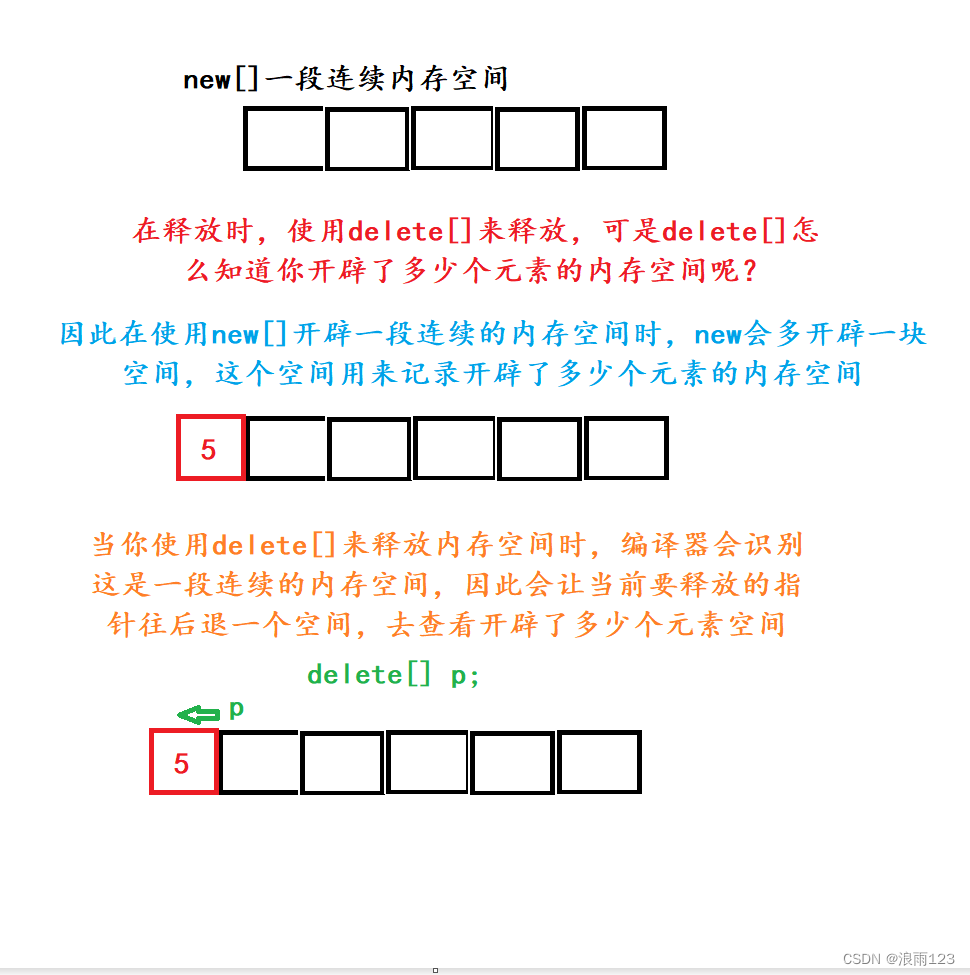
Qt Quick - Popup使用总结
- 一、概述
- 二、Popup 的布局
- 三、弹出分级
- 四、弹出定位
- 五、定制化
一、概述
Popup是类似弹出式用户界面控件的基本类型。它可以与Window或ApplicationWindow一起使用。
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12
ApplicationWindow {
id: window
width: 400
height: 400
visible: true
Button {
text: "Open"
onClicked: popup.open()
}
Popup {
id: popup
x: 100
y: 100
width: 200
height: 300
modal: true
focus: true
closePolicy: Popup.CloseOnEscape | Popup.CloseOnPressOutsideParent
}
}
为了确保场景中其他项目上方显示一个弹出框,建议使用ApplicationWindow。
ApplicationWindow还提供背景调光效果。
Popup不提供自己的布局,这就要求我们自己定位其内容,例如通过创建RowLayout或ColumnLayout。
声明为弹出框子元素的项自动成为弹出框内容项的父元素。动态创建的项需要显式地赋给contentItem。
二、Popup 的布局
下图展示了窗口中弹出框的布局:
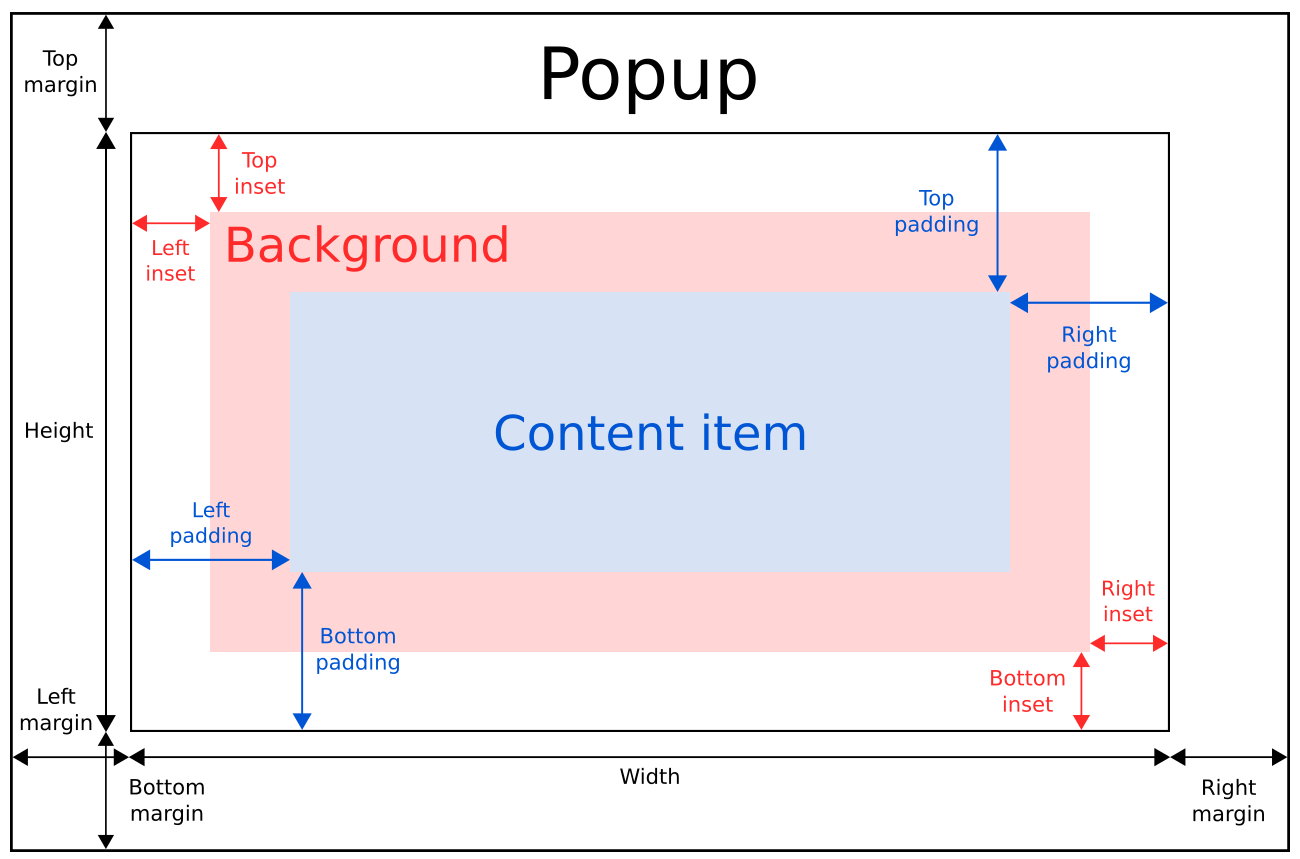
弹出框的implicitWidth和implicittheight通常是基于背景和内容项的隐式大小加上任何内嵌和内边距。当没有明确指定宽度或高度时,这些属性决定了弹出框的大小。
内容项的几何形状由内边距决定。下面的例子在弹出框的边界和内容之间保留了10px的内边距:
Popup {
padding: 10
contentItem: Text {
text: "Content"
}
}
背景元素会填满整个弹出框的宽度和高度,除非为其设置了insets或明确的尺寸。
负插图可以用来使背景比弹出框大。下面的例子使用负插图在弹出框边界外放置阴影:
Popup {
topInset: -2
leftInset: -2
rightInset: -6
bottomInset: -6
background: BorderImage {
source: ":/images/shadowed-background.png"
}
}
三、弹出分级
如果在弹出框中只使用单个元素,它将调整大小以适应其包含的元素的隐式大小。这使得它特别适合与布局一起使用。
Popup {
ColumnLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
CheckBox { text: qsTr("E-mail") }
CheckBox { text: qsTr("Calendar") }
CheckBox { text: qsTr("Contacts") }
}
}
有时,弹出框中可能有两项:
Popup {
SwipeView {
// ...
}
PageIndicator {
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
}
}
在这种情况下,Popup无法计算出合理的隐式大小。由于我们将PageIndicator锚定在了SwipeView上,我们可以简单地将内容大小设置为视图的隐式大小:
Popup {
contentWidth: view.implicitWidth
contentHeight: view.implicitHeight
SwipeView {
id: view
// ...
}
PageIndicator {
anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
}
}
四、弹出定位
与Qt Quick中的Item类似,Popup的x和y坐标是相对于其父元素的。这意味着打开一个按钮的子弹出框,将导致该弹出框相对于按钮的位置。
下面的例子使用附加的覆盖层。属性Overlay将一个弹出窗口定位在窗口的中心,而不管打开弹出窗口的按钮在什么位置:

Button {
onClicked: popup.open()
Popup {
id: popup
parent: Overlay.overlay
x: Math.round((parent.width - width) / 2)
y: Math.round((parent.height - height) / 2)
width: 100
height: 100
Label{
text: "弹出内容!"
}
}
}
另一种让弹出窗口居中的方法是使用anchors.centerIn,而不用考虑它的父元素:
ApplicationWindow {
id: window
// ...
Pane {
// ...
Popup {
anchors.centerIn: Overlay.overlay
}
}
}
为了确保弹出窗口位于包围窗口的边界内,可以将margin属性设置为非负值。
五、定制化
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12
Popup {
id: popup
background: Rectangle {
implicitWidth: 200
implicitHeight: 200
border.color: "#444"
}
contentItem: Column {}
}