1.engine.Run(port string)
这个就是gin框架的启动语句,看看就好了,下面我们解析一下那个engine.Handler()
listenandserve 用于启动http包进行监听,获取链接conn
// ListenAndServe listens on the TCP network address addr and then calls
// Serve with handler to handle requests on incoming connections.
// Accepted connections are configured to enable TCP keep-alives.
//
// The handler is typically nil, in which case the DefaultServeMux is used.
//
// ListenAndServe always returns a non-nil error.
func ListenAndServe(addr string, handler Handler) error {
server := &Server{Addr: addr, Handler: handler}
return server.ListenAndServe()
}
// Run attaches the router to a http.Server and starts listening and serving HTTP requests.
// It is a shortcut for http.ListenAndServe(addr, router)
// Note: this method will block the calling goroutine indefinitely unless an error happens.
func (engine *Engine) Run(addr ...string) (err error) {
defer func() { debugPrintError(err) }()
if engine.isUnsafeTrustedProxies() {
debugPrint("[WARNING] You trusted all proxies, this is NOT safe. We recommend you to set a value.\n" +
"Please check https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-don-t-trust-all-proxies for details.")
}
address := resolveAddress(addr)
debugPrint("Listening and serving HTTP on %s\n", address)
err = http.ListenAndServe(address, engine.Handler())
return
}
2、func (engine *Engine) Handler() http.Handler
这边的Handler是个语法糖,handler本质是一个接口,接口内部有一个方法ServeHttp,也是非常重要的,是http的核心,之后讲的内容也会围绕这个
type Handler interface {
ServeHTTP(ResponseWriter, *Request)
}
func (engine *Engine) Handler() http.Handler {
if !engine.UseH2C {
return engine
}
h2s := &http2.Server{}
return h2c.NewHandler(engine, h2s)
}3、func (engine *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request)
写完了博客回来再补充一下:这边是实现了http.Handler interface
前面见过了这个interface下面有个ServeHttp方法,因此engine可以作为http.Handler的参数传递,也就是上面那个函数的h2c.NewHandler中的参数传engine可行的原因
所以调用ListenAndServe时 底层的包装函数就会去调用接口的
ServerHTTP这里的ListenAndServe属于http包的范畴,我大致看了源码,源码流程如下:
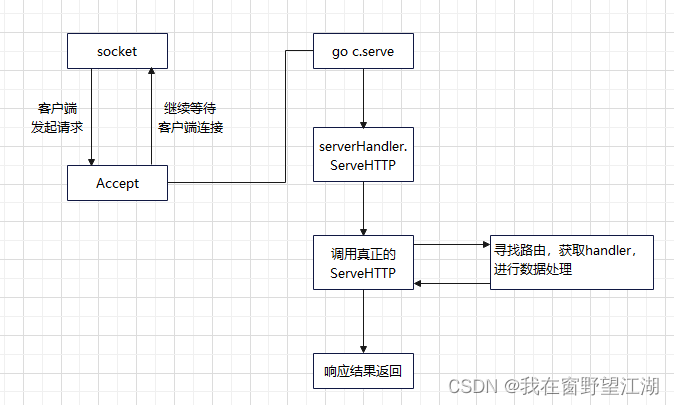
其实主要http中有实现ServeHTTP,然后gin是调用http包进行socket等一些列操作的,而gin中的engine实现了ServeHTTP,当http中运行到c.serve时,会获取其中的Handler,然后Handler调用ServerHTTP,gin中调用http的listenandServe传入的就是engine实例,所以此时的Handler也就是engine,因此调用的ServeHTTP函数也是engine实现的那个函数,这也就是刚刚说的类似语法糖的东西,http包实现了百分之七十的功能在gin。(socket/bind/listen/accept/read/write/close)
看似就是只有几行完成了我们对http响应的处理
第一engine内部有缓冲池一开始介绍engine的时候有提到一下,此外engine pool也就是go自带的对对象缓存复用的设施,主要缓解部分gc压力
第二我们取出来了如果不存在就新建,存在就直接取出来,对于取出来的context进行重置reset,更新各种字段,context是我们装载此次请求的核心,还有当调用这个函数的时候,这里的req都是封装好了此次请求的请求体了,所以我们的context只不过是gin为了我们方便使用 将请求体和响应体对我们包装好了,同时提供了我们操作响应体的函数例如:c.JSON,c.String,c.Set c.Get等等函数方便我们使用请求体和响应体
总的来说这里的context就是为了包装请求和响应,然后实现了方便操作请求和响应的函数————接下看看engine.handleHTTPRequest(c)了 这里才是这里面的核心
func (c *Context) reset() {
c.Writer = &c.writermem
c.Params = c.Params[:0]
c.handlers = nil
c.index = -1
c.fullPath = ""
c.Keys = nil
c.Errors = c.Errors[:0]
c.Accepted = nil
c.queryCache = nil
c.formCache = nil
c.sameSite = 0
*c.params = (*c.params)[:0]
*c.skippedNodes = (*c.skippedNodes)[:0]
}
// ServeHTTP conforms to the http.Handler interface.
func (engine *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
c := engine.pool.Get().(*Context)
c.writermem.reset(w)
c.Request = req
c.reset()
engine.handleHTTPRequest(c)//核心
engine.pool.Put(c)
}
从 sync.pool 里面拿去一块内存, 对这块内存做初始化工作,防止数据污染, 处理请求 handleHTTPRequest, 请求处理完成后,把这块内存归还到 sync.pool 中, 现在看起来这个实现很简单,其实不然,这才是 gin 能够处理数据的第一步,也仅仅将请求流转入 gin 的处理流程而已。
4、func (engine *Engine) handleHTTPRequest(c *Context)
简单介绍下这个函数,前面的部分就是通过context中请求体指针获取url和请求类型,然后从engine获取字典树,接着根据请求类型获取对应树的根结点再遍历到对应的结点,然后从结点中取出对应的信息,例如handler函数,
接着就是c.Next()遍历得到的handler链进行执行
// nodeValue holds return values of (*Node).getValue method type nodeValue struct { handlers HandlersChain params *Params tsr bool fullPath string } -------------------------------------- root := t[i].root // Find route in tree value := root.getValue(rPath, c.params, c.skippedNodes, unescape) if value.params != nil { c.Params = *value.params } if value.handlers != nil { c.handlers = value.handlers c.fullPath = value.fullPath c.Next() c.writermem.WriteHeaderNow() return } // Next should be used only inside middleware. // It executes the pending handlers in the chain inside the calling handler. // See example in GitHub. func (c *Context) Next() { c.index++ for c.index < int8(len(c.handlers)) { c.handlers[c.index](c) c.index++ } } -------------------------------------- func (engine *Engine) handleHTTPRequest(c *Context) { httpMethod := c.Request.Method//method rPath := c.Request.URL.Path//url unescape := false if engine.UseRawPath && len(c.Request.URL.RawPath) > 0 { rPath = c.Request.URL.RawPath unescape = engine.UnescapePathValues } if engine.RemoveExtraSlash { rPath = cleanPath(rPath) } // Find root of the tree for the given HTTP method t := engine.trees//trie Tree for i, tl := 0, len(t); i < tl; i++ { if t[i].method != httpMethod { continue } root := t[i].root // Find route in tree value := root.getValue(rPath, c.params, c.skippedNodes, unescape)//这个是下部分讲的核心,就是获取对应结点 if value.params != nil { c.Params = *value.params } if value.handlers != nil { c.handlers = value.handlers//放入context中 c.fullPath = value.fullPath c.Next() c.writermem.WriteHeaderNow() return } if httpMethod != http.MethodConnect && rPath != "/" { if value.tsr && engine.RedirectTrailingSlash { redirectTrailingSlash(c) return } if engine.RedirectFixedPath && redirectFixedPath(c, root, engine.RedirectFixedPath) { return } } break } if engine.HandleMethodNotAllowed { for _, tree := range engine.trees { if tree.method == httpMethod { continue } if value := tree.root.getValue(rPath, nil, c.skippedNodes, unescape); value.handlers != nil { c.handlers = engine.allNoMethod serveError(c, http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, default405Body) return } } } c.handlers = engine.allNoRoute serveError(c, http.StatusNotFound, default404Body) }
5、func (n *node) getValue(path string, params *Params, skippedNodes *[]skippedNode, unescape bool) (value nodeValue)
这边函数太长,截取片段讲。
第一个片段就是匹配前缀,如果path长度大于前缀进行匹配,如果都能找到那就是一个个片段进行匹配,匹配成功就会进入下一个片段
第二个片段就是匹配成功了,然后从这个结点中获取handler并返回
walk: // Outer loop for walking the tree
for {
prefix := n.path
if len(path) > len(prefix) {
if path[:len(prefix)] == prefix {
path = path[len(prefix):]
// Try all the non-wildcard children first by matching the indices
idxc := path[0]
for i, c := range []byte(n.indices) {
if c == idxc {
// strings.HasPrefix(n.children[len(n.children)-1].path, ":") == n.wildChild
....
....
....
n = n.children[i]
continue walk
}
}
-----
if path == prefix {
// If the current path does not equal '/' and the node does not have a registered handle and the most recently matched node has a child node
// the current node needs to roll back to last vaild skippedNode
...
...
....
// We should have reached the node containing the handle.
// Check if this node has a handle registered.
if value.handlers = n.handlers; value.handlers != nil {
value.fullPath = n.fullPath
return
}
}
------------
// Returns the handle registered with the given path (key). The values of
// wildcards are saved to a map.
// If no handle can be found, a TSR (trailing slash redirect) recommendation is
// made if a handle exists with an extra (without the) trailing slash for the
// given path.
func (n *node) getValue(path string, params *Params, skippedNodes *[]skippedNode, unescape bool) (value nodeValue) {
var globalParamsCount int16
walk: // Outer loop for walking the tree
for {
prefix := n.path
if len(path) > len(prefix) {
if path[:len(prefix)] == prefix {
path = path[len(prefix):]
// Try all the non-wildcard children first by matching the indices
idxc := path[0]
for i, c := range []byte(n.indices) {
if c == idxc {
// strings.HasPrefix(n.children[len(n.children)-1].path, ":") == n.wildChild
if n.wildChild {
index := len(*skippedNodes)
*skippedNodes = (*skippedNodes)[:index+1]
(*skippedNodes)[index] = skippedNode{
path: prefix + path,
node: &node{
path: n.path,
wildChild: n.wildChild,
nType: n.nType,
priority: n.priority,
children: n.children,
handlers: n.handlers,
fullPath: n.fullPath,
},
paramsCount: globalParamsCount,
}
}
n = n.children[i]
continue walk
}
}
if !n.wildChild {
// If the path at the end of the loop is not equal to '/' and the current node has no child nodes
// the current node needs to roll back to last vaild skippedNode
if path != "/" {
for l := len(*skippedNodes); l > 0; {
skippedNode := (*skippedNodes)[l-1]
*skippedNodes = (*skippedNodes)[:l-1]
if strings.HasSuffix(skippedNode.path, path) {
path = skippedNode.path
n = skippedNode.node
if value.params != nil {
*value.params = (*value.params)[:skippedNode.paramsCount]
}
globalParamsCount = skippedNode.paramsCount
continue walk
}
}
}
// Nothing found.
// We can recommend to redirect to the same URL without a
// trailing slash if a leaf exists for that path.
value.tsr = path == "/" && n.handlers != nil
return
}
// Handle wildcard child, which is always at the end of the array
n = n.children[len(n.children)-1]
globalParamsCount++
switch n.nType {
case param:
// fix truncate the parameter
// tree_test.go line: 204
// Find param end (either '/' or path end)
end := 0
for end < len(path) && path[end] != '/' {
end++
}
// Save param value
if params != nil && cap(*params) > 0 {
if value.params == nil {
value.params = params
}
// Expand slice within preallocated capacity
i := len(*value.params)
*value.params = (*value.params)[:i+1]
val := path[:end]
if unescape {
if v, err := url.QueryUnescape(val); err == nil {
val = v
}
}
(*value.params)[i] = Param{
Key: n.path[1:],
Value: val,
}
}
// we need to go deeper!
if end < len(path) {
if len(n.children) > 0 {
path = path[end:]
n = n.children[0]
continue walk
}
// ... but we can't
value.tsr = len(path) == end+1
return
}
if value.handlers = n.handlers; value.handlers != nil {
value.fullPath = n.fullPath
return
}
if len(n.children) == 1 {
// No handle found. Check if a handle for this path + a
// trailing slash exists for TSR recommendation
n = n.children[0]
value.tsr = (n.path == "/" && n.handlers != nil) || (n.path == "" && n.indices == "/")
}
return
case catchAll:
// Save param value
if params != nil {
if value.params == nil {
value.params = params
}
// Expand slice within preallocated capacity
i := len(*value.params)
*value.params = (*value.params)[:i+1]
val := path
if unescape {
if v, err := url.QueryUnescape(path); err == nil {
val = v
}
}
(*value.params)[i] = Param{
Key: n.path[2:],
Value: val,
}
}
value.handlers = n.handlers
value.fullPath = n.fullPath
return
default:
panic("invalid node type")
}
}
}
if path == prefix {
// If the current path does not equal '/' and the node does not have a registered handle and the most recently matched node has a child node
// the current node needs to roll back to last vaild skippedNode
if n.handlers == nil && path != "/" {
for l := len(*skippedNodes); l > 0; {
skippedNode := (*skippedNodes)[l-1]
*skippedNodes = (*skippedNodes)[:l-1]
if strings.HasSuffix(skippedNode.path, path) {
path = skippedNode.path
n = skippedNode.node
if value.params != nil {
*value.params = (*value.params)[:skippedNode.paramsCount]
}
globalParamsCount = skippedNode.paramsCount
continue walk
}
}
// n = latestNode.children[len(latestNode.children)-1]
}
// We should have reached the node containing the handle.
// Check if this node has a handle registered.
if value.handlers = n.handlers; value.handlers != nil {
value.fullPath = n.fullPath
return
}
// If there is no handle for this route, but this route has a
// wildcard child, there must be a handle for this path with an
// additional trailing slash
if path == "/" && n.wildChild && n.nType != root {
value.tsr = true
return
}
if path == "/" && n.nType == static {
value.tsr = true
return
}
// No handle found. Check if a handle for this path + a
// trailing slash exists for trailing slash recommendation
for i, c := range []byte(n.indices) {
if c == '/' {
n = n.children[i]
value.tsr = (len(n.path) == 1 && n.handlers != nil) ||
(n.nType == catchAll && n.children[0].handlers != nil)
return
}
}
return
}
// Nothing found. We can recommend to redirect to the same URL with an
// extra trailing slash if a leaf exists for that path
value.tsr = path == "/" ||
(len(prefix) == len(path)+1 && prefix[len(path)] == '/' &&
path == prefix[:len(prefix)-1] && n.handlers != nil)
// roll back to last valid skippedNode
if !value.tsr && path != "/" {
for l := len(*skippedNodes); l > 0; {
skippedNode := (*skippedNodes)[l-1]
*skippedNodes = (*skippedNodes)[:l-1]
if strings.HasSuffix(skippedNode.path, path) {
path = skippedNode.path
n = skippedNode.node
if value.params != nil {
*value.params = (*value.params)[:skippedNode.paramsCount]
}
globalParamsCount = skippedNode.paramsCount
continue walk
}
}
}
return
}
}
总结总结:
gin框架大体运行最核心的部分已经讲完了
从第一篇到现在其实是大致上已经把gin框架利用net/http包的httplistenserve函数利用和保存前缀树结点,查询前缀树结点,最后到运行handler讲完了
博主写这些参考了很多文章,大致上其实和某些博主相似,但是很多地方加入了自己的想法,我自己在原文看不懂的地方,我都自己加了批注,便于理解。
然后的话,其实前面serveHttp那块讲的非常含糊,我看原文的时候也是半知半解,下篇博客的话会结合别的博客解释http包的底层,对于为啥handler那里那个语法糖可以那样用,解释解释。








![[数据结构]:16-归并排序(顺序表指针实现形式)(C语言实现)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/41c9940f80594b03be87a9bb81752916.png)