1.1 为什么要启动优化?
用户希望应用能够及时响应并快速加载,启动时间过长的应用不能满足这个期望,并且可能使用户失望。
启动太慢的结果:
- 体验效果差
- 用户放弃使用你的应用
- 时间越长用户流失越高
- 产品死掉
1.2 启动优化流程及分类
1.2.1 开机启动流程

1.2.2 启动分类
- 冷启动:应用从头开始启动(应用自设备启动后或系统终止应用后首次启动);
- 热启动:将
Activity带到前台(如果应用的所有Activity都还驻留在内存中,则应用无需重复对象初始化、布局扩充和呈现。需要注意的是,如果程序的某些内存被系统清除,比如调用了onTrimMemory方法,则需要重新创建这些对象以响应热启动事件); - 温启动:涵盖在冷启动期间发生的操作的一些子集,同时它的开销比热启动多(它与热启动最大的区别在于,必须通过调用
onCreate方法开始重新创建活动,也可以从传递给onCreate方法中保存的实例状态中获得某些对象的恢复)。
冷启动流程:
- 加载并启动
APP;- 启动后立即为该
APP显示一个空白启动窗口;- 创建
APP进程(创建应用程序对象);- 启动主线程,创建主
Activity;- 加载布局,绘制。
启动总结:
App从被系统调用,再到第一个页面渲染到手机屏幕,我们通常只需要关注Application中的onCreate方法,第一个Activity中onCreate、onStart、onResume方法。
注意:如果在App启动第一个Activity时,该Activity不但有自己的逻辑,还在onCreate、onStart或者onResume方法中直接有跳转到了其它Activity页面,那么跳转后的Activity的这三个方法也需要进行优化。
1.2.3 黑白屏优化
在系统加载并启动App时,需要耗费相应的时间,即使时间不到1S,用户也会感觉到当点击App图标时会有“延迟”现象,为了解决这一个问题,Google的做法是在App创建的过程中,先展示一个空白的页面,让用户体会到点击图标之后立马就有响应,而这个空白页面的颜色则是根据我们在Manifest文件中配置的主题颜色 来决定的,现在一般默认为白色。
可以为应用的加载设置主题背景,从而使应用的启动屏幕在主题背景上与应用的后续效果保持一致,而不是采用系统主题。
方案一:设置LauncherTheme
在LauncherTheme中,设置系统“取消预览(空白窗体)”为true,或者设置空白窗体为透明,这样用户从视觉上就无法看出黑白屏的存在:
<style name="AppTheme.LauncherTheme">
<!--设置系统的取消预览(空白窗口)为true-->
<item name="android:windowDisablePreview">true</item>
<!--设置背景为透明-->
<item name="android:windowIsTranslucent">true</item>
</style>
方案二:自定义Theme主题
- 自定义继承自
AppTheme的主题;- 将启动
Activity的Theme设置为自定义主题;- 在启动
Activity的onCreate方法中,在super.onCreate和setContentView方法之前调用setTheme方法,将主题设置为最初的AppTheme。
① 自定义主题
<style name="AppTheme.LaunchTheme1">
<item name="android:windowBackground">@mipmap/ic_launcher</item>
</style>
② 设置启动Activity主题
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme.LaunchTheme1">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
③ 在代码中将主题设置回来
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
setTheme(R.style.AppTheme)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
1.3 测量启动时间
1.3.1 测量方式
-
系统日志输出:在
Android4.4及更高的版本中,logcat包括一个输出行,其中包含命令为Displayed的值,此值代表从启动进程到在屏幕上完成对应用Activity绘制所经过的时间(MI6测试,并没有);- 启动进程;
- 初始化对象;
- 创建并初始化
Activity:ActivityManager:displayed com.sty.ne.appperformance/.MainActivity: +550ms; - 扩充布局;
- 首次绘制应用。
-
adb命令:adb shell Activity Manager:
adb [ -d | -e | -s <serialNumber>] shell am start -S -W
com.sty.ne.appperformance/.MainActivity
-c android.intent.category.LAUNCHER
-a android.intent.action.MAIN
adb shell am start -W com.sty.ne.appperformance/.MainActivity
显示结果如下:
GGGdeMac-mini:NeAppPerformance tian$ adb shell am start -W com.sty.ne.appperformance/.activity.SplashActivity
Starting: Intent { act=android.intent.action.MAIN cat=[android.intent.category.LAUNCHER] cmp=com.sty.ne.appperformance/.activity.SplashActivity }
Status: ok
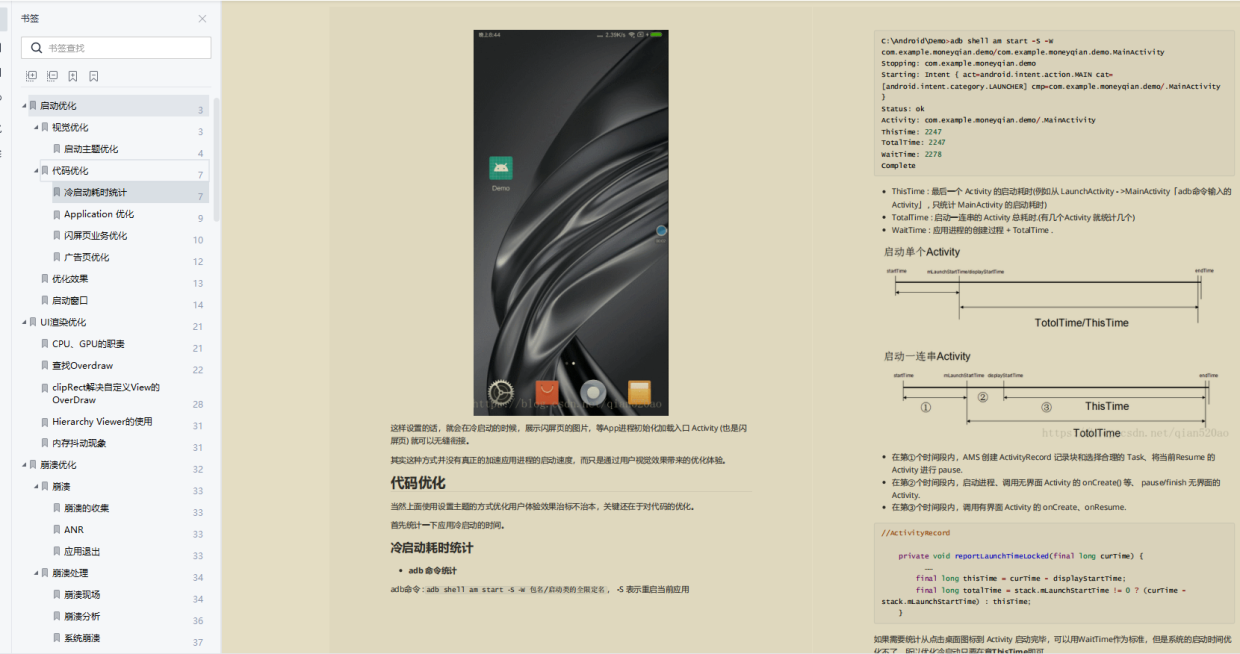
Activity: com.sty.ne.appperformance/.MainActivity
ThisTime: 186 (最后一个Activity启动耗时)
TotalTime: 395 (所有Activity启动耗时)
WaitTime: 417 (AMS启动Activity的总耗时)
Complete
- 手动获取:手动打印日志计算启动时间,只能记录应用内耗时。
private void findViews() {
final View viewRoot = findViewById(R.id.root);
viewRoot.getViewTreeObserver().addOnPreDrawListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener() {
@Override
public boolean onPreDraw() {
viewRoot.getViewTreeObserver().removeOnPreDrawListener(this);
LauncherTimer.logEnd("tag3");
return false;
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
LauncherTimer.logEnd("tag1");
}
@Override
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
LauncherTimer.logEnd("tag2");
}
// D/Time: 2/tag1 launcher time=101
// D/Time: 2/tag3 launcher time=139
// D/Time: 2/tag2 launcher time=146
1.3.2 方法耗时统计
-
traceview统计:可以用代码统计,也可以用Android Studio自带的cup profiler来统计;缺点是代码侵入性强,会拖慢程序运行。①
Debug Trace:@Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); Debug.startMethodTracing("Launcher"); coreSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Math.max(2, Math.min(coreSize - 1, 4))); application = this; context = this.getApplicationContext(); AppProfile.context = context; ScreenUtil.init(context); initLog(); AppForegroundWatcher.init(context); CrashReport.initCrashReport(getApplicationContext(), "e9bf59bd43", false); Debug.stopMethodTracing(); //sdcard/Android/data/com.sty.ne.appperformance/files/Launcher.trace --> save as 导出来,用Profiler打开 }sdcard/Android/data/com.sty.ne.appperformance/files/Launcher.trace-->save as导出来,用Profiler打开,如下图所示:
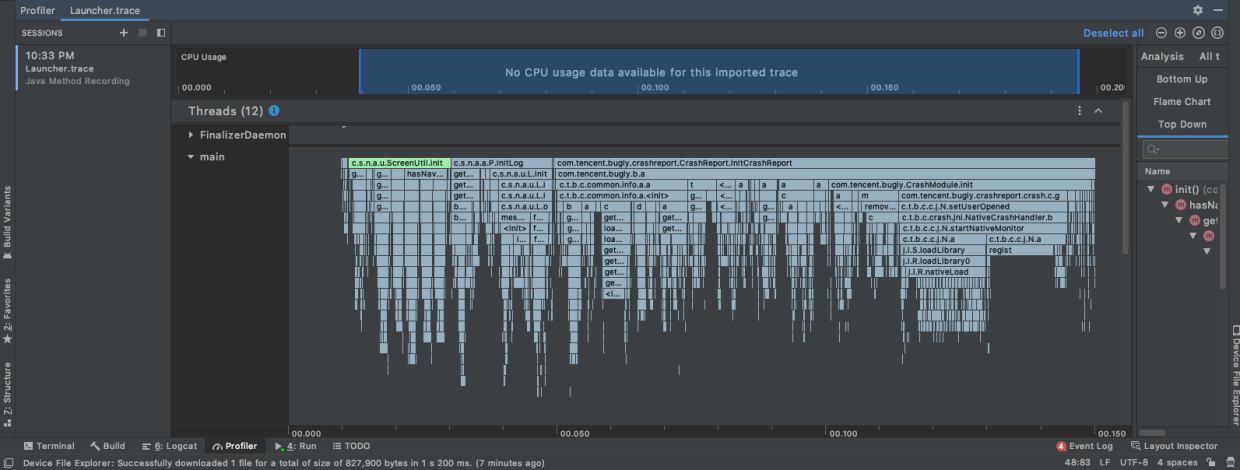
缺点:只能记录应用内程序执行时间。
②CPU Profiler:
不需要侵入代码(无需写Debug.startMethodTracing("Launcher"),但是需要做如下配置:
run->edit configurations;- 勾选
start recording a method trace on startup;- 从菜单中选择
cpu记录配置(profiling菜单下勾选两个复选框);apply-->profile模式部署。
-
systrace统计在代码中添加命令:
@Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); //systemtrace方式 Trace.beginSection("Launcher"); coreSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Math.max(2, Math.min(coreSize - 1, 4))); application = this; context = this.getApplicationContext(); AppProfile.context = context; ScreenUtil.init(context); initLog(); AppForegroundWatcher.init(context); CrashReport.initCrashReport(getApplicationContext(), "e9bf59bd43", false); Trace.endSection(); }
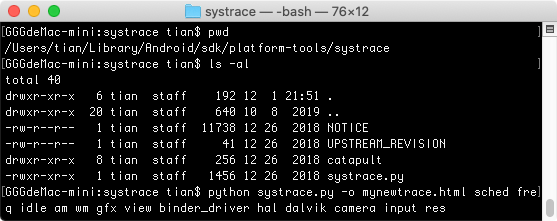
命令行终端进入如下目录:/Users/tian/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools/systrace
输入如下命令进入监听状态:
python systrace.py -o mynewtrace.html sched freq idle am wm gfx view binder_driver hal dalvik camera input res
此时运行代码,完成之后在命令行窗口按Enter键结束监听,然后会生成目标文件mynewtrace.html:
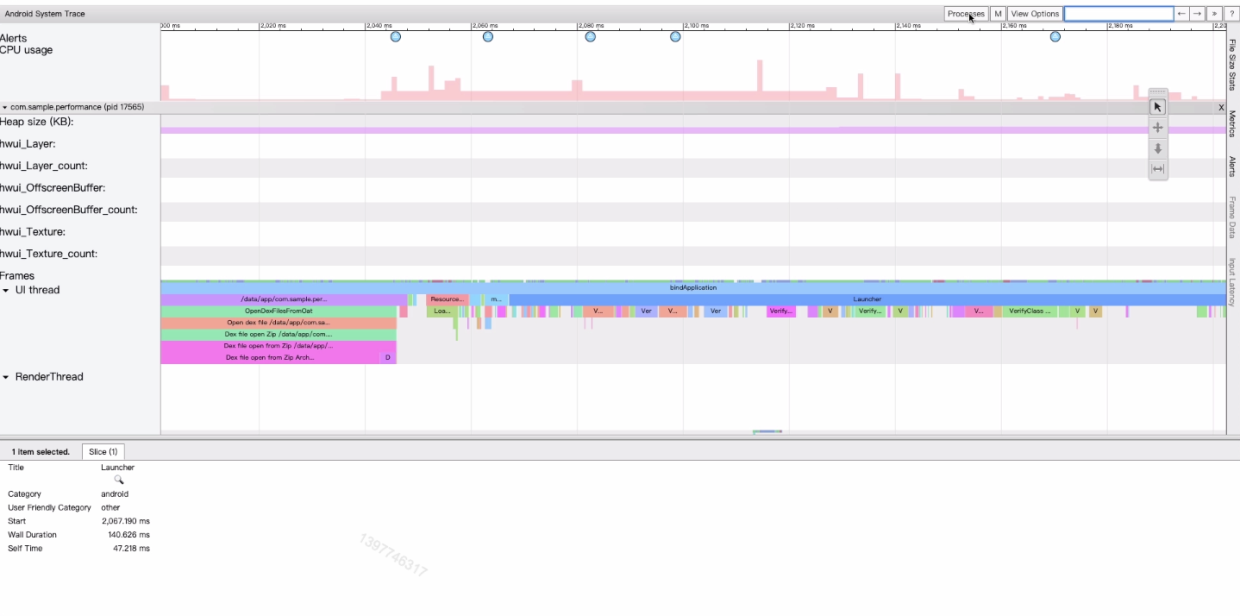
分析目标文件:
aop方式统计
1.4 优化方式
1.4.1 异步优化
异步优化主要是采用子线程来进行线程初始化,并行执行,减少执行时间。
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
coreSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Math.max(2, Math.min(coreSize - 1, 4)));
application = this;
context = this.getApplicationContext();
AppProfile.context = context;
ScreenUtil.init(context);
async(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
initLog();
}
});
async(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
AppForegroundWatcher.init(context);
}
});
async(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
CrashReport.initCrashReport(getApplicationContext(), "e9bf59bd43", false);
}
});
}
异步优化需要关注的点:
- 确定能不能异步优化;
- 执行的方法是否有先后顺序;
- 需要注意异步后程序能否正常执行;
- 异步线程中使用的
api不能创建Handler;- 不能有
UI操作。
1.4.2 延迟初始化
仅初始化立即需要的对象,不要创建全局静态对象,而是移动到单例模式,其中应用仅在第一次访问对象时初始化它们。
1.4.3 空闲时初始化
可以监听应用空闲时间,在空闲时间进行初始化。
public class DelayInit {
private Queue<Runnable> delayQueue = new LinkedList<>();
public void add(Runnable runnable) {
delayQueue.add(runnable);
}
public void start() {
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new MessageQueue.IdleHandler() {
@Override
public boolean queueIdle() {
Runnable poll = delayQueue.poll();
if(poll != null) {
poll.run();
}
return !delayQueue.isEmpty();
}
});
}
}
其实出了启动优化外,Android 性能优化中还有 内存优化、网络优化、卡顿优化、存储优化……等,为了让大家一次都可以了解全,所以将其整合成名为《Android 性能优化核心知识点手册》,大家可以参考下:
《APP 性能调优进阶手册》:https://qr18.cn/FVlo89
启动优化
内存优化

UI优化
网络优化

Bitmap优化与图片压缩优化

多线程并发优化与数据传输效率优化
体积包优化
《Android 性能调优核心笔记汇总》:https://qr18.cn/FVlo89
《Android 性能监控框架》:https://qr18.cn/FVlo89