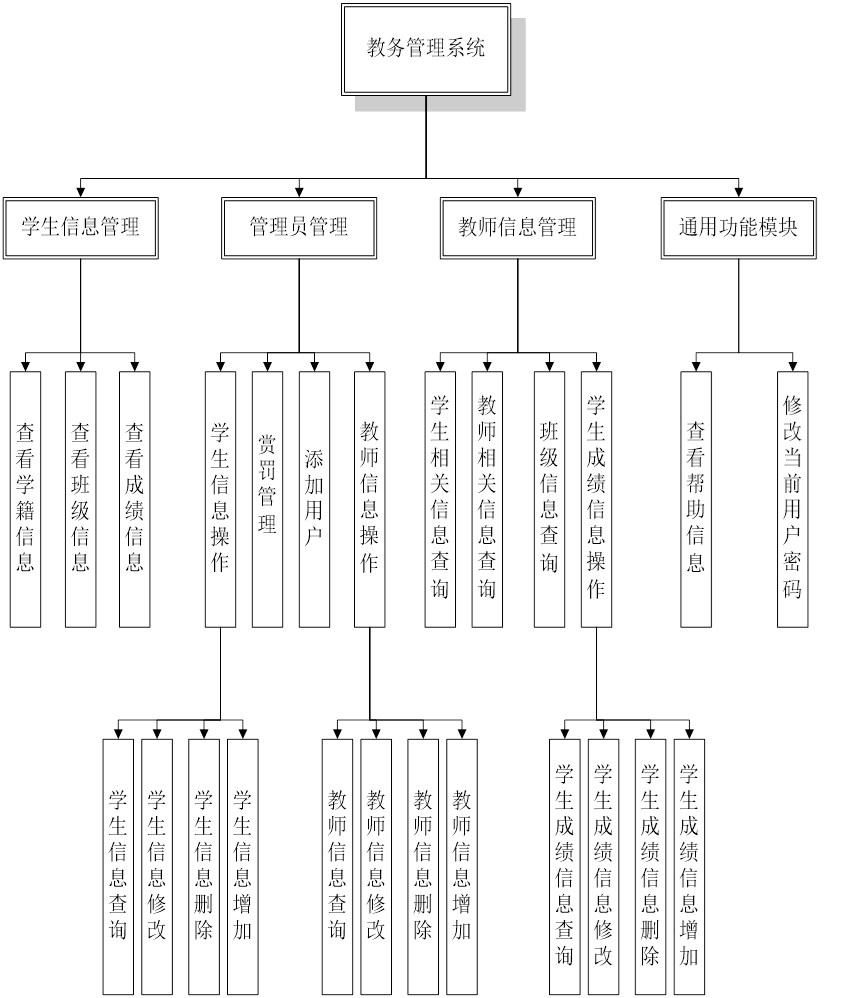
目录
- 1.线性表
- 2.顺序表
- SeqList.h
- SeqList.c
- Test.c
- 数组习题
- 移除元素
- 删除有序数组中的重复项
- 合并两个有序数组
- 顺序表的问题及思考
- 3.链表
- SList.h
- SList.c
- Test.c
1.线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使
用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,
线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储
顺序表:
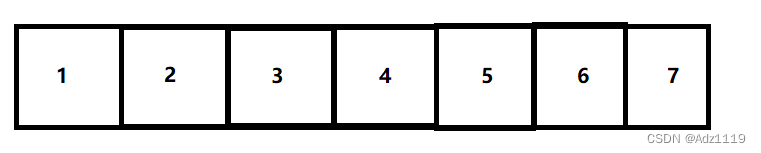
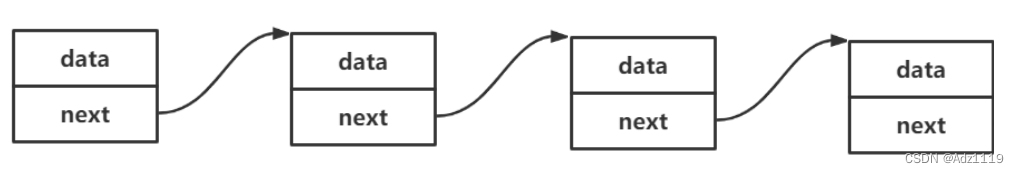
链表:
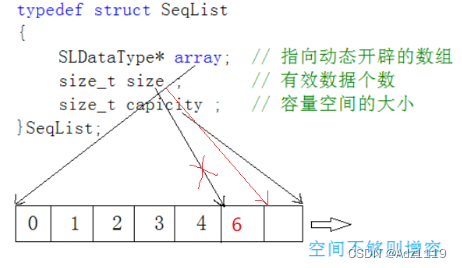
2.顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存
储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
1、静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
2、动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
主要介绍动态
SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
// 静态的顺序表
// 给小了不够用,给多了浪费
//#define N 10000
//typedef int SLDatatype;
//struct SeqList
//{
// SLDatatype a[N];
// int size;
//};
// 动态顺序表
//typedef double SLDatatype;
typedef int SLDatatype;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDatatype* a;
int size; // 存储的有效数据的个数
int capacity; // 容量
}SL;
void SLInit(SL* psl);
void SLDestroy(SL* psl);
void SLPrint(SL* psl);
//STL命名风格
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDatatype x);
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDatatype x);
void SLPopBack(SL* psl);
void SLPopFront(SL* psl);
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDatatype x);
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos);
// 找到返回下标,没有找到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDatatype x);
void SLModify(SL* psl, int pos, SLDatatype x);
SeqList.c
void SLInit(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
psl->a = (SLDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(SLDatatype)*4);
if (psl->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
psl->capacity = 4;
psl->size = 0;
}
void SLDestroy(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
free(psl->a);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = 0;
psl->capacity = 0;
}
void SLPrint(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", psl->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->size == psl->capacity)
{
SLDatatype* tmp = (SLDatatype*)realloc(psl->a, sizeof(SLDatatype) * psl->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
psl->a = tmp;
psl->capacity *= 2;
}
}
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(psl);
//psl->a[psl->size] = x;
//psl->size++;
//SLCheckCapacity(psl);
//psl->a[psl->size++] = x;
SLInsert(psl, psl->size, x);
}
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(psl);
//SLCheckCapacity(psl);
挪动数据
//int end = psl->size - 1;
//while (end >= 0)
//{
// psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
// --end;
//}
//psl->a[0] = x;
//psl->size++;
SLInsert(psl, 0, x);
}
void SLPopBack(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
// 暴力检查
//assert(psl->size > 0);
温柔的检查
if (psl->size == 0)
return;
psl->a[psl->size - 1] = 0;
//psl->size--;
SLErase(psl, psl->size-1);
}
void SLPopFront(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
// 暴力检查
//assert(psl->size > 0);
///*int start = 0;
//while (start < psl->size-1)
//{
// psl->a[start] = psl->a[start + 1];
// start++;
//}*/
//int start = 1;
//while (start < psl->size)
//{
// psl->a[start-1] = psl->a[start];
// start++;
//}
//psl->size--;
SLErase(psl, 0);
}
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(psl);
//assert(0 <= pos <= psl->size);
assert(0 <= pos && pos<= psl->size);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
--end;
}
psl->a[pos] = x;
psl->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos)
{
assert(psl);
assert(0 <= pos && pos < psl->size);
//assert(psl->size > 0);
int start = pos + 1;
while (start < psl->size)
{
psl->a[start - 1] = psl->a[start];
++start;
}
psl->size--;
}
int SLFind(SL* psl, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(psl);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
if (psl->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void SLModify(SL* psl, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{
assert(psl);
assert(0 <= pos && pos < psl->size);
psl->a[pos] = x;
}
Test.c
注意:如果scanf()函数使用的是%d转换说明符,那么当程序读取的第一个字符为非数字字符比如‘A’时,scanf()将会读取失败,‘A’会待在缓冲区,所以得先清空缓冲区才能让scanf继续读取
void menu()
{
printf("***************************************\n");
printf("1、尾插数据 2、尾删数据\n");
printf("3、头插数据 4、头删数据\n");
printf("5、打印数据 -1、退出\n");
printf("***************************************\n");
}
int main()
{
int option = 0;
SL s;
SLInit(&s);
while (option != -1)
{
menu();
printf("请输入你的操作:>");
scanf("%d", &option);
if (option == 1)
{
/*printf("请输入要尾插的数据,以-1结束:");
int x = 0;
scanf("%d", &x);
while (x != -1)
{
SLPushBack(&s, x);
scanf("%d", &x);
}*/
int n = 0;
printf("请输入要尾插的数据个数,再依次输入要插入的数据:");
scanf("%d", &n);
int x = 0;
while (n > 0)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
SLPushBack(&s, x);
n--;
}
}
else if (option == 5)
{
SLPrint(&s);
}
else if (option == -1)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("无此选项,请重新输入\n");
}
}
SLDestroy(&s);
return 0;
}
数组习题
移除元素
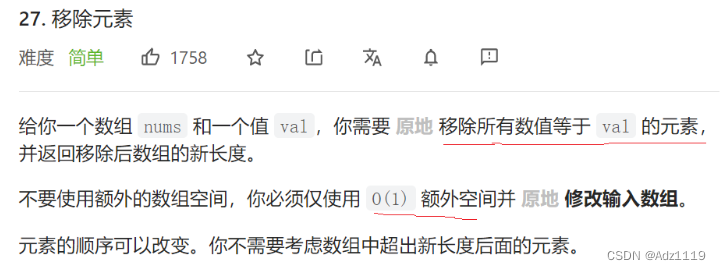
暴力求解:

空间换时间:
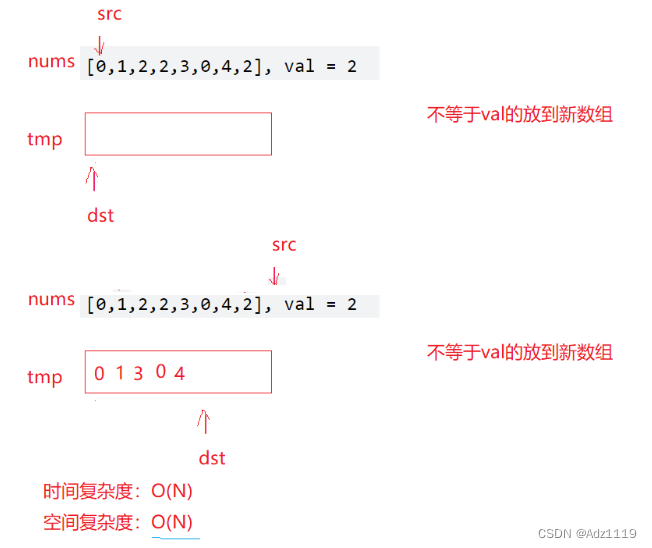
双指针:

int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
int pos=0,prev=0;
for(int i=0;i<numsSize;i++)
{
if(nums[pos]==val)
{
pos++;
}
else
{
nums[prev++]=nums[pos++];
}
}
return prev;
}
删除有序数组中的重复项
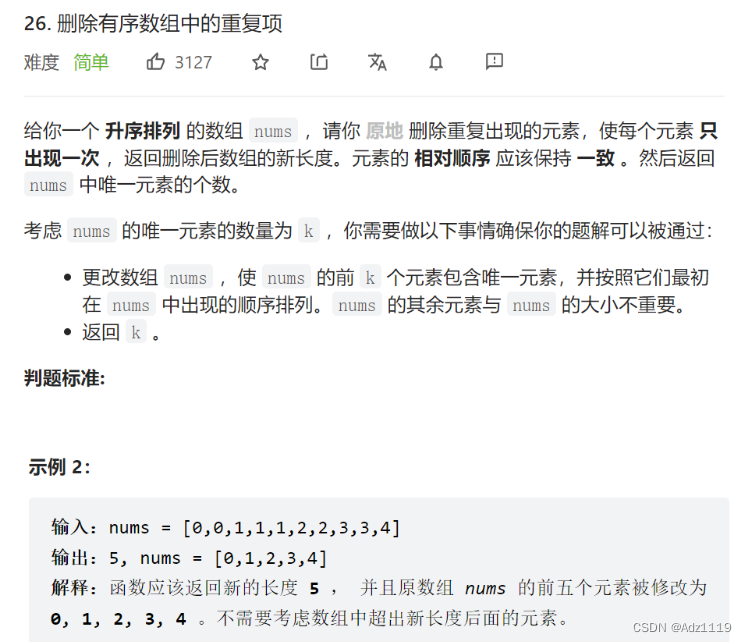
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){
int pos=0,prev=0;
while(pos<numsSize)
{
if(nums[pos]==nums[prev])
{
pos++;
}
else
{
prev++;
nums[prev]=nums[pos];
}
}
return prev+1;
}
合并两个有序数组
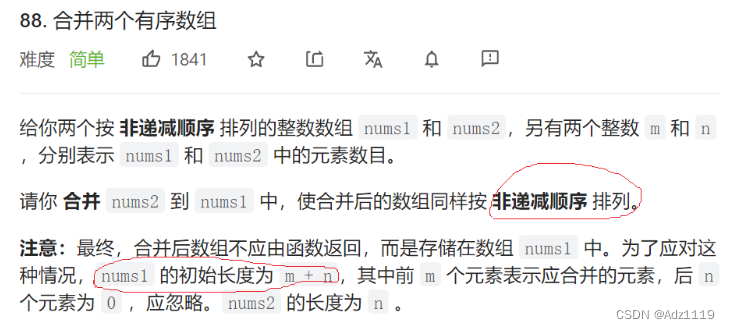
两个数组都从后往前比较可以节省空间
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){
//归并,从后往前比较,放到nums1中
int len1=m-1;
int len2=n-1;
int k=m+n-1;
while(len1>=0 && len2>=0)
{
if(nums1[len1]>nums2[len2])
{
nums1[k--]=nums1[len1--];
}
else
{
nums1[k--]=nums2[len2--];
}
}
while(len2>=0)
{
nums1[k--]=nums2[len2--];
}
}
顺序表的问题及思考
顺序表优势:下标的随机访问
问题:
- 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
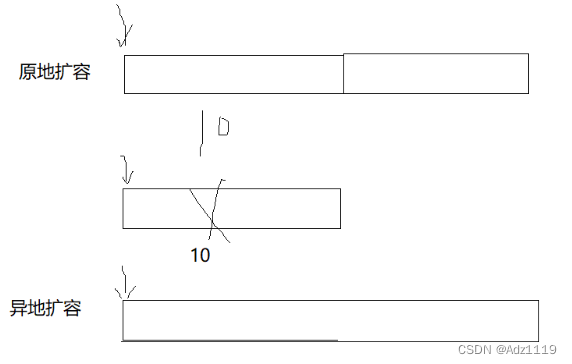
- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
- 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到
200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。

3.链表
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表
中的指针链接次序实现的 。
SList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);
void SLPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
void SLPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
void SLPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
// 单链表查找
SLTNode* STFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
// 在pos之前插入
void SLInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
void SLInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
// 删除pos位置的值
void SLErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
// 删除pos位置后面的值
void SLEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);
SList.c
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
SLTNode* BuyLTNode(SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void SLPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead); // 链表为空,pphead也不为空,因为他是头指针plist的地址
//assert(*pphead); // 不能断言,链表为空,也需要能插入
SLTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
//void SLPushBack(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
//{
// SLTNode* tail = phead;
// while (tail != NULL)
// {
// tail = tail->next;
// }
//
// SLTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);
// tail = newnode;
//}
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead); // 链表为空,pphead也不为空,因为他是头指针plist的地址
//assert(*pphead); // 链表为空,可以尾插
SLTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);
// 1、空链表
// 2、非空链表
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
void SLPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead); // 链表为空,pphead也不为空,因为他是头指针plist的地址
assert(*pphead); // 链表为空,不能头删。(当然你还可以用温柔的检查)
SLTNode* del = *pphead;
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
free(del);
// 一个节点
// 多个节点
//if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
//{
// free(*pphead);
// *pphead = NULL;
//}
//else
//{
// SLTNode* del = *pphead;
// //*pphead = del->next;
// *pphead = (*pphead)->next;
// free(del);
//}
}
void SLPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead); // 链表为空,pphead也不为空,因为他是头指针plist的地址
assert(*pphead); // 链表为空,不能头删。(当然你还可以用温柔的检查)
// 没有节点(空链表)
// 暴力检查
//assert(*pphead);
// 温柔的检查
/*if (*pphead == NULL)
{
return;
}*/
// 一个节点
// 多个节点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
//SLTNode* prev = NULL;
//SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
找尾
//while (tail->next)
//{
// prev = tail;
// tail = tail->next;
//}
//free(tail);
//prev->next = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
// 找尾
while (tail->next->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail->next);
tail->next = NULL;
}
}
SLTNode* STFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
//assert(phead);
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 在pos之前插入
void SLInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
//assert(*pphead);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SLPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
SLTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
// 在pos之后插入
void SLInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
// 删除pos位置的值
void SLErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SLPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}
void SLEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
SLTNode* next = pos->next;
pos->next = next->next;
free(next);
}
Test.c
void TestSList4()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLPushBack(&plist, 4);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTNode* pos = STFind(plist, 3);
if (pos)
{
SLInsert(&plist, pos, 30);
}
SLTPrint(plist);
pos = STFind(plist, 2);
if (pos)
{
SLInsertAfter(pos, 20);
}
SLTPrint(plist);
pos = STFind(plist, 2);
if (pos)
{
SLErase(&plist, pos);
}
SLTPrint(plist);
}
int main()
{
TestSList4();
return 0;
}