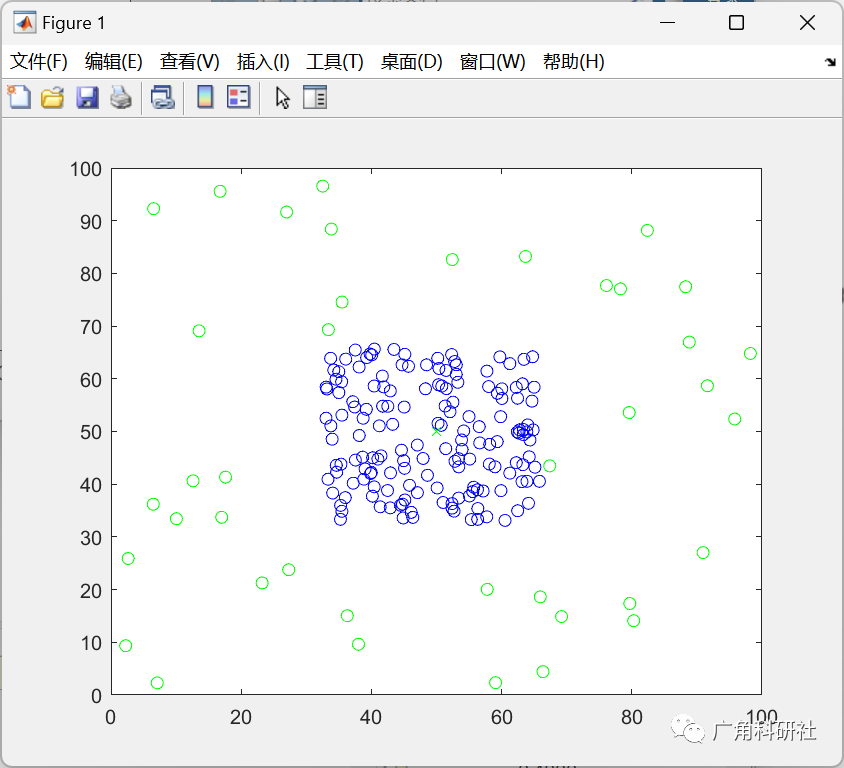
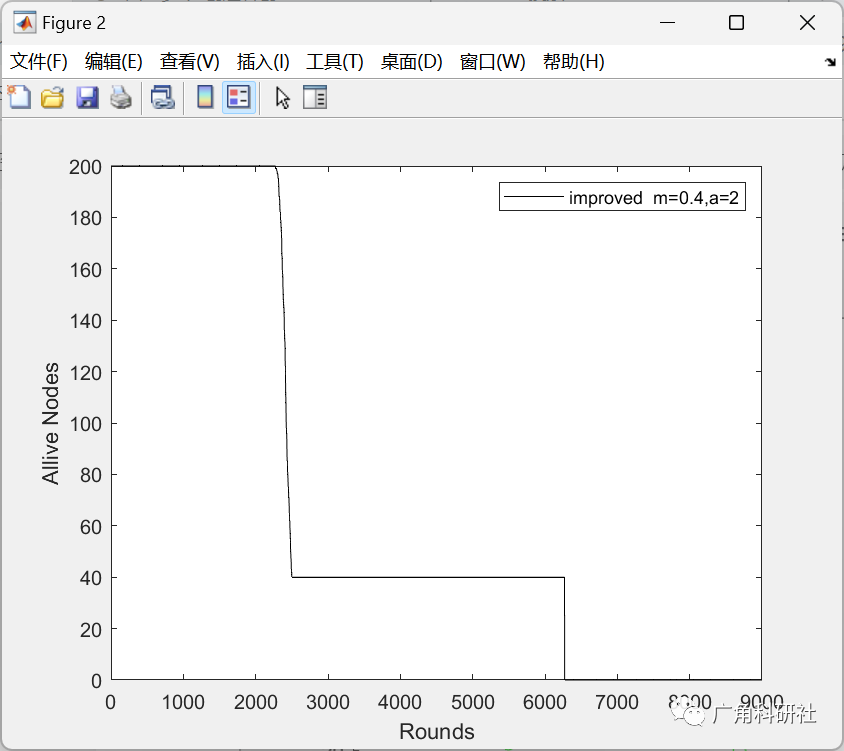
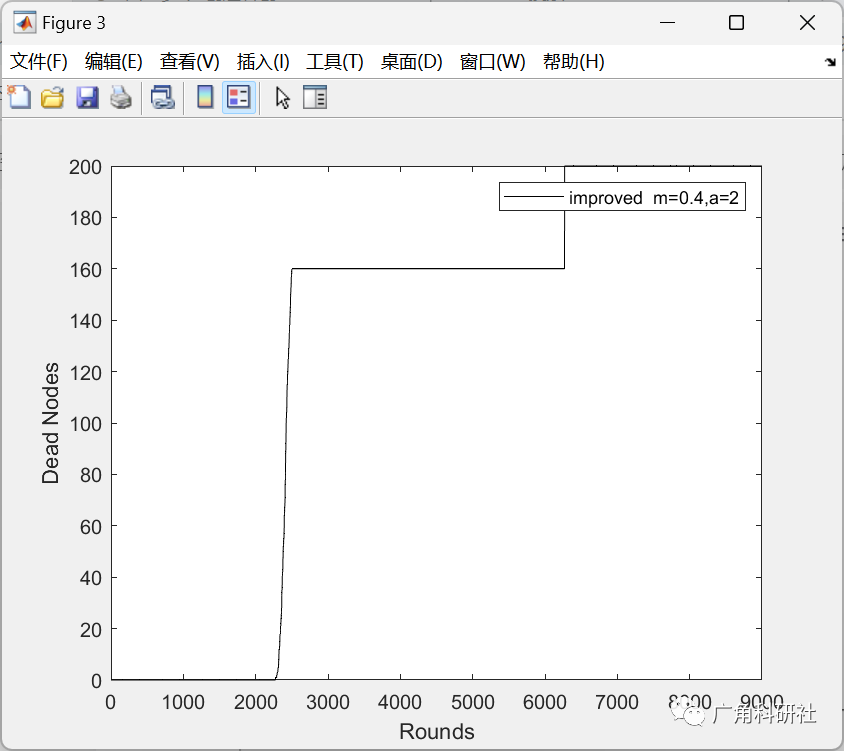
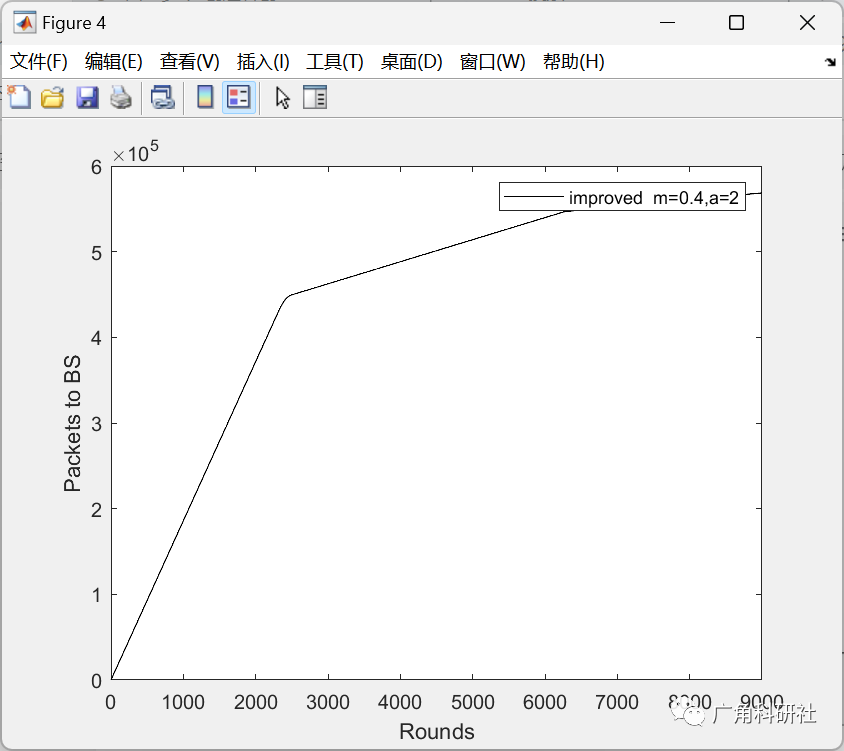
主函数部分代码:
clear;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% PARAMETERS %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%Field Dimensions - x and y maximum (in meters)
xm=100;
ym=100;
%x and y Coordinates of the Sink
sink.x=50;
sink.y=50;
%Number of Nodes in the field
n=200;
%Optimal Election Probability of a node
%to become cluster head
p=0.1;
%Energy Model (all values in Joules)
%Initial Energy
Eo=0.5;
%Eelec=Etx=Erx
ETX=50*0.000000001;
ERX=50*0.000000001;
%Transmit Amplifiers types
Efs=10*0.000000000001;
Emp=0.0013*0.000000000001;
%Data Aggregation Energy
EDA=5*0.000000001;
yd1=33;
%Values for Hetereogeneity
%Percentage of nodes than are advanced
m=0.4;
%\alpha times advance nodes have energy greater than normal nodes
a=2;
%maximum number of rounds
rmax=9000;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%Computation of do
do=sqrt(Efs/Emp);
Et=0;
%Creation of the random Sensor Network
%figure(1);
for i=1:1:n
S(i).xd=rand(1,1)*xm;
XR(i)=S(i).xd;
S(i).yd=rand(1,1)*ym;
YR(i)=S(i).yd;
S(i).G=0;
%initially there are no cluster heads only nodes
S(i).type='N';
temp_rnd0=i;
%Random Election of Normal Nodes
if (temp_rnd0>=m*n+1)
S(i).E=Eo;
E(i)=S(i).E;
S(i).ENERGY=0;
% plot(S(i).xd,S(i).yd,'o');
% hold on;
end
%Random Election of Advanced Nodes
if (temp_rnd0<m*n+1)
S(i).E=Eo*(1+a);
E(i)=S(i).E;
S(i).ENERGY=1;
% plot(S(i).xd,S(i).yd,'+');
% hold on;
end
Et=Et+S(i).E;
end
S(n+1).xd=sink.x;
S(n+1).yd=sink.y;
%plot(S(n+1).xd,S(n+1).yd,'x');
%First Iteration
%figure(1);
%counter for CHs
countCHs=0;
%counter for CHs per round
rcountCHs=0;
cluster=1;
countCHs;
rcountCHs=rcountCHs+countCHs;
flag_first_dead=0;
allive=n;
packets_TO_BS=0;
packets_TO_CH=0;
for r=0:1:rmax
% r
%Election Probability for Normal Nodes
pnrm=( p/ (1+a*m) );
%Election Probability for Advanced Nodes
padv= ( p*(1+a)/(1+a*m) );
%Operation for heterogeneous epoch
if(mod(r, round(1/pnrm) )==0)
for i=1:1:n
S(i).G=0;
S(i).cl=0;
end
end
🎉3 参考文献
[1]吴承辉. 基于SEP协议的无线传感网络的能量优化研究[D].南京邮电大学,2020.
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。