目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
👨💻4 Matlab代码
💥1 概述
模型预测控制(Model Predictive Control,MPC)是一种基于在线计算的控制优化算法,能够统一处理带约束的多参数优化控制问题。当被控对象结构和环境相对复杂时,模型预测控制需选择较大的预测时域和控制时域,因此大大增加了在线求解的计算时间,同时降低了控制效果。从现有的算法来看,模型预测控制通常只适用于采样时间较大、动态过程变化较慢的系统中。因此,研究快速模型预测控制算法具有一定的理论意义和应用价值。
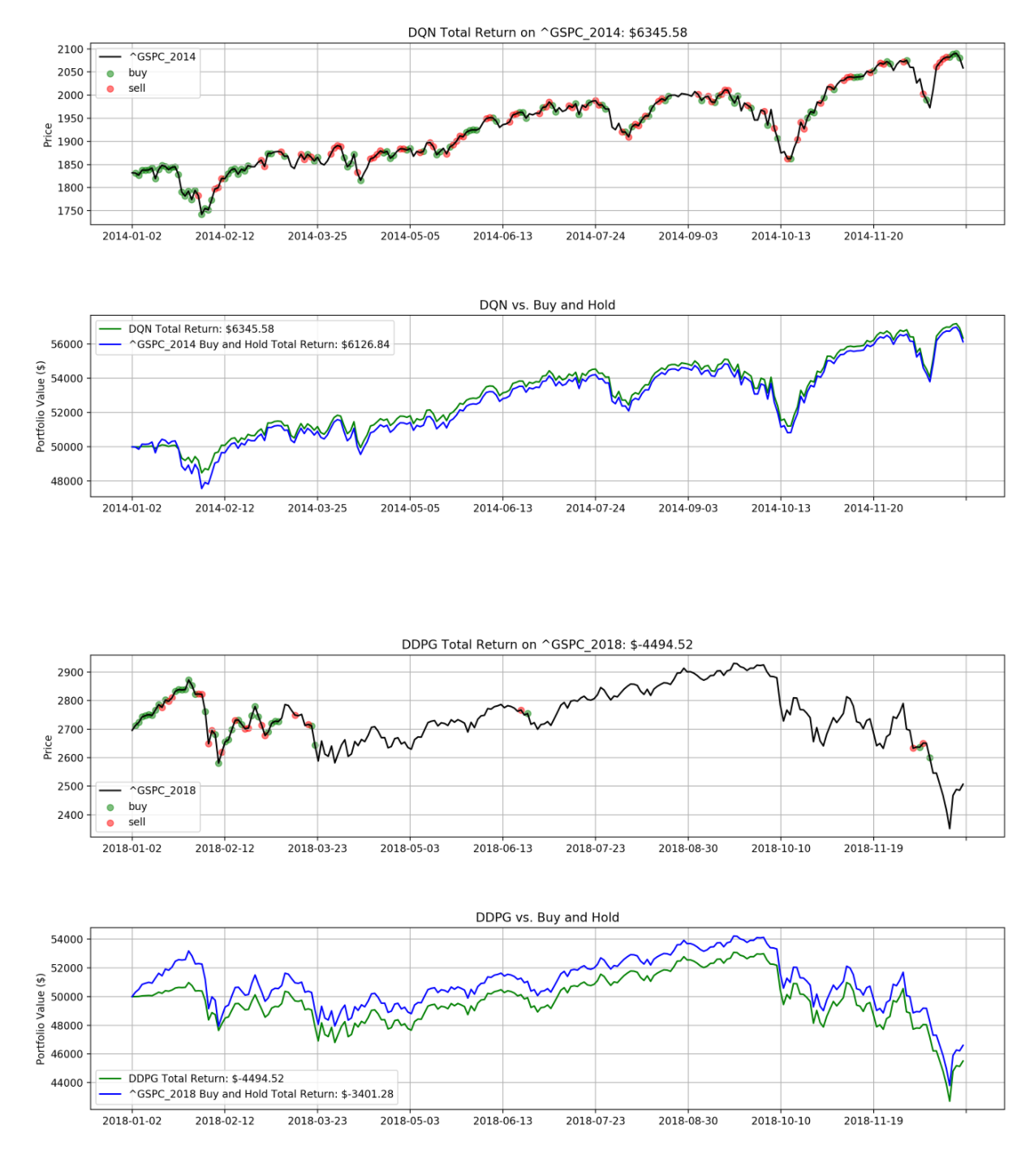
📚2 运行结果

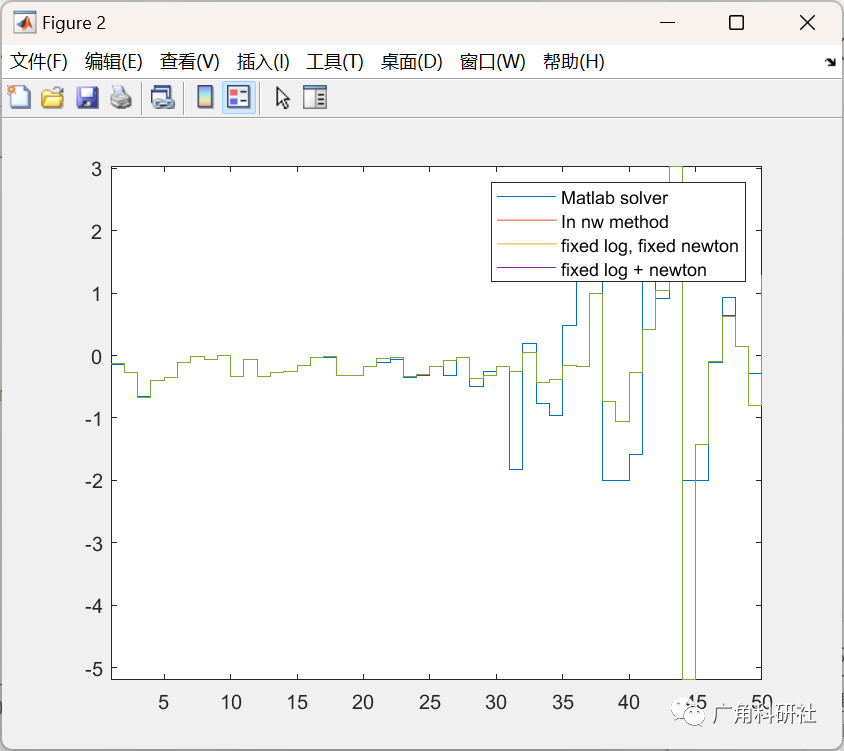
主函数部分代码:
% Testing FAST MPC class
clear;
clc;
close all;
addpath('Fast_MPC');
%% Parameters
n = 8; % Dimension of state
m = 5; % Dimension of control
Q = eye(n); % State stage cost
R = eye(m); % Control stage cost
S = []; % State control coupled cost
Qf = 50*eye(n); % Terminal state cost
q = []; % Linear state cost
r = []; % Linear control cost
qf = []; % Terminal state cost
Xmax = 10; % State upper limit
Umax = 2; % Control upper limit
xmin = -Xmax*ones(n,1); % State lower bound
xmax = Xmax*ones(n,1); % State upper bound
umin = -Umax*ones(m,1); % Cotrol lower bound
umax = Umax*ones(m,1); % Control upper bound
high_limit = 1;
low_limit = 0;
A = (high_limit-low_limit).*rand(n,n) + ones(n,n)*low_limit; % Random A (State transition) matrix
B = (high_limit-low_limit).*rand(n,m) + ones(n,m)*low_limit; % Random B (Control matrix) matrix
A = A./(max(abs(eig(A)))); % Spectral radius of A within 1
high_limit_w = 1;
low_limit_w = 0;
w = (high_limit_w-low_limit_w).*rand(n,1) + ones(n,1)*low_limit_w; % Random noise vector
T = 10; % Horizon length
x0 = rand(n,1); % Initial state (random)
xf = 1*ones(n,1); % Terminal state
test = Fast_MPC2(Q,R,S,Qf,q,r,qf,xmin,xmax,umin,umax,T,x0,...
A,B,w,xf,[]); % Build class
%% Solve
% Native matlab solver
tic;
[x_opt_mat] = test.matlab_solve; % Solving using native matlab solver fmincon
t_mat = toc;
% Structured MPC full solve
tic;
[x_opt_full] = test.mpc_solve_full; % Solving structure problem as log barrier method with infeasible start newton
t_full = toc;
% Fixed log barrier method k=0.01
k_fix = 0.01;
tic;
[x_opt_log] = test.mpc_fixed_log(k_fix); % Fixed log(k) iteration method
t_log = toc;
% Fixed newton step = 5
n_fix = 5;
tic;
[x_opt_nw] = test.mpc_fixed_newton(n_fix); % Fixed newton steps(5) method
t_nw = toc;
% Fixed log barrier + fixed newton step
tic;
[x_opt_lgnw] = test.mpc_fixed_log_newton(n_fix,k_fix);
t_lgnw = toc;
fprintf('Matlab solver=%d sec\n',t_mat);
fprintf('Infeasible start newton =%d sec\n',t_full);
fprintf('Infeasible start newton with fixed k(%d) =%d sec\n',k_fix,t_log);
fprintf('Infeasible start newton with fixed newton step(%d) =%d sec\n',n_fix,t_nw);
fprintf('Infeasible start newton with fixed newton and barrier =%d sec\n',t_lgnw);
%% Plotting
x_mat = zeros(T*n,1);
u_mat = zeros(T*m,1);
for i=1:(m+n):length(x_opt_mat)
if i==1
u_mat(i:i+m-1) = x_opt_mat(i:i+m-1);
x_mat(i:i+n-1) = x_opt_mat(i+m:i+m+n-1);
else
u_mat((i-1)/(m+n)*m+1:(i-1)/(m+n)*m+m) = x_opt_mat(i:i+m-1);
x_mat((i-1)/(m+n)*n+1:(i-1)/(m+n)*n+n) = x_opt_mat(i+m:i+m+n-1);
end
end
x_full = zeros(T*n,1);
u_full = zeros(T*m,1);
for i=1:(m+n):length(x_opt_full)
if i==1
u_full(i:i+m-1) = x_opt_full(i:i+m-1);
x_full(i:i+n-1) = x_opt_full(i+m:i+m+n-1);
else
u_full((i-1)/(m+n)*m+1:(i-1)/(m+n)*m+m) = x_opt_full(i:i+m-1);
x_full((i-1)/(m+n)*n+1:(i-1)/(m+n)*n+n) = x_opt_full(i+m:i+m+n-1);
end
end
x_log = zeros(T*n,1);
u_log = zeros(T*m,1);
for i=1:(m+n):length(x_opt_log)
if i==1
u_log(i:i+m-1) = x_opt_log(i:i+m-1);
x_log(i:i+n-1) = x_opt_log(i+m:i+m+n-1);
else
u_log((i-1)/(m+n)*m+1:(i-1)/(m+n)*m+m) = x_opt_log(i:i+m-1);
x_log((i-1)/(m+n)*n+1:(i-1)/(m+n)*n+n) = x_opt_log(i+m:i+m+n-1);
end
end
🎉3 参考文献
[1]黄彦春. 基于神经网络的快速模型预测控制算法研究[D].浙江大学,2018.
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。