力扣54和59题
54.顺时针打印矩阵
题目:

思路:将矩阵分为若干层,首先打印最外层的元素,然后一直往里打印
对于每层,从左上方开始以顺时针的顺序遍历所有元素。假设当前层的左上角位于(top,left),右下角位于 (bottom,right),按照如下顺序遍历当前层的元素。
(1)从左到右遍历上侧元素,依次为(top,left) 到(top,right);
(2)从上到下遍历右侧元素,依次为(top+1,right) 到 (bottom,right);
如果 left<right 且top<bottom,则
(3)从右到左遍历下侧元素,依次为(bottom,right−1)到(bottom,left+1);
(4)从下到上遍历左侧元素,依次为(bottom,left)到 (top+1,left)。
遍历完当前层的元素之后,将 left 和 top 分别增加 1,将right 和 bottom 分别减少 1,进入下一层继续遍历,直到遍历完所有元素为止。

C++代码:
//按层模拟
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if (!matrix.size() || !matrix[0].size()) return {};
vector<int> res;
int rows = matrix.size(); //最外层行数
int columns = matrix[0].size(); //最外层列数
int top = 0, left = 0, bottom = rows - 1, right = columns - 1; //左上角:[top, left] 右下角:[bottom, right]
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
//遍历top行:left --> right
for (int column = left; column <= right; ++column) {
res.push_back(matrix[top][column]);
}
//遍历right列:top+1 --> bottom
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; ++row) {
res.push_back(matrix[row][right]);
}
//判断是否已经到了最里层
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
//遍历bottom行:right-1 --> left+1
for (int column = right - 1; column > left; --column) {
res.push_back(matrix[bottom][column]);
}
//遍历left列:bottom --> top+1
for (int row = bottom; row > top; --row) {
res.push_back(matrix[row][left]);
}
}
top++;
left++;
bottom--;
right--;
}
return res;
}
};
59.螺旋矩阵
题目描述:
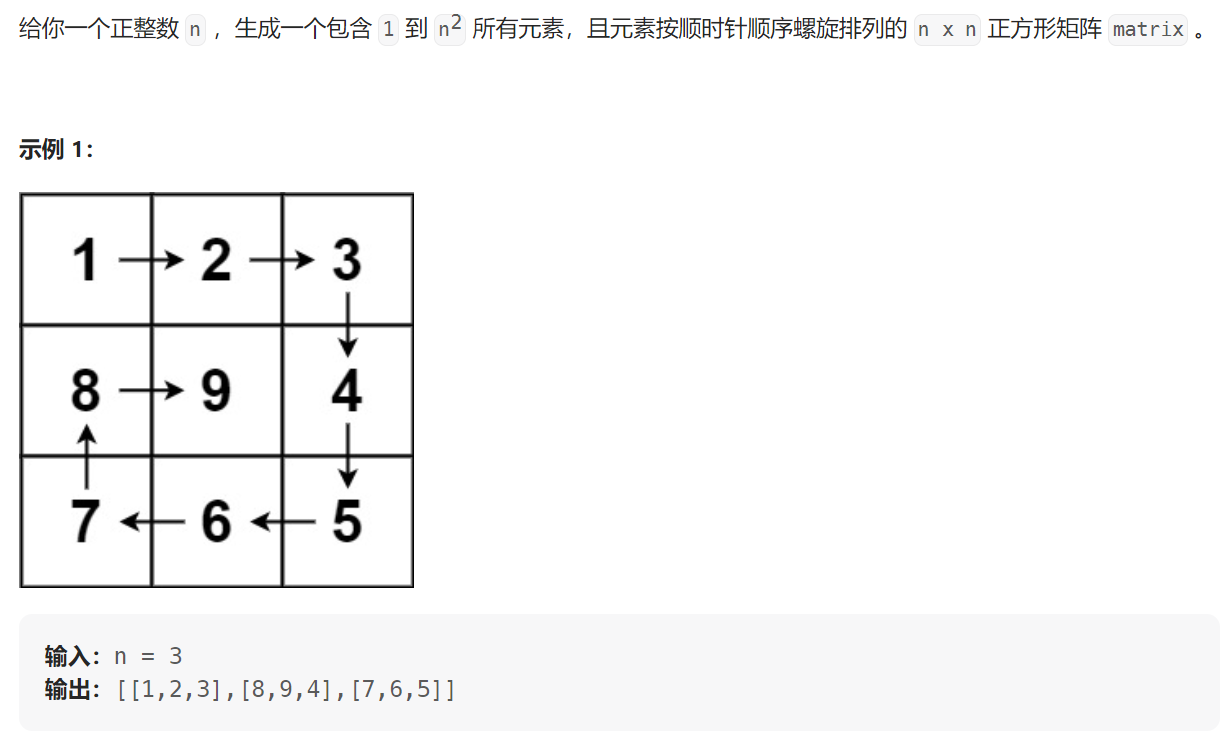
思路:由于矩阵是n*n的,可以将矩阵分为n/2层来考虑,分层按照顺时针依次填充数字
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {
vector<vector<int>> res(n, vector<int>(n, 0)); // 使用vector定义一个二维数组
int startx = 0, starty = 0; // 定义每循环一个圈的起始位置
int loop = n / 2; // 每个圈循环几次,例如n为奇数3,那么loop = 1 只是循环一圈,矩阵中间的值需要单独处理
int mid = n / 2; // 矩阵中间的位置,例如:n为3, 中间的位置就是(1,1),n为5,中间位置为(2, 2)
int count = 1; // 用来给矩阵中每一个空格赋值
int offset = 1; // 需要控制每一条边遍历的长度,每次循环右边界收缩一位
int i, j;
while (loop--) {
// 下面开始的四个for就是模拟转了一圈
// 模拟填充上行从左到右(左闭右开)
for (j = starty; j < n - offset; j++) {
res[startx][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充右列从上到下(左闭右开)
for (i = startx; i < n - offset; i++) {
res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充下行从右到左(左闭右开)
for (; j > starty; j--) {
res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 模拟填充左列从下到上(左闭右开)
for (; i > startx; i--) {
res[i][j] = count++;
}
// 第二圈开始的时候,起始位置要各自加1, 例如:第一圈起始位置是(0, 0),第二圈起始位置是(1, 1)
startx++;
starty++;
// offset 控制每一圈里每一条边遍历的长度
offset += 1;
}
// 如果n为奇数的话,需要单独给矩阵最中间的位置赋值
if (n % 2) {
res[mid][mid] = count;
}
return res;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution solution1;
int n = 5;
vector<vector<int>> res = solution1.generateMatrix(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cout << res[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
螺旋矩阵本身不涉及算法,而是考察数据的一种遍历方式