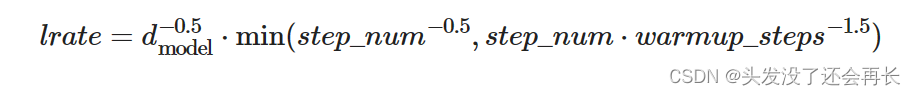Machine Translation
1. Goal
给定一段英文,翻译成繁体中文
2. Introduction
2.1 Dataset
training dataset
- TED2020: TED talks with transcriptions translated by a global community of volunteers to more than 100 language.
- we will use (en, zh-tw) aligned pairs.
Monolingual data
- More TED talks in traditional chinese.
2.2. Evaluation
如何评估我们的模型的表现?
使用BLUE
brevity penalty: penalizes short hypotheses

c是假设长度,r是参考长度
也就说,我们的模型翻译出来的句子和标签中的句子作比较,当二者相似的词越多,则翻译的准确率越高
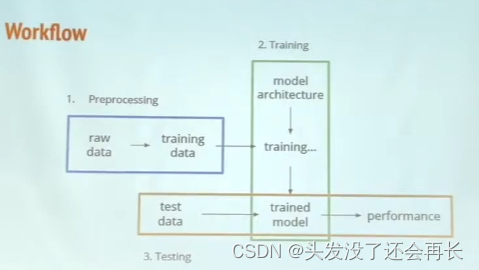
2.3. Workflow
Preprocessing
- download raw data
- clean and normalize
- remove bad data(too long/short)
Training
- initialize a model
- train it with training data
Testing
- generate translation of data
- evaluate the performance
2.4. Training tips
- Tokenize data with sub_word units
- For one, we can reduce the vocabulary size
- For another, alleviate the open vocabulary problem
- example: transportation => trans port ation
- Lable smoothing regularization
- When calculating loss, reserve some probability for incorrect labels
- Avoids overfitting
- Learning rate scheduling
- Linearly increase le and then decay by inverse square root of steps
- Stablilize training of transformers in early stage
2.5 Back-translation(BT)
得到单语言的数据是很容易的,比如想要中文数据,可以在网站上直接爬下来,但不是所有的英文句子都能得到中文翻译,所以,这里使用得到的中文(也就是数据集里的monolingual data)翻译成英文,做一个BT,就得到了又一个训练数据集,数据集变多,模型相应的得到更多训练,表现也可能会更好。(但是给的数据集中,monolingual data=》test/test.zh全是句号)
3. Code
3.1 数据预处理
数据集
双眼平行语料库2020年:
原始:398066(句子)
已处理:393980(句子)
测试数据:
大小:4000句子
中文翻译未公开,每一行都是“。”
- 处理的内容
- 下载并解压缩文件
- 将文件重命名
# 下载档案并解压缩
data_dir = './DATA/rawdata'
dataset_name = 'ted2020'
urls = (
'"https://onedrive.live.com/download?cid=3E549F3B24B238B4&resid=3E549F3B24B238B4%214989&authkey=AGgQ-DaR8eFSl1A"',
'"https://onedrive.live.com/download?cid=3E549F3B24B238B4&resid=3E549F3B24B238B4%214987&authkey=AA4qP_azsicwZZM"',
# # If the above links die, use the following instead.
# "https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r09922057/ML2021-hw5/ted2020.tgz",
# "https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r09922057/ML2021-hw5/test.tgz",
# # If the above links die, use the following instead.
# "https://mega.nz/#!vEcTCISJ!3Rw0eHTZWPpdHBTbQEqBDikDEdFPr7fI8WxaXK9yZ9U",
# "https://mega.nz/#!zNcnGIoJ!oPJX9AvVVs11jc0SaK6vxP_lFUNTkEcK2WbxJpvjU5Y",
)
file_names = (
'ted2020.tgz', # train & dev
'test.tgz', # test
)
prefix = Path(data_dir).absolute() / dataset_name
prefix.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
for u, f in zip(urls, file_names):
path = prefix/f
if not path.exists():
if 'mega' in u:
!megadl {u} --path {path}
else:
!wget {u} -O {path}
if path.suffix == ".tgz":
!tar -xvf {path} -C {prefix}
elif path.suffix == ".zip":
!unzip -o {path} -d {prefix}
# 重命名文件,加上前缀train_dev/test
!mv {prefix/'raw.en'} {prefix/'train_dev.raw.en'}
!mv {prefix/'raw.zh'} {prefix/'train_dev.raw.zh'}
!mv {prefix/'test.en'} {prefix/'test.raw.en'}
!mv {prefix/'test.zh'} {prefix/'test.raw.zh'}
#设定语言
src_lang = 'en'
tgt_lang = 'zh'
data_prefix = f'{prefix}/train_dev.raw'
test_prefix = f'{prefix}/test.raw'
!head {data_prefix+'.'+src_lang} -n 5
!head {data_prefix+'.'+tgt_lang} -n 5
Thank you so much, Chris.
And it’s truly a great honor to have the opportunity to come to this stage twice; I’m extremely grateful.
I have been blown away by this conference, and I want to thank all of you for the many nice comments about what I had to say the other night.
And I say that sincerely, partly because I need that.
Put yourselves in my position.
非常謝謝你,克里斯。能有這個機會第二度踏上這個演講台
真是一大榮幸。我非常感激。
這個研討會給我留下了極為深刻的印象,我想感謝大家 對我之前演講的好評。
我是由衷的想這麼說,有部份原因是因為 —— 我真的有需要!
請你們設身處地為我想一想!
- 处理的内容
- 把字符串全形转半形
- 将字符串的特殊字符与内容以‘ ’分割
- 去掉或者替换掉一些特殊字符
# 去掉或者替换掉一些特殊字符
def clean_s(s, lang):
if lang == 'en':
s = re.sub(r"\([^()]*\)", "", s) # remove ([text])
s = s.replace('-', '') # remove '-'
s = re.sub('([.,;!?()\"])', r' \1 ', s) # keep punctuation
elif lang == 'zh':
s = strQ2B(s) # Q2B
s = re.sub(r"\([^()]*\)", "", s) # remove ([text])
s = s.replace(' ', '')
s = s.replace('—', '')
s = s.replace('“', '"')
s = s.replace('”', '"')
s = s.replace('_', '')
s = re.sub('([。,;!?()\"~「」])', r' \1 ', s) # keep punctuation
s = ' '.join(s.strip().split()) # 将字符串以空格分割
return s
def len_s(s, lang):
if lang == 'zh':
return len(s)
return len(s.split())
# clean后文件名称是:train_dev.raw.clean.en, train_dev.raw.clean.zh, text.raw.clean.en. test.raw.clean.zh
def clean_corpus(prefix, l1, l2, ratio=9, max_len=1000, min_len=1):
if Path(f'{prefix}.clean.{l1}').exists() and Path(f'{prefix}.clean.{l2}').exists():
print(f'{prefix}.clean.{l1} & {l2} exists. skipping clean.')
return
with open(f'{prefix}.{l1}', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as l1_in_f:
with open(f'{prefix}.{l2}', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as l2_in_f:
with open(f'{prefix}.clean.{l1}', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as l1_out_f:
with open(f'{prefix}.clean.{l2}', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as l2_out_f:
for s1 in l1_in_f:
s1 = s1.strip()
s2 = l2_in_f.readline().strip()
s1 = clean_s(s1, l1)
s2 = clean_s(s2, l2)
s1_len = len_s(s1, l1)
s2_len = len_s(s2, l2)
if min_len > 0: # remove short sentence
if s1_len < min_len or s2_len < min_len:
continue
if max_len > 0: # remove long sentence
if s1_len > max_len or s2_len > max_len:
continue
if ratio > 0: # remove by ratio of length
if s1_len / s2_len > ratio or s2_len / s1_len > ratio:
continue
print(s1, file=l1_out_f)
print(s2, file=l2_out_f)
clean_corpus(data_prefix, src_lang, tgt_lang)
clean_corpus(test_prefix, src_lang, tgt_lang, ratio=-1, min_len=-1, max_len=-1)
Thank you so much , Chris .
And it’s truly a great honor to have the opportunity to come to this stage twice ; I’m extremely grateful .
I have been blown away by this conference , and I want to thank all of you for the many nice comments about what I had to say the other night .
And I say that sincerely , partly because I need that .
Put yourselves in my position .
非常謝謝你 , 克里斯 。 能有這個機會第二度踏上這個演講台
真是一大榮幸 。 我非常感激 。
這個研討會給我留下了極為深刻的印象 , 我想感謝大家對我之前演講的好評 。
我是由衷的想這麼說 , 有部份原因是因為我真的有需要 !
請你們設身處地為我想一想 !
3.2 划分训练集和验证集
验证集只需要3000~4000个句子即可,将上面处理完的训练集进行划分,分别放到train.clean.en/.zh、valid.clean.zn/.zh文件中。
# 划分训练集和验证集
# 验证集300~400句即可
valid_ratio = 0.01
train_ratio = 1 - valid_ratio
data_dir = './data'
dataset_name = 'prefix'
# 最后划分为训练集和验证集 文件名称分别为 train.clean.en train.clean.zh valid.clean.en valid.clean.zh
if Path(f'{prefix}/train.clean.{src_lang}').exists() \
and Path(f'{prefix}/train.clean.{tgt_lang}').exists() \
and Path(f'{prefix}/valid.clean.{src_lang}').exists() \
and Path(f'{prefix}/valid.clean.{tgt_lang}').exists():
print(f'train/valid splits exists. skipping split.')
else:
line_num = sum(1 for line in open(f'{data_prefix}.clean.{src_lang}', encoding='utf-8'))
labels = list(range(line_num))
random.shuffle(labels)
for lang in [src_lang, tgt_lang]:
train_f = open(os.path.join(data_dir, dataset_name, f'train.clean.{lang}'), 'w', encoding='utf-8')
valid_f = open(os.path.join(data_dir, dataset_name, f'valid.clean.{lang}'), 'w', encoding='utf-8')
count = 0
for line in open(f'{data_prefix}.clean.{lang}', 'r', encoding='utf-8'):
if labels[count]/line_num < train_ratio:
train_f.write(line)
else:
valid_f.write(line)
count += 1
train_f.close()
valid_f.close()
划分的最后结果如下
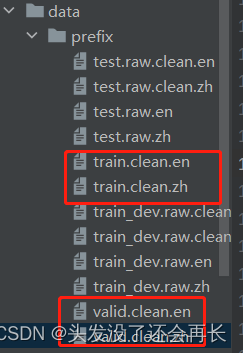
3.3 Subword Units(分词)
翻译中存在一大问题是未登录词(out of vocabulary),可以使用subword units作为短词单位来解决。
- 使用
sentencepiece套件 - 用
unigram或byte-pair encoding(BPE)
# Subword Units
# 分词
# 使用sentencepiece中的spm对训练集和验证集进行分词建模,模型名称是spm8000.model,同时产生词汇库spm8000.vocab
# 使用模型对训练集、验证集、测试集进行分词处理,得到文件train.en, train.zh, valid.en, valid.zh, test.en, test.zh
import sentencepiece as spm
vocab_size = 8000
if Path(f'{prefix}/spm{vocab_size}.model').exists():
print(f'{prefix}/spm{vocab_size},model exits. skipping spm_train')
else:
spm.SentencePieceTrainer.train(
input=','.join([f'{prefix}/train.clean.{src_lang}',
f'{prefix}/valid.clean.{src_lang}',
f'{prefix}/train.clean.{tgt_lang}',
f'{prefix}/valid.clean.{tgt_lang}']),
model_prefix=f'{prefix}/spm{vocab_size}',
vocab_size=vocab_size,
character_coverage=1,
model_type='unigram', # 'bpe' 也可
input_sentence_size=1e6,
shuffle_input_sentence=True,
normalization_rule_name='nmt_nfkc_cf',
)
spm_model = spm.SentencePieceProcessor(model_file=str(f'{prefix}/spm{vocab_size}.model'))
in_tag = {
'train': 'train.clean',
'valid': 'valid.clean',
'test': 'test.raw.clean',
}
for split in ['train', 'valid', 'test']:
for lang in [src_lang, tgt_lang]:
out_path = Path(f'{prefix}/{split}.{lang}')
if out_path.exists():
print(f"{out_path} exists. skipping spm_encode.")
else:
with open(f'{prefix}/{split}.{lang}', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as out_f:
with open(f'{prefix}/{in_tag[split]}.{lang}', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as in_f:
for line in in_f:
line = line.strip()
tok = spm_model.encode(line, out_type=str)
print(' '.join(tok), file=out_f)
分词后得到的词汇表spm8000.vocab中的部分内容如下:
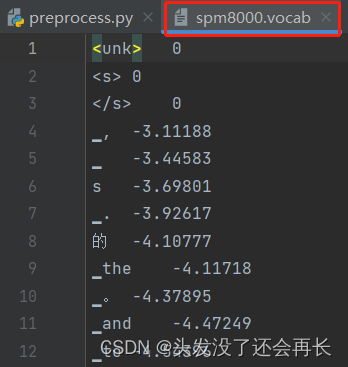
分词处理后的train.en和对应的train.zh文件内容:
▁thank ▁you ▁so ▁much ▁, ▁chris ▁.
▁and ▁it ’ s ▁ t ru ly ▁a ▁great ▁ho n or ▁to ▁have ▁the ▁ op port un ity ▁to ▁come ▁to ▁this ▁st age ▁ t wi ce ▁; ▁i ’ m ▁ex t re me ly ▁gr ate ful ▁.
▁i ▁have ▁been ▁ bl ow n ▁away ▁by ▁this ▁con fer ence ▁, ▁and ▁i ▁want ▁to ▁thank ▁all ▁of ▁you ▁for ▁the ▁many ▁ ni ce ▁ com ment s ▁about ▁what ▁i ▁had ▁to ▁say ▁the ▁other ▁night ▁.
▁and ▁i ▁say ▁that ▁since re ly ▁, ▁part ly ▁because ▁i ▁need ▁that ▁.
▁put ▁your s el ve s ▁in ▁my ▁po s ition ▁.
▁ 非常 謝 謝 你 ▁, ▁ 克 里 斯 ▁。 ▁ 能 有 這個 機會 第二 度 踏 上 這個 演講 台
▁ 真 是 一 大 榮 幸 ▁。 ▁我 非常 感 激 ▁。
▁這個 研 討 會 給我 留 下 了 極 為 深 刻 的 印 象 ▁, ▁我想 感 謝 大家 對我 之前 演講 的 好 評 ▁。
▁我 是由 衷 的 想 這麼 說 ▁, ▁有 部份 原因 是因為 我 真的 有 需要 ▁!
▁ 請 你們 設 身 處 地 為 我想 一 想 ▁!
3.4用fairseq将资料转为二进制
下面的程序可以在jupyter中运行,或者在python解释器
# 使用fairseq将数据二进制化 最终生成的文件在目录./data/data_bin下
binpath = Path('./data/data-bin')
if binpath.exists():
print(binpath, "exists, will not overwrite!")
else:
!python -m fairseq_cli.preprocess \
--source-lang en\
--target-lang zh\
--trainpref ./data/prefix/train\
--validpref ./data/prefix/valid\
--testpref ./data/prefix/test\
--destdir ./data/data_bin\
--joined-dictionary\
--workers 2
生成了一系列文件在data_bin目录下
4. 实验准备
4.1 实验参数设定
config = Namespace(
datadir = "./data/data_bin",
savedir = "./checkpoints/rnn",
source_lang = "en",
target_lang = "zh",
# cpu threads when fetching & processing data.
num_workers=2,
# batch size in terms of tokens. gradient accumulation increases the effective batchsize.
max_tokens=8192,
accum_steps=2,
# the lr s calculated from Noam lr scheduler. you can tune the maximum lr by this factor.
lr_factor=2.,
lr_warmup=4000,
# clipping gradient norm helps alleviate gradient exploding
clip_norm=1.0,
# maximum epochs for training
max_epoch=30,
start_epoch=1,
# beam size for beam search
beam=5,
# generate sequences of maximum length ax + b, where x is the source length
max_len_a=1.2,
max_len_b=10,
# when decoding, post process sentence by removing sentencepiece symbols.
post_process = "sentencepiece",
# checkpoints
keep_last_epochs=5,
resume=None, # if resume from checkpoint name (under config.savedir)
# logging
use_wandb=False,
)
4.2 logging
# logging套件记录一般讯息 wandb记录训练过程的loss, blue, model, weight等
logging.basicConfig(
format="%(asctime)s | %(levelname)s | %(name)s | %(message)s",
datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",
level="INFO", # "DEBUG" "WARNING" "ERROR"
stream=sys.stdout,
)
proj = "hw5.seq2seq"
logger = logging.getLogger(proj)
if config.use_wandb:
import wandb
wandb.init(project=proj, name=Path(config.savedir).stem, config=config)
4.3 cuda环境
cuda_env = utils.CudaEnvironment()
utils.CudaEnvironment.pretty_print_cuda_env_list([cuda_env])
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
4.4 读取资料集
借用fairsq的TranslationTask
- 用来加载上面创建的二进制数据
- 实现良好的数据迭代器(dataloader)
- 字典task.source_directionary 和 task.targrt_directionary也很好用
- 有實做 beam search
from fairseq.tasks.translation import TranslationConfig, TranslationTask
## setup task
task_cfg = TranslationConfig(
data=config.datadir,
source_lang=config.source_lang,
target_lang=config.target_lang,
train_subset="train",
required_seq_len_multiple=8,
dataset_impl="mmap",
upsample_primary=1,
)
task = TranslationTask.setup_task(task_cfg)
logger.info("loading data for epoch 1")
task.load_dataset(split="train", epoch=1, combine=True) # combine if you have back-translation data.
task.load_dataset(split="valid", epoch=1)
sample = task.dataset("valid")[1]
pprint.pprint(sample)
pprint.pprint(
"Source: " + \
task.source_dictionary.string(
sample['source'],
config.post_process,
)
)
pprint.pprint(
"Target: " + \
task.target_dictionary.string(
sample['target'],
config.post_process,
)
)
运行结果:
{‘id’: 1,
‘source’: tensor([ 18, 14, 6, 2234, 60, 19, 80, 5, 256, 16, 405, 1407,
1706, 7, 2]),
‘target’: tensor([ 140, 690, 28, 270, 45, 151, 1142, 660, 606, 369, 3114, 2434,
1434, 192, 2])}
“Source: that’s exactly what i do optical mind control .”
‘Target: 這實在就是我所做的–光學操控思想’
4.5 数据集迭代器
- 将每个batch控制在
N个token让GPU记忆体更有效被利用 - 让training set每个
epoch有不同shuffling - 滤掉长度太长的句子
- 将每个batch内的句子**
pad成一样长**,好让GPU平行运算 - 加上
eos并shift一格- teacher forcing:为了训练模型根据prefix生成下个字,decoder的输入会是输出目标序列往右shift一格。
- 一般是会在输入开头加个
bos token(如下图)
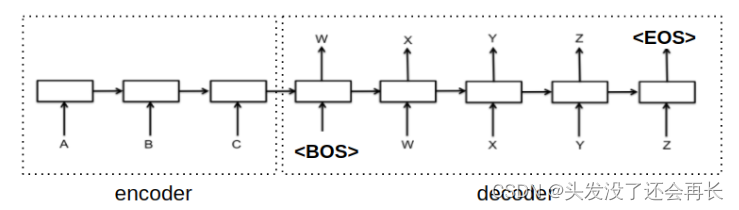
fairseq则是直接吧eos挪到begining,训练起来其实效果差不多。例如:
输出目标 (target) 和 Decoder输入 (prev_output_tokens): eos = 2 target = 419, 711, 238, 888, 792, 60, 968, 8, 2 prev_output_tokens = 2, 419, 711, 238, 888, 792, 60, 968, 8
def load_data_iterator(task, split, epoch=1, max_tokens=4000, num_workers=1, cached=True):
batch_iterator = task.get_batch_iterator(
dataset=task.dataset(split),
max_tokens=max_tokens,
max_sentences=None,
max_positions=utils.resolve_max_positions(
task.max_positions(),
max_tokens,
),
ignore_invalid_inputs=True,
seed=seed,
num_workers=num_workers,
epoch=epoch,
disable_iterator_cache=not cached,
# Set this to False to speed up. However, if set to False, changing max_tokens beyond
# first call of this method has no effect.
)
return batch_iterator
if __name__=='__main__':
demo_epoch_obj = load_data_iterator(task, "valid", epoch=1, max_tokens=20, num_workers=1, cached=False)
demo_iter = demo_epoch_obj.next_epoch_itr(shuffle=True)
sample = next(demo_iter)
print(sample)
输出信息和解释说明如下:
{‘id’: tensor([723]), # 每个example的id
‘nsentences’: 1, # batch size 句子数
‘ntokens’: 18, # batch size 字数
‘net_input’: {
‘src_tokens’: tensor([[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 18, 26, 82, 8, 480, 15, 651,
1361, 38, 6, 176, 2696, 39, 5, 822, 92, 260, 7, 2]]), # 来源语言的序列
‘src_lengths’: tensor([19]), # 每句话没有pad过的长度
‘prev_output_tokens’: tensor([[ 2, 140, 296, 318, 1560, 51, 568, 316, 225, 1952, 254, 78, # 上面提到shift 一格后的目标序列
151, 2691, 9, 215, 1680, 10, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
},
‘target’: tensor([[ 140, 296, 318, 1560, 51, 568, 316, 225, 1952, 254, 78, 151,
2691, 9, 215, 1680, 10, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]) # 目标序列
}
5. 定义模型架构
- 继承
fairseq的Encoder,decoder,model,这样测试阶段才能直接用它写好的beam search函式
5.1 Encoder编码器
seq2seq模型的编码器为RNN或Transformer Encoder,一下说明以RNN为例。
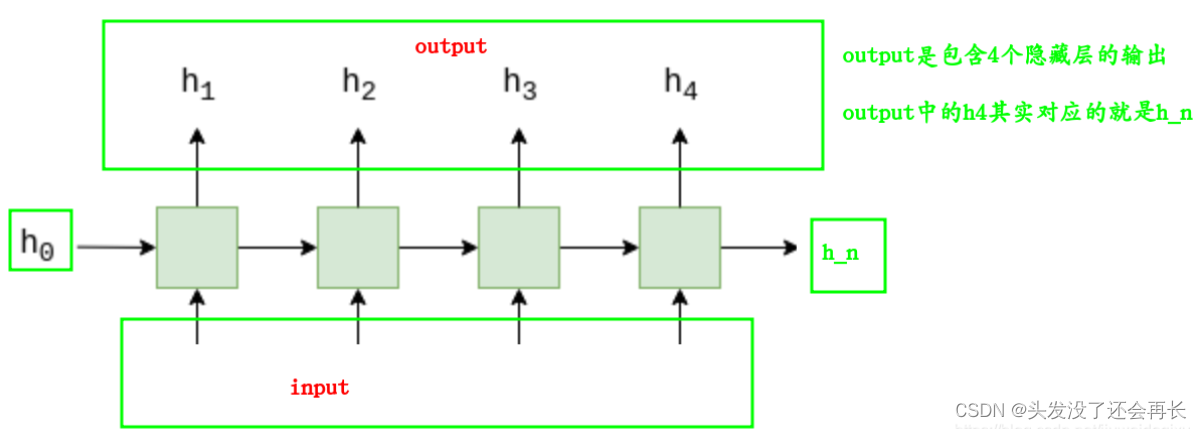
对应每一个输入,Encoder会输出一个向量和一个隐藏状态(hidden state),并将隐藏状态用于下一个输入。换句话说,Encoder会逐步读取输入序列,并在每个timestep输出单个向量,以及在最后timestep输出隐藏状态(content vector)。
下面解释一下本实验中的GRU
本实验使用的是
GRU,GRU的输入输出参数如下:
输入的参数有两个,分别是input和h_0。
Inputs: input, h_0
①input的shape
The shape of input:(seq_len, batch, input_size) : tensor containing the feature of the input sequence. The input can also be a packed variable length sequence。See functorch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequencefor details.
②h_0的shape
从下面的解释中也可以看出,这个参数可以不提供,那么就默认为0.
The shape of h_0:(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch. Defaults to zero if not provided. If the RNN is bidirectional num_directions should be 2, else it should be 1.
输出有两个,分别是output和h_n
①output
output 的shape是:(seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size): tensor containing the output features h_t from the last layer of the GRU, for each t.
If a class:torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence has been given as the input, the output will also be a packed sequence. For the unpacked case, the directions can be separated using output.view(seq_len, batch, num_directions, hidden_size), with forward and backward being direction 0 and 1 respectively.
Similarly, the directions can be separated in the packed case.
②h_n
h_n的shape是:(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor containing the hidden state for t = seq_len
Like output, the layers can be separated using
h_n.view(num_layers, num_directions, batch, hidden_size).
当双向 = True 时,h_n将分别包含最终正向和反向隐藏状态的串联。
大致如下图所示:
# 定义模型架构
# 使用fairsq的Encoder,decoder and model
class RNNEncoder(FairseqEncoder):
def __init__(self, args, dictionary, embed_tokens):
'''
:param args:
encoder_embed_dim 是embedding的维度,主要将one-hot vect的单词向量压缩到指定的维度
encoder_ffn_embed_dim 是RNN输出和隐藏状态的维度(hidden dimension)
encoder_layers 是RNN要叠多少层
dropout 是决定有大欧少的几率会将某个节点变为0,主要是为了防止overfitting,一般来说训练时用
:param dictionary: fairseq帮我们做好的dictionary 再次用来得到padding index,好用来得到encoder padding mask
:param embed_tokens: 事先做好的词嵌入(nn.Embedding)
'''
super().__init__(dictionary)
self.embed_tokens = embed_tokens
self.embed_dim = args.encoder_embed_dim
self.hidden_dim = args.encoder_ffn_embed_dim
self.num_layers = args.encoder_layers
self.dropout_in_module = nn.Dropout(args.dropout)
self.rnn = nn.GRU(
self.embed_dim,
self.hidden_dim,
self.num_layers,
dropout=args.dropout,
batch_first=False,
bidirectional=True,
)
self.dropout_out_module = nn.Dropout(args.dropout)
self.padding_idx = dictionary.pad()
def combine_bidir(self, outs, bsz:int):
out = outs.view(self.num_layers, 2, bsz, -1).transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
return out.view(self.num_layers, bsz, -1)
def forward(self, src_tokens, **unused):
'''
:param src_tokens: 英文的整数序列
:param unused:
:return:
outputs: 最上层RNN每个timestep的输出,最后可以用Attention再进行处理
final_hiddens: 每层最终timestep的隐藏状态,将传递到Decoder进行解码
encoder_padding_mask: 告诉我们那些事位置的资讯不重要
'''
bsz, seqlen = src_tokens.size()
# get embeddings
x = self.embed_tokens(src_tokens)
x = self.dropout_in_module(x)
# B x T x C => T x B x C
x = x.transpose(0, 1)
# 过双向RNN
h0 = x.new_zeros(2 * self.num_layers, bsz, self.hidden_dim)
x, final_hiddens = self.rnn(x, h0)
outputs = self.dropout_out_module(x)
# outputs = [sequence len, batch size, hid dim * directions] 是最上面RNN的输出
# hidden = [num_layers * directions, batch size , hid dim]
# 因为Encoder是双向的,我们需要链接两个方向的隐藏状态
final_hiddens = self.combine_bidir(final_hiddens, bsz)
# hidden = [num_layers x batch x num_directions*hidden]
encoder_padding_mask = src_tokens.eq(self.padding_idx).t()
return tuple(
(
outputs, # seq_len x batch x hidden
final_hiddens, # num_layers x batch x num_directions*hidden
encoder_padding_mask, # seq_len x batch
)
)
def reorder_encoder_out(self, encoder_out, new_order):
return tuple(
(
encoder_out[0].index_select(1, new_order),
encoder_out[1].index_select(1, new_order),
encoder_out[2].index_select(1, new_order),
)
)
5.2 Attention
- 当输入过长,或是单独靠“content vector”无法取得整个输入的意思时,用
Attention Mechanism来提供Decoder更多的资讯- 根据现在
Decoder embeddings,去计算在Encoder outputs中,那些与其有较高的关系,根据关系的数值来把Encoder outputs平均起来作为Decoder RNN的输入- 常见Attention的作用是用Neural Network / Dot Product来算
query(decoder embedding)和key(Encoder outputs)之间的关系,再对所有算出来的数值做softmax得到分布,最后根据这个分布对values(Encoder outputs)做weight sum
# Attention
class AttentionLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_embed_dim, source_embed_dim, output_embed_dim, bias=False):
'''
:param input_embed_dim: key 的维度,应是 decoder 要做 attend 时的向量的维度
:param source_embed_dim: query 的维度,应是要被 attend 的向量(encoder outputs)的维度
:param output_embed_dim: value 的维度,应是做完 attention 后,下一层预期的向量维度
:param bias:
'''
super().__init__()
self.input_proj = nn.Linear(input_embed_dim, source_embed_dim, bias=bias)
self.output_proj = nn.Linear(
input_embed_dim + source_embed_dim, output_embed_dim, bias=bias
)
def forward(self, inputs, encoder_outputs, encoder_padding_mask):
'''
:param inputs: 就是key,要attend别人的向量
:param encoder_outputs: 是query/value,被attend的向量
:param encoder_padding_mask: 告诉我们哪些是位置的资讯不重要
:return:
output: 做完attention后的context vector
attention score: attention的分布
'''
# inputs: T, B, dim
# encoder_outputs: S x B x dim
# padding mask: S x B
# convert all to batch first
inputs = inputs.transpose(1, 0) # B, T, dim
encoder_outputs = encoder_outputs.transpose(1, 0) #B, S, dim
encoder_padding_mask = encoder_padding_mask.transpose(1, 0) # B, S
# 投影到encoder_outputs的维度
# (B, T, dm) x (B, dim, S) = (B, T, S)
attn_scores = torch.bmm(x, encoder_outputs.transpose(1, 2))
# 挡住padding位置的attention
if encoder_padding_mask is not None:
# 利用broadcast B, S -> (B, 1, S)
encoder_padding_mask = encoder_padding_mask.unsqueeze(1)
attn_scores = (
attn_scores.float()
.masked_dill_(encoder_padding_mask, float("-inf"))# 用来mask掉当前时刻后面时刻的序列信息
.type_as(attn_scores)# 按照给定的tensor进行类型转换
)
# 在source对应维度softmax
attn_scores = F.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1)
# 形状(B, T, S) x (B, S, dim) = (B, T, dim)加权平均
x = torch.bmm(attn_scores, encoder_outputs)
# (B, T, dim)
x = torch.cat((x, inputs), dim=-1)
x = torch.tanh(self.output_proj(x)) # output + linear + tanh
# 回复形状(B, T, dim) -> (T, B, dim)
return x.transpose(1, 0), attn_scores
5.3 Decoder解码器
- 解码器的hidden states会用编码器最终隐藏状态来初始化
- 解码器同时也根据目前timestep的输入(也就是前一个timestep的output),改变hidden states,并输出结果
- 如果加入attention可以使其表现更好
- 我们把seq2seq步骤写在解码器里,好让等等seq2seq这个类可以通用RNN和Transformer,而不用再改写
# Decoder
class RNNDecoder(FairseqIncrementalDecoder):
def __init__(self, args, dictionary, embed_tokens):
super().__init__(dictionary)
self.embed_tokens = embed_tokens
assert args.decoder_layers == args.encoder_layers, f"""seq2seq rnn requires that encoder
and decoder have same layers of rnn. got: {args.encoder_layers, args.decoder_layers}"""
assert args.decoder_ffn_embed_dim == args.encoder_ffn_embed_dim * 2, f"""seq2seq-rnn requires
that decoder hidden to be 2*encoder hidden dim. got: {args.decoder_ffn_embed_dim, args.encoder_ffn_embed_dim * 2}"""
self.embed_dim = args.decoder_embed_dim
self.hidden_dim = args.decoder_ffn_embed_dim
self.num_layers = args.decoder_layers
self.dropout_in_module = nn.Dropout(args.dropout)
self.rnn = nn.GRU(
self.embed_dim,
self.hidden_dim,
self.num_layers,
dropout=args.dropout,
batch_first=False,
bidirectional=False,
)
self.attention = AttentionLayer(
self.embed_dim, self.hidden_dim, self.embed_dim, bias=False
)
# self.attention = None
self.dropout_out_module = nn.Dropout(args.dropout)
if self.hidden_dim != self.embed_dim:
self.project_out_dim = nn.Linear(self.hidden_dim, self.embed_dim)
else:
self.project_out_dim = None
if args.share_decoder_input_output_embed:
self.output_projection = nn.Linear(
self.embed_tokens.weight.shape[1],
self.embed_tokens.weight.shape[0],
bias=False,
)
self.output_projection.weight = self.embed_tokens.weight
else:
self.output_projection = nn.Linear(
self.output_embed_dim, len(dictionary), bias=False
)
nn.init.normal_(
self.output_projection.weight, mean=0, std=self.output_embed_dim ** -0.5
)
def forward(self, prev_output_tokens, encoder_out, incremental_state=None, **unused):
# 取出encoder的输出
encoder_outputs, encoder_hiddens, encoder_padding_mask = encoder_out
# outputs: seq_len x batch x num_directions*hidden
# encoder_hiddens: num_layers x batch x num_directions*encoder_hidden
# padding_mask: seq_len x batch
if incremental_state is not None and len(incremental_state
)>0:
# 如果保留了上一个timestep留下的资讯,我们可以从那里进来,而不是从bos开始
prev_output_tokens = prev_output_tokens[:, -1:]
cache_state = self.get_incremental_state(incremental_state, "cache_state")
prev_hiddens = cache_state["prev_hiddens"]
else:
# 沒有incremental state代表这是training或者是test time时的第一步
# 准备seq2seq: 把encoder_hiddens pass进去decoder的hidden states
prev_hiddens = encoder_hiddens
bsz, seqlen = prev_output_tokens.size()
# embed tokens
x = self.embed_tokens(prev_output_tokens)
x = self.dropout_in_module(x)
# B x T x C -> T x B x C
x = x.transpose(0, 1)
# 做decoder-to-encoder attention
if self.attention is not None:
x, attn = self.attention(x, encoder_outputs, encoder_padding_mask)
# 过单向RNN
x, final_hiddens = self.rnn(x, prev_hiddens)
# outputs = [sequence len, batch size, hid dim]
# hidden = [num_layers * directions, batch size , hid dim]
x = self.dropout_out_module(x)
# 投影到embedding size (如果hidden 和embed size不一样,然后share_embedding又变成True,需要额外project一次)
if self.project_out_dim != None:
x = self.project_out_dim(x)
# 投影到vocab size 的分布
x = self.output_projection(x)
# T x B x C -> B x T x C
x = x.transpose(1, 0)
# 如果是Incremental, 记录这个timestep的hidden states, 下个timestep读回来
cache_state = {
"prev_hiddens": final_hiddens,
}
self.set_incremental_state(incremental_state, "cached_state", cache_state)
return x, None
def reorder_incremental_state(
self,
incremental_state,
new_order,
):
# 这个beam search时会用到,意思并不是很重要
cache_state = self.get_incremental_state(incremental_state, "cached_state")
prev_hiddens = cache_state["prev_hiddens"]
prev_hiddens = [p.index_select(0, new_order) for p in prev_hiddens]
cache_state = {
"prev_hiddens": torch.stack(prev_hiddens),
}
self.set_incremental_state(incremental_state, "cached_state", cache_state)
return
5.4 Seq2Seq
- 由
Encoder和Decoder组成 - 接收输入并传给
Encoder - 将
Encoder的输出传给Decoder Decoder根据前一个timestep的输出和Encoder输出进行解码- 当解码完成后,将
Decoder的输出传回
# Seq2Seq
class Seq2Seq(FairseqEncoderDecoderModel):
def __init__(self, args, encoder, decoder):
super().__init__(encoder, decoder)
self.args = args
def forward(self, src_tokens, src_lengths, prev_output_tikens, return_all_hiddens: bool = True):
encoder_out = self.encoder(
src_tokens, src_lengths=src_lengths, return_all_hiddens=return_all_hiddens
)
logits, extra = self.decoder(
prev_output_tikens,
encoder_out=encoder_out,
src_lengths=src_lengths,
return_all_hiddens=return_all_hiddens,
)
return logits, extra
5.5 模型初始化
# 模型初始化
def build_model(args, task):
src_dict, tgt_dict = task.source_dictionary, task.target_dictionary
# 词嵌入
encoder_embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(len(src_dict), args.encoder_embed_dim, src_dict.pad())
decoder_embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(len(tgt_dict), args.decoder_embed_dim, tgt_dict.pad())
# 编码器和解码器
encoder = RNNEncoder(args, src_dict, encoder_embed_tokens)
decoder = RNNDecoder(args, tgt_dict, decoder_embed_tokens)
# 序列到序列模型
model = Seq2Seq(args, encoder, decoder)
# 序列到序列模型的初始化很重要 需要特别处理
def init_params(module):
from fairseq.modules import MultiheadAttention
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=0.02)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
if isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=0.02)
if module.padding_idx is not None:
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
if isinstance(module, MultiheadAttention):
module.q_proj.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=0.02)
module.k_proj.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=0.02)
module.v_proj.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=0.02)
if isinstance(module, nn.RNNBase):
for name, param in module.named_parameters():
if "weight" in name or "bias" in name:
param.data.uniform_(-0.1, 0.1)
# 初始化模型
model.apply(init_params)
return model
5.6 设置模型相关参数
arch_args = Namespace(
encoder_embed_dim=256,
encoder_ffn_embed_dim=512,
encoder_layers=1,
decoder_embed_dim=256,
decoder_ffn_embed_dim=1024,
decoder_layers=1,
share_decoder_input_output_embed=True,
dropout=0.3,
)
model = build_model(arch_args, task)
logger.info(model)
Seq2Seq(
(encoder): RNNEncoder(
(embed_tokens): Embedding(8000, 256, padding_idx=1)
(dropout_in_module): Dropout(p=0.3, inplace=False)
(rnn): GRU(256, 512, dropout=0.3, bidirectional=True)
(dropout_out_module): Dropout(p=0.3, inplace=False)
)
(decoder): RNNDecoder(
(embed_tokens): Embedding(8000, 256, padding_idx=1)
(dropout_in_module): Dropout(p=0.3, inplace=False)
(rnn): GRU(256, 1024, dropout=0.3)
(attention): AttentionLayer(
(input_proj): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=1024, bias=False)
(output_proj): Linear(in_features=1280, out_features=256, bias=False)
)
(dropout_out_module): Dropout(p=0.3, inplace=False)
(project_out_dim): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=256, bias=True)
(output_projection): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=8000, bias=False)
)
)
5.7 Optimization 最佳化
Loss : Label Smoothing Regularization
- 让模型学习输出较不集中的分布,防止模型过度自信
- 有时候Cround Truth并非唯一答案,所以在算loss时,我们会保留一部分概率给正确答案以外的label
- 可以有效防止过度拟合
class LabelSmoothedCrossEntropyCriterion(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, smoothing, ignore_index=None, reduce=True):
super().__init__()
self.smoothing = smoothing
self.ignore_index = ignore_index
self.reduce = reduce
def forward(self, lprobs, target):
if target.dim() == lprobs.dim() - 1:
target = target.unsqueeze(-1)
# nll: Negative log likelihood,當目標是one-hot時的cross-entropy loss. 以下同 F.nll_loss
nll_loss = -lprobs.gather(dim=-1, index=target)
# 將一部分正確答案的機率分配給其他label 所以當計算cross-entropy時等於把所有label的log prob加起來
smooth_loss = -lprobs.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
if self.ignore_index is not None:
pad_mask = target.eq(self.ignore_index)
nll_loss.masked_fill_(pad_mask, 0.0)
smooth_loss.masked_fill_(pad_mask, 0.0)
else:
nll_loss = nll_loss.squeeze(-1)
smooth_loss = smooth_loss.squeeze(-1)
if self.reduce:
nll_loss = nll_loss.sum()
smooth_loss = smooth_loss.sum()
# 計算cross-entropy時 加入分配給其他label的loss
eps_i = self.smoothing / lprobs.size(-1)
loss = (1.0 - self.smoothing) * nll_loss + eps_i * smooth_loss
return loss
# 一般都用0.1效果就很好了
criterion = LabelSmoothedCrossEntropyCriterion(
smoothing=0.1,
ignore_index=task.target_dictionary.pad(),
)
5.8 Optimizer: Adam + lr scheduling
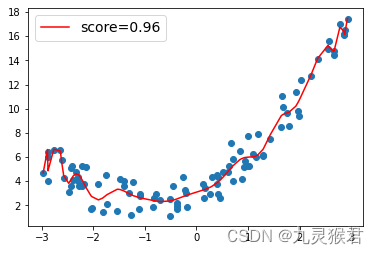
Inverse square root 排程对于训练 Transformer 时的稳定性很重要,后来也用在 RNN 上。 根据底下公式来更新 learning rate,前期线性增长,后期根据更新步数方根的倒数来递减。
class NoamOpt:
"Optim wrapper that implements rate."
def __init__(self, model_size, factor, warmup, optimizer):
self.optimizer = optimizer
self._step = 0
self.warmup = warmup
self.factor = factor
self.model_size = model_size
self._rate = 0
@property
def param_groups(self):
return self.optimizer.param_groups
def multiply_grads(self, c):
"""Multiplies grads by a constant *c*."""
for group in self.param_groups:
for p in group['params']:
if p.grad is not None:
p.grad.data.mul_(c)
def step(self):
"Update parameters and rate"
self._step += 1
rate = self.rate()
for p in self.param_groups:
p['lr'] = rate
self._rate = rate
self.optimizer.step()
def rate(self, step = None):
"Implement `lrate` above"
if step is None:
step = self._step
return 0 if not step else self.factor * \
(self.model_size ** (-0.5) *
min(step ** (-0.5), step * self.warmup ** (-1.5)))
排程视觉化
optimizer = NoamOpt(
model_size=arch_args.encoder_embed_dim,
factor=config.lr_factor,
warmup=config.lr_warmup,
optimizer=torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=0, betas=(0.9, 0.98), eps=1e-9, weight_decay=0.0001))
plt.plot(np.arange(1, 100000), [optimizer.rate(i) for i in range(1, 100000)])
plt.legend([f"{optimizer.model_size}:{optimizer.warmup}"])
None
6. train
def train_one_epoch(epoch_itr, model, task, criterion, optimizer, accum_steps=1):
itr = epoch_itr.next_epoch_itr(shuffle=True)
itr = iterators.GroupedIterator(itr, accum_steps) # 梯度累积: 每 accum_steps 个 sample 更新一次
stats = {"loss":[]}
scaler = GradScaler()
model.train()
progress = tqdm.tqdm(itr, desc=f"train epoch {epoch_itr}", leave=False)
for samples in progress:
model.zero_grad()
accum_loss = 0
sample_size = 0
# 梯度累积:没accum_steps个sample更新一次
for i, sample in enumerate(samples):
if i == 1:
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
sample = utils.move_to_cuda(sample, device=device)
traget = sample["traget"]
sample_size_i = sample["ntokens"]
sample_size += sample_size_i
# 混合精度训练
with autocast():
net_output = model.forward(**sample["net_input"])
lprobs = F.log_softmax(net_output[0], -1)
loss = criterion(lprobs.view(-1, lprobs.size(-1)), target.view(-1))
# logging
accum_loss += loss.item()
# back-prop
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
scaler.unscale_(optimizer)
optimizer.multiply_grads(
1 / (sample_size or 1.0)) # (sample_size or 1.0) handles the case of a zero gradient
gnorm = nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), config.clip_norm) # 梯度裁剪 防止梯度爆炸
scaler.step(optimizer)
scaler.update()
# logging
loss_print = accum_loss / sample_size
stats["loss"].append(loss_print)
progress.set_postfix(loss=loss_print)
# if config.use_wandb:
# wandb.log({
# "train/loss": loss_print,
# "train/grad_norm": gnorm.item(),
# "train/lr": optimizer.rate(),
# "train/sample_size": sample_size,
# })
loss_print = np.mean(stats["loss"])
logger.info(f"training loss: {loss_print:.4f}")
return stats
7. Validation & Inference 检验和推论
为了防止过拟合,每个epoch都要进行验证,计算模型在未看过的资料上的表现
- 过程基本上和training一样,另外加上inference
- 验证后,我们可以保存模型权重
仅验证损失,无法描述模型真实的性能 - 直接用当前模型去生成翻译结果(hypothesis),再和正确答案(reference)计算BLUE score
- 我们用fairseq写好的sequence generator来进行beam search生成翻译结果
# fairseq 的 beam search generator
# 給定模型和輸入序列,用 beam search 生成翻譯結果
sequence_generator = task.build_generator([model], config)
def decode(toks, dictionary):
# 從 Tensor 轉成人看得懂的句子
s = dictionary.string(
toks.int().cpu(),
config.post_process,
)
return s if s else "<unk>"
def inference_step(sample, model):
gen_out = sequence_generator.generate([model], sample)
srcs = []
hyps = []
refs = []
for i in range(len(gen_out)):
# 對於每個 sample, 收集輸入,輸出和參考答案,稍後計算 BLEU
srcs.append(decode(
utils.strip_pad(sample["net_input"]["src_tokens"][i], task.source_dictionary.pad()),
task.source_dictionary,
))
hyps.append(decode(
gen_out[i][0]["tokens"], # 0 代表取出 beam 內分數第一的輸出結果
task.target_dictionary,
))
refs.append(decode(
utils.strip_pad(sample["target"][i], task.target_dictionary.pad()),
task.target_dictionary,
))
return srcs, hyps, refs
import shutil
import sacrebleu
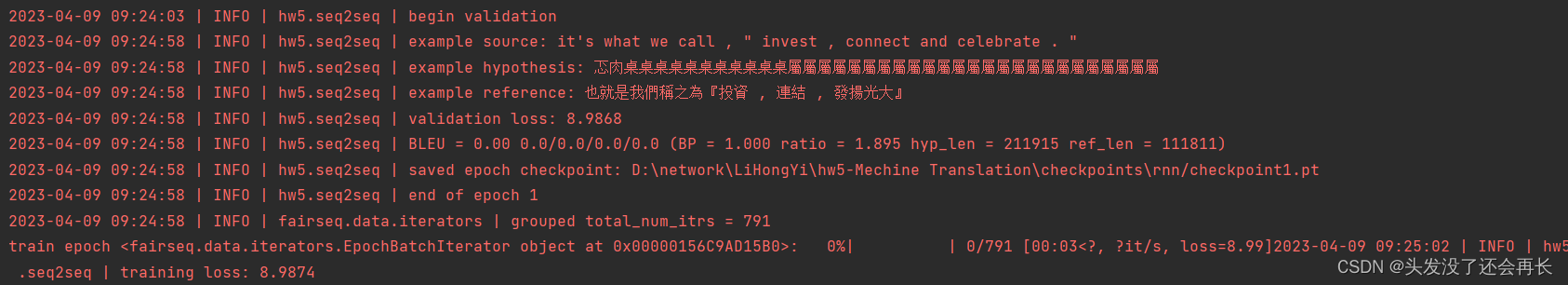
def validate(model, task, criterion, log_to_wandb=True):
logger.info('begin validation')
itr = load_data_iterator(task, "valid", 1, config.max_tokens, config.num_workers).next_epoch_itr(shuffle=False)
stats = {"loss":[], "bleu": 0, "srcs":[], "hyps":[], "refs":[]}
srcs = []
hyps = []
refs = []
model.eval()
progress = tqdm.tqdm(itr, desc=f"validation", leave=False)
with torch.no_grad():
for i, sample in enumerate(progress):
# validation loss
sample = utils.move_to_cuda(sample, device=device)
net_output = model.forward(**sample["net_input"])
lprobs = F.log_softmax(net_output[0], -1)
target = sample["target"]
sample_size = sample["ntokens"]
loss = criterion(lprobs.view(-1, lprobs.size(-1)), target.view(-1)) / sample_size
progress.set_postfix(valid_loss=loss.item())
stats["loss"].append(loss)
# 進行推論
s, h, r = inference_step(sample, model)
srcs.extend(s)
hyps.extend(h)
refs.extend(r)
tok = 'zh' if task.cfg.target_lang == 'zh' else '13a'
stats["loss"] = torch.stack(stats["loss"]).mean().item()
stats["bleu"] = sacrebleu.corpus_bleu(hyps, [refs], tokenize=tok) # 計算BLEU score
stats["srcs"] = srcs
stats["hyps"] = hyps
stats["refs"] = refs
if config.use_wandb and log_to_wandb:
wandb.log({
"valid/loss": stats["loss"],
"valid/bleu": stats["bleu"].score,
}, commit=False)
showid = np.random.randint(len(hyps))
logger.info("example source: " + srcs[showid])
logger.info("example hypothesis: " + hyps[showid])
logger.info("example reference: " + refs[showid])
# show bleu results
logger.info(f"validation loss:\t{stats['loss']:.4f}")
logger.info(stats["bleu"].format())
return stats
8. 储存及载入模型参数
def validate_and_save(model, task, criterion, optimizer, epoch, save=True):
stats = validate(model, task, criterion)
bleu = stats['bleu']
loss = stats['loss']
if save:
# save epoch checkpoints
savedir = Path(config.savedir).absolute()
savedir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
check = {
"model": model.state_dict(),
"stats": {"bleu": bleu.score, "loss": loss},
"optim": {"step": optimizer._step}
}
torch.save(check, savedir/f"checkpoint{epoch}.pt")
shutil.copy(savedir/f"checkpoint{epoch}.pt", savedir/f"checkpoint_last.pt")
logger.info(f"saved epoch checkpoint: {savedir}/checkpoint{epoch}.pt")
# save epoch samples
with open(savedir/f"samples{epoch}.{config.source_lang}-{config.target_lang}.txt", "w") as f:
for s, h in zip(stats["srcs"], stats["hyps"]):
f.write(f"{s}\t{h}\n")
# get best valid bleu
if getattr(validate_and_save, "best_bleu", 0) < bleu.score:
validate_and_save.best_bleu = bleu.score
torch.save(check, savedir/f"checkpoint_best.pt")
del_file = savedir / f"checkpoint{epoch - config.keep_last_epochs}.pt"
if del_file.exists():
del_file.unlink()
return stats
def try_load_checkpoint(model, optimizer=None, name=None):
name = name if name else "checkpoint_last.pt"
checkpath = Path(config.savedir)/name
if checkpath.exists():
check = torch.load(checkpath)
model.load_state_dict(check["model"])
stats = check["stats"]
step = "unknown"
if optimizer != None:
optimizer._step = step = check["optim"]["step"]
logger.info(f"loaded checkpoint {checkpath}: step={step} loss={stats['loss']} bleu={stats['bleu']}")
else:
logger.info(f"no checkpoints found at {checkpath}!")
9. 开始训练
model = model.to(device=device)
criterion = criterion.to(device=device)
logger.info("task: {}".format(task.__class__.__name__))
logger.info("encoder: {}".format(model.encoder.__class__.__name__))
logger.info("decoder: {}".format(model.decoder.__class__.__name__))
logger.info("criterion: {}".format(criterion.__class__.__name__))
logger.info("optimizer: {}".format(optimizer.__class__.__name__))
logger.info(
"num. model params: {:,} (num. trained: {:,})".format(
sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters()),
sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad),
)
)
logger.info(f"max tokens per batch = {config.max_tokens}, accumulate steps = {config.accum_steps}")
epoch_itr = load_data_iterator(task, "train", config.start_epoch, config.max_tokens, config.num_workers)
try_load_checkpoint(model, optimizer, name=config.resume)
while epoch_itr.next_epoch_idx <= config.max_epoch:
# train for one epoch
train_one_epoch(epoch_itr, model, task, criterion, optimizer, config.accum_steps)
stats = validate_and_save(model, task, criterion, optimizer, epoch=epoch_itr.epoch)
logger.info("end of epoch {}".format(epoch_itr.epoch))
epoch_itr = load_data_iterator(task, "train", epoch_itr.next_epoch_idx, config.max_tokens, config.num_workers)
终于跑起来了!!!
虽然翻译的略微离谱hhh